Abstract
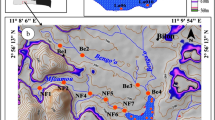
This paper discussed the source area-weathering and tectonic settings of alluvial sediments from the Lake Chad Basin (LCB). Four profiles of different levels characterised by variation in colours and textures have been examined. The textural variation was linked to the alternation of wet and dry periods in the LCB. Micro-textural observations by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) revealed sub-rounded to angular particles with collision impact and sometimes adhered particles on their surfaces. This suggested fluvial transport and short periods of aeolian movements. The bulk mineralogy performed with X-TRA Thermo-ARL Diffractometer showed that the clayey and clayey sandy facies are dominated by kaolinite, quartz and illite whilst the sandy samples are made up of quartz, kaolinite, illite, goethite and rutile. The geochemistry of whole samples was assessed by X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry. Amount the major elements, SiO2, Al2O3 and Fe2O3 have the highest contents, and this is consistent with the mineralogical composition. The sediments are mature and classified as Fe-shale, Fe-sand and (sub)litharenite. Trace elements behaviour suggested a detrital origin, low sediment recycling and oxic depositional environment. The rock sources underwent variable degrees of weathering which revealed once more the impact of climate change prevailing in LCB. The discriminant plots indicated a felsic nature of the original source rocks in a context of passive margin.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data of the compounds are not available from the authors.
References
Adatte, T., Stinnesbeck, W., Keller, G., Ryder, G., & Fastovsky, D. (1996). Lithostratigraphic and mineralogic correlations of near K/T boundary clastic sediments in northeastern Mexico: Implications for origin and nature of deposition. Geological Society of America Special Papers, 307, 211–226. https://doi.org/10.1130/0-8137-2307-8.211
Ambassa Bela, V., Ekoa Bessa, A. Z., Armstrong-Altrin, J. S., Kamani, F. A., Nya, E. D. B., & Ngueutchoua, G. (2023). Provenance of clastic sediments: A case study from Cameroon. Central Africa. Solid Earth Sciences, 8(2), 105–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sesci.2023.03.002
Armstrong-Altrin, J. S., Lee, Y. I., Kasper-Zubillaga, J. J., Carranza-Edwards, A., Garcia, D., Eby, G. N., Balaram, V., & Cruz-Ortiz, N. L. (2012). Geochemistry of beach sands along the western Gulf of Mexico, Mexico: Implication for provenance. Geochemistry, 72(4), 345–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2012.07.003
Armstrong-Altrin, J. S., Lee, Y. I., Verma, S. P., & Ramasamy, S. (2004). Geochemistry of sandstones from the upper Miocene Kudankulam formation, southern India: Implications for provenance, weathering, and tectonic setting. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 74(2), 285–297. https://doi.org/10.1306/082803740285
Armstrong-Altrin, J. S., Machain-Castillo, M. L., Rosales-Hoz, L., Carranza-Edwards, A., Sanchez-Cabeza, J. A., & Ruíz-Fernandez, A. C. (2015). Provenance and depositional history of continental slope sediments in the Southwestern Gulf of Mexico unraveled by geochemical analysis. Continental Shelf Research, 95, 15–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2015.01.003
Babechuk, M. G., Widdowson, M., & Kamber, B. S. (2014). Quantifying chemical weathering intensity and trace element release from two contrasting basalt profiles, Deccan Traps, India. Chemical Geology, 363, 56–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.10.027
Badapalli, P. K., Kottala, R. B., Rajasekhar, M., Ramachandra, M., & Krupavathi, C. (2022). Modeling of comparative studies on surface micro morphology of Aeolian, River, Lake, and Beach sand samples using SEM and EDS/EDAX. Materials Today: Proceedings, 50, 655–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.04.049
Begg, G. C., Griffin, W. L., Natapov, L. M., O’Reilly, S. Y., Grand, S. P., O’Neill, C. J., Hronsky, J. M. A., Poudjom-Djomani, Y., Swain, C. J., Deen, T., & Bowden, P. (2009). The lithospheric architecture of Africa: Seismic tomography, mantle petrology, and tectonic evolution. Geosphere, 5, 23–50. https://doi.org/10.1130/GES00179.1
Bhaskar, J. S., Satya, R. G., Borthakur, R., Indu, B. R., & Rashmi, R. B. (2015). Spectroscopic characterization and quantitative estimation of natural weathering of silicates in sediments of Dikrong River, India. International Journal of Modern Physics, 6, 1631–1641. https://doi.org/10.4236/jmp.2015.611164
Bhatia, M. R. (1983). Plate tectonics and geochemical composition of sandstones. Journal of Geology, 91, 611–627. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30064711
Bhatia, M. R., & Crook, K. A. W. (1986). Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 92, 181–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00375292
Bhuiyan, M. A. H., Rahman, M. J., Dampare, S. B., & Suzuki, S. (2011). Provenance, tectonics and source weathering of modern fluvial sediments of the Brahmaputra-Jamuna River, Bangladesh: Inference from geochemistry. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 111, 113–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.06.008
Black, R. (1992). Mission géologique au Tchad du 14. 1. au 8. 2. 1992. In: Rapport inédit, 15.
