Abstract
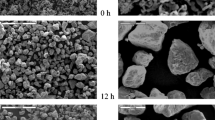
In this article, equiatomic multicomponent alloys with the compositions of Co20Cr20Fe20Mn20Ti20 and Co20Cr20Fe20Mn20Ti20Ni20 were synthesized by mechanical alloying with 5, 10 and 15 h of milling. During mechanical alloying, there is refinement of particles up to 10 h of milling following which there is agglomeration of particles till 15 h of milling in Co20Cr20Fe20Mn20Ti20 whereas, for Co20Cr20Fe20Mn20Ti20Ni20, the phenomenon of cold-welding predominated up to 10 h of milling following which refinement of particles were observed till 15 h of milling due to fragmentation. X-ray diffraction technique confirmed the presence of body-centered cubic and face-centered cubic phases in both the alloys. There is a considerable decrease in crystallite size and increment in the lattice strain with increase in the milling duration for both the alloys. Both the alloys exhibited nanocrystalline nature after 15 h of milling which was confirmed by high resolution transmission electron microscopy.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
M.C. Gao, J.W. Yeh, P.K. Liaw, Y. Zhang, High Entropy Alloys: Fundamentals and Application (Springer, Cham, 2016)
D.B. Miracle, High entropy alloys as a bold step forward in alloy development. Nat. Commun. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09700-1
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.Y. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principle elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200300567
D.B. Miracle, O.N. Senkov, A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.08.081
Y.F. Ye, Q. Wang, J. Lu, C.T. Liu, Y. Yang, High-entropy alloy: challenges and prospects. Mater. Today (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2015.11.026
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw, Z.P. Lu, Microstructure and properties of high entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2013.10.001
S.W. Goodrich, S. Haas, U. Glatzel, C.H. Liebscher, Towards superior high temperature properties in low density ferritic AlCrFeNiTi compositionally complex alloys. Acta Mater. 216, 117113 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117113
H. Inui, K. Kishida, C. Zhengo, Recent progress in our understanding of phase stability, atomic structures and mechanical and functional properties of high-entropy alloys. Mater. Trans. (2022). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.MT-M2021234
B.S. Murty, J.W. Yeh, S. Ranganathan, High-entropy Alloys (Butterworth-Heinemann, Elsevier, United Kingdom, 2014)
M.H. Tsai, J.W. Yeh, High-entropy alloys: a critical review. Mater. Res. Lett. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2014.912690
D.B. Miracle, High-entropy alloys: a current evaluation of founding ideas and core effects and exploring “Nonlinear Alloys.” J. Mater. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2527-z
J. Chen, X. Zhou, W. Wang, A review on fundamental of high entropy alloys with promising high-temperature properties. J. Alloy. Compd. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.067
J. Kumar, A. Linda, K. Biswas, Lattice distortion in FCC HEAs and its effect on mechanical properties: critical analysis and way forward. J. Appl. Phys. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0144456
A. Seaone, D. Farkas, X.M. Bai, Influence of compositional complexity on species diffusion behavior in high-entropy solid-solution alloys. J. Mater. Res. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2018.1446466
K.K. Alaneme, M.O. Bodunrin, S.R. Oke, Processing, alloy composition and phase transition effect of the mechanical and corrosion properties of high entropy alloys: a review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2016.03.004
R. Sharma, A. Roy, P.S. De, Equimolar AlCuFeMn: a novel oxidation resistant alloy. Intermetallics (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2021.107215
H. Peng, L. Hu, S. Huang, L. Li, I. Baker, A comparison of thermo-mechanically-treated and electron-beam welded strong, ductile medium-entropy alloy: microstructural evolution and deformation mechanisms. Mater. Sci. Eng. A (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2023.145449
X. Gao, Y. Lu, B. Zhang, N. Liang, G. Wu, G. Sha, Z. Liu, Y. Zhao, Microstructural origins of high strength and high ductility in an AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.07.041
C. Suryanarayana, Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Science. (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6425(99)00010-9
