Abstract
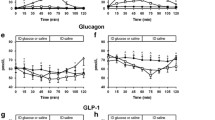
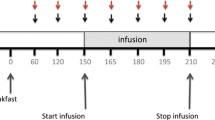
Postprandial absorptive augmentation of water and electrolytes occurs in the small intestine and colon. The role of intraluminal nutrients in this response is poorly understood. Our aim was to determine whether postprandial absorptive augmentation of water and electrolytes in the colon requires the presence of intraluminal glucose. Four adult dogs underwent enteric isolation of a 50 cm segment of proximal colon. An ileal-like electrolyte solution (Na+, 130 mEq/L; K+, 10 mEq/L; Cl-, 115 mEq/L; and HCO3 -, 25 mEq/L), alone or containing glucose (10 mmol/L), was infused at 4 ml/min into the colonic segment. Experiments were performed during fasting and postprandially after a 400 Kcal mixed-nutrient meal. Effluent was collected in 60-minute intervals after steady state was achieved. Net absorptive flux of water was increased in the presence of intraluminal glucose during the fasted state (11 ± 0.8 vs 7.4 ± 0.9 µl/min/ cm, P < 0.01). The net absorptive flux of water and electrolytes increased postprandially only in the presence of intraluminal glucose (P < 0.05). Our finding that glucose augments both baseline and postprandial absorption of water and electrolytes in the proximal colon suggests that luminal factors have a role in postprandial absorptive augmentation. Whether this is specific to glucose or occurs with other nutrients remains to be determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anthone GJ, Zinner MJ, Yeo CJ. Small bowel origin and calorie dependence of a signal for meal-induced jejunal absorption. Ann Surg 1993;217:57–63.
Anthone GJ, Wang BH, Zinner MJ, Yeo CJ. Site-specific variations in basal and meal-stimulated intestinal absorption. J Surg Res 1992;52:454–458.
Bastidas JA, Orandle MS, Zinner MJ, Yeo CJ. Small-bowel origin of the signal for meal-induced jejunal absorption. Surgery 1990;108:376–383.
Ashton KA, Chang LK, Anthone GJ, Ortega AE, Simons AJ, Beart RW. Basal and meal-stimulated colonic absorption. Dis Colon Rectum 1996;39:865–870.
Theodorou V, Fioramonti J, Bueno L. Water absorption from the pig proximal colon: Relations with feeding and flow of digesta. QJ Exp Physiol 1989;74:521–529.
Sarr MG, Kelly KA, Phillips SF. Feeding augments canine jejunal absorption via a hormonal mechanism. Dig Dis Sci 1981;26:961–965.
Barry KM, Aloisi JD, Yeo CJ. Neural mechanisms in basal and meal-stimulated ileal absorption. J Surg Res 1995;58:425–431.
Yeo CJ, Varry KM, Gontarek JD, Donowitz M. Na/H exchange mediates meal-stimulated ileal absorption. Surgery 1994;116:388–395.
Hines OJ, Bilchik AJ, McFadden DW, Rodgers PJ, Bautista N, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW. Na/H exchange mediates postprandial ileal water and electrolyte transport. Dig Dis Sci 1995;40:774–780.
Welton ML, Ashley SW, Barquist ES, Miller JL, Zinner MJ. Role of Na/glucose cotransport in meal-induced jejunal absorption. Surg Forum 1992;48:147–148.
Hines OJ, Bilchik AJ, Zinner MJ, Lane J, Hirmand M, Welton ML, Ashley SW. The Na/glucose cotransporter modulates jejunal postprandial absorption [abstr]. Gastroenterology 1993;104:A252.
Kendrick ML, Meile T, Zyromski NJ, Tanaka T, Sarr MG. Extrinsic neural innervation mediates absorption of water and electrolytes in canine proximal colon in vivo. J Surg Res 2001;97:76–80.
Yeo CJ, Bastidas AJ, Schmieg RE, Zinner MJ. Meal-stimulated absorption of water and electrolytes in canine jejunum. Am J Physiol 1990;259:402–409.
McFadden DW, Jaffe BM, Ferrara A, Zinner MJ. Jejunal absorptive response to a test meal and its modification by cholinergic and calcium channel blockage in the awake dog. Surg Forum 1984;35:174–176.
Bastidas AJ, Yeo CJ, Schmieg RE, Zinner MJ. Endogenous opiates in the mediation of early meal-induced jejunal absorption of water and electrolytes. Am J Surg 1989;157:27–32.
Liu CD, Aloia T, Adrian TE, Newton TR, Bilchik AJ, Zin-ner MJ, Ashley SW, McFadden DW. Peptide YY: A potential proabsorptive hormone for the treatment of malabsorptive disorders. Am Surg 1996;62:232–236.
Long CL, Geiger JW, Kinney JM. Absorption of glucose from the colon and rectum. Metabolism 1967;16:413–418.
Hines OJ, Bilchik AJ, Zinner MH, Skotzko MJ, Moser AJ, McFadden DW, Ashley SW. Adaptation of the Na+/glucose cotransporter following intestinal resection. J Surg Res 1994;57:22–27.
Read NW. The relationships between colonic motility and transport. ScandJ Gastroenterol 1984;93(Suppl):35–42.
Cummings JH. Short chain fatty acids in the human colon. Gut 1981;22:763–779.
Cummings JH. Colonic absorption: The importance of short chain fatty acids in man. Scand J Gastroenterol 1984; 93:89–99.
Roediger WE. Short chain fatty acids as metabolic regulators of ion absorption in the colon. Acta Vet Scand 1989;86:116–125.
Sandle GI. Mechanisms of colonic electrolyte absorption and secretion. Dig Dis 1988;6:1–14.
Sandle GI. Salt and water absorption in the human colon: A modern appraisal. Gut 1998;43:294–299.
Liu CD, Newton TR, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW, McFadden DW. Intraluminal peptide YY induces colonic absorption in vivo. Dis Colon Rectum 1997;40:478–482.
Liu CD, Hines OJ, Newton TR, Adrian TE, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW, McFadden DW. Cholecystokinin mediation of colonic absorption via peptide YY: Foregut-hindgut axis. World J Surg 1996;20:221–227.
Argenzio RA, Southworth M, Lowe JE, Stevens CE. Inter-relationship of Na, HCO3 and volatile fatty acid transport by equine large intestine. Am J Physiol 1988;233:469–478.
Campos MS, Galindo MC, Garcia JA, Lisbona F, Lopez-Aliaga I. A comparative study of electrolyte and water transport in the rabbit ileum and colon in vitro and in vivo: Influence of D-glucose. Biomed Biochim Acta 1991;50:279–283.
Sullivan SK, Smith PL. Bicarbonate secretion by rabbit proximal colon. AmJ Physiol 1986;251:436–445.
Fleming LL, Floch MH. Digestion and absorption of fiber carbohydrate in the colon. Am J Gastroenterol 1986;81:507–511.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kendrick, M.L., Zyromski, N.J., Tanaka, T. et al. Postprandial absorptive augmentation of water and electrolytes in the colon requires intraluminal glucose. J Gastrointest Surg 6, 310–315 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(01)00069-5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(01)00069-5