Abstract
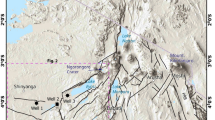
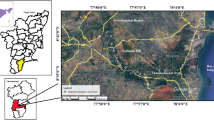
Texture, mineralogy, heavy minerals, and major and trace elements, including REE, from surface sediment samples collected along the Nyong River (NR) were analyzed in the current study to characterize and discuss the intensity of weathering, provenance, and tectonic settings of the source area and estimate the chemical features that reflect the parental rocks, known from literature. The sediments are mainly fine- and coarse-grained sands, and the mineralogy is predominantly composed of quartz, accompanied by kaolinite, illite, opaque oxides, kyanite, rutile, zircon, tourmaline, sillimanite, garnet, and hypersthene. Geochemically, the sediments are classified as Fe–shale, Fe–sand, and quartz arenite. The CIA, PIA, CIW, and the A–CN–K and (A–K)–C–N plots indicate the high intensity of chemical weathering. The values of SiO2/Al2O3, Al2O3/Na2O, K2O/Na2O, ICV, and the ZTR index indicate the maturity of many samples. Most of the sediment samples experienced recycling, as revealed by the Al2O3–TiO2–Zr plot. Several bivariate plots such as Zr vs TiO2 and Th/Co vs La/Sc, and the REE pattern and size of Eu, indicate derivation from a source area composed mostly of intermediate and felsic rocks and, in a lesser extent, of mafic source rocks. Tectonic discriminant diagrams based on major and trace elements indicate rift and passive margin settings, which is consistent with several tectonic history models of the Ntem complex and the Pan-African belt.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the sediment samples for major, trace, including REE, and mineralogical analysis were performed at the geology and sedimentary environment laboratories (AGEs), University of Liège, Belgium.
Code availability
The XLSTAT software was used to determine the Pearson correlation coefficient.
References
Armstrong-Altrin JS (2009) Provenance of sands from Cazones, Acapulco, and Bahίa Kino beaches, Mexίco. Rev Mex Cienc Geol 26(3):764–782
Armstrong-Altrin JS (2020) Detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the Riachuelos and Palma Sola beach sediments, Veracruz State, Gulf of Mexico: a new insight on palaeoenvironment. J. Palaeogeogr 9(4). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42501-020-00075-9
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Verma SP (2005) Critical evaluation of six tectonic setting discrimination diagrams using geochemical data of Neogene sediments from known tectonic settings. Sed Geol 177:115–129
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Lee YI, Verma SP, Ramasamy S (2004) Geochemistry of sandstones from the Upper Miocene Kudankulam Formation, southern India: implications for provenance, weathering, and tectonic setting. J Sediment Res 74:285–297
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Lee YI, Kasper-Zubillaga JJ, Carranza-Edwards A, Garcia D, Eby N, Balaram V, Cruz-Ortiz NI (2012) Geochemistry of beach sands along the Western Gulf of Mexico, Mexico: implication for provenance. Chem Erde 72:345–362
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Nagarajan R, Madhavaraju J, Rosalez-Hoz L, Lee YI, Balaram V, Cruz-Martinez A, Avila-Ramirez G (2013) Geochemistry of Jurassic and Upper Cretaceous shales from the Molango Region, Hildago, eastern Mexico: implications for source-area weathering, provenance, and tectonic setting. CR Geosci 345(4):185–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/jcrt.2013.03.004
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Nagarajan R, Balaram V, Natalhy-Pineda O (2015) Petrography and geochemistry of sands from the Chachalacas and Veracruz beach areas, western Gulf of Mexico, Mexico: constraints on provenance and tectonic setting. J South Am Earth Sci 64:199–216
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Lee YI, Kasper-Zubillaga JJ, Trejo-Ramírez E (2016) Mineralogy and geochemistry of sands along the Manzanillo and El Carrizal beach areas, southern Mexico: implications for palaeoweathering, provenance and tectonic setting. Geol J. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.2792