M.H. Enayati, F.A. Mohamed, Application of mechanical alloying/milling for synthesis of nanocrystalline and amorphous materials. Int. Mater. Rev. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1179/1743280414Y.0000000036
C.C. Coch, Structural nanocrystalline materials: an overview. J. Mater. Sci. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0609-3
S. Gorsse, J.P. Couzinie, D.B. Miracle, From high entropy alloys to complex concentrated alloys. C. R. Phys. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crhy.2018.09.004
J. Saha, R. Saha, P.P. Bhatacharjee, Microstructure and texture of severely warm-rolled and annealed coarse-grained CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy (MEA): a perspective on the initial grain size effect. J. Alloy. Compd. 904, 163954 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.163954
Y. Zhang, High Entropy Materials: Advances and Applications (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2023)
O.N. Senkov, G.B. Wilks, D.B. Miracle, Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2010.05.014
A. Sharma, S. Dasari, V. Soni, Z. Kloenne, J.P. Couzinnie, O.N. Senkov, D.B. Miracle, S.G. Srinivasan, H. Fraser, R. Banerjee, B2 to ordered omega transformation during isothermal annealing of refractory high entropy alloys: Implications for high temperature phase stability. J. Alloy. Compd. 953, 170065 (2023)
K.C. Lo, H. Murakami, J.W. Yeh, A.C. Yeh, Oxidation behavior of a novel refractory high entropy alloy at elevated temperatures. Intermetallics (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2020.106711
C. Varvenne, W.A. Curtin, Strengthening of high entropy alloys by dilute solute additions: CoCrFeNiAlx and CoCrFeNiMnAlx alloys. Scr. Mater. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.05.035
T. Gu, L. Wang, Q. Hu, X.B. Liang, D.X. Fu, Y.X. Chen, X.M. Zhao, Y.W. Sheng, Effect of mechanical alloying and sintering behavior on the microstructure and properties of NbMTaWRe refractory high entropy alloy. Met. Mater. Int. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-021-01165-6
B. Gludovatz, A. Hohenwarter, D. Catoor, E.H. Chang, E.P. George, R.O. Ritchie, A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science (2014). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254581
T. Yang, Y.L. Zhao, J.H. Luan, B. Han, J. Wei, J.J. Kai, C.T. Liu, Nanoparticles-strengthened high-entropy alloys for cryogenic applications showing an exceptional strength-ductility synergy. Scr. Mater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciptmat.2019.01.034
H. Cheng, Y. Xie, Q. Tang, C. Rong, Microstructure and mechanical properties of FeCoCrNiMn high entropy alloy produced by mechanical alloying and vacuum hot pressing sintering. Trans. Nonferr. Metal Soc. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64774-0
N. Eibmann, B. Kloden, T. Weibgarber, B. Kieback, High-entropy alloy CoCrFeMnNi produced by powder metallurgy. Powder Metall. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/00325899.2017.1318480
S. Mohanty, T.N. Maity, S. Mukhopadhaya, S. Sarkar, N.P. Gurao, S. Bhowmick, K. Biswas, Powder metallurgical processing of equiatomic AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy: microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.09.062
K.B. Zhang, Z.Y. Fu, J.Y. Zhang, W.M. Wang, S.W. Lee, K. Niihara, Characterization of nanocrystalline CoCrFeNiTiAl high-entropy solid solution processed by mechanical alloying. J. Alloy. Compd. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.12.010
K.B. Zhang, Z.Y. Fu, J.Y. Zhang, J. Shi, W.M. Wang, H. Wang, Y.C. Wang, Q.J. Zhang, Nanocrystalline CoCrFeNiCuAl high-entropy solid solution synthesized by mechanical alloying. J. Alloy. Compd. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.05.144
W. Ji, W. Wang, H. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Wang, F. Zhang, Z. Fu, Alloying behavior and novel properties of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Intermetallics (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2014.08.008
S. Guo, C.T. Li, Phase stability in high-entropy alloys: formation of solid solution phase or amorphous phase. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0071(12)60080-X
S. Das, P.S. Robi, A novel refractory WMoVCrTa high-entropy alloy possessing fine combination of compressive stress-strain and high hardness properties. Adv. Powder Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.10.008
W. Chen, A. Hilhorst, G. Bokas, S. Gorsse, J.P. Jacques, G. Hautier, A map of single-phase high-entropy alloys. Nat. Commun. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38423-7
