Abstract
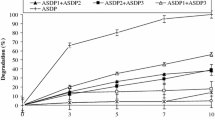
The present research work highlights the biosurfactant application toward enhanced pyrene degradation by Pseudomonas sp. Lipopeptide-type biosurfactant was produced from Free Air CO2 Enriched (FACE) soil bacterium Bacillus sp. SS105. The different concentrations of biosurfactant at different time intervals were optimized for maximum pyrene degradation and quantified through analytical methods such as the scanning process of UV–Vis spectrophotometer and GC–MS analysis. In the absence of biosurfactant, Pseudomonas sp. could degrade only 8% of pyrene at the concentration of 5 mg per 100 ml, while the degradation rate enhanced by 95% in presence of biosurfactant (5 mg/100 ml of culture). This result demonstrated that biosurfactant produced from Bacillus sp. SS105 has potential to enhance the bioavailability and biodegradation of pyrene by Pseudomonas sp.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Das K, Mukherjee AK. Differential utilization of pyrene as the sole source of carbon by Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains: role of biosurfactants in enhancing bioavailability. J Appl Microbiol. 2007;102:195–203.
Garcia-Junco M, Gomez-Lahoz C, Niqui-Arroyo JL, Ortega-Calvo JJ. Biosurfactant and Biodegradation enhanced partitioning of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from nonaqueous-phase liquids. Environ Sci Technol. 2003;37:2988–96.
Seo JS, Keum YS, Li QX. Bacterial degradation of aromatic compounds. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2009;6(1):278–309.
Jorfi S, Rezaee A, Jaafarzadeh NA, Esrafili A, Akbari H, Ali G, Ali M. Bioremediation of pyrene-contaminated soils using biosurfactant. Jentashapir J Heal Res. 2014;5:1–7.
Hadibarata T, Teh ZC. Optimization of pyrene degradation by white-rot fungus Pleurotus pulmonarius F043 and characterization of its metabolites. Bioproc Biosyst Eng. 2014;37:1679–84.
Hwang HM, Hu X, Zhao X. Enhanced bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by environmentally friendly techniques. J Environ Sci Heal Part C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2007;25:313–52.
Arulazhagan P, Vasudevan N. Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a halotolerant bacterial strain Ochrobactrum sp. VA1. Mar Pollut Bull. 2011;62:388–94.
Feng TC, Cui CZ, Dong F, Feng YY, Liu YD, Yang XM. Phenanthrene biodegradation by halophilic Martelella sp. AD-3. J Appl Microbiol. 2012;113:779–89.
Keith LH. The source of US EPA’S sixteen PAH priority pollutants. Polycyclic Aromat Compd. 2015;35:2–4.
Balmer JE, Hung H, Yu Y, Letcher RJ, Muir DCG. Sources and environmental fate of pyrogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Arctic. Emerg Contam. 2019;5:128–42.
Patowary K, Patowary R, Kalita MC, Deka S. Characterization of biosurfactant produced during degradation of hydrocarbons using crude oil as sole source of carbon. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:279.
Lu S, Teng Y, Wang J, Sun Z. Enhancement of pyrene removed from contaminated soils by Bidens maximowicziana. Chemosphere. 2010;81:645–50.
González N, Simarro R, Molina MC, Bautista LF, Delgado L, Villa JA. Effect of surfactants on PAH biodegradation by a bacterial consortium and on the dynamics of the bacterial community during the process. Bioresour Technol. 2011;102:9438–46.
Abed RMM, Al-Sabahi J, Al-Maqrashi F, Al-Habsi A, Al-Hinai M. Characterization of hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria isolated from oil-contaminated sediments in the sultanate of Oman and evaluation of bioaugmentation and biostimulation approaches in microcosm experiments. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad. 2014;89:58–66.
Yao Z, Li J, Xie H, Yu C. Review on remediation technologies of soil contaminated by heavy metals. Procedia Environ Sci. 2012;16:722–9.
Zeng YU, Hong PKA, Wavrek DA. Chemical—biological treatment of pyrene. Water Res. 2000;34:1157–72.
