Abstract
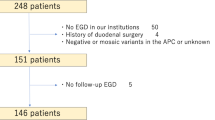
Variable endoscopic surveillance protocols and treatment strategies have been proposed for periampullary neoplasia in familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), primarily because of the lack of long-term, prospective natural history data. A total of 115 patients with FAP were followed prospectively for 10 years with periodic side-viewing upper gastrointestinal endoscopy by a single surgeon. The appearance of the duodenum was classified as stages 1 to 5. Statistical analysis included one-way analysis of variance for age comparisons between stage groupings and Kaplan-Meier analysis for the lifetime risks of having a particular stage of duodenal polyposis. Eighty-seven patients had multiple endoscopies over an average of 6.6 years. Thirty-three subjects had a change in stage, within an average time of 3.9 years at an average age of 41 years. The risk of having stage 3 or 4 duodenal neoplasia increased exponentially after the age of 40. The degree of dysplasia did not correlate with stage at initial classification. Progression of neoplasia in the duodenum of patients with FAP is slow. The severity of duodenal polyposis increases with age and is not influenced by the initial stage. The average time for progression of adenoma to carcinoma is likely long.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Griffioen G, Bus PJ, Vasen HFA, Verspaget HW, Lamers CB. Extracolonic manifestations of familial adenomatous polyposis: Desmoid tumors, and upper gastrointestinal adenomas and carcinomas. Scand J Gastroenterol 1998;33 225(Suppl):85–91.
Offerhaus GJA, Entlus MM, Giardiello FM. Upper gastrointestinal polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis. Hepatogastroenterology 1999;46:667–669.
Spigelman AD. Screening modalities in familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Gastrointest Endosc Clin North Am 1997;81/2-86.
Belchetz LA, Berk T, Bapat BV, Cohen Z, Gallinger S. Changing causes of mortality in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Dis Colon Rectum 1996;39:384–387.
Galle TS, Juel K, Bulow S. Causes of death in familial adenomatous polyposis. Scand J Gastroenterol 1999;34:808–812.
Wallace MH, Phillips RK. Upper gastrointestinal disease in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg 1998;85:742–750.
Norton ID, Gostout CJ. Management of periampullary adenomas. Dig Dis 1998;16:266–273.
Sanabria JR, Croxford R, Berk T, Cohen Z, Bapat BV, Gallinger S. Familial segregation in the occurrence and severity of periampullary neoplasms in familial adenomatous polyposis. Am J Surg 1996;171:136–141.
Nugent KP, Spigelman AD, Phillips RKS. Risk of extracolonic cancer in familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg 1996;83:1121–1122.
Jagleman DG, DeCosse JJ, Bussey HJR, and The Leeds Castle Polyposis Group. Upper gastrointestinal cancer in familial adenomatous polyposis. Lancet 1988;8595:1149–1150.
Nugent KP, Spigelman AD, Williams CB, Talbot IC, Phillips KS. Surveillance of duodenal polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis: Progress report. J R Soc Med 1994;87:704–706.
Spigelman AD, Talbot IC, Penna C, Nugent KP, Phillips RK, Costello C, DeCosse JJ. Evidence for adenoma-carcinoma sequence in the duodenum of patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. J Clin Pathol 1994;47:709–710.
Kashiwagi H, Spigelman AD. Gastroduodenal lesions in familial adenomatous polyposis. Surg Today 2000;30:675–682.
Goedde TA, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Herrera L, Petrelli NJ. Gastroduodenal polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis. Surg Oncol 1992;1:357–361.
Debinski HS, Spigelman AD, Hatfield A, Williams CB, Phillips RKS. Upper intestinal surveillance in familial adenomatous polyposis. Eur J Cancer 1995;31:1149–1153.
Bulow S, Alm T, Fausa O, Hultcrantz R, Jarvinen H, Vasen H, the DAF Project Group. Duodenal adenomatosis in familial adenomatous polyposis. Int J Colorectal Dis 1995;10:43–46.
Sawada T, Muto T. Role of upper gastrointestinal surveillance in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Gastrointest Endosc Clin North Am 1997;7:99–110.
Björk J, Akerbrant H, Iselius L, Bergman A, Engwall Y, Wahlstrom J, Martinsson T, Nordling M, Hultcrantz R. Periampullary adenomas and adenocarcinomas in familial adenomatous polyposis: Cumulative risks and APC gene mutations. Gastroentelology 2001;121:1127–1135.
Matsumoto T, Iida M, Nakamura S, Hizawa K, Yao T, Tsuneyoshi M, Fujishima M. Natural history of ampullary adenoma in familial adenomatous polyposis: Reconfirmation of benign nature during extended surveillance. Am J Gastroenterol 2000;95:1557–1562.
Burke CA, Beck GJ, Church JM, van Stolk RU. The natural history of untreated duodenal and ampullary adenomas in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis followed in an endoscopic surveillance program. Gastrointest Endosc 1999; 49:358–364.
Bertoni G, Sassatelli R, Nigrisoli E, Pennazio M, Tansini P, Arrigoni A, Ponz de Leon M, Rossini FP, Bedogni G. High prevalence of adenomas and microadenomas of the duodenal papilla and periampullary region in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1996;8:1201–1206.
Groves CJ, Saunders BP, Spigelman AD, Phillips RSK, Duodenal cancer in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP): Results of a 10 year prospective study. Gut 2002;50:636–641.
Penna C, Phillips RKS, Tiret E, Spigelman AD. Surgical polypectomy of duodenal adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis: Experience of two European centres. Br J Surg 1993;80:1027–1029.
Heiskanan I, Kellokumpu I, Jarvinen H. Management of duodenal adenomas in 98 patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Endoscopy 1999;31:412–416.
Kadmon M, Tandara A, Herfarth C. Duodenal adenomatosis in familial adenomatous polyposis coli. A review of the literature and results from the Heidelberg Register. Int J Colorect Dis 2001;16:63–75.
Soravia C, Berk T, Haber G, Cohen Z, Gallinger S. Management of advanced duodenal polyposis in familial adenomatous polyposis. J G ASTROINTEST SURG 1997;1:474–478.
Richard CS, Berk T, Bapat BV, Haber G, Cohen Z, Gallinger S. Sulindac for periampullary polyps in FAP patients. Int J Colorect Dis 1997;12:14–18.
Oshima M, Dinchuk JE, Kargman SL, Oshima H, Hancock B, Kwong E, Trzaskos JM, Evans JF, Taketo MM. Suppression of intestinal polyposis in APC knockout mice by inhibition of cylooxygenase2 (COX-2). Cell 1996;87:803–809.
Steinbach G, Lynch PM, Phillips RK, Wallace MH, Hawk E, Gordon GB, Wakabayashi N, Saunders B, Shen Y, Fujimura T, Su LK, Levin B. The effect of celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, in familial adenomatous polyposis. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1946–1952.
Phillips RKS, Wallace MH, Lynch P, Hawk E, Gordon GB, Saunders B, Wakabayashi N, Shen Y, Zimmerman S, Godio L, Rodrigues-Bigas M, Li-Kuo Su, Sherman J, Kelloff G, Levin B, Steinbach G, The FAP Study Group. A randomised double blind placebo controlled study of celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, on duodenal polyposis in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut 2002;50:857–860.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by the National Cancer Institute of Canada (NCIC) and the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moozar, K.L., Madlensky, L., Berk, T. et al. Slow progression of periampullary neoplasia in familial adenomatous polyposis. J Gastrointest Surg 6, 831–837 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(02)00062-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(02)00062-8