Abstract
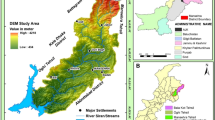
Soil loss estimation is the prerequisite for deciding priorities for watershed management which in turn is important to maintain human needs and ecosystem services. Karnali River Basin in Nepal is highly susceptible to soil erosion but limited studies have elucidated its basin-specific erosion status utilizing advanced computations. This study was designed with the objectives of delineating the river basin and estimating its soil loss using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) and Geographical Information System (GIS). The study individually calculated the required factors through Google Earth Engine and raster analysis in Arc GIS to create the potential soil loss map. The map depicted that the largest proportion (27%) of the area of the river basin was expected within the erosion category of 3 to 10 t ha−1 year−1, followed by 10 to 25 t ha−1 year−1 (22%) and less than 1 t ha−1 year−1 (22%). Only 2% of the land within the basin was at risk of erosion of more than 50 t ha−1 year−1. The Average soil loss from Karnali was estimated at 9.85 t ha-1 year−1. The total soil being lost per year from the Karnali River is 48,279,696 tonnes. The highest amount of soil loss was estimated in Dolpa followed by Mugu, Humla, Rukum East, and then Rukum West districts of the Karnali river basin. The results can be of pivotal inference in further planning, and prioritizing management and protection areas for the local and provincial governments.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya, K. P., & Paudel, P. K. (2020). Biodiversity in Karnali Province: Current status and conservation. Ministry of Industry, Tourism, Forest and Environment, Karnali Province Government, Surkhet, Nepal Cover Photograph: Tibetan Wild Ass in Limi Valley\copyright Tashi R. Ghale Keywords: Biodiversity, Conservation, Karnali Province, People-Wildlife Nexus, Biodiversity Profile, 5
Atoma, H., Suryabhagavan, K. V., & Balakrishnan, M. (2020). Soil erosion assessment using RUSLE model and GIS in Huluka watershed, Central Ethiopia. Sustainable Water Resources Management, 6, 1–17.
Bai, Z. G., Dent, D. L., Olsson, L., & Schaepman, M. E. (2008). Proxy global assessment of land degradation. Soil Use and Management, 24(3), 223–234.
Bianchi, S. R., Miyazawa, M., Oliveira, E. L. D., & Pavan, M. A. (2008). Relationship between the mass of organic matter and carbon in soil. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 51(2), 263–269. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132008000200005
Biswas, S. S., & Pani, P. (2015). Estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS techniques: A case study of Barakar River basin, Jharkhand, India. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 1, 1–13.
Borrelli, P., Robinson, D. A., Panagos, P., Lugato, E., Yang, J. E., Alewell, C., Wuepper, D., Montanarella, L., & Ballabio, C. (2020). Land use and climate change impacts on global soil erosion by water (2015–2070). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(36), 21994–22001.
Brady, N. C., & Weil, R. (2017). The nature and properties of soils: Pearson New International edition. London: Pearson.
Cerdan, O., Govers, G., Le Bissonnais, Y., Van Oost, K., Poesen, J., Saby, N., & Dostal, T. (2010). Rates and spatial variations of soil erosion in Europe: A study based on erosion plot data. Geomorphology, 122(1–2), 167–177.
Chadli, K. (2016). Estimation of soil loss using RUSLE model for Sebou watershed (Morocco). Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2, 1–10.
Chalise, D., Kumar, L., & Kristiansen, P. (2019). Land degradation by soil erosion in nepal: a review. Soil Systems, 3(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems3010012
Chalise, D., Kumar, L., Shriwastav, C. P., & Lamichhane, S. (2018). Spatial assessment of soil erosion in a hilly watershed of Western Nepal. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77, 1–11.
CBS, N. (2012). National population and housing census 2011. National Report.