Bolarinwa, A. T., Idakwo, S. O., & Bish, D. L. (2019). Rare-earth and trace elements and hydrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions of Cretaceous kaolinitic sediments from the Lower Benue Trough, Nigeria: Provenance and paleoclimatic significance. Acta Geochimica, 38(3), 350–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-019-00328-y
Bourman, R. P., & Ollier, C. D. (2002). A critique of the Schellmann definition and classification of ‘laterite.’ CATENA, 47, 117–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0341-8162(01)00178-3
Cheverry C. (1974). Contribution à l’étude pédologique des polders du lac Tchad : dynamique des sels en milieu continental subaride dans des sédiments argileux et organiques. Paris: ORSTOM, multigr. Th.: Sci. Nat., Université Louis Pasteur, Strasbourg, 280 p.
Condie, K. C. (1993). Chemical composition and evolution of the upper continental crust: Contrasting results from surface samples and shales. Chemical Geology, 104, 1–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(93)90140-E
Cox, R., Lowe, D. R., & Cullers, R. L. (1995). The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 59, 2919–2940. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(95)00185-9
Cullers, R. L. (2002). Implications of elemental concentrations for provenance, redox conditions, and metamorphic studies of shales and limestones near Pueblo, CO, USA. Chemical Geology, 191, 305–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00133-X
Déruelle, B., Moreau, C., Nkoumbou, C., Kambou, R., Lissom, N., Ghogomu, R. T., & Nono, A. (1991). The Cameroon line: a review. In A. B. Kampuzu & R. T. Lubala (Eds.), Magmatism in extentional structural settings. The phanerozoic african plate (pp. 274–327). Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
Ekoa Bessa, A. Z., Armstrong-Altrin, J. S., Fuh, G. C. B., Betsi, T., Kelepile, T., & Ndjigu, P.-D. (2021a). Mineralogy and geochemistry of the Ngaoundaba Crater Lake sediments, northern Cameroon: Implications for provenance and trace metals status. Acta Geochimica, 40, 718–738. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-021-00463-5
Ekoa Bessa, A. Z., Ndjigui, P. D., Fuh, G. C., Armstrong-Altrin, J. S., & Betsi, T. B. (2021b). Mineralogy and geochemistry of the Ossa lake Complex sediments, Southern Cameroon: Implications for paleoweathering and provenance. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 14(4), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06591-9
Fedo, C. M., Nesbitt, H. W., & Young, G. M. (1995). Unraveling the effect of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance. Geology, 23, 921–924. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023%3c0921:UTEOPM%3e2.3.CO;2
Floyd, P. A., & Leveridge, B. E. (1987). Tectonic environments of the Devonian Gramscatho basin, south Cornwall: Framework mode and geochemical evidence from turbidite sandstones. Journal of the Geological Society of London, 144, 531–542. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsjgs.144.4.0531
Garrels, R. M., & Christ, C. L. (1965). Solutions, Minerals, and Equilibria. Harper and Row.