El-Naas MH, Al-Muhtaseb SA, Makhlouf S. Biodegradation of phenol by Pseudomonas putida immobilized in polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) gel. J Hazard Mater. 2009;164:720–5.
Gupta G, Chandra A, Varjani SJ, Banerjee C, Kumar V. Role of biosurfactants in enhancing the microbial degradation of pyrene. Bioremediation: applications for environmental protection and management. Singapore: Springer; 2017. p. 375–86.
Bezza FA, Chirwa EMN. The role of lipopeptide biosurfactant on microbial remediation of aged polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)-contaminated soil. Chem Eng J. 2017;309:563–76.
Cao B, Nagarajan K, Loh KC. Biodegradation of aromatic compounds: current status and opportunities for biomolecular approaches. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009;85:207–28.
Haritash AK, Kaushik CP. Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): a review. J Hazard Mater. 2009;169:1–15.
Deng Y, Zhang Y, Hesham AEL, Liu R, Yang M. Cell surface properties of five polycyclic aromatic compound-degrading yeast strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010;86:1933–9.
Brinda Lakshmi M, Muthukumar K, Velan M. Optimization of minimal salt medium for efficient phenanthrene biodegradation by Mycoplana sp. MVMB2 isolated from petroleum contaminated soil using factorial design experiments. Clean Soil Air Water. 2013;41:51–9.
Weissenfels W, Klewer HJ, Langhoff J. Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by soil particles: influence on biodegradability and biotoxicity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1992;36:689–96.
Ghosh U, Talley JW, Luthy RG. Particle-scale investigation of PAH desorption kinetics and thermodynamics from sediment. Environ Sci Technol. 2001;35:3468–75.
Ghosh I, Mukherji S. Diverse effect of surfactants on pyrene biodegradation by a Pseudomonas strain utilizing pyrene by cell surface hydrophobicity induction. Int Biodeter Biodegr. 2016;108:67–75.
Xia W, Du Z, Cui Q, Dong H, Wang F, He P, Tang Y. Biosurfactant produced by novel Pseudomonas sp. WJ6 with biodegradation of n-alkanes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Hazard Mater. 2014;276:489–98.
Silva RCFS, Almeida DG, Rufino RD, Luna JM, Santos VA, Sarubbo LA. Applications of biosurfactants in the petroleum industry and remediation of oil spills. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:12523–42.
Sundaram S, Das MT, Thakur IS. Biodegradation of cypermethrin by Bacillus sp. in soil microcosm and in-vitro toxicity evalution on human cell line. Int Biodeter Biodegr. 2013;77:39–44.
Chen WC, Juang RS, Wei YH. Applications of a lipopeptide biosurfactant, surfactin, produced by microorganisms. Biochem Eng J. 2015;103:158–69.
Gupta G, Kumar V, Pal AK. Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by microbial consortium: a distinctive approach for decontamination of soil. Soil Sediment Contam. 2016;25:597–623.
Fooladi T, Moazami N, Kadier A, Mohtar W, Yusoff W, Abdul A. Characterization, production and optimization of lipopeptide biosurfactant by new strain Bacillus pumilus 2IR isolated from an Iranian oil field. J Pet Sci Eng. 2016;145:510–9.
Bezza FA, Chirwa EMN. Pyrene biodegradation enhancement potential of lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by Paenibacillus dendritiformis CN5 strain. J Hazard Mater. 2017;321:218–27.
Stoimenova E, Vasileva-Tonkova E, Sotirova A, Galabova D, Lalchev Z. Evaluation of different carbon sources for growth and biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas fluorescens isolated from wastewaters. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2009;64:96–102.
Pacwa-Płociniczak M, Płaza GA, Piotrowska-Seget Z, Cameotra SS. Environmental applications of biosurfactants: recent advances. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12:633–54.
Maheshwari N, Kumar M, Thakur IS, Srivastava S. Recycling of carbon dioxide by free air CO2 enriched (FACE) Bacillus sp. SS105 for enhanced production and optimization of biosurfactant. Bioresour Technol. 2017;242:2–6.
