Abstract
Thermoluminescence (TL) materials are well known for a very large number of applications in various fields such as medical research, in vivo dosimetry, environmental dosimetry, personal dosimetry, etc. There are several TL materials available in the market such as fluoride, borate, phosphate, silicate, borosilicate glasses, etc. The TL properties of materials change with the doping of rare-earth and transition impurities in different hosts which are useful for different applications. These doped TL materials can be prepared by different techniques such as, the melt-quenching technique, combustion method, sol–gel method, and others. Radiations such as γ-rays, X-rays, β-rays, photon beam, electron beam, neutron beam, etc., can be used to irradiate these TL materials. In the present state of research, interest is being raised to develop new thermoluminescent materials for various applications in the field of material science and radiation therapy for in vivo dosimetry in view of the rise in the number of cancer patients across the globe. In the last few years, borate and phosphate-based TL dosimeters got more attention in radiation dosimetry. So, this review deals with the recent developments and advancements in borate- and phosphate-based TL materials for in vivo dosimetry.




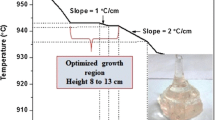
(Reproduced from ref. [59], Open access under Common Creative Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International (CC-BY-NC 4.0) https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)

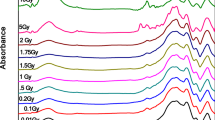
(Reproduced from ref. [104], Open access under Common Creative Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0)

(Reproduced from ref. [95], open access under Common Creative Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Shortland, E. Katherine, D. Patrick, K. Susanna, W. Marc, The origins of glasses: the near East or Egypt? Annual meeting of the American Schools of Oriental Research, (San Antonio, 2016)
J.A.J. Gowlett, High definition archaeology: threads through the past (Routledge, 1997)
A. Kanungo, B. Robert, Kopia, India’s first glassmaking site: dating and chemical analysis. J Glass Stud 51, 11–25 (2009)
D.M. Bose, A concise history of science in India (Indian National Science Academy, 1971), p.15. (ISBN 8173716196)
A. Ghosh, An encyclopaedia of Indian archaeology (BRILL, 1990). (ISBN 90-04-09262-5)
C. Braghin, “Introduction” pp. XI-XIV in Braghin, C. (ed) Chinese glass. Archaeological studies on the uses and social contest of glass artefacts from the Warring States to the Northern Song Period (fifth century B.C. to twelfth century A.D.). ISBN 8822251628(2002).
R. Pinder-Wilson, The Islamic lands and China, in Five thousand years of glass. ed. by H. Tait (University of Pennsylvania Press, 1991), p.140
J. P. Toner, Popular culture in ancient Rome. ISBN 0-7456-4310-8. (2009), p. 19
J. Krogh-Moe, The structure of vitreous and liquid boron oxide. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1(4), 269–284 (1969)
C. Gautam, A.K. Yadav, A.K. Singh, A review on infrared spectroscopy of borate glasses with effects of different additives. ISRN Ceram. (2012). https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/428497
M. Bengisu, Borate glasses for scientific and industrial applications: a review. J. Mater. Sci. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9537-4
J.E. Shelby, Introduction to glass science and technology (Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 2015)
N.M. Bobkova, Thermal expansion of binary borate glasses and their structure. Glass Phys. Chem. 29, 501–507 (2003)
M. Yamane, Glasses for photonics (Cambridge University Press, Port Chester, 2000)
K. Terashima, S. Tamura, S.H. Kim, T. Yoko, Structure and nonlinear optical properties of lanthanide borate glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 2903–2909 (1997)
W. Nie, Optical nonlinearity: phenomena, applications, and materials. Adv. Mater. 5, 520–545 (1993)
O. Deparis, F.P. Mezzapesa, C. Corbari, P.G. Kazansky, K. Sakaguchi, Origin and enhancement of the second-order non-linear optical susceptibility induced in bismuth borate glasses by thermal poling. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 351, 2166–2177 (2005)