A.M. Manzoni, U. Glatzel, New multiphase compositionally complex alloys driven by high entropy alloy approach. Mater Charact 147, 512 (2019)
X. Yang, Y. Zhang, Prediction of high-entropy stabilized solid-solution in multi-component alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.11.021
S. Guo, Ng. Chun, J. Lu, C.T. Liu, Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3587228
S. Luo, L. Vitos, C. Zhao, Y. Su, Z. Wang, Predicting phase formation in complex concentrated alloys from first-principles. Comput. Mater. Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2020.110021
Z. Wang, Y. Huang, Y. Yang, Atomic-size effect and solid solubility of multicomponent alloys. Scr. Mater. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.09.010
J.S. Benjamin, T.E. Volin, The mechanism of mechanical alloying. Metall. Trans. (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02644161
Z. Chen, W. Chen, B. Wu, X. Cao, L. Liu, Z. Fu, Effects of Co and Ti on microstructure and mechanical behavior of Al07.5FeNiCrCo high entropy alloy prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.08.056
Y.L. Chen, Y.H. Hu, C. Hsieh, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, Competition between elements during mechanical alloying in an octonary-multi-principal-element alloy system. J. Alloy. Compd. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.03.087
S.K. Pabi, J. Joarder, B.S. Murty, Mechanism and kinetics of alloying and nanostructure formation by mechanical methods. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. Part A. 67, 1–30 (2001)
H. Okamoto, M. E. Schlesinger, E. M. Mueller, Alloy Phase Diagrams: Volume 3 (Materials Park, Ohio 2016)
S. Praveen, B.S. Murty, R.S. Kottada, Phase evolution and densification behavior of nanocrystalline multicomponent high entropy alloys during spark plasma sintering. J. Mater. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-013-0759-0
V.K. Portnoi, A.V. Leonov, S.E. Filippova, A.N. Streletskii, A.I. Logacheva, Mechanochemical synthesis and heating-induced transformations of a high-entropy Cr–Fe–Co–Ni–Al–Ti alloy. Inorg. Mater. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168514120188
Z. Fu, W. Chen, H. Wen, Z. Chen, Effect of Co and sintering method on microstructure and mechanical behavior of a high-entropy Al07.6NiFeCrCo alloy prepared by powder metallurgy. J. Alloy. Compd. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.04.238
P. Wang, H. Cai, X. Cheng, Effect of Ni/Cr ratio on phase, microstructure and mechanical properties of NixCoCuFeCr2-x(x= 1.0, 1.2, 1.5, 1.8 mol) high entropy alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.11.205
M. Vaidya, A. Prasad, A. Parakh, B.S. Murty, Influence of sequence of elemental addition on phase evolution in nanocrystalline AlCoCrFeNi: novel approach to alloy synthesis using mechanical alloying. Mater. Des. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.04.027
S.H. Joo, H. Kato, M.H. Jang, J. Moon, E.B. Kim, S.J. Hong, H.S. Kim, Structure and properties of ultrafine-grained CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy produced by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. J. Alloy. Compd. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/jjallcom.2016.12.010
B.D. Cullity, S.R. Stock, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction (Pearson Education, London, 1978)
V. Shivam, J. Basu, V.K. Pandey, Y. Shadangi, N.K. Mukhopadhyay, Alloying behavior, thermal stability and phase evolution in quinary AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Adv. Powder Technol. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2018.06.006
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Central Research Facility (CRF), IIT Kharagpur for assistance in carrying out the experimental work. TD would like to thank MHRD, Govt. of India for financial support. Partial financial grants from Alexander von Humboldt (AvH) (Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel Award), Department of Science and Technology (POWER Fellowship) to JDM and Department of Science and Technology (J.C.Bose Fellowship) to IM are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Datta, T., Manna, I. & Majumdar, J.D. Synthesis of Multi-component Alloys (Co20Cr20Fe20Mn20Ti20 and Co20Cr20Fe20Mn20Ti20Ni20) by Mechanical Alloying Route. High Entropy Alloys & Materials (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44210-023-00025-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44210-023-00025-9