Abstract
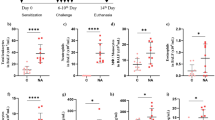
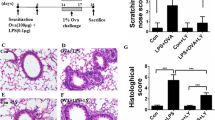
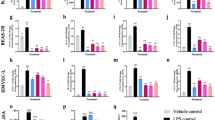
Acute lung injury is characterized by alveolar-capillary barrier rupture, neutrophil-mediated airway inflammation, and tissue hypoxia. Since no effective pharmacotherapy is currently available, alternatives to improve its condition are mandatory. Recent studies demonstrated that curine, a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid from Chondrodendron platyphyllum (A.St.-Hil.) Miers, Menispermaceae, with anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory properties, inhibited lipopolysaccharide-mediated acute pulmonary response in mice. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate curine’s mechanism of action in a lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury model. Curine inhibited the recruitment of inflammatory cells to the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, mainly dependent on neutrophil migration, and restored the pulmonary architecture by reducing edema, vascular permeability, and the total protein content as well as the wet/dry ratio of the lung. Curine also decreased the TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 production through downregulating the toll-like receptor 4 receptor expression and the nuclear factor-kappa B (p65) phosphorylation. In silico analysis demonstrated that curine made hydrophobic interactions with the Leu78, Ile80, Phe121, Ile124, Phe126, and Ile 152 amino acids of the hydrophobic cavity of the MD-2 receptor. This curine interaction presented stability during the simulation, remaining linked to the active site, indicating an antagonistic interaction with the molecular complex lipopolysaccharides/toll-likereceptor/4 myeloid differentiation factor 2.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham MJ, Murtola T, Schulz R, Páll S, Smith JC, Hess B, Lindah E (2015) Gromacs: high performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 1–2:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001
Albiger B, Dahlberg S, Henriques-Normark B, Normark S (2007) Role of the innate immune system in host defence against bacterial infections: focus on the Toll-like receptors. J Intern Med 261:511–528. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2796.2007.01821.x
Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, Fan E, Brochard L, Esteban A, Gattinoni L, Van Haren FMP, Larsson A, McAuley DF, Ranieri M, Rubenfeld G, Thompson BT, Wrigge H, Slutsky AS, Pesenti A (2016) Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries. J Am Med Assoc 315:788–800. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.0291
Berendsen HJC, van der Spoel D, van Drunen R (1995) GROMACS: a message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Comput Phys Commun 91:43–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-4655(95)00042-E
Bhattacharya J, Matthay MA (2013) Regulation and repair of the alveolar-capillary barrier in acute lung injury. Annu Rev Physiol 75:593–615. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-030212-183756
Bitencourt-Ferreira G, de Azevedo WF (2019) Molegro virtual docker for docking. In: Methods in molecular biology. Humana Press Inc., pp. 149–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9752-7_10
Cheung OY, Graziano P, Smith ML (2017) Acute lung injury, 3rd ed. Practical pulmonary pathology: a diagnostic approach A Volume in the Pattern Recognition Series. Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-44284-8.00006-5
Dantas BB, Faheina-Martins GV, Coulidiati TH, Bomfim CCB, Da Silva DC, Barbosa-Filho JM, Araújo DAM (2015) Effects of curine in HL-60 leukemic cells: cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction. J Nat Med 69:218–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-014-0881-5
Dias CS, Barbosa-Filho JM, Lemos VS, Côrtes SF (2002) Mechanisms involved in the vasodilator effect of curine in rat resistance arteries. Planta Med 68:1049–1051. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2002-35662
do Nascimento Xavier BM, Ferreira LAMP, Ferreira LKDP, Gadelha FAAF, Monteiro TM, de Araújo Silva LA, Rodrigues LC, Piuvezam MR (2019) MHTP, a synthetic tetratetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid, attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via p38MAPK/p65NF-κB signaling pathway-TLR4 dependent. Inflamm Res 68:1061–1070. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-019-01291-3
Fan E, Brodie D, Slutsky AS (2018) Acute respiratory distress syndrome advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA 319:698–710. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.21907
Guedes DN, Barbosa-Filho JM, Lemos VS, Côrtes SF (2002) Mechanism of the vasodilator effect of 12-O-methylcurine in rat aortic rings. J Pharm Pharmacol 54:853–858. https://doi.org/10.1211/0022357021779032
Jiang Q, Yi M, Guo Q, Wang C, Wang H, Meng S, Liu C, Fu Y, Ji H, Chen T (2015) Protective effects of polydatin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 29:370–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2015.10.027
Leite FC, Ribeiro-Filho J, Costa HF, Salgado PRR, Calheiros AS, Carneiro AB, De Almeida RN, Dias CDS, Bozza PT, Piuvezam MR (2014) Curine, an alkaloid isolated from Chondrodendron platyphyllum inhibits prostaglandin E2 in experimental models of inflammation and pain. Planta Med 80:1072–1078. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1382997