V. Nazabal, E. Fargin, B. Ferreira, G. Le Flem, B. Desbat, T. Buffeteau, M. Couzi, V. Rodriguez, S. Santran, L. Canioni, L. Sarger, Thermally poled new borate glasses for second harmonic generation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 290, 73–85 (2001)
R.W. Boyd, G.L. Fischer, Nonlinear optical materials, in Encyclopedia of materials: science and technology. ed. by K.H.J. Buschow et al. (Elsevier, New York, 2001)
R.A. Myers, N. Mukherjee, S.R.J. Brueck, Large second order nonlinearity in poled fused silica. Opt. Lett. 16, 1732–1734 (1991)
C. Corbari, L.C. Ajitdoss, I.C.S. Carvalho, O. Deparis, F.P. Mezzapesa, P.G. Kazansky, K. Sakaguchi, The problem of achieving high second-order nonlinearities in glasses: the role of electronic conductivity in poling of high index glasses. J. Non- Cryst. Solids 356, 2742–2749 (2010)
X. Tiefeng, C. Feifei, D. Shixun, N. Qiuhua, S. Xiang, W. Xunsi, Third-order optical nonlinear characterizations of Bi2O3–B2O3–TiO2 ternary glasses. Phys. B 404, 2012–2015 (2009)
J. Qiu, N. Tanaka, N. Sugimoto, K. Hirao, Faraday effect in Tb3+-containing borate, fluoride and fluorophosphates glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 213, 193–198 (1997)
C.K. Bomfork, I.H. Kunkler, J. Walter, Textbook of radiotherapy: radiation physics, therapy and oncology (Churchill Livingstone, China, 2002)
R. Chen, S.W.S. McKeever, Theory of thermoluminescence and related phenomenon (World Scientific Publishing, Singapore, 1997)
M.R. Ioan, Amorphous and crystalline optical materials used as instruments for high gamma radiation doses estimations. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B: Beam. Interact. Mater. Atoms (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2016.04.009
G.A. Alharshan, D.A. Aloraini, Thermoluminescence properties of slate relevant to radiation measurements. AIP Conf. Proc. 2043, 020004 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5080023
S.B. Lochab, S.P. Pratik Kumar, CaSO4: Dy, Mn: a new and highly sensitive thermoluminescence phosphor for versatile dosimetry. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 119, 136–141 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2015.10.004
R.L. Nyenge, H.C. Swart, D. Poelman, P.F. Smet, L.I.D.J. Martin, L.L. Noto, S. Som, O.M. Ntwaeaborwa, Thermal quenching, cathodoluminescence and thermoluminescence study of Eu2+ doped CaS powder. J. Alloy. Compd. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.10.143
N.J. Shivaramu, B.N. Lakshminarasappa, K.R. Nagabhushana, F. Singh, Thermoluminescence of sol–gel derived Y2O3: Nd3+ nanophosphor exposed to 100MeV Si8+ ions and gamma rays. J. Alloys Compd. 637, 564–573 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.02.218. (ISSN 0925-8388)
K.K. Gupta, R.M. Kadam, N.S. Dhoble, S.P. Lochab, V. Singh, S.J. Dhoble, Photoluminescence, thermoluminescence and evaluation of some parameters of Dy3+ activated Sr5(PO4)3F phosphor synthesized by sol-gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 688, 982–993 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.07.114. (ISSN 0925-8388)
F. Daniels, C.A. Boyd, D.F. Saunders, Thermoluminescence as a research tool. Science 117(3040), 343–349 (1953). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.117.3040.343
P.J. Fox, R.A. Akber, J.R. Prescott, Spectral characteristics of six phosphors used in thermoluminescence dosimetry. J. Phys. D: Appl Phys. 21(1), 189–193 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/21/1/026
A. Kumar, A.K. Sharma, R. Dogra, M. Manhas, R. Kumar, Thermoluminescence studies of γ-irradiated LiF: Sm3+ nanophosphor, AIP Conference Proceedings [NATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RECENT ADVANCES IN EXPERIMENTAL AND THEORETICAL PHYSICS (RAETP-2018) - Jammu, India (17–18 April 2018)] - 2006, 030013, (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5051269.
J.H. Schulman, R.D. Kirk, E.J. West, Proc. 1st Int. Conf. on luminescence dosimetry (Standford, 1965), p.113
W. Binder, S. Disterhoft, J.R. Cameron, In: Proc. 2nd Conf. on Luminescence Dosimetry, Gatlinburg. Conf. 680920 (NTIS, Springfield, VA), 113 pp (1968).
