Abstract
Objective
Maintenance of normal glucose tolerance is achieved in subjects with a wide range of insulin sensitivity. It follows, therefore, that the body must possess a sensor mechanism that assesses the body’s sensitivity to insulin and appropriately adjusts the secretion of insulin to maintain normal glucose homeostasis. We evaluated the relation between insulin action and insulin secretion.
Methods
Euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp (1 m U/kg · minute) and hyperglycemic clamp (+ 125 mg/dL) studies were performed in 32 non-obese women with normal oral glucose tolerance tests. The subjects were stratified into quartiles based upon their insulin-mediated rate of glucose uptake during the euglycemic insulin clamp.
Results
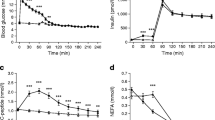
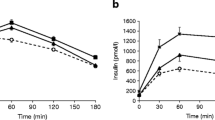
Total body glucose disposal varied threefold, ranging from 4.00 to HAS mg/kg · minute. A significant inverse relation (r = − 0.50, P < .01) was noted between the rate of total body insulin-mediated glucose disposal (insulin clamp) and the total plasma insulin response during the hyperglycemic clamp. Women in the lowest quartile of insulin sensitivity (mean glucose uptake 5.01 ± 0.20 mg/kg · minute) had the highest plasma insulin response during the hyperglycemic clamp (109 ± 20 μ U/mL). In contrast, women in the highest quartile of insulin sensitivity (glucose uptake 9.90 ± 0.38 mg/kg · minute) had the lowest plasma insulin response during the hyperglycemic clamp (55 ± 16 μ U/mL; P < .001 versus the lowest quartile).
Conclusions
These results demonstrate that among subjects with normal glucose tolerance, there exists a large variation in both insulin-mediated glucose uptake and pancreatic insulin secretion. Nonetheless, normal glucose tolerance is maintained because of a finely regulated balance, which couples the demand for insulin secretion by the pancreatic beta cells to the level of whole-body insulin sensitivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeFronzo RA. Lilly lecture. The triumvirate: β-cell, muscle, liver. A collusion responsible for NIDDM. Diabetes 1988;37:667–87.
DeFronzo RA, Bonadonna RC, Ferraninni E. Pathogenesisof NIDDM: A balanced overview. Diabetes Care 1992;15: 318–68.
Golay A, Felber JP, Jequier E, DeFronzo RA, Ferraninni E. Metabolicbasis of obesity and noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Rev 1989;4:727–47.
Saad MF, Knowler WC, Pettitt DJ, Nelson RG, Mott DM, Bennett PH. Sequential changes in serum insulin concentration during development of non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet 1989;i:1356-9.
Reaven GM. Banting lecture: Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988;37:1595–607.
Reaven GM, Hollenbeck CB, Chen Y-DI. Relationship between glucose tolerance, insulin secretion, and insulin action in non-obese individuals with varying degrees of glucose tolerance. Diabetologia 1989;32:52–5.
Lillioja S, Mott DM, Howard BV, et al. Impaired glucose tolerance as a disorder of insulin action: Longitudinal and cross-sectional studies in Pima Indians. N Engl J Med 1988;318:1217–25.
Saad MF, Knowler WC, Pettitt DJ, Nelson RG, Mott DM, Bennett PH. The natural history of impaired glucose tolerance in the Pima Indians. N Engl J Med 1988;319:1500–5.
Sims EAH, Danford E, Horton ES, Bray GA, Glennon JA, Salans LB. Endocrine and metabolic effects of experimental obesity in man. Recent Prog Horm Res 1973;29:457–96.
Bonadonna RC, Groop L, Kraemer N, Ferraninni E, Del Prato S, DeFronzo RA. Obesity and insulin resistance in man: A dose response study. Metabolism 1990;39:452–9.
Henry RR, Wallace P, Olefsky JM. Effects of weight loss on mechanisms of hyperglycemia in obese non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1986;35:990–8.
Hansen BC, Bodkin NL. Heterogeneity of insulin responses: Phases leading to type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in the rhesus monkey. Diabetologia 1986;29:713–9.
Bodkin NL, Metzger BL, Hansen BC. Hepatic glucose production and insulin sensitivity preceding diabetes in monkeys. Am J Physiol 1989;256:E676–81.
Hollenbeck A, Reaven GM. Variations in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in healthy individuals with normal glucose tolerance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1987;64:1169–73.
Bogardus C, Lillioja S, Howard B, Reaven GM, Mott D. Relationshipsbetween insulin secretion, insulin action and fasting plasma glucose concentration in non-diabetic and non-insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest 1984;74:1238–46.
DeFronzo RA. Glucose intolerance and aging: Evidence for tissue insensitivity to insulin. Diabetes 1979;28:1095–101.
Diamond MP, Simonson DC, DeFronzo RA. Menstrual cyclicity has a profound effect on glucose homeostasis. Fer-til Steril 1991;52:204–6.
Diamond MP, Grainger DA, Laudano AJ, Starick-Zych K, DeFronzo RA. Effect of acute physiologic elevations of insulin on circulating androgen levels in non-obese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1991;72:883–7.
Diamond MP, Jacob R, Connolly-Diamond M, DeFronzo R. Glucosemetabolism during the menstrual cycle: Assessment by the euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp technique. J Reprod Med 1993;38:417–21.
DeFronzo RA, Tobin JD, Andres R. Glucoseclamp technique: A method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol 1979;237:E214-23.