Dahal, R. (2020). Soil erosion estimation using RUSLE modeling and geospatial tool: case study of Kathmandu District, Nepal. Forestry: Journal of Institute of Forestry, Nepal, 17, 118–134. https://doi.org/10.3126/forestry.v17i0.33627
De Vente, J., & Poesen, J. (2005). Predicting soil erosion and sediment yield at the basin scale: Scale issues and semi-quantitative models. Earth-Science Reviews, 71(1–2), 95–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2005.02.002
Devatha, C. P., Deshpande, V., & Renukaprasad, M. S. (2015). Estimation of soil loss using USLE model for Kulhan Watershed, Chattisgarh-A case study. Aquatic Procedia, 4, 1429–1436.
Esri, R. (2011). ArcGIS desktop: Release 10. Environmental Systems Research Institute, CA.
FAO. (2021). The state of the world’s land and water resources for food and agriculture—systems at breaking point. Synthesis report. Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Rome.
Farr, T. G., Rosen, P. A., Caro, E., Crippen, R., Duren, R., Hensley, S., Kobrick, M., Paller, M., Rodriguez, E., Roth, L., Seal, D., Shaffer, S., Shimada, J., Umland, J., Werner, M., Oskin, M., Burbank, D., & Alsdorf, D. (2007). The shuttle radar topography mission. Reviews of Geophysics, 45(2), RG2004. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005RG000183
Francis, C. F., & Thornes, J. B. (1990). Runoff hydrographs from three Mediterranean vegetation cover types. Vegetation and erosion Processes and environments (pp. 363–384). Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Fu, G., Chen, S., & McCool, D. K. (2006). Modeling the impacts of no-till practice on soil erosion and sediment yield with RUSLE, SEDD, and ArcView GIS. Soil and Tillage Research, 85(1–2), 38–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2004.11.009
Funk, C., Peterson, P., Landsfeld, M., Pedreros, D., Verdin, J., Shukla, S., Husak, G., Rowland, J., Harrison, L., Hoell, A., & Michaelsen, J. (2015). The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Scientific Data, 2(1), 150066. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2015.66
Gao, G. Y., Fu, B. J., Lü, Y. H., Liu, Y., Wang, S., & Zhou, J. (2012). Coupling the modified SCS-CN and RUSLE models to simulate hydrological effects of restoring vegetation in the Loess Plateau of China. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 16(7), 2347–2364. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-16-2347-2012
Ganasri, B. P., & Ramesh, H. (2016). Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS-A case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geoscience Frontiers, 7(6), 953–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2015.10.007
Gardner, R. A. M., & Gerrard, A. J. (2003). Runoff and soil erosion on cultivated rainfed terraces in the Middle Hills of Nepal. Applied Geography, 23(1), 23–45.
Gelagay, H. S., & Minale, A. S. (2016). Soil loss estimation using GIS and Remote sensing techniques: A case of Koga watershed, Northwestern Ethiopia. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 4(2), 126–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2016.01.002
Getu, L. A., Nagy, A., & Addis, H. K. (2022). Soil loss estimation and severity mapping using the RUSLE model and GIS in Megech watershed, Ethiopia. Environmental Challenges, 8, 100560.
Girmay, G., Moges, A., & Muluneh, A. (2020). Estimation of soil loss rate using the USLE model for Agewmariayam Watershed, northern Ethiopia. Agriculture & Food Security, 9(1), 1–12.
GSP., (2017). Global Soil Partnership Endorses Guidelines on Sustainable Soil Management. from http://www.fao.org/global-soil-partnership/resources/highlights/detail/en/c/416516/. Accessed 11 Oct 2021.
Gyeltshen, S., Adhikari, R., Bahadur Budha, P., Thapa, G., Kumar Subedi, K., & Kumar Singh, B. (2022). Remote Sensing and GIS based Soil Loss Estimation for Bhutan, using RUSLE model. Geocarto International, 37(21), 6331–6350. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2021.1936210
Harper, D. (1987). Improving the accuracy of the universal soil loss equation in Thailand. In fifth international conservation conferences, Bangkok, Thailand
Hu, S., Li, L., Chen, L., Cheng, L., Yuan, L., Huang, X., & Zhang, T. (2019). Estimation of soil erosion in the chaohu lake basin through modified soil erodibility combined with gravel content in the RUSLE model. Water, 11(9), 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091806
Jain, M. K., & Kothyari, U. C. (2000). Estimation of soil erosion and sediment yield using GIS. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 45(5), 771–786. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626660009492376
Jetten, V., Govers, G., & Hessel, R. (2003). Erosion models: Quality of spatial predictions. Hydrological Processes, 17(5), 887–900.