S.K. Mehta, S. Sengupta, Al203 phosphor for thermoluminescence dosimetry. Health Phys. 31(2), 176–177 (1976)
A.C. Lucas, B. Kaspar, In: Proc 5th Conf. on luminescence dosimetry, Sau Paulo (I Phys. Inst. Univ. Giessen), 131 pp (1977).
T. Nakajima, Y. Murayama, T. Matsuzawa, Preparation and dosimetric properties of a highly sensitive LiF thermoluminescent dosimeter. Health Phys. 36(1), 79–82 (1979)
M. Takenga, O. Yamamoto, T. Yamashita, Nucl. Instum. Methods 175, 77 (1980)
M.S. Akselrod, V.S. Kortov, D.J. Kravetsky, V.I. Gotlib, Highly sensitive thermoluminescent anion-defective alpha-Al203: C single crystal detectors. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 32(1), 15–20 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a080715
A. El-Adawy, N.E. Khaled, A.R. El-Sersy, A. Hussein, H. Donya, TL dosimetric properties of Li2O–B2O3 glasses for gamma dosimetry. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 68(6), 1132–1136 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2010.01.017
M. Santiago, J. Marcazzó, C. Grasselli, A. Lavat, P. Molina, F. Spano, E. Caselli, Thermo- and radioluminescence of undoped and Dy-doped strontium borates prepared by sol-gel method. Radiat. Meas. 46(12), 1488–1491 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2011.01.006
E. Ekdal, T. Karalı, A. Kelemen, M. Ignatovych, V. Holovey, C. Harmansah, Thermoluminescence characteristics of Li2B4O7 single crystal dosimeters doped with Mn. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 96, 201–204 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2013.10.009
A. Saidu, H. Wagiran, M.A. Saeed, Y.S.M. Alajerami, Thermoluminescence characteristics of zinc lithium borate glass activated with Cu+(ZnO–Li2O–B2O3:Cu+) for radiation dosimetry. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 304(2), 627–632 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3846-y
A. Ab Rasid, H. Wagiran, S. Hashim, Z. Ibrahim, H. Ali, Dosimetric properties of dysprosium doped lithium borate glass irradiated by 6MV photons. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 112, 29–33 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2015.02.003
B. Sanyal, M. Goswami, S. Shobha, V. Prakasan, S.P. Chawla, M. Krishnan, S.K. Ghosh, Synthesis and characterization of Dy 3+ doped lithium borate glass for thermoluminescence dosimetry. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 475, 184–189 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.09.016
S. İflazoğlu, A. Yılmaz, V.E. Kafadar, M. Topaksu, A.N. Yazıcı, Neutron+Gamma response of undoped and Dy doped MgB4O7 thermoluminescence dosimeter. Appl. Radiat. Isot. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2019.02.014
E. Salama, H.A. Soliman, Thermoluminescence glow curve deconvolution and trapping parameters determination of dysprosium doped magnesium borate glass. Radiat. Phys. Chem. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2018.03.003
S. Hashim, M.H.A. Mhareb, S.K. Ghoshal, Y.S.M. Alajerami, D.A. Bradley, M.I. Saripan, N. Tamchek, K. Alzimami, Luminescence characteristics of Li2O-MgO-B2O3 doped with Dy3+ as a solid TL detector. Radiat. Phys. Chem. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2015.04.007
S. Hashim, R.S. Omar, S.K. Ghoshal, Realization of dysprosium doped lithium magnesium borate glass based TLD subjected to 1–100 Gy photon beam irradiations. Radiat. Phys. Chem. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2019.05.016
S. Meghnath, S. Rakesh, V. Sathian, M.S. Kulkarni, A.K. Tyagi, Thermoluminescence based personnel neutron dosimetry study of LiMgBO3:Dy3+. Ceram. Int. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.105
M. Oglakci, M. Topaksu, N. Can, Thermoluminescence glow curves of beta irradiated NaBaBO3: Ce3+ phosphor synthesized by combustion method. Sens. Actuators, A 315, 112299 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2020.112299
D. Nakauchi, G. Okada, Y. Fujimoto, N. Kawano, K. Noriaki, Y. Takayuki, Optical and radiation-induced luminescence properties of Ce-doped magnesium aluminoborate glasses. Opt. Mater. 72, 190–194 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2017.05.063
D. Nakauchi, G. Okada, Y. Fujimoto, N. Kawano, K. Noriaki, Y. Takayuki, Optical and radiation-induced luminescence properties of Sn-doped magnesium aluminoborate glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses: Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol. Part B 60, 10–14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.13036/17533562.60.1.029