Garzanti, E., Wang, J. G., Vezzoli, G., & Limonta, M. (2016). Tracing provenance and sediment flfluxes in the Irrawaddy River basin (Myanmar). Chemical Geology, 440, 73–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.06.010
Guiraud, R., Binks, R. M., Fairhead, J. D., & Wilson, M. (1992). Chronology and geodynamic setting of Cretaceous-Cenozoic rifting in West and Central Africa. Tectonophysics, 213(1–2), 227–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(92)90260-D
Hayashi, K., Fujisawa, H., Holland, H. D., & Ohmoto, H. (1997). Geochemistry of 1.9 Ga sedimentary rocks from northeastern Labrador. Canada. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 61, 4115–4137. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00214-7
Hernández-Hinojosa, V., Montiel-García, P. C., Armstrong-Altrin, J. S., Nagarajan, R., & Kasper-Zubillaga, J. J. (2018). Textural and geochemical characteristics of beach sands along the western Gulf of Mexico. Carpathian Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences, 13, 161–174. https://doi.org/10.26471/cjees/2018/013/015
Herron, M. M. (1988). Geochemical classification of terrigenous sands and shales from core or log data. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 58, 820–829. https://doi.org/10.1306/212F8E77-2B24-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Hossain, H. M. Z., Armstrong-Altrin, J. S., Jamil, A. H. M. N., Rahman, M. M., Hernandez-Coronado, C. J., & Ramos-Vazquez, M. A. (2020). Microtextures on quartz grains in the Kuakata beach, Bangladesh: Implications for provenance and depositional environment. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13, 291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5265-4
Hossain, H. M. Z., Kawahata, H., Roser, B. P., Sampei, Y., Manaka, T., & Otani, S. (2017). Geochemical characteristics of modern river sediments in Myanmar and Thailand: Implications for provenance and weathering. Chemistry, 77, 443–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2017.07.005
Huyan, Y., Yao, W., Xie, X., & Wang, L. (2021). Provenance, source weathering, and tectonics of the Yarlung Zangbo River overbank sediments in Tibetan Plateau, China, using major, trace, and rare earth elements. Geological Journal, 57, 37–51. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.4282
Jafarzadeh, M., Harami, R. M., Friis, H., Amini, A., Mahboubi, A., & Lenaz, D. (2014). Provenance of the Oligocene-Miocene Zivah Formation, NW Iran, assessed using heavy mineral assemblage and detrital clinopyroxene and detrital apatite analyses. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 89, 56–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2013.10.005
Jones, B., & Manning, D. C. (1994). Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of paleo-redox conditions in ancient mudstones. Chemical Geology, 111(1–4), 111–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(94)90085-X
Koch, F. W., Wiens, D. A., Nyblade, A. A., Shore, P. J., Tibi, R., Ateba, B., Tabod, C. T., & Nnange, J. M. (2012). Upper-mantle anisotropy beneath the Cameroon Volcanic Line and Congo Craton from shear wave splitting measurements. Geophysical Journal International, 190, 75–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2012.05497.x
Krinsley, D. H., & Doornkamp, J. C. (1973). Atlas of quartz sand surface textures (p. 91p). Cambridge University Press.
Long, X. P., Yuan, C., Sun, M., Xiao, W. J., Wang, Y. J., Cai, K. D., & Jiang, Y. D. (2012). Geochemistry and Nd isotopic composition of the Early Paleozoic flysch sequence in the Chinese Altai, Central Asia: Evidence for a northward-derived mafic source and insight into Nd model ages in accretionary orogen. Gondwana Research, 22, 554–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2011.04.009
Louis, P. (1970). Contribution géophysique à la connaissance géologique du bassin du lac Tchad. Mémoires ORSTOM. ORSTOM.
Mann, D. G., & Droop, S. J. M. (1996). Biodiversity, biogeography and conservation of diatoms. Hydrobiologia, 336, 19–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010816
Massuel, S. (2001). Modélisation hydrodynamique de la nappe phréatique quaternaire du bassin du lac Tchad (p. 85). DEA Univ Montp.