Kidane, M., Bezie, A., Kesete, N., & Tolessa, T. (2019). The impact of land use and land cover (LULC) dynamics on soil erosion and sediment yield in Ethiopia. Heliyon, 5(12), e02981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02981
Koirala, P., Thakuri, S., Joshi, S., & Chauhan, R. (2019). Estimation of soil erosion in nepal using a RUSLE modeling and geospatial tool. Geosciences, 9(4), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9040147
KPPR. (2020). Nepal provincial planning: Baseline and strategic options for Karnali Province. Karnali: Province Government.
Lama, Y. C., Ghimire, S. K., & Aumeeruddy-Thomas, Y. (2001). Medicinal plants of Dolpo. Amchis’ Knowledge and Conservation. Katmandu: WWF Nepal Program.
Luvai, A., Obiero, J., & Omuto, C. (2022). Soil loss assessment using the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) model. Applied and Environmental Soil Science, 2022, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2122554
Markose, V. J., & Jayappa, K. S. (2016). Soil loss estimation and prioritization of sub-watersheds of Kali River basin, Karnataka, India, using RUSLE and GIS. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 188, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5218-2.
Merritt, W. S., Letcher, R. A., & Jakeman, A. J. (2003). A review of erosion and sediment transport models. Environmental Modelling & Software, 18(8–9), 761–799.
Millward, A. A., & Mersey, J. E. (1999). Adapting the RUSLE to model soil erosion potential in a mountainous tropical watershed. CATENA, 38(2), 109–129.
Mishra, P. K., Rai, A., Abdelrahman, K., Rai, S. C., & Tiwari, A. (2022). Land degradation, overland flow, soil erosion, and nutrient loss in the Eastern Himalayas, India. Land, 11(2), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020179
Mishra, P. K., Rai, A., & Rai, S. C. (2020a). Land use and land cover change detection using geospatial techniques in the Sikkim Himalaya, India. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 23(2), 133–143.
Mishra, P. K., Rai, A., & Rai, S. C. (2020b). Indigenous knowledge of terrace management for soil and water conservation in the Sikkim Himalaya, India. New Delhi: NISCAIR-CSIR.
Morgan, R. P. C. (1985). Soil erosion measurement and soil conservation research in cultivated areas of the UK. The Geographical Journal, 151(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.2307/633274
Nearing, M. A. (2013). Soil erosion and conservation. Environmental Modelling: Finding Simplicity in Complexity (pp. 365–378). Hoboken: Wiley.
Pan, J., & Wen, Y. (2014). Estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE in Caijiamiao watershed, China. Natural Hazards, 71, 2187–2205.
Panagos, P., Borrelli, P., Poesen, J., Ballabio, C., Lugato, E., Meusburger, K., Montanarella, L., & Alewell, C. (2015). The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environmental Science & Policy, 54, 438–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2015.08.012
Pandey, A., Mishra, S. K., Gautam, A. K., & Kumar, D. (2015). Soil erosion assessment of a Himalayan river basin using TRMM data. Proceedings of the International Association of Hydrological Sciences, 366, 200–200. https://doi.org/10.5194/piahs-366-200-2015
Pham, T. G., Nguyen, H. T., & Kappas, M. (2018). Assessment of soil quality indicators under different agricultural land uses and topographic aspects in Central Vietnam. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 6(4), 280–288.
Phinzi, K., & Ngetar, N. S. (2019). The assessment of water-borne erosion at catchment level using GIS-based RUSLE and remote sensing: A review. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 7(1), 27–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2018.12.002
Prasannakumar, V., Vijith, H., Abinod, S., & Geetha, N. (2012). Estimation of soil erosion risk within a small mountainous sub-watershed in Kerala, India, using Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) and geo-information technology. Geoscience Frontiers, 3(2), 209–215.
