Abstract
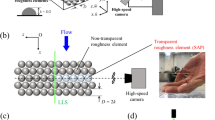
The bending rigidity of submerged vegetation is closely related with vegetative drag force. This work aims at determining the effects of flow conditions and characteristics of vegetation on the bending rigidity of submerged vegetation. Based on the dimensional analysis method, the factors influencing the bending rigidity of individual submerged vegetation were analyzed. The relationship between the relative bending rigidity and its influencing factors was investigated by experimental observation, and a relative bending rigidity expression for submerged vegetation was obtained by means of multiple linear regression method. The results show that the submerged vegetation has three states under different inflow conditions, and the each critical relative bending rigidity of individual submerged vegetation was determined for the different states of submerged vegetation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WU Zhen-bin, QIU Dong-ru and HE Feng et al. Effects of rehabilitation of submerged macrophytes on nutrient level of a eutrophic lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(8): 1351–1353. (in Chinese).
YANG Ming, WU Xiao-gang and ZHANG Wei-hao et al. Application of aquatic plant in ecological restoration of eutrophic water[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2007, 30(7): 98–102. (in Chinese).
WU Fu-sheng, JIANG Shu-hai and YANG Xue-lin. Characteristics of 2D-vortex field in open channel flow with submerged rigid vegetation[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2010, 25(1): 8–15. (in Chinese).
LAOUNIA N. Study of the flow through non-submerged vegetation[D]. Ph. D. Thesis, Nanjing: Hohai University, 2005.
WANG Pei-fang, WANG Chao and ZHU David Z. Hydraulic resistance of submerged vegetation related to effective height[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2010, 22(2): 265–273.
CHEN Gang, HUAI Wen-xin and HAN Jie et al. Flow structure in partially vegetated rectangular channels[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2010, 22(4): 590–597.
WU Fu-sheng, WANG Wen-ye and JIANG Shu-hai. Hydrodynamics development in vegetated open channel[ J]. Advances in Water Science, 2007, 18(3): 456–461. (in Chinese).
WHITE B. L., NEPF H. M. A vortex-based model of velocity and shear stress in a partially vegetated shallow channel [J]. Water Resources Research, 2008, 44(1): W01412.
NEPF H. M., VIVONI E. R. Flow structure in depthlimited, vegetated flow[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2000, 105(12): 28547–528557.
RIGHETTI M., ARMANINI A. Flow resistance in open channel flows with sparsely distributed bushes[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2002, 269(1–2): 55–64.
MUSLESH F. A., CRUISE J. F. Functional relationships of resistance in wide flood plains with rigid unsubmerged vegetation[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2006, 132(2): 163–171.
SHI Zhong, LI Yan-hong. Experimental studies of mean velocity profiles in vegetated river flow[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2003, 37(8): 1254–1260. (in Chinese).
YUJI T., SYUNSUKE I. and KENTARO K. et al. Effects of flood flow on flood plain soil and riparian vegetation in a gravel river[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2005, 131(11): 950–960.
VELASCO D., BATEMAN A. and REDONDO J. M. et al. An open channel flow experimental and theoretical study of resistance and turbulent characterization over flexible vegetated linings[J]. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion, 2003, 70(1–4): 69–88.
CAROLLO F. G., FERRO V. and TERMINI D. Flow velocity measurement in vegetated channels[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2002, 128(7): 664–673.
CAROLLO F. G., FERRO V. and TERMINI D. Flow resistance law in channels with flexible submerged vegetation[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2005, 131(7): 554–564.
KOUWEN N. Effect of riparian vegetation on flow resistance and flood potential-Discussion[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2000, 126(12): 954.
SAMANI J. M. V., KOUWEN N. Stability and erosion in grassed channels[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2002, 128(1): 40–45.
HUI Er-qing, HU Xing-e and JIANG Chun-bo et al. A study of drag coefficient related with vegetation based on the flume experiment[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2010, 22(3): 329–337.
NIKORA V., LARNED S. and NIKORA N. et al. Hydraulic resistance due to aquatic vegetation in small streams: Field study[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2008, 134(9): 1326–1332.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. 2010B01514, 2010B01314) the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51179057).
Biography: WU Long-hua (1974-), Male, Ph. D., Associate Professor
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Lh., Yang, Xl. Factors Influencing Bending Rigidity of Submerged Vegetation. J Hydrodyn 23, 723–729 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(10)60169-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(10)60169-2