Mathieu, P. (1978). Lexique stratigraphique du Postpaléozoïque du Tchad. Centre ORSTOM de N'Djamena, 62 p
Mbale Ngama, E., Sababa, E., Bayiga, E. C., Ekoa Bessa, A. Z., Ndjigui, P. D., & Bilong, P. (2019). Mineralogical and geochemical characterization of the unconsolidated sands from the Mefou River terrace, Yaounde area, Southern Cameroon. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 159, 103570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2019.103570
Mbanga Nyobe, J., Sababa, E., Bayiga, E. C., & Ndjigui, P.-D. (2018). Geochemistry and provenance of rutile-bearing fine-grained sediments in the Lobo watershed from the Neoproterozoic Pan-African belt, Southern Cameroon. Comptes Rendus Géoscience, 350, 119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crte.2017.08.003
Mbog, M. B., Ngon Ngon, G. F., Tassongwa, B., Tehna, N., Lotse Tedontsah, V. P., & Etame, J. (2022). Clay deposits of Ngoma (Douala sedimentary subbasin Cameroon, Central Africa): A provenance study. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 15, 1122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10130-5
McLennan, S. M., Hemming, S., McDaniel, D. K., & Hanson, G. N. (1993). Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance, and tectonics. Processes Controlling the Composition of Clastic Sediments. Geological Society of America Special Papers. https://doi.org/10.1130/SPE284-p21
Mohtar, W. H. M. W., Bassa, S. A., & Porhemmat, M. (2017). Grain size analysis of surface fluvial sediments in rivers in Kelantan. Malaysia. Sains Malaysia, 46(5), 685–693. https://doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2017-4605-02
Moreno, T., Querol, X., Castillo, S., Alastuey, A., Cuevas, E., Herrmann, L., & Gibbons, W. (2006). Geochemical variations in aeolian mineral particles from the Sahara-Sahel Dust Corridor. Chemosphere, 65(2), 261–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.02.052
Mothersill, J. S. (1975). Lake Chad; geochemistry and sedimentary aspects of a shallow polymictic lake. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 45(1), 295–309. https://doi.org/10.1306/212F6D48-2B24-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Moussa, A., Novello, A., Lebatard, A.-E., Decarreau, A., Fontaine, C., Barboni, D., Sylvestre, F., Boulès, D., Paillès, C., Buchet, G., Duringer, P., Ghienne, J.-F., Maley, J., Mazur, J.-C., Roquin, C., Schuster, M., Vignaud, P., & Brunet, M. (2016). Lake Chad sedimentation and environments during the late Miocene and Pliocene: New evidence from mineralogy and chemistry of the Bol core sediments. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 118, 192–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2016.02.023
Nagarajan, R., Armstrong-Altrin, J. S., Kessler, F. L., Hidalgo-Moral, E. L., Dodge-Wan, D., & Taib, N. I. (2015). Provenance and tectonic setting of Miocene siliciclastic sediments, Sibuti Formation, northwestern Borneo. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(10), 8549–8565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1833-4
Nagarajan, R., Madhavaraju, J., Nagendra, R., Armstrong-Altrin, J. S., & Moutte, J. (2007). Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic shales of Rabanpalli Formation, Bhima basin, northern Karnataka, southern India: Implications for provenance and paleoredox conditions. Revista Mexicana De Ciencias Geológicas, 24, 150–160.
Nagarajan, R., Roy, P. D., Kessler, F. L., Jong, J., Dayong, V., & Jonathan, M. P. (2017). An integrated study of geochemistry and mineralogy of the Upper Tukau Formation, Borneo Island (East Malaysia): Sediment provenance, depositional setting and tectonic implications. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 143, 77–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.04.002
Ndjigui, P.-D., Onana, V. L., Sababa, E., & Bayiga, E. C. (2018). Mineralogy and geochemistry of the Lokoundje alluvial clays from the Kribi deposits, Cameroonian Atlantic coast: Implications for their origin and depositional environment. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 143, 102–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2018.03.023
Nesbitt, H. W., & Young, G. M. (1982). Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature, 279, 715–717. https://doi.org/10.1038/299715a0
Nesbitt, H. W., & Young, G. M. (1984). Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 48, 1523–1534. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(84)90408-3
Ngagoum Kontchipe, Y. S., Temgo Sopie, F., Ngueutchoua, G., Sonfack, A. N., Nkouathio, D. G., Tchatchueng, R., Kenfack Nguemo, G. R., & Njanko, T. (2021). Mineralogy and geochemistry study of the Nyong River sediments, SW Cameroon: Implications for provenance, weathering, and tectonic setting. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 14, 1018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07145-9
Ngako, V., Njonfang, E., Tongwa Aka, F., Affaton, P., & Metuk Nnange, J. (2006). The North-South Paleozoic to Quaternary trend of alkaline magmatism from Niger-Nigeria to Cameroun: Complex interaction between hotspots and Precambrian faults. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 45(3), 241–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2006.03.003
Ngueutchoua, G., Ekoa Bessa, A. Z., Eyong, J. T., Demanou Zandjio, D., Baba Djaoro, H., & Tchami Nfada, L. (2019). Geochemistry of cretaceous fine-grained siliciclastic rocks from Upper Mundeck and Logbadjeck Formations, Douala sub-basin, SW Cameroon: Implications for weathering intensity, provenance, paleoclimate, redox condition, and tectonic setting. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 152, 215–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2019.02.021
Olivry, J.-C., Chouret, A., Vuillaume, G., Lemoalle, J., & Bricquet, J. P. (1996). Hydrologie du lac Tchad. Monographie hydrologique 12, 302 p
Pias, J. (1962). Les sols du moyen et bas Logone, du bas Chari, des régions riveraines du lac Tchad et du Bahr-el Ghazal. Mém. Orstom 2, 438 p.