National Diabetes Data Group. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and other categories of glucose intolerance. Diabetes 1979;28:1039–57.
Somogyi M. Determinationof blood sugar. J Biol Chem 1945;160:69–73.
Radziuk J, Norwich KH, Vranic M. Experimentalvalidation of measurements of glucose turnover in non-steady state. Am J Physiol 1978;234:E84–93.
DeFronzo RA, Ferraninni E, Hendler R, Felig P, Wahren J. Regulationof splanchnic and peripheral glucose uptake by insulin and hyperglycemia. Diabetes 1983;32:35–45.
Grainger D, Thornton K, Rossi G, et al. Influence of basal androgen levels in euandrogenic women on glucose homeostasis. Fertil Steril 1992;58:113–8.
DeFronzo RA, Ferraninni E. Insulinresistance: A multifac-eted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 1991;14:173–202.
DeFronzo RA. Insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and coronary artery disease: A complex metabolic web. Cor Art Dis 1992;3:11–25.
Ferraninni E, Haffner SM, Mitchell BD, Stern MP. Hyperinsulinemia: The key feature of a cardiovascular and metabolic syndrome. Diabetologia 1991;3:416–22.
Dall’Aglio E, Chang H, Hollenbeck CB, Mondon CE, Sims C, Reaven GM. In vivo and in vitro resistance to maximal insulin-stimulated glucose disposal in insulin deficiency. Am J Physiol 1985;249:E312–6.
Gulli G, Ferraninni E, Stern M, Haffner S, DeFronzo RA. The metabolic profile of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus is fully established in glucose tolerant offspring of two Mexican American non-insulin dependent diabetic parents. Diabetes 1992;41:1575–86.
Erickson J, Franssila-Kallunki A, Ekstrand A, et al. Early metabolic defects in persons at increased risk for non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1989;34: 343–7.
Perley N, Kipnis DM. Effect of glucocorticoids on plasma insulin. N Engl J xMed 1966;274:1237–40.
Modigliani E, Strauch G, Luton JP. Effect of glucose and arginine on insulin secretion in Cushing’s syndrome. Diabetologia 1970;6:8–14.
Rizza RA, Mandarino LJ, Gerich JE. Cortisol-induced insulin resistance in man: Impaired suppression of glucose production and stimulation of glucose utilization due to a post-receptor defect of insulin action. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1982;54:131–8.
Rizza RA, Mandarino LJ, Gerich JE. Effects of growth hormone on insulin action in man. Mechanisms of insulin resistance, impaired suppression of glucose production and impaired stimulation of glucose utilization. Diabetes 1982;31:663–9.
Bratusch-Marrain PR, Smith D, DeFronzo RA. The effect of growth hormone on glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1982;55:973–82.
Kahn SE, Prigeon RL, McCulloch DK, et al. Quantification of the relationship between insulin sensitivity and β-cell function in human subjects. Diabetes 1993;42:1663–72.
DeFronzo RA, Ferraninni E. Regulationof hepatic glucose metabolism in humans. Diabetes Metab Rev 1987;3:415–59.
Cherrington AD, Stevenson RW, Steiner KE, et al. Insulin, glucagon, and glucose as regulators of hepatic glucose uptake and production in vivo. Diabetes Metab Rev 1987;3: 307–32.
Adkins BA, Myers SR, Hendrick GK, Stevenson RW, Williams PE, Cherrington AD. Importance of the route of intravenous glucose delivery to hepatic glucose balance in the conscious dog. J Clin Invest 1987;79:557–65.
DeFronzo RA, Gunnarsson R, Bjorkman O, Olsson M, Wahren J. Effectsof insulin on peripheral and splanchnic glucose metabolism in non-insulin dependent diabetes mel-litus. J Clin Invest 1985;76:149–55.
Ferraninni E, Buzzigoli A, Bonadonna R, et al. Insulin resistance in essential hypertension. N Engl J Med 1987;317: 350–7.
Pollare T, Lithell H, Berne C. Insulinresistance is a characteristic feature of primary hypertension independent of obesity. Metabolism 1990;39:167–74.
Olefsky JM, Farquhar JW, Reaven GM. Reappraisal of the role of insulin in hypertriglyceridemia. Am J Med 1974;57:551–60.
Tokey TA, Greenfield M, Kraemer F, Reaven GM. Relationship between insulin resistance, insulin secretion, very low density lipoprotein kinetics and plasma triglyceride levels in normal triglyceridemic women. Metabolism 1981;30:167–71.
Fontbonne AM, Eschwege EM. Insulin and cardiovascular disease: Paris prospective study. Diabetes Care 1991;14: 461–9.
Pyorala K. Relationshipof glucose tolerance and plasma insulin to the incidence of coronary heart disease: Results from two population studies in Finland. Diabetes Care 1979;2:131–41.
Bressler P, Bailey S, Saad R, DeFronzo RA. Insulin resistance and coronary artery disease: The missing link. Diabetes 1992.(41.suppl 1):24A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by National Institutes of Health grants HD 28984 and AM 24092, a VA Merit Award, funds from the VA Medical Research Service, the GRECC, and General Clinical Research Center grant no. RR-125.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diamond, M.P., Thornton, K., Connolly-Diamond, M. et al. Reciprocal Variations in Insulin-Stimulated Glucose Uptake and Pancreatic Insulin Secretion in Women With Normal Glucose Tolerance. Reprod. Sci. 2, 708–715 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/1071-5576(95)00023-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/1071-5576(95)00023-8