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Ramos-Vázquez MA, Zavala-León AC, Montiel-García PC (2018) Provenance discrimination between Atasta and Alvarado beach sands, western Gulf of Mexico, Mexico: constraints from detrital zircon chemistry and U–Pb geochronology. Geol J:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3122
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Alfonso V, Botello AV, Villanueva SF, Soto LA (2019) Geochemistry of surface sediments from the northwestern Gulf of Mexico: implications for provenance and heavy metal contamination. Geol Q 63(3):522–538
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Ramos-Vázquez MA, Hermenegildo-Ruiz NY, Madhavaraju J (2020) Microtexture and U–Pb geochronology of detrital zircon grains in the Chachalacas beach, Veracruz State. Gulf of Mexico Geol J:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3984
Bakkiaraj D, Nagendra R, Nagarajan R, Armstrong-Altrin JS (2010) Geochemistry of sandstones from the upper Cretaceous Sillakkudi Formation, Cauvery Basin, southern India: implication for provenance. J Geol Soc India 76:453–467
Barbey P, Macaudière J, Nzenti JP (1990) High-pressure melting of metapelites: evidence from the migmatites of Yaoundé. J Petrol 31(2):401–427
Bhatia MR (1983) Plate tectonics and geochemical composition of sandstone. J Geol 91:611–627
Bhatia MR, Crook KAW (1986) Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic discrimination of sedimentary basins. Contrib Mineral Petrol 92:181–193
Carranza-Edwards A, Centeno-García L, Rosales-Hoz L, Lozano-Santa Cruz R (2001) Provenance of beach gray sands from western Mexico. J South Am Earth Sci 14:291–301
Carrol D (1970) Clay minerals: a guide to their x-ray identification. Geol Soc Am 80
Chen M, Sun M, Cai K, Buslov MM, Zhao G, Rubanova ES (2014) Geochemical study of the Cambrian-Ordovician meta-sedimentary rocks from the northern Altai-Mongolian terrane northwesten Central Asian Orogenic Belt: implications on the provenance and tectonic setting. J Asian Earth Sci 96:69–83
Cox R, Low DR, Culler RL (1995) The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:219–2940
Cullers RL (2000) The geochemistry of shales, siltstones, and sandstones of Pennsylvanian-Permian age, Colorado, USA: implications for provenance and metamorphic studies. Lithos 51:181–203
Cullers RL (2002) Implications of elemental of elemental concentrations for provenance, redox conditions, and metamorphic studies of shales and limestones near Pueblo, CO, USA. Chem Geol 191:305–327
Cullers RL, Barrett T, Carlson R, Robinson B (1987) Rare earth element and mineralogic changes in Holocene soil and stream sediment: a case study in the Wet Mountains, Colorado, U.S.A. Chem Geol 63:275–297
Cullers RL, Basu A, Suttner LJ (1988) Geochemical signature of provenance in sand-mixed material in soils and stream sediments near the Tobacco Root batholith, Montana, U.S.A. Chem Geol 70:335–348
Dinis P, Oliveira A (2016) Provenance of Pliocene clay deposits from the Iberian Atlantic Margin and compositional changes during recycling. Sed Geol 336:171–182
Ekoa Bessa AZ, Ngueutchoua G, Ndjigui PD (2018) Mineralogy and geochemistry of sediments from Simbock Lake, Yaoundé area (southern Cameroon): provenance and environmental implications. Arab J Geosci 11(22):710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4061-x
Ekoa Bessa AZ, Ngueutchoua G, Kwewouo Janpou A, El-Amier YA, Njike Njome Mbella Nguetnga OA, Kankeu Kayou UR, Bisse SB, Ngo Mapuna EC, Armstrong-Altrin JS (2020) Heavy metal contamination and its ecological risks in the beach sediments along the Atlantic Ocean (Limbe coastal fringes, Cameroon). Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-020-00167-5