A. Saidu, H. Wagiran, M.A. Saeed, Y.S.M. Alajerami, A.B.A. Kadir, Effect of co-doping of sodium on the thermoluminescence dosimetry properties of copper-doped zinc lithium borate glass system. Appl. Radiat. Isot. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2016.10.005
T. Ahamad, Z.A. Alothman, M. Naushad, K. Yusuf, Synthesis and characterization of CuO doped lithium magnesium borate glasses for thermoluminescence dosimetry. Optik 231, 166369 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166369
I. Rammadhan, S. Taha, H. Wagiran, Thermoluminescence characteristics of Cu2O doped calcium lithium borate glass irradiated with the cobalt-60 gamma rays. J. Lumin. 186, 117–122 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2017.02.026
N. Salleh, T. Abd Rahman, M. Saeed, Effect of strontium concentration on thermoluminescence glow curve of copper doped lithium magnesium borate glass. Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. (2017). https://doi.org/10.11113/mjfas.v13n3.570
V. Chopra, S.J. Dhoble, K.K. Gupta, A. Singh, A. Pandey, Thermoluminescence of Li2B4O7: Cu phosphor exposed to proton beam for dosimetric application. Radiat. Meas. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2018.05.002
I. Hossain, N.K. Shekaili, H. Wagiran, Thermoluminescence response of copper-doped potassium borate glass subjected to 6 megavolt X-Ray irradiation. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 82(1), 149–152 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-015-0078-z
N.S. Prabhu, V. Hegde, M.I. Sayyed, O. Agar, S.D. Kamath, Investigations on structural and radiation shielding properties of Er3+ doped zinc bismuth borate glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.03.074
V. Hegde, N.S. Prabhu, W. Akshatha, M.I. Sayyed, O. Agar, S.D. Kamath, Influence of 125 MeV gamma rays on optical and luminescent features of Er3+ doped zinc bismuth borate glasses. Results Phys. 12(1), 1762–1769 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.02.003
V. Bhatia, D. Kumar, H. Singh, N. Kaur, S.M. Rao, A. Kumar, V. Mehta, S.P. Singh, Structural, optical and thermoluminescence properties of newly developed MnKB: Er3+ glass system. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 543, 120113 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2020.120113
V. Bhatia, D. Kumar, H. Singh, N. Kaur, S.M. Rao, A. Kumar, V. Mehta, S.P. Singh, Effects of Sm3+ ions on the structural, optical and thermoluminescence properties of MnKB glass system. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 161, 110408 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2021.110408
J. Anjaiah, C. Laxmikanth, N. Veeraiah, Spectroscopic properties and luminescence behaviour of europium doped lithium borate glasses. Phys. B: Condens Matter 454, 148–156 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2014.07.070
J. Anjaiah, C. Laxmikanth, N. Veeraiah, P. Kistaiah, Infrared luminescence and thermoluminescence of lithium borate glasses doped with Sm3+ ions. Mater. Science-Poland (2014). https://doi.org/10.1515/msp-2015-0028
V. Hegde, N. Chauhan, V. Kumar, C.D. Viswanath, K.K. Mahato, D.K. Sudha, Effects of high dose gamma irradiation on the optical properties of Eu3+ doped zinc sodium bismuth borate glasses for red LEDs. J. Lumin. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.11.023
K. Sudhakar, M. Srinivasa Reddy, L. Rao, N. Veeraiah, Influence of modifier oxide on spectroscopic and thermoluminescence characteristics of Sm3+ ion in antimony borate glass system. J. Lumin. 128, 1791–1798 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2008.04.010
H. Obayes, O. Obayes, Q. Kadhim, A. Saidu, M.H. Al-Maamori, Improved thermoluminescence and kinetic parameters of new strontium/ copper co-doped lithium borate glass system. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B: Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2019.06.028
H. Ono, Y. Fujimoto, T. Yahaba, T. Yanagida, M. Koshimizu, K. Asai, Thermoluminescence properties of Tb3+-doped CaO–Al2O3–B2O3-based glasses. Optic. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2018.07.004
M. Ismail, A. Saddon, M. Fahmi, Impact of Zn2+ ions co-doping on the TL properties of Cu2+ ion-doped calcium lithium borate glass irradiated by various radiation sources. J. Lumin. 236, 118091 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2021.118091
E. M. Abou Hussein, S.M. Gafar, Effect of gamma rays on Zn/Cu doped strontium borate glass system for dosimetric applications. Radiochimica Acta (2022). https://doi.org/10.1515/ract-2022-0029.
