Abstract
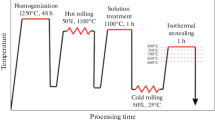
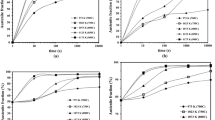
Grain refinement eficiency of electropulsing treatment (EPT) for metastable austenitic manganese steel was investigated. The mean grain size of original austenite is 300μm. However, after EPT, the microstructure exhibits a bimodal grain size distribution, and nearly 70vol. % grains are less than 60μm. The refined austenite results in ultrafine martensitic microstructure. The tensile strengths of refined austenitic and martensitic microstructures were improved from 495 to 670, and 794 to 900 MPa respectively. The fine grained materials possess beter fracture toughness. The workGhardening capacity and wear resistance of the refined austenitic microstructure are improved. The reasonable mechanism of grain refinement is the combination of accelerating new phase nucleation and restraiG ning the growth of neonatal austenitic grain during reverse transformation and rapid recrystalization induced by electropulsing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. F. Jing, F. C. Zhang, Mater. Lett. 31 (1997) 275–279.
J.P. Xie, A. Q. Wang, W. Y. Wang, J. W. Li, X. L. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 483–484 (2008) 743–746.
J. Qichuan, H. Zhenming, C. Donghuan, W. Shoushi, Y. Jiulin, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 9 (1990) 616–617.
Y. Jiang, G. Tang, C. Shek, Y. Zhu, Z. Xu, Acta Mater. 57 (2009) 4797–4808.
G. Hu, Y. Zhu, G. Tang. C. Shek, J. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 27 (2011) 1034–1038.
Y. Zhao, B. Ma, H. Guo, J. Ma, Q. Yang, J. Song, Mater. Des. 43 (2013) 195–199.
J.Z. Wang, Q. F. Chen, L. Y. Cao, L. C. Zhao, T. Nonlerr. Metal. Soc. 12 (2002) 400–403.
H. Conrad, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 287 (2000) 227–237.
Q. C. Li, R. X. Li, D. S. Lin, G. W. Chang, Q. J. Zhi J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 19 (2012) No. 12, 66–72.
K. Andrews, J. Iron Steel Inst. 203 (1965) 721–727.
H. Yang, H. Bhadeshia, Scripta Mater. 60 (2009) 493–495.
O. Modi, D. Mondai, B. Prasad, M. Singh, H. Khaira, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 343 (2003) 235–242.
Y. Dolinsky, T. Elperin, Phys. Rev. B 47 (1993) 14778–14785.
Y. Dolinsky, T. Elperin, Phys. Rev. B 50 (1994) 52–58.
Y. Z. Zhou, W. Zhang, B. Q. Wang, J. D. Guo, J. Mater. Res. 18 (2003) 1991–1997.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51071075)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Yg., Zhang, Jt., Tan, J. et al. Microstructure Refinement and Property Improvement of Metastable Austenitic Manganese Steel Induced by Electropulsing. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21, 685–689 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(14)60106-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(14)60106-0