Etemad-Saeed N, Hosseini-Barzi M, Armstrong-Altrin JS (2011) Petrography and geochemistry of clastic sedimentary rocks as evidence for provenance of the Lower Cambrian Lalun Formation, Posht-e-badam block, central Iran. J Afr Earth Sci 61:142–159
Etemad-Saeed N, Hosseini-Barzi M, Adabi MH, Sadeghi A, Houshmandzadeh A (2015) Provenance of Neoproterozoic sedimentary basement of northern Iran, Kahar Formation. J Afr Earth Sci 111:54–75
Fedo CM, Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1995) Unravelling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance. Geology 23:921–924
Feybesse JL, Johan V, Triboulet C, Guerrot C, Mayaga-Mokolo F, Bouchot V, Eko N’Dong J (1998) The West Central African belt: a model of 2.5-2.0 Ga accretion and two-phase orogenic evolution. Precambrian Res 87:161–216
Folk RL (1980) Petrology of sedimentary rocks. Hemphill Publishing, Austin, Texas
Fu XG, Wang J, Zeng YH, Tan FW, He JI (2011) Geochemistry and origin of rare earth elements (REEs) in the Shengli River oil shale, northern Tibet, China. Chem Erde 71(1):21–30
Gallala W, Gaied ME, Montacer M (2009) Detrital mode, mineralogy and geochemistry of the Sidi Aїch Formation (Early Cretaceous) in central and southwestern Tunisia: implication for provenance, tectonic setting and paleoenvironment. J Afr Earth Sci 53:159–170
Ganno S, Njiosseu Tanko EL, Kouankap Nono GD, Djoukouo Soh A, Moudio C, Ngnotué T, Nzenti JP (2017) A mixed seawater and hydrothermal origin of superior-type banded iron formation (BIF)-hosted Kouambo iron deposit, Palaeoproterozoic Nyong series, Southwesthern Cameroon: constraints from petrography and geochemistry. Ore Geol Rev 80:860–875
Ganno S, Tsozué D, Kouankap Nono D, Tchouatcha MS, Ngnotué T, Gamgne Takam R, Nzenti JP (2018) Geochemical constraints on the origin of Banded Iron Formation-hosted iron ore from the Archean Ntem complex (Congo craton) in the Meyomessi area, southern Cameroon. Resour Geol. https://doi.org/10.1111/rge.12172
Garcia D, Fonteilles M, Moutte J (1994) Sedimentary fractionations between Al, Ti, and Zr, and the genesis of strongly peraluminous granites. J Geol 102:411–422
Garver JI, Royce PR, Smick TA (1996) Chromium and nickel in shale of the Taconic foreland: a case study for the provenance of fine-grained sediments with an ultramafic source. J Sediment Res 100:100–106
Garzanti E, Ando S (2007) Heavy mineral concentration in modern sands: implications for provenance interpretation. Dev Sedimentolotogy 58:517–545
Gromet LP, Dymek RF, Hasky LA, Korotev RL (1984) The “North American shale composite”: its compilation, major and trace element characteristics. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:2469–2482
Harnois L (1988) The CIW index: a new chemical index of weathering. Sed Geol 55:319–322
Hayashi KI, Fujisawa H, Holland HD, Ohmoto H (1997) Geochemistry of ~ 1.9 Ga sedimentary rocks from northeastern Labrador, Canada. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61:4115–4137
Hegde VS, Chavadi VC (2009) Geochemistry of Late Archaean metagreywackes from the western Dharwar Craton, south India: implications for provenance and nature of the Late Archaean crust. Gondwana Res 15(2):178–187
Hernández-Hinojosa V, Montiel-García PC, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Nagarajan R, Kasper-Zubillaga JJ (2018) Textural and geochemical characteristics of beach sands along the western Gulf of Mexico, Mexico. Carpathian J Earth Environ Sci 13(1):161–174
Herron MM (1988) Geochemical classification of terrigenous sands and shales from core or log data. J Sediment Petrol 58:820–829
Hubert JF (1962) A zircon-tourmaline–rutile maturity index and the interdependence of the composition of heavy mineral assemblages with the gross composition and texture of sandstone. J Sediment Petrol 32:440–450
Jarvis K (1990) A critical evaluation of two sample preparation techniques for low-level determination of some geologically incompatible elements by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Chem Geol 83:89–103
