Abstract
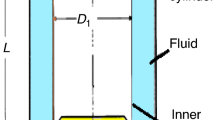
A new electromagnetic stirring technique that is driven by hydrodynamic forces was presented. This technique offers the following advantages. First, the stirrer can be immersed in the liquid metal, thereby significantly increasing the penetration depth of the electromagnetic forces and significantly improving the stirring efficiency; thus, this technique is particularly suitable for large-scale liquid metal. Second, under certain conditions, this technique can overcome difficulties that are encountered with traditional stirrers, such as accessing regions that are difficult to reach in working spaces with complex or narrow shapes. This stirrer also has a simpler structure than a traditional stirrer; thus, the design can be easily modified, and no external power supply is required. An experimental prototype was also presented for controlling the fluid flow rate, thereby controlling the electromagnetic force and velocity field of the driven liquid metal. The velocity distribution in a liquid GaInSn alloy under fluid-driven electromagnetic stirring was quantitatively measured using ultrasonic Doppler velocimetry (UDV). The primary results show that a remarkable velocity field has been achieved and that fluid-driven electromagnetic stirring is an effective means of stirring liquid metal. Finally, the potential applications of this technique in industry, along with key challenges, were discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Braunbek, Z. Physik. 78 (1932) 312–334.
J. Stiller, K. Koal, W. E. Nagel, J. Pal, A. Cramer, Eur. Phys. J. (Special Topics) 220 (2013) 111–122.
H. Yasuda, T. Toh, K. Iwai, K. Morita, ISIJ Int. 47 (2007) 619–626.
K. Okazawa, T. Toh, J. Fukuda, T. Kawase, M. Toki, ISIJ Int. 41 (2001) 851–858.
R. Hirayama, K. Fujisaki, T. Yamada, IEEE Trans. Magn. 40 (2004) 2095–2097.
J. R. Hull, L. R. Turner, IEEE Trans. Magn. 36 (2000) 2004–2011.
S. W. Wang, X. D. Wang, M. J. Ni, X. D. Zhang, Z. H. Wang, X. Z. Na, Acta Metall. Sin. 49 (2013) 544–552.
P. A. Nikrityuk, S. Eckert, K. Eckert, Eur. J. Mech. B 27 (2008) 177–201.
S. Eckert, P. A. Nikrityuk, D. Raebiger, K. Eckert, G. Gerbeth, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 38 (2007) 977–988.
X. D. Wang, Y. Fautrelle, J. Etay, R. Moreau, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 40 (2009) 82–90.
N. B. Morley, J. Burris, L. C. Cadwallader, M. D. Nornberg, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79 (2008) 056107.
X. D. Wang, Y. Kolesnikov, Magnetohydrodynamics 50 (2014) 139–156.
User’s Manual for DOP 3010, Version4. 02. 1.
O. Andreev, Y. Kolesnikov, A. Thess, Exp. Fluids 46 (2009) 77–83.
S. Eckert, G. Gerbeth, Exp. Fluids 32 (2002) 542–546.
S. Eckert, B. Willers, G. Gerbeth, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36 (2005) 267–270.
H. Kikura, Y. Takeda, T. Sawada, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 201 (1999) 276–280.
Y. Takeda, Exp. Therm. Fluid. Sci. 10 (1995) 444–453.
A. Cramer, S. Eckert, G. Gerbeth, Eur. Phys. J. (Special Topics) 220 (2013) 25–41.
A. Cramer, J. Pal, G. Gerbeth, Phys. Fluids 19 (2007) 118109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by the Program of “One Hundred Talented People” of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (111800M105); Chinese Academy Sciences Funding (04078400)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Wang, Xd., Kolesnikov, Y. et al. An experimental prototype of an innovative fluid-driven electromagnetic stirring technique. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 23, 422–427 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(16)30067-X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(16)30067-X