Pias, J. (1970). La végétation du Tchad: ses rapports avec les sols, variations paléobotaniques au quaternaire. Contribution à la connaissance du bassin tchadien 6, 45 p
Picard, M. D. (1971). Classification of fine-grained sedimentary rocks. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 41(1), 179–195. https://doi.org/10.1306/74D7221B-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Pourmand, A., Dauphas, N., & Ireland, T. J. (2012). A novel extraction chromatography and MC-ICP-MS technique for rapid analysis of REE, Sc and Y: Revising CI-chondrite and Post-Archean Australian Shale (PAAS) abundances. Chemical Geology, 291, 38–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.08.011
Reusch, A. M., Nyblade, A. A., Wiens, D. A., Shore, P. J., Ateba, B., Tabod, C. T., & Nnange, J. M. (2010). Upper mantle structure beneath Cameroon from body wave tomography and the origin of the Cameroon Volcanic Line. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 11, Q10W07. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GC003200
Rieu, M. (1975). Les polders du lac Tchad milieu naturel et formation des sols conséquences de la sécheresse. Notes Techniques Du Centre ORSTOM De N’djamena, 3, 2–18.
Roder, J. (1964). Régimes hydrologiques de l’Afrique Noire à l’ouest du Congo. ORSTOM.
Roser, B. P., Cooper, R. A., Nathan, S., & Tulloch, A. J. (1996). Reconnaissance sandstone geochemistry, provenance and tectonic setting of the lower Paleozoic terranes of the West Coast and Nelson, New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Geology & Geophysics, 39, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/00288306.1996.9514690
Roser, B. P., & Korsch, R. J. (1986). Determination of tectonic setting of sandstones and mudstones suites using SiO2 content and K2O/Na2O ratio. The Journal of Geology, 94, 635–650. https://doi.org/10.1086/629071
Roser, B. P., & Korsch, R. J. (1988). Provenance signatures of sandstone-mudstone suites determined using discrimination function analysis of major element data. Chemical Geology, 67(1–2), 119–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(88)90010-1
Sababa, E., Essomba Owona, L. G., Temga, J. P., & Ndjigui, P.-D. (2021). Petrology of weathering materials developed on granites in Biou area, North-Cameroon: implication for rare-earth elements (REE) exploration in semi-arid regions. Heliyon, 7(12), e08581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08581
Sababa, E., Mbesse, C. O., Wandji Mouko, C. N., Ekoa Bessa, A. Z., & Ndjigui, P.-D. (2022). Geochemistry of stream sediments from Eséka area (SW Cameroon): Implications for surface process assessment and precious metals (Au, Pd, and Pt) exploration. Journal of Sedimentary Environments, 7, 43–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-021-00082-3
Schuster, M., Duringer, P., Ghienne, J.-F., Roquin, C., Sepulchre, P., Moussa, A., Lebatard, A.-E., Mackaye, H. T., Likius, A., Vignaud, P., & Brunet, M. (2009). Chad Basin: Paleoenvironments of the Sahara since the Late Miocene. Comptes Rendus Géoscience, 341(8–9), 603–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crte.2009.04.001
Schuster, M., Roquin, C., Duringer, P., Brunet, M., Caugy, M., Fontugne, M., Mackaye, H. T., Vignaud, P., & Ghienne, J.-F. (2005). Holocene lake Mega-Chad palaeoshorelines from space. Quaternary Science Reviews, 24(16–17), 1821–1827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2005.02.001
Sebag, D., Durand, A., Garba, Z., & Verrecchia, E. P. (2013). Paleohydrological Reconstruction from late Holocene records in Interdune Lakes (N’Guigmi, Northern Bank of the Lake Chad, Niger). Open Journal of Geology, 3(2), 143–155. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2013.32018
Sebag, D., Verrecchia, E. P., Lee, S. J., & Durand, A. (2001). The natural hydrous sodium silicates from the northern bank of Lake Chad: Occurrence, petrology and genesis. Sedimentary Geology, 139(1), 15–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0037-0738(00)00152-4
Shaw, D. M. (1968). A review of K–Rb fractionation trends by covariance analysis. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 32(6), 573–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(68)90050-1
Shephard, F. P., & Young, R. (1961). Distinguishing between beach and dune sands. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 31(2), 196–214. https://doi.org/10.1306/74D70B37-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Smith, B. J., & Whalley, W. B. (1981). Late Quaternary drift deposits of north central Nigeria examined by scanning electron microscopy. CATENA, 8(1), 345–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0341-8162(81)80023-9
