Abstract
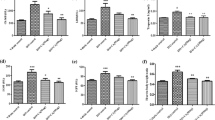
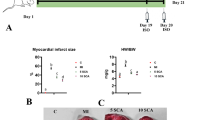
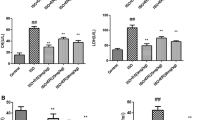
Carnosic acid possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Early evidence indicates that this phenolic diterpenoid protects the heart against myocardial infarction, although the mechanism is unknown. For this research, male rats were divided into four groups: the control group, the myocardial infarction group (85 mg/kg, isoproterenol on the 19th and 20th days of experiment), and myocardial infarction groups pretreated with 10 and 20 mg/kg/bw of carnosic acid for 21 days. Following animal sacrifice, serum cardiac markers, cardiac oxidative stress, inflammation, and histological and molecular analysis were conducted. Pretreatment of carnosic acid to myocardial infarction–induced rats showed to reduce the ratio of cardiac weight/body weight ratio as well as the size of the infarction. Furthermore, serum cardiac biomarkers and lipid peroxidation were significantly reduced, but antioxidant enzymes were significantly increased in myocardial infarction–induced rats pretreated with carnosic acid. Carnosic acid significantly lowers cardiac inflammatory markers as well as improved histological abnormalities in isoproterenol-injected rats. Carnosic acid has been shown to efficiently reverse isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction by lowering infraction size and decreasing oxidative stress and inflammation by activating Nrf2/HO-1 and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathways.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam SH, Giribabu N, Bakar NMA, Salleh N (2017) Marantodes pumilum (Kacip fatimah) enhances in-vitro glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocyte cells and reduces pancreatic complications in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced male diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 96:716–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.042
Albalawi A, Alhasani RHA, Biswas L, Reilly J, Akhtar S, Shu X (2018) Carnosic acid attenuates acrylamide-induced retinal toxicity in zebrafish embryos. Exp Eye Res 175:103–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2018.06.018
Alonso A, Aparicio FHJ, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson FAP, Chamberlain FAM, Kissela BM, Knutson FKL, Lee CD (2021) Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021 update. Circulation 143:e254–e743. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000950
Bellezza I, Giambanco I, Minelli A, Donato R (2018) Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1865:721–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.02.010
Byrne NJ, Rajasekaran NS, Abel ED, Bugger H (2021) Therapeutic potential of targeting oxidative stress in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Free Radic Biol Med 169:317–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.03.046
Chen QM, Maltagliati AJ (2018) Nrf2 at the heart of oxidative stress and cardiac protection. Physiol Genomics 50:77–97. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00041.2017
Cheng J, Xu T, Xun C, Guo H, Cao R, Gao S, Sheng W (2021) Carnosic acid protects against ferroptosis in PC12 cells exposed to erastin through activation of Nrf2 pathway. Life Sci 266:118905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118905
Devi A, Dwibedi V, Khan ZA (2021) Natural antioxidants in new age-related diseases. Rev Bras Farmacogn 31:387–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-021-00175-0
Dizaji NM, Garjani A, Mousavi S, Mohammadi M, Vaez H (2021) Time-dependent influence of infliximab on hemodynamic responses and cardiac injuries of isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 903:174122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174122
Erkan N, Ayranci G, Ayranci E (2008) Antioxidant activities of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) extract, blackseed (Nigella sativa L.) essential oil, carnosic acid, rosmarinic acid and sesamol. Food Chem 110:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.01.058
Giribabu N, Roslan J, Rekha SS, Salleh N (2016) Methanolic seed extract of Vitis vinifera ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation and ATPase dysfunction in infarcted and non-infarcted heart of streptozotocin–nicotinamide induced male diabetic rats. Int J Cardiol 222:850–865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.07.250
Hu M, Li T, Bo Z, Xiang F (2019) The protective role of carnosic acid in ischemic/reperfusion injury through regulation of autophagy under T2DM. Exp Biol Med 244:602–611. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370219840987
Jin W, Zhang Y, Xue Y, Han X, Zhang X, Ma Z, Sun S, Chu X, Cheng J, Guan S (2020) Crocin attenuates isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis by targeting TLR4/NF-κB signaling: connecting oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 393:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01704-4