Renard, K. G., & Foster, G. R. (1983). Soil conservation: principles of erosion by water. In H. E. Dregne & W. O. Willis (Eds.), Dryland agriculture. Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Renard, K. G., Foster, G. R., Weesies, G. A., McCool, D. K., & Yoder, D. C. (1996). Predicting soil erosion by water: A guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). Agriculture handbook (p. 703). Washington: United States Government Printing.
Rivera, A., Bravo, C., & Buob, G. (2017). Climate Change and Land Ice. In D. Richardson, N. Castree, M. F. Goodchild, A. Kobayashi, W. Liu, & R. A. Marston (Eds.), International Encyclopedia of Geography: People, the Earth, Environment and Technology (pp. 1–15). Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118786352.wbieg0538
Roslee, R., & Sharir, K. (2019). Soil erosion analysis using RUSLE model at the Minitod area, Penampang, Sabah Malaysia. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1358(1), 012066.
Sekyi-Annan, E., Gaisie, E., Issaka, R. N., Quansah, G. W., Adams, S., & Bessah, E. (2021). Estimating soil loss for sustainable crop production in the semi-deciduous forest zone of Ghana. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 5, 674816.
Sharpley, A. N., & Williams, J. R. (1990). EPIC. Erosion/Productivity impact calculator: 1. Model documentation. 2. User manual.v
Shin, G.J. (1999). The analysis of soil erosion analysis in watershed using GIS. Ph. D. Dissertation. Department of Civil Engineering, Gangwon National University. Chuncheon, South Korea.
Shrestha, R. (2019). Governance and institutional risks and challenges in Nepal. Mandaluyong: Asian Development Bank.
Shukla, P. R., Skea, J., Calvo Buendia, E., Masson-Delmotte, V., Pörtner, H. O., Roberts, D. C., Zhai, P., Slade, R., Connors, S., & Van Diemen, R. (2019). IPCC, 2019: Climate change and land: An IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems. Geneva: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
Tanyaş, H., Kolat, Ç., & Süzen, M. L. (2015). A new approach to estimate cover-management factor of RUSLE and validation of RUSLE model in the watershed of Kartalkaya Dam. Journal of Hydrology, 528, 584–598.
Thapa, P. (2020). Spatial estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE modeling: A case study of Dolakha district, Nepal. Environmental Systems Research, 9(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-020-00177-2
Uddin, K., Murthy, M. S. R., Wahid, S. M., & Matin, M. A. (2016). Estimation of soil erosion dynamics in the koshi basin using GIS and remote sensing to assess priority areas for conservation. Plos one, 11(3), e0150494. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150494
UNCCD., (2022). The Global Land Outlook, second edition. United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification, Bonn.
Van der Knijff, J. M., Jones, R. J. A., & Montanarella, L. (2000). Soil erosion risk: assessment in Europe.
Xiong, Y., Wang, G., Teng, Y., & Otsuki, K. (2013). Modeling the impacts of land use changes on soil erosion at the river basin scale. Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University, 58(2), 377–387.
Yin, S., Xie, Y., Liu, B., & Nearing, M. A. (2015). Rainfall erosivity estimation based on rainfall data collected over a range of temporal resolutions. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 19(10), 4113–4126. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-4113-2015
Funding
The authors hereby declare that no funds, grants, or other logistical support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KRA, SP, RKB and RK conceived and planned the study and its design. All authors were involved in the analysis, and interpretation. RK took the lead in writing the draft manuscript integrating the inputs from all the authors. All the authors provided critical feedback and assisted to shape the research, analysis and preparing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors hold no relevant financial or any non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
‘Not applicable’ due to the observational/computational nature of the study.
Consent to participate
‘Not applicable’ as the study does not involve human subjects.
Consent to publication
“The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the contents of the manuscript along with the images in Figs. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 and 11.”
Additional information
Communicated by M. V. Alves Martins
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aryal, K.R., Panthi, S., Basukala, R.K. et al. Soil loss estimation of Karnali river basin, Nepal. J. Sediment. Environ. 8, 409–423 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-023-00140-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-023-00140-y