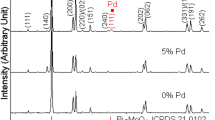
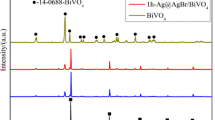
Abstract
This study focused on synthesizing and applying gold nanoparticle (Au NP) decorated barium titanate (BaTiO3) nanoparticles for photocatalytic purposes. BaTiO3 NPs were synthesized using a facile hydrothermal method. Various techniques were employed to characterize the structure and morphological characteristics of the prepared materials. The photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B over the Au NPs-modified BaTiO3 photocatalysts was studied. Trapping experiments were conducted using different scavengers to elucidate the degradation mechanism and the involvement of photogenerated species. The incorporation of an appropriate amount of Au NPs into the composites resulted in a significant improvement in photocatalytic activity, attributed to the combined effect of Schottky junction at the interface and the surface plasmon resonance of Au NPs.
Graphical abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
S. Francis et al., Green synthesis and characterization of gold and silver nanoparticles using Mussaenda glabrata leaf extract and their environmental applications to dye degradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 24(21), 17347–17357 (2017)
T.A. Saleh, M. Tuzen, A. Sarı, Evaluation of poly (ethylene diamine-trimesoyl chloride)-modified diatomite as efficient adsorbent for removal of rhodamine B from wastewater samples. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28(39), 55655–55666 (2021)
P.V. Nidheesh, R. Gandhimathi, Electrolytic removal of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution by peroxicoagulation process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 21(14), 8585–8594 (2014)
J. Guo et al., Adsorption and photocatalytic degradation behaviors of rhodamine dyes on surface-fluorinated TiO 2 under visible irradiation. RSC Adv. 6(5), 4090–4100 (2016)
S.P. Selvin et al., Visible light driven photodegradation of Rhodamine B using cysteine capped ZnO/GO nanocomposite as photocatalyst. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28(9), 6722–6730 (2017)
V.K. Garg et al., Basic dye (methylene blue) removal from simulated wastewater by adsorption using Indian Rosewood sawdust: a timber industry waste. Dyes Pigm. 63(3), 243–250 (2004)
S. Allen, B. Koumanova, Decolourisation of water/wastewater using adsorption. J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Metall. 40(3), 175–192 (2005)
S. Karimifard, M.R.A. Moghaddam, Application of response surface methodology in physicochemical removal of dyes from wastewater: a critical review. Sci. Total. Environ. 640, 772–797 (2018)
W.S. Koe et al., An overview of photocatalytic degradation: photocatalysts, mechanisms, and development of photocatalytic membrane. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27(3), 2522–2565 (2020)
S. Pai, M.S. Kini, R. Selvaraj, A review on adsorptive removal of dyes from wastewater by hydroxyapatite nanocomposites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28(10), 11835–11849 (2021)
U.I. Gaya, A.H. Abdullah, Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants over titanium dioxide: a review of fundamentals, progress and problems. J. Photochem. Photobiol., C 9(1), 1–12 (2008)
D. Chen et al., Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using TiO2-based photocatalysts: a review. J. Clean. Prod. 268, 121725 (2020)
R. Gusain et al., Adsorptive removal and photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using metal oxides and their composites: a comprehensive review. Adv. Coll. Interface. Sci. 272, 102009 (2019)
Z. Cai et al., An overview of nanomaterials applied for removing dyes from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 24(19), 15882–15904 (2017)
M.T. Buscaglia, V. Buscaglia, R. Alessio, Coating of BaCO3 crystals with TiO2: Versatile approach to the synthesis of BaTiO3 tetragonal nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 19(4), 711–718 (2007)
P. Wang et al., A dual chelating sol–gel synthesis of BaTiO3 nanoparticles with effective photocatalytic activity for removing humic acid from water. Mater. Res. Bull. 48(2), 869–877 (2013)
C. Gao et al., Nanocrystalline semiconducting donor-doped BaTiO3 ceramics for laminated PTC thermistor. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37(4), 1523–1528 (2017)
Z. Zhou, H. Tang, H.A. Sodano, Vertically aligned arrays of BaTiO3 nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5(22), 11894–11899 (2013)
P. Castera et al., Electro-optical modulation based on pockels effect in BaTiO 3 with a multi-domain structure. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 28(9), 990–993 (2016)
Y. Mao, H. Zhou, S.S. Wong, Synthesis, properties, and applications of perovskite-phase metal oxide nanostructures. Material Matters 5(2), 50 (2010)
M. Ali et al., Barium titanate nanocubes as a dual electrochemical sensor for detection of dopamine and acetaminophen. J. Electrochem. Soc. 169, 067512 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ac7a67
M. Thamima, Y. Andou, S. Karuppuchamy, Microwave assisted synthesis of perovskite structured BaTiO3 nanospheres via peroxo route for photocatalytic applications. Ceram. Int. 43(1), 556–563 (2017)
A. Rani et al., A review on the progress of nanostructure materials for energy harnessing and environmental remediation. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 8(3), 255–291 (2018)
C. Xu et al., Nanostructured materials for photocatalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 48(14), 3868–3902 (2019)
M. Kamali et al., Nanostructured materials via green sonochemical routes–sustainability aspects. Chemosphere 276, 130146 (2021)