Kassi AM, Grigsby JD, Khan AS, Kasi AK (2015) Sandstone petrology and geochemistry of the Oligocene-Early Miocene Panjgur Formation, Makran accretionary wedge, southwest Pakistan: implications for provenance, weathering and tectonic setting. J Asian Earth Sci 105:192–207
Khan T, Khan MS (2015) Clastic rock geochemistry of Punagarh basin, trans-Aravalli region, NW Indian shield: implications for paleoweathering, provenance, and tectonic setting. Arabian J Geosci 8:3621–3644
Krӧner A, Stern RJ (2004) Pan-African orogeny, vol 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–12
Krumm S (1996) WINFIT 1.2: version of November 1996 (The Erlangen geological and mineralogical software collection) of ‘WINFIT’ 1.0: a public domain program for interactive profile-analysis under WINDOWS. In: Conference on Clay Mineralogy and Petrology, vol 38. Acta Universitatis Carolinae Geologica, Praha, pp 253–261
Li B, Zhuang X, Liu X, Wu C, Zhou J, Ma X (2016) Mineralogical and geochemical composition of Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation in the southern Junggar Basin, China: implications for paleoenvironment, provenance, and tectonic setting. Arab J Geosci 9:174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2154-3
Madhavaraju J (2015) Geochemistry of Late Cretaceous sedimentary rocks of the Cauvery Basin, south India: constraints on paleoweathering, provenance, and end Cretaceous environment. Chemostratigraphy:185–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-419968-2.00008-X
Madhavaraju J, Ramírez-Montoya E, Monreal R, González-León CM, Pi-Puig T, Espinoza-Maldonado IG, Grijalva-Noriega FJ (2016) Paleoclimate, paleoweathering and paleoredox conditions of Lower Cretaceous shales from the Mural Limestone, Tuape section, northern Sonora, Mexico: constraints from clay mineralogy and geochemistry. Rev Mex Cien Geol 33(1):34–48
Maslov JM, Podkovyrov VN, Mizens GA, Noshkin AD, Fazliakhmetov AM, Malinovsky AI, Khudoley AK, Kovota LN, Kuptsova AV, Gareev EZ, Zainullin RI (2016) Tectonic setting discrimination diagrams for terrigenous rocks: a comparison. Geochem Int 54(7):569–583
Mbale Ngama E, Sababa E, Bayiga EC, Ekoa Bessa AZ, Ndjigui P-D, Bilong P (2019) Mineralogical and geochemical characterization of the unconsolidated sands from the Mefou River terrace, Yaoundé area, Southern Cameroon. J Afr Earth Sci 159:103570
McDonough WF, Sun S-S (1995) The composition of the Earth. Chem Geol 120:223–253
McLennan SM (1989) Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: influences of provenance and sedimentary processes. Rev Mineral 21:169–200
McLennan SM (1993) Weathering and global denudation. J Geol 101:295–303
Mclennan SM, Taylor SR (1991) Sedimentary rocks and crustal evolution: tectonic setting and secular trends. J Geol 99:1–2
Mioumnde AP, Mboui FAK, Kue PRM, Kabir SA, Bessong M, Liqiang Z (2019) Sedimentological studies of alluvium deposits along Ngovayang-Bipindi of Lokoundje River, Southwestern Cameroon. Int J Geosci 10:119–139
Mongelli G, Critelli S, Perri F, Sonnino M, Perrone V (2006) Sedimentary recycling, provenance and paleoweathering from chemistry and mineralogy of Mesozoic continental redbeb mudrocks, Peloritani Mountains, Southern Italy. Geochem J 40:197–209
Nagarajan R, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Nagendra R, Madhavaraju J, Moutte J (2007) Petrography and geochemistry of terrigenous sedimentary rocks in the Neoproterozoic Rabanpalli formation, Bhima Basin, northern Karnataka, Southern India: implications for paleoweathering condition, provenance, and source rocks composition. J Geol Soc India 70:297–312
Nascimento DR, Sawakuchi AO, Guedes CCF, Giannini PCF, Grohmann CH, Ferreira MP (2015) Provenance of sands from the confluence of the Amazon and Madeira rivers based on detrital heavy minerals and luminescence of quartz and feldspar. Sed Geol 316:1–2
Ndjigui P-D, Ebah Abeng SA, Ekomane E, Nzeukou NA, Ngo Mandeng FS, Lindjeck MM (2015) Mineralogy and geochemistry of pseudogley soils and recent alluvial clastic sediments in the Ngog-Lituba region, Southern Cameroon: an implication to their genesis. J Afr Earth Sci 108:1–14