Kocak C, Kocak FE, Akcilar R, Isiklar OO, Kocak H, Bayat Z, Simsek H, Taser F, Altuntas I (2016) Molecular and biochemical evidence on the protective effects of embelin and carnosic acid in isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial injury in rats. Life Sci 147:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.01.038
Kones R (2013) Molecular sources of residual cardiovascular risk, clinical signals, and innovative solutions: relationship with subclinical disease, undertreatment, and poor adherence: implications of new evidence upon optimizing cardiovascular patient outcomes. Vasc Health Risk Manag 9:617–670. https://doi.org/10.2147/VHRM.S37119
Li J, Thangaiyan R, Govindasamy K, Wei J (2021) Anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effect of zingiberene on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in experimental animals. Hum Exp Toxicol 4:915–927. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327120975131
Lin KI, Lin CC, Kuo SM, Lai JC, Wang YQ, You HL, Hsu ML, Chen CH, Shiu LY (2018) Carnosic acid impedes cell growth and enhances anticancer effects of carmustine and lomustine in melanoma. Biosci Rep 38:BSR20180005. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20180005
Maehly A, Chance B (1954) Catalases and peroxidases. Methods Biochem Anal 1:357–424. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470110171.ch14
Mimura J, Kosaka K, Maruyama A, Satoh T, Harada N, Yoshida H, Satoh K, Yamamoto M, Itoh K (2011) Nrf2 regulates NGF mRNA induction by carnosic acid in T98G glioblastoma cells and normal human astrocytes. J Biochem 150:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvr065
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175
Neri M, Fineschi V, Di Paolo M, Pomara C, Riezzo I, Turillazzi E, Cerretani D (2015) Cardiac oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines response after myocardial infarction. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 13:26–36. https://doi.org/10.2174/15701611113119990003
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Rotruck J, Pope A, Ganther HE, Swanson A, Hafeman DG, Hoekstra W (1973) Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science 179:588–590. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.179.4073.588
Sahu BD, Putcha UK, Kuncha M, Rachamalla SS, Sistla R (2014) Carnosic acid promotes myocardial antioxidant response and prevents isoproterenol-induced myocardial oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice. Mol Cell Biochem 394:163–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2092-5
Su Q, Li L, Sun Y, Yang H, Ye Z, Zhao J (2018) Effects of the TLR4/Myd88/NF-κB signaling pathway on NLRP3 inflammasome in coronary microembolization-induced myocardial injury. Cell Physiol Biochem 47:1497–1508. https://doi.org/10.1159/000490866
Su S, Zhang P, Zhang Q, Yin Z (2019) GSK-3β inhibitor induces expression of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway to protect against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury during rat kidney transplantation. Inflammation 42:2105–2118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01074-2
Zhang D, Lee B, Nutter A, Song P, Dolatabadi N, Parker J, Sanz-Blasco S, Newmeyer T, Ambasudhan R, McKercher SR (2015) Protection from cyanide-induced brain injury by the Nrf2 transcriptional activator carnosic acid. J Neurochem 133:898–908. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13074
Zhang QL, Yang JJ, Zhang HS (2019) Carvedilol (CAR) combined with carnosic acid (CAA) attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by suppressing excessive oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy. Biomed Pharmacother 109:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.037
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to HOD of the Department Cardiology, Hongze District People’s Hospital, for help in technical and instrumental support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RN carried out the animal experiments and wrote the manuscript first draft. XD carried out the qPCR, histopathology, and statistical analysis. QW carried out immunohistochemistry and preparation of figures. YG carried out experimental design, funding, and editing the manuscript. All authors have contributed to the writing of the manuscript and approved the final submission.
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ning, R., Deng, X., Wang, Q. et al. Carnosic Acid Protects Against Myocardial Infarction by Controlling Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Rats. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 31, 794–804 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-021-00216-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-021-00216-8