Cooper DG, Macdonald TCR, Duff SJB, Kosaric N. Enhanced production of surfactin from Bacillus subtilis by continuous product removal and metal cation additions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981;42:408–12.
Bharti RK, Srivastava S, Thakur IS. Production and characterization of biodiesel from carbon dioxide concentrating chemolithotrophic bacteria, Serratia sp. ISTD04. Bioresour Technol. 2014;153:189–97.
Rathour R, Gupta J, Tyagi B, Kumari T, Thakur IS. Biodegradation of pyrene in soil microcosm by Shewanella sp. ISTPL2, a psychrophilic, alkalophilic and halophilic bacterium. Bioresour Technol Rep. 2018;4:129–36.
Kumar G, Singla R, Kumar R. Plasmid associated anthracene degradation by Pseudomonas sp. isolated from filling station site. Nat Sci. 2010;8:89–94.
Nanca CL, Neri KD, Ngo ACR, Bennett RM, Dedeles GR. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by moderately halophilic bacteria from Luzon salt beds. J Health Pollut. 2018;8(19):180915.
Nayarisseri A, Singh P, Singh SK. Screening, isolation and characterization of biosurfactant producing Bacillus subtilis strain ANSKLAB03. Bioinformation. 2018;14:304–14.
Cooper DG, Zajic JE. Surface-active compounds from microorganisms. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1980;26:229.
Banat IM, et al. Microbial biosurfactant production, applications and future potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010;87:427–44.
Zang T, Wu H, Yan B, Zhang Y. Enhancement of PAHs biodegradation in biosurfactant/phenol system by increasing the bioavailability of PAHs. Chemosphere. 2020;266:128941.
Karlapudi AP, Kodali VP. Role of biosurfactants in bioremediation of oil pollution-a review. Petroleum. 2018;4:241–9.
Mehetre GT, Dastager SG, Dharne MS. Science of the total environment biodegradation of mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by pure and mixed cultures of biosurfactant-producing thermophilic and thermo-tolerant bacteria. Sci Total Environ. 2019;679:52–60.
Xu P, Du H, Peng X, Tang Y, Zhou Y, Chen X, Fei J, Meng Y, Yuan L. Science of the total environment degradation of several polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by laccase in reverse micelle system. Sci Total Environ. 2019;708:134970.
Ward OP (eds) (2010) Microbial Biosurfactants and Biodegradation. In: Biosurfactants. Springer, New York, pp 65-74
Martínez-Checa F, Toledo FL, Mabrouki KE, Quesada E, Calvo C. Characteristics of bioemulsifier V2–7 synthesized in culture media added of hydrocarbons: chemical composition, emulsifying activity and rheological properties. Bioresour Technol. 2007;98:3130–5.
Chirwa EMN, Lutsinge TB. Biological degradation of pyrene and fluoranthene in porous media and attached growth systems by biosurfactant producing bacteria. Chem Eng Trans. 2018;70:1777–82.
Gupta B, Puri S, Thakur IS, Kaur J. Enhanced pyrene degradation by a biosurfactant-producing Acinetobacter baumannii BJ5: growth kinetics, toxicity and substrate inhibition studies. Environ Technol Innovation. 2020;19:100804.
Acknowledgements
The author is grateful to DST-SERB, Government of India, New Delhi, for providing start up research grant (Srivastava, S), and CSIR-New Delhi for providing doctoral fellowship (Maheshwari, N). We would also like to thank Advanced Instrumentation Research Facility (AIRF) Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi for GC–MS analysis.
Funding
Experimental cost was funded by DST-SERB, Government of India, New Delhi and CSIR-New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Experiments were designed by SS and IST. NM performed the all experiments under the guidance of SS. Manuscript wrote by NM and edited by SS. At last, all authors revised and finalized the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maheshwari, N., Thakur, I.S. & Srivastava, S. Enhanced microbial degradation of pyrene using biosurfactant isolated from Bacillus sp. SS105. Syst Microbiol and Biomanuf 2, 723–731 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43393-022-00097-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43393-022-00097-5