Ndjigui P-D, Onana VL, Sababa E, Bayiga EC (2018) Mineralogy and geochemistry of the Lokoundje alluvial clays from the Kribi deposits, Cameroonian Atlantic coast: implications for their origin and depositional environment. J Afr Earth Sci 143:102–117
Nédelec A, Macaudière J, Nzenti JP, Barbey P (1986) Evolution métamorphique et structurale des schistes de Mbalmayo (Cameroun). Implications pour la structure de la zone mobile panafricaine d’Afrique centrale, au contact du craton du Congo. CR Acad Sci Paris 303:75–80
Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1982) Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 299:715–717
Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1984) Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic consideration. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:1523–1534
Nesbitt HW, Young GM (2004) Ancient climatic and tectonic settings inferred from paleosols developed on igneous rocks. In: Eriksson PG, Alternan W, Nelson DR, Mueller WU, Catuneanu O (eds) The Precambrian earth: tempos and events. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 482–493
Nesbitt HW, Fedo CM, Young GM (1997) Quartz and feldspar stability, steady and non-steady-state weathering, and petrogenesis of siliciclastic sands and muds. J Geol 105(2):173–192
Ngnotue T, Nzenti JP, Tchoua FM (2000) The Ntui-Betamba high-grade gneisses: a northward extension of Pan-African Yaoundé gneisses in Cameroon. J Afr Earth Sci 2:369–381
Ngueutchoua G, Ekoa Bessa AZ, Eyong TJ, Demanou ZD, Baba Djaoro H, Tchami NL (2019a) Geochemistry of cretaceous fine-grained siliciclastic rocks from Upper Mundeck and Logbadjeck formations, Douala sub-basin, SW Cameroon: implications for weathering intensity, provenance, paleoclimate, redox condition, and tectonic setting. J Afr Earth Sci 152:215–236
Ngueutchoua G, Eyong TJ, Ekoa Bessa AZ, Azanji Agheenwi ZB, Emane Maschouer A, Sobdjou Kemteu C, Lontchi Dzoti Y, Hamadou T, Ongbassouek Baboule B-M, Kenfack Nguemo GR (2019b) Provenance and depositional history of Mesozoic sediments from the Mamfe basin and Douala sub-basin (SW Cameroon) unraveled by geochemical analysis. J Afr Earth Sci 158:103550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2019.103550
Nzenti JP (1998) Neoproterozoic alkaline meta-igneous rocks from the Pan-African North Equatorial fold belt (Yaoundé, Cameroon): biotitites and magnetite rich pyroxenites. J Afr Earth Sci 26:37–47
Nzenti JP, Barbey P, Jegouzo P, Moreau C (1984) Un nouvel exemple de ceinture granulitique dans une chaine proterozique de collision: les migmatites de Yaoundé au Cameroun. CR Acad Sci Paris 299:1197–1199
Nzenti JP, Barbey P, Macaudière J, Soba D (1988) Origin and evolution of late Precambrian high-grade Yaoundé gneisses (Cameroon). Precambrian Res 38:91–109
Olivry JC (1986) Fleuves et rivières du Cameroun. Collection Monographies Hydrologiques, ORSTOM, No. 9, Paris p 733
Penaye J, Toteu SF, Van Schmus WR, Nzenti JP (1993) Données géochronologiques préliminaires (U-Pb et Sm-Nd) sur la série de Yaoundé: âge du métamorphisme granulitique de la zone mobile panafricaine à proximité du craton du Congo. CR Acad Sci Paris 317:789–797
Penaye J, Toteu SF, Tchameni R, Van Schmus WR, Tchakounte J, Ganwa A, Minyem D, Nsifa EN (2004) The 2.1 Ga West central African Belt in Cameroon: extension and evolution. J Afr Earth Sci 39:159–164
Pouclet A, Tchameni R, Mezger K, Vidal M, Nsifa NE, Shang CK (2007) Archaean crustal accretion at the northern border of the Congo craton (South Cameroon), the charnockite-TTG link. Bull Soc Geol Fr 178:331–342
Ramos-Vázquez MA, Armstrong-Altrin JS (2019) Sediment chemistry and detrital zircon record in the Bosque and Paseo del Mar coastal areas from the southwestern Gulf of Mexico. Mar Petrol Geol 110:650–675
Roddaz M, Viers J, Brusset S, Baby P, Boucayrand C, Hérail G (2006) Controls on weathering and provenance in the Amazonian foreland basin: insights from major and trace element geochemistry of Neogene Amazonian sediments. Chem Geol 226:31–65