Medeiros MAA, Pinho JF, De-Lira DP, Barbosa-Filho JM, Araújo DAM, Cortes SF, Lemos VS, Cruz JS (2011) Curine, a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid, blocks L-type Ca 2+ channels and decreases intracellular Ca 2+ transients in A7r5 cells. Eur J Pharmacol 669:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.07.044
Orlando BJ, Malkowski MG (2016)Substrate-selective inhibition of cyclooxygeanse-2 by fenamic acid derivatives is dependent on peroxide tone. J Biol Chem 291:15069–15081. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.725713
Petrovska BB (2012) Historical review of medicinal plants’ usage. Pharmacogn Rev 6:1–5. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.95849
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera - a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20084
Proudfoot AG, McAuley DF, Griffiths MJD, Hind M (2011) Human models of acute lung injury. Dis Model Mech 4:145–153. https://doi.org/10.1242/DMM.006213
Rezoagli E, Fumagalli R, Bellani G (2017) Definition and epidemiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann Transl Med 5:282. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2017.06.62
Ribeiro-Filho J, Calheiros AS, Vieira-de-Abreu A, de Carvalho KIM, da Silva MD, Melo CB, Martins MA, da Silva DC, Piuvezam MR, Bozza PT (2013) Curine inhibits eosinophil activation and airway hyper-responsiveness in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 273:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2013.08.015
Ribeiro-Filho J, Carvalho Leite F, Surrage Calheiros A, de Brito Carneiro A, Alves Azeredo J, Fernandes de Assis E, da Silva Dias C, Regina Piuvezam M, Bozza PT (2019) Curine inhibits macrophage activation and neutrophil recruitment in a mouse model of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. Toxins 11:705. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120705
Ribeiro-Filho J, Leite FC, Costa HF, Calheiros AS, Torres RC, De Azevedo CT, Martins MA, Da Silva DC, Bozza PT, Piuvezam MR (2014) Curine inhibits mast cell-dependent responses in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 155:1118–1124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2014.06.041
Thomsen R, Christensen MH (2006) MolDock: a new technique for high-accuracy molecular docking. J Med Chem 49:3315–3321. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm051197e
van Rijt LS, Kuipers H, Vos N, Hijdra D, Hoogsteden HC, Lambrecht BN (2004) A rapid flow cytometric method for determining the cellular composition of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cells in mouse models of asthma. J Immunol Methods 288:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2004.03.004
Yang CY, Chen CS, Yiang GT, Cheng YL, Yong SB, Wu MY, Li CJ (2018) New insights into the immune molecular regulation of the pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Int J Mol Sci 19:588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020588
Funding
This study was sponsored by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES)- Finance Code 001 and CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico - Brasil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MRP, LAMPF, and LKDPF outlined and designed the experiments, wrote the original draft, and revised and edited the manuscript for submission. LAMPF and LKDPF performed the experimental model of ALI. LAMPF, LKDPF, and LML performed the ELISA protocol. LAMPF, LKDPF, and TMM performed the flow cytometry protocol. FAAFG performed the lung histology. MRP, LAMPF, and LKDPF analyzed the data. MSM and MTS performed the molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. JRF reviewed the manuscript. CSD was responsible for the alkaloid curine extraction and purification and made it available for the study. MRP was responsible for conceptualization, visualization, resources, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, and writing—review and editing. All the authors have read the final manuscript and approved the submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Protection of Human and Animal Subjects
The authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans. All studies were conducted by following the guidelines of the National Animal Experimentation Control Council (CONCEA) and adhered strictly to the guidelines of the Brazilian Law (n°. 11.794/2008) which establishes rules for use and care of laboratory animals. The Committee on Ethics in Uses of Animals (CEUA/UFPB) approved the experimental procedures under certificate n° 7316150420. The used animals were purchased from the Animal Production Unit of the Institute for Research on Drugs and Medicines (IPeFarM) of the Federal University of Paraíba, João Pessoa, PB, Brazil.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paiva Ferreira, L.A.M., Paiva Ferreira, L.K.D., Monteiro, T.M. et al. Curine Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Downregulating the TLR4/MD-2/NF-κB(p65) Signaling Pathway. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 32, 111–121 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-022-00230-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-022-00230-4