Suttner, L., & Dutta, P. (1986). Alluvial sandstone composition and paleoclimate, I. Framework mineralogy. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 56(3), 329–345. https://doi.org/10.1306/212F8909-2B24-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1985). The continental crust: Its composition and evolution (Vol. 312). Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Tchouatcha, M. S., Kassi Kassi, P., Mbesse, C. O., Kuété Noupa, R., Junior Mam, W., & Préat, A. (2022). Geochemistry of onshore deposits from Rio del Rey sub-basin of the western Atlantic margin of Cameroon (Coastal basin, Southwest Cameroon): Provenance and environments of sedimentation. Environmental Earth Sciences, 81, 321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10440-7
Tchouatcha, M. S., Kouske, A. P., Azinwi Tamfuh, P., Tchameni Ngouabe, E. G., & Chuye Yango, G. (2023). Provenance, depositional process, and tectonic setting of gold placer from the Bétaré-Oya Gold District (East-Cameroon, Central Africa) along the Precambrian Sanaga fault. International Journal of Sediment Research, 38(4), 576–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2023.03.002
Tian, D. Z., Leng, B. C., & Zhang, X. C. (2020). Provenance and tectonic setting of the Neoproterozoic meta-sedimentary rocks at southeastern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for the tectonic affinity of Yidun terrane. Precambrian Research, 344, 105736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2020.105736
Torsvik, T. H., Rousse, S., Labails, C., & Smethurst, M. A. (2009). A new scheme for the opening of the South Atlantic Ocean and the dissection of an Aptian salt basin. Geophysical Journal International, 177(3), 1315–1333. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04137.x
Toteu, S. F., Penaye, J., & Djomani, Y. P. (2004). Geodynamic evolution of the Pan-African belt in central Africa with special reference to Cameroon. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 41(1), 73–85. https://doi.org/10.1139/e03-079
Toteu, S. F., Van Schmus, W. R., Penaye, J., & Michard, A. (2001). New U-Pb and Sm-Nd datafrom north-central Cameroon and its bearing on the pre-Pan African history of centralAfrica. Precambrian Research, 108(1–2), 45–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00149-2
Verma, S. P. (2012). Geochemometrics. Revista Mexicana De Ciencias Geológicas, 29, 276–298.
Verma, S. P., & Armstrong-Altrin, J. S. (2013). New multi-dimensional diagrams for tectonic discrimination of siliciclastic sediments and their application to Precambrian basins. Chemical Geology, 355, 117–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.07.014
Verma, S. P., & Armstrong-Altrin, J. S. (2016). Geochemical discrimination of siliciclastic sediments from active and passive margin settings. Sedimentary Geology, 332, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2015.11.011
Whalen, J. B., Currie, K. L., & Chappell, B. W. (1987). A-type granites: Geo-chemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95, 407–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00402202
Wignall, P. B., & Myers, K. J. (1988). Interpreting the benthic oxygen levels in mud rocks, a new approach. Geology, 16, 452–455. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016%3c0452:IBOLIM%3e2.3.CO;2
Workman, R. K., & Hart, S. R. (2005). Major and trace element composition of the depleted MORB mantle (DMM). Earth Planetary Science Letters, 231(1–2), 53–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2004.12.005
Zaid, S. M., & Al Gahtani, F. (2015). Provenance, diagenesis, tectonic setting, and geochemistry of Hawkesbury Sandstone (Middle Triassic), southern Sydney Basin. Australia. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 24(1), 72–98. https://doi.org/10.3906/yer-1407-5
Acknowledgements
Many thanks to the editor and three anonymous reviewers for their reviews that greatly improved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Elisé Sababa, Armel Zacharie Ekoa Bessa and Beyanu Anehumbu Aye wrote the main manuscript text, Ahounta Shan-Bah Loubahndem assisted in field work and laboratory analyses, Moïse Welba prepared figures, All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by M. V. Alves Martins
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sababa, E., Ekoa Bessa, A.Z., Aye, B.A. et al. Alluvial sediments in Bol area (Lake Chad Basin): implications for source area-weathering and tectonic settings. J. Sediment. Environ. 8, 563–586 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-023-00148-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-023-00148-4