Roser BP, Korsch RJ (1986) Determination of tectonic setting of sandstone-mudstone suites using Si2O content and K2O/Na2O ratio. J Geol 94:635–650
Roser BP, Korsch RJ (1988) Provenance signature of sandstone-mudstone suites determined using discrimination function analysis of major-element data. Chem Geol 67:119–139
Ross DJK, Bustin RM (2009) Investigating the use of sedimentary geochemical proxies for paleoenvironment interpretation of thermally mature organic-rich strata: examples from the Devonian-Mississippian shales, western Canadian sedimentary basin. Chem Geol 220:1–19
Roy PD, Caballero M, Lozano R, Smykatz-Kloss W (2008) Geochemistry of Late Quaternary sediments from Tecocomulco Lake, central Mexico: implication to chemical weathering and provenance. Chem Erde 68:383–393
Sabaou N, Ait-Salem H, Zazoum RS (2009) Chemostratigraphy, tectonic setting and provenance of the Cambro-Ordovician clastic deposits of the subsurface Algerian Sahara. J Afr Earth Sci 55:158–174
Saha S, Banerjee S, Burley SD, Ghosh A, Saraswati PK (2010) The influence of flood basaltic source terrains on the efficiency of tectonic setting discrimination diagrams: an example from the Gulf of Khambhat, western India. Sed Geol (1–2):1–13
Selvaraj K, Chen C-TA (2006) Moderate chemical weathering of subtropical Taiwan: constraints from solid-phase geochemistry of sediments and sedimentary rocks. J Geol 114:101–116
Shang CK, Satir M, Siebel W, Nsifa EN, Taubald H, Liégeois J-P, Tchoua FM (2004) TTG magmatism in the Congo craton; a view from major and trace element geochemistry, Rb-Sr and Sm-Nd systematics: case of the Sangmelima region, Ntem complex, southern Cameroon. J Afr Earth Sci 40:61–79
Shang CK, Satir M, Nsifa EN, Liégeois J-P, Siebel W, Taubald H (2007) Archean high-K granitoids produced by remelting of earlier Tonalite-Trondhjemite-Granodiorite (TTG) in the Sangmelima region of the Ntem complex of the Congo craton, southern Cameroon. Int J Earth Sci 96:817–841
Shao JQ, Yang SY (2012) Does chemical index of alteration (CIA) reflect silicate weathering and monsoonal climate in the Changjiang River basin? Chin Sci Bull 57:1178–1187
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Tchameni R, Mezger K, Nsifa NE, Pouclet A (2000) Late Archean crustal evolution in the Congo craton: evidence from the K-rich granitoids of the Ntem Complex, southern Cameroon. J Afr Earth Sci 30:133–147
Toteu SF, Bertrand JM, Penaye J, Macaudière J, Angoua S, Barbey P (1991) Cameroon: a tectonic keystone in the Pan-African network. In Lewry JF, Stauffer MR (ed) The Early Proterozoic Trans-Hudson Orogen of North America. Geosci Can Special paper 37:483–496
Toteu SF, Van Schmus WR, Penaye J, Michard A (2001) New U-Pb and Sm-Nd data from north-central Cameroon and its bearing on the Pre-Pan-African history of central Africa. Precambrian Res 108:45–73
Toteu SF, Penaye J, Poudjom Djomani YH (2004) Geodynamic evolution of the Pan-African belt in Central Africa with special reference to Cameroon. Can J Earth Sci 41:73–85
Trendall AF (2002) The significance of iron formation, in Precambrian stratigraphic record. Sedimentol Spec Publ 33:33–66
Tsoungui PNE, Ganno S, Njiosseu Tanko EL, Mbongue JLN, Woguia BK, Tamehe L, Takodjou Wambo JD, Nzenti JP (2019) Geochemical constraints on the origin and tectonic setting of the serpentinized peridotites from the Paleoproterozoic Nyong series, Eseka area, SW Cameroon. Acta Geochim. https://doi.org/10.1007.s11631-019-00368-4
Újvári G, Varga A, Balogh-Brunstad ZS (2008) Origin, weathering, and geochemical composition of loess in southwestern Hungary. Quat Res 69:421–437
Verma SP, Armstrong-Altrin JS (2013) New multi-dimensional diagrams for tectonic discrimination of siliciclastic sediments and their application to Pre-Cambrian basins. Chem Geol 355:117–180
Verma SP, Armstrong-Altrin JS (2016) Geochemical discrimination of siliciclastic sediments from active and passive margin settings. Sed Geol 332:1–12