C. Yu et al., Remarkably enhanced piezo-photocatalytic performance in BaTiO3/CuO heterostructures for organic pollutant degradation. J. Adv. Ceram. 11(3), 414–426 (2022)
D. Masekela et al., Application of BaTiO3-based catalysts for piezocatalytic, photocatalytic and piezo-photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants and bacterial disinfection in wastewater: a comprehensive review. Arab. J. Chem. 16, 104473 (2022)
J. Wu et al., Enhanced pyroelectric catalysis of BaTiO3 nanowires for utilizing waste heat in pollution treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10(44), 37963–37973 (2018)
G. Panthi, M. Park, Approaches for enhancing the photocatalytic activities of barium titanate: a review. J. Energy Chem. 73, 160–188 (2022)
Y. Cui et al., Enhanced photocatalytic activity of heterostructured ferroelectric BaTiO3/α-Fe2O3 and the significance of interface morphology control. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(29), 24518–24526 (2017)
X. Shen et al., Assembly of colloidal nanoparticles directed by the microstructures of polycrystalline ice. ACS Nano 5(10), 8426–8433 (2011)
S. Zhang et al., SPR enhanced photocatalytic properties of Au-dispersed amorphous BaTiO3 nanocomposite thin films. J. Alloy. Compd. 654, 112–119 (2016)
Y. Cui, J. Briscoe, S. Dunn, Effect of ferroelectricity on solar-light-driven photocatalytic activity of BaTiO3 influence on the carrier separation and stern layer formation. Chem. Mater. 25(21), 4215–4223 (2013)
Z. Miao et al., Gold nanoparticles decorated on BaTiO3 as photocatalyst: effect of SPR and ferroelectricity. Mater. Res. Express 5(2), 025505 (2018)
Y. Liu et al., Pyroelectric synthesis of metal–BaTiO3 hybrid nanoparticles with enhanced pyrocatalytic performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7(2), 2602–2609 (2018)
A. Patterson, The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 56(10), 978 (1939)
S. Xu et al., Piezotronic effect enhanced plasmonic photocatalysis by Au NPs/BaTiO3 heterostructures. Adv. Func. Mater. 29(13), 1808737 (2019)
Z. Li, D. Kurouski, Nanoscale structural characterization of plasmon-driven reactions. Nanophotonics 10(6), 1657–1673 (2021)
J. Tauc, Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous Ge and Si. Mater. Res. Bull. 3(1), 37–46 (1968)
M.D.C.B. López et al., Characterization of barium titanate powders: barium carbonate identification. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82(7), 1777–1786 (1999)
C. Chao et al., Ferroelectric polarization-enhanced photocatalytic properties and photo-induced charge carrier behavior of Au/BaTiO3. J. Alloy. Compd. 825, 154060 (2020)
M.M. Khan et al., BaTiO 3@ rGO nanocomposite: enhanced photocatalytic activity as well as improved electrode performance. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 12911–12921 (2021)
W. Wang et al., Large third-order optical nonlinearity in BaTiO3 matrix-embedded metal nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 218(1–4), 24–28 (2003)
Y. Ao et al., Graphene and TiO2 co-modified flower-like Bi2O2CO3: a novel multi-heterojunction photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 355, 411–418 (2015)
W.Y. Teoh, J.A. Scott, R. Amal, Progress in heterogeneous photocatalysis: from classical radical chemistry to engineering nanomaterials and solar reactors. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3(5), 629–639 (2012)
T. Tachikawa, M. Fujitsuka, T. Majima, Mechanistic insight into the TiO2 photocatalytic reactions: design of new photocatalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(14), 5259–5275 (2007)
A. Tarafdar et al., The hazardous threat of bisphenol A: toxicity, detection and remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 423, 127097 (2022)
X. Mao et al., RhB-sensitized effect on the enhancement of photocatalytic activity of BiOCl toward bisphenol-A under visible light irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 317, 517–525 (2014)
J. Mei et al., Photo-induced dye-sensitized BiPO4/BiOCl system for stably treating persistent organic pollutants. Appl. Catal. B 285, 119841 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Science and Engineering Research Board, New Delhi (File No. ECR/2016/000298). MA is thankful to CSIR India for the SRF fellowship (File No. 09/013(0921)/2019-EMR-I). DG and CSPT would like to thank Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi for providing seed grant under IoE scheme (Dev. Scheme No. 6031). The authors also acknowledge IIT-BHU and the department of Chemistry for the use of instrumentation facilities.
Funding
This project has received funding from the Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi under IoE scheme (Dev. Scheme No. 6031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DG and CSPT designed the study. MA, PS, and AK contributed to the sample preparation, measurements, data analysis, and discussion. MA wrote the main manuscript with inputs and helps from CSPT and DG. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare the absence of all known competing financial interests or personal relationships which could influence this work.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies comply with ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, M., Swami, P., Kumar, A. et al. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B using gold nanoparticles decorated on BaTiO3 with surface plasmon resonance enhancement. ANAL. SCI. 40, 643–654 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-023-00496-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-023-00496-1