Abstract
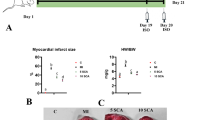
Phytomedicine has shown a promising potential for the prevention of cardiovascular system diseases and disorders. This study aimed to evaluate protective effect of ergosterol (ER) on isoproterenol (ISO)-induced myocardial cardiotoxicity. We found that pretreatment with ER significantly decreased levels of myocardial CK-MB and LDH, and alleviated myocardial damage induced by ISO in rat model. In addition, ER restored Nrf2 and HO-1 expression and inhibited apoptosis through upregulating Bcl-2 and downregulating Bax, cytochrome c, cleaved caspase-3, caspase-9, and PARP in rat hearts. Hypoxia-reoxygenation model in H9C2 cells confirmed the cardioprotective effects of ER. In conclusion, we provide both in vitro and in vivo evidence that ER significantly enhances Nrf2-mediated anti-oxidative activities, and exerts a protective effect on cardiomyocyte apoptosis. ER could be considered as a potential therapeutic agent to prevent myocardial injury.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 May 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-023-09796-4
References
Thygesen, K., Alpert, J. S., Jaffe, A. S., Chaitman, B. R., Bax, J. J., Morrow, D. A., et al. (2018). Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 72, 2231–2264.
Adameova, A. D., Bhullar, S. K., Elimban, V., & Dhalla, N. S. (2018). Activation of β1-adrenoceptors may not be involved in arrhythmogenesis in ischemic heart disease. Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine, 19, 97–101.
Neri, M., Fineschi, V., Di Paolo, M., Pomara, C., Riezzo, I., Turillazzi, E., et al. (2015). Cardiac oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines response after myocardial infarction. Current Vascular Pharmacology, 13, 26–36.
Caccioppo, A., Franchin, L., Grosso, A., Angelini, F., D'Ascenzo, F., & Brizzi, M. F. (2019). Ischemia reperfusion injury: Mechanisms of damage/protection and novel strategies for cardiac recovery/regeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20, 5024.
Neri, M., Riezzo, I., Pascale, N., Pomara, C., & Turillazzi, E. (2017). Ischemia/reperfusion injury following acute myocardial infarction: a critical issue for clinicians and forensic pathologists. Mediators of Inflammation, 2017, 7018393.
Radhiga, T., Rajamanickam, C., Sundaresan, A., Ezhumalai, M., & Pugalendi, K. V. (2012). Effect of ursolic acid treatment on apoptosis and DNA damage in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction. Biochimie, 94, 1135–1142.
Hwa, J. S., Jin, Y. C., Lee, Y. S., Ko, Y. S., Kim, Y. M., Shi, L. Y., et al. (2012). 2-Methoxycinnamaldehyde from Cinnamomum cassia reduces rat myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury in vivo due to HO-1 induction. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 139, 605–615.
Hao, E., Lang, F., Chen, Y., Zhang, H., Cong, X., Shen, X., et al. (2013). Resveratrol alleviates endotoxin-induced myocardial toxicity via the Nrf2 transcription factor. PLoS ONE, 8, e69452.
Wei, B., Li, W. W., Ji, J., Hu, Q. H., & Ji, H. (2014). The cardioprotective effect of sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate and the optimizing of therapeutic time window in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Atherosclerosis, 235, 318–327.
Lee, T.-M., Lin, S.-Z., & Chang, N.-C. (2014). Antiarrhythmic effect of lithium in rats after myocardial infarction by activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 77, 71–81.
Montes, F. Q., Vázquez-Hernández, A., & Fenton-Navarro, B. (2019). Active compounds of medicinal plants, mechanism for antioxidant and beneficial effects. Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, 88, 1–10.
Villa-Hernández, J. M., García-Ocón, B., Sierra-Palacios, E. C., & Pelayo-Zaldivar, C. (2018). Molecular biology techniques as new alternatives for medicinal plant identification. Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, 87, 72–78.
Huan, W., Tianzhu, Z., Yu, L., & Shumin, W. (2017). Effects of ergosterol on COPD in mice via JAK3/STAT3/NF-κB pathway. Inflammation, 40(3), 884–893.
Kaplan, A., Yabluchanskiy, A., Ghali, R., Altara, R., Booz, G. W., & Zouein, F. A. (2018). Cerebral blood flow alteration following acute myocardial infarction in mice. Bioscience Report, 38(5), 20180382.
Fu, L., Liu, Y., Wang, J., Sun, Y., Zhang, L., Wu, T., et al. (2017). Cardioprotection by low-dose of estrogen and testosterone at the physiological ratio on ovariectomized rats during ischemia/reperfusion injury. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology, 70(2), 87–93.
Zhou, C., Busso, C. A., Yang, Y. G., Zhang, Z., Wang, Z. W., Yang, Y. F., et al. (2017). Effect of mixed salt stress on malondialdehyde, proteins and antioxidant enzymes of Leymus chinensis in three leaf colors. Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, 86, 205–213.
Bellezza, I. (2018). Oxidative stress in age-related macular degeneration: Nrf2 as therapeutic target. Frontier in Pharmacology, 9, 1280.
Gottlieb, R. A., Burleson, K. O., Kloner, R. A., Babior, B. M., & Engler, R. L. (1994). Reperfusion injury induces apoptosis in rabbit cardiomyocytes. J Clin Invest, 94, 1621–1628.
Frangogiannis, N. G. (2015). Pathophysiology of myocardial infarction. Comprehensive Physiology, 5(4), 1841–1875.
Turillazzi, E., Cerretani, D., Cantatore, S., Fiaschi, A. I., Frati, P., Micheli, L., et al. (2017). Myocardial oxidative damage is induced by cardiac Fas-dependent and mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathways in human cocaine-related overdose. Scientific Reports, 7, 44262.
Wu, Y., Dai, W. D., & Fu, Q. S. (2018). Increased apoptosis of trophoblasts from pregnancies complicated by intrauterine growth restriction is associated with aberrant Fas-associated death domain (FADD) expression. Clinical and Experimental Obstetrics and Gynecology, 45, 747–751.
Funding
This study was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81700346) and the Natural Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20160549).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QX, SL, YG, LJ, and CD performed in vivo and in vitro experiments and collected the data; JS designed the study and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Y. James Kang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-023-09796-4
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Q., Li, S., Gao, Y. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Ergosterol Attenuates Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Cardiotoxicity. Cardiovasc Toxicol 20, 500–506 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-020-09574-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-020-09574-6