Vicat JP, Pouclet A (1995) Nature du magmatisme lié à une extension pré-panafricaine : les dolérites des bassins de Comba et de Sembé-Ouesso. Bull Soc Geol Fr 166(4):355–364
Vicat JP, Léger JM, Nsifa NE, Piguet P, Zenith JP, Tchameni R, Pouclet A (1996) Distinction au sein du craton congolais du Sud-Ouest du Cameroun de deux épisodes doléritiques initiant les cycles orogéniques éburnéen (paleoprotérozoique) et panafricain (Néoprotérozoique). CR Acad Sci Paris 323:575–582
Vosoughi Moradi A, Sari A, Akkaya P (2016) Geochemistry of the Miocene oil shale (Hançilli Formation) in the Çankiri-Çorum Basin, Central Turkey: implications for paleoclimate conditions, source-area weathering, provenance, and tectonic setting. Sed Geol 78:136–150
Wang W, Zhou M-F (2013) Petrological and geochemical constraints on provenance, paleoweathering, and tectonic setting of the Neoproterozoic sedimentary basin in the eastern Jiangnan Orogen, South China. J Sediment Res 83:975–994
Xie Y, Chi Y (2016) Geochemical investigation of dry- and wet-deposited dust during the same dust-storm event in Harbin, China: constraint on provenance and implications for formation of Aeolian loess. J Asian Earth Sci 120:43–61
Zhang Y, Gao X (2015) Rare earth elements in surface sediments of a marine coast under heavy anthropogenic influence: the Bohai Bay, China. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 164:86–93
Acknowledgements
This work represents part of the ongoing Ph.D. of the first author. The authors are grateful to the University of Liege (Belgium) for XRD and geochemical analysis. We are also indebted to the anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful examination of the manuscript and their constructive comments that greatly improved its final version.
Funding
This research was partly supported by the Department of Earth Sciences, Faculty of Sciences, University of Dschang, Cameroon, through an internal project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Each author has made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data, or have drafted the work or substantively revised it. Field and laboratory works were performed by Yannick Steve Ngagoum Kontchipe, Aristide Nadine Sonfack, and Francis Temgo Sopie. The first draft of manuscript was written by Yannick Steve Ngagoum Kontchipe.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All co-authors have approved the submitted version (and any substantially modified version that involves the author’s contribution to the study) and have agreed to be personally accountable for the author’s own contributions.
Also, the following are worth nothing:
- Original data/materials/code upon which the submission is based are preserved following the best practices in the field so that they are retrievable for reanalysis.
- Data/materials/code presentation accurately reflects the original.
Consent to participate
All authors whose names appear on the submission participated to the study; made substantial contributions to the conception of the work or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data; drafted the work or revised it critically for important intellectual content; approved the version to be published; and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed with the content and gave explicit consent to submit and that they obtained consent from the responsible authorities at the institute/organization where the work has been carried out, before the work is submitted.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Domenico M. Doronzo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ngagoum Kontchipe, Y.S., Temgo Sopie, F., Ngueutchoua, G. et al. Mineralogy and geochemistry study of the Nyong River sediments, SW Cameroon: Implications for provenance, weathering, and tectonic setting. Arab J Geosci 14, 1018 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07145-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07145-9