Abstract
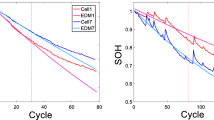
Accurately predicting the state of health (SOH) and remaining useful life (RUL) of Li-ion batteries is the key to Li-ion battery health management. In this paper, a novel GPR-based method for SOH and RUL prediction is proposed. First, five features are extracted from the cyclic charging currents of batteries, and a grey correlation analysis (GRA) shows that these five features are highly correlated with battery capacity. A novel Li-ion battery SOH prediction model is established by improving a basic Gaussian process regression model. Meanwhile, a polynomial regression model is developed to update the feature values in the future. Then the RUL of a battery is predicted by combining the SOH prediction model. Finally, the prediction effect of the proposed model is compared with other models using four Li-ion battery degradation data. The obtained results show that the model proposed in this paper has the highest accuracy. The robustness of the proposed model is verified by random walk battery data.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akash, B., Zineb, S., Eric, G., et al.: Review on State of Health estimation methodologies for lithium-ion batteries in the context of circular economy. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 32, 517–528 (2021)
Yu, Z., Xiao, L., Li, H., et al.: Model parameter identification for lithium batteries using the coevolutionary particle swarm optimization method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64(7), 5690–5700 (2017)
Bian, X., Liu, L., Yan, J.: A model for state-of-health estimation of lithium ion batteries based on charging profiles. Energy 177, 57–65 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227401
Bian, X., Liu, L., Yan, J., et al.: An open circuit voltage-based model for state-of-health estimation of lithium-ion batteries: model development and validation. J. Power Sources 448, 227401 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.04.070
Bian, X., Wei, Z., He, J., et al.: A novel model-based voltage construction method for robust state-of-health estimation of lithium-ion batteries. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2020.3044779
Li, S., Wang, B., Peng, H., et al.: An electrochemistry-based impedance model for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 258, 9–18 (2014)
Ruan, H., He, H., Wei, Z., et al.: State of health estimation of lithium-ion battery based on constant-voltage charging reconstruction. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/JESTPE.2021.3098836
He, J., Wei, Z., Bian, X., et al.: State-of-health estimation of Lithium-Ion batteries using incremental capacity analysis based on voltage-capacity model. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 6(2), 417–426 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TTE.2020.2994543
Wei, J., Dong, G., Chen, Z.: Remaining useful life prediction and state of health diagnosis for Lithium-Ion batteries using particle filter and support vector regression. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 65(7), 5634–5643 (2018)
Nuhic, A., Terzimehic, T., Soczka-Guth, T., et al.: Health diagnosis and remaining useful life prognostics of lithium-ion batteries using data-driven methods. J. Power Sources 239, 680–688 (2013)
Zhou, Y., Huang, M.: Lithium-ion batteries remaining useful life prediction based on a mixture of empirical mode decomposition and ARIMA model. Microelectron. Reliab. 65, 265–273 (2016)
Bai, G., Wang, P., Hu, C., et al.: A generic model-free approach for lithium-ion battery health management. Appl. Energy 135, 247–260 (2014)
He, Z., Gao, M., Ma, G., et al.: Online state-of-health estimation of lithium-ion batteries using Dynamic Bayesian Networks. J. Power Sources 267, 576–583 (2014)
Piao, C., Li, Z., Lu, S., et al.: Analysis of real-time estimation method based on hidden markov models for battery system states of health. J. Power Electron. 16(1), 217–226 (2016)
Zhou, Y., Huang, M., Chen, Y., et al.: A novel health indicator for on-line lithium-ion batteries remaining useful life prediction. J. Power Sources 321(6), 1–10 (2016)
Liu, D., Zhou, J., Liao, H., et al.: A Health Indicator Extraction and Optimization Framework for Lithium-Ion Battery Degradation Modeling and Prognostics. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern.: Syst. 45(6), 915–928 (2015)
Feng, H., Song, D.: A health indicator extraction based on surface temperature for lithium-ion batteries remaining useful life prediction. J. Energy Storage 34, 102118 (2021)
Wang, R., Feng, H.: Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion battery using a novel health indicator. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 37(3), 1232–1243 (2021)
Schwunk, S., Armbruster, N., Straub, S., et al.: Particle filter for state of charge and state of health estimation for lithium-iron phosphate batteries. J. Power Sources. 239, 705–710 (2013)
Wang, R., Feng, H.: Lithium-ion batteries remaining useful life prediction using Wiener process and unscented particle filter. J. Power Electron. 20, 270–278 (2020)
Dong, G., Yang, F., Wei, Z., et al.: Data-driven battery health prognosis using adaptive brownian motion model. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 16(7), 4736–4746 (2020)
Dong, G., Chen, Z., Wei, J., et al.: Battery health prognosis using brownian motion modeling and particle filtering. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 65(11), 8646–8655 (2018)
Li, X., Wang, Z., Zhang, L., et al.: State-of-health estimation for Li-ion batteries by combing the incremental capacity analysis method with grey relational analysis. J. Power Sources 410–411, 106–114 (2019)
Li, X., Wang, Z., Yan, J., et al.: Prognostic health condition for lithium battery using the partial incremental capacity and Gaussian process regression. J. Power Sources 421, 56–67 (2019)
Li, X., Yuan, C., Wang, Z., et al.: Multi-time-scale framework for prognostic health condition of lithium battery using modified Gaussian process regression and nonlinear regression. J. Power Sources 467, 228358 (2020)
Yang, D., Zhang, X., Pan, R., et al.: A novel Gaussian process regression model for state-of-health estimation of lithium-ion battery using charging curve. J. Power Sources 384, 387–395 (2018)
Liu, D., Pang, J., Zhou, J., et al.: Prognostics for state of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on combination Gaussian process functional regression. Microelectron. Reliab. 53(6), 832–839 (2013)
Liang, J., Shi, J., Wen, Y., et al.: SOH and RUL prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on Gaussian process regression with indirect health indicators. Energies 13(2), 375 (2020)
Goebelk, S., Saxena, A., et al.: Prognostics in battery health management. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 11(4), 33–40 (2008)
Bole, B., Kulkarni, C.S., Daigle, M.: Adaptation of an electrochemistry-based Li-ion battery model to account for deterioration observed under randomized use. SGT. Inc. Moffett. Field, United States (2014). https://doi.org/10.36001/phmconf.2014.v6i1.2490
Tosun, N.: Determination of optimum parameters for multi-performance characteristics in drilling by using grey relational analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 28(5–6), 450–455 (2006)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (program No.2021JZ -19) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (program No.61877067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, H., Shi, G. SOH and RUL prediction of Li-ion batteries based on improved Gaussian process regression. J. Power Electron. 21, 1845–1854 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-021-00318-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-021-00318-5