M. Bahra, M. Jaafar, H. Wagiran, Thermoluminescence dosimetry properties and kinetic parameters of zinc borate silica glass doped with Cu2O and co-doped with SnO2. J. Lumin. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.08.020
A.S. El-Bayoumi, H. Alazab, F. Ezz-Eldin, The impact of γ-irradiation on Cd-B2O3 glass doped WO3: new evidences by TL and ESR spectroscopy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 551, 120459 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2020.120459
C. Ivascu, A. Timar Gabor, O. Cozar, L. Daraban, I. Ardelean, FT-IR, Raman and thermoluminescence investigation of P2O5–BaO–Li2O glass system. J. Mol. Struct. 993(1–3), 249–253 (2011)
R. Swamy, S. Bhaskar, Y. Gandhi, R. Kadam, N. Venkatarman, P. Raghava, N. Veeraiah, Thermoluminescence study of MnO doped borophosphate glass samples for radiation dosimetry. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 368, 40–44 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2013.02.020
B.J.R. Swamy, S. Bhaskar, R. Vijay, P. Ramesh Babu, D. Krishna Rao, N. Veeraiah, Influence of copper ions on thermoluminescence characteristics of CaF2–B2O3–P2O5 glass system. Ceram. Int. 40, 3707–3713 (2014)
B. Biró, A. Pascu, A. Timar-Gabor, V. Simon, Thermoluminescence investigations on xY2O3 (60–x)P2O5·40SiO2 vitroceramics. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 98, 49–53 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2015.01.019
M.A.K. Abdelhalim, B.M. Al-Shamrani, Improvement of the thermoluminescence properties of the P2O5-Li2O glass system by using nanoparticles. J. Lumin. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2016.08.028
T. Kalpana, Y. Gandhi, S. Bhaskar, V. Sudarsan, P. Bragiel, M. Piasecki, V. Ravi Kumar, N. Veeraiah, Influence of alumina on photoluminescence and thermoluminescence characteristics of Gd3+ doped barium borophosphate glasses. J. Lumin. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2016.06.053
T. Kalpana, S. Bhaskar, Y. Gandhi, V. Ravi Kumar, G.S. Baskaran, P. Bragiel, M. Piasecki, N. Veeraiah, Thermoluminescence features of alumina-mixed borophosphate glasses with Tb3+ ions for dosimetric applications. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 8(2), 188–195 (2017)
H. Tanaka, Y. Fujimoto, K. Saeki, M. Koshimizu, T. Yanagida, K. Asai, Radiophotoluminescence properties of Ag-doped mixed phosphate glasses. Radiat. Meas. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2017.01.010
M.A. Vallejo, M. Perez, P.V. Ceron, R. Navarro, C. Villaseñor, T. Cordova, M. Sosa, Photoluminescence and thermoluminescence of phosphate glasses doped with Dy3+ and containing silver nanoparticles. Nano (2017). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793292017501454
T. Sunil, M.L. Chithambo, Thermoluminescence of K-Mg-Al-Zn fluorophosphate glass. Optic. Mater. 64, 302–309 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2016.12.035
A. El-Kheshen, C. Woda, M. Discher, N. El-Faramawy, Investigation of phosphate glass doped lanthanum as beta dosimeter. J. Lumin. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.04.001
H.F. El-Nashar, M. El-Kinawy, N.A. El-Faramawy, Investigations of the kinetic energy parameters of irradiated (La)-doped phosphate glass. Lumin. J. Biol. Chem. Lumin. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.3703
M.A.K. Abdelhalim, M.S. Al-Ayed, B.M. Al-Shamrani, Synthesizing new glass 40P2O5 – 50BaO - 25Na2O – 25MgO - 5TiO2 for the application in high radiation environmental dosimetry. AIP Adv. 8, 095212 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5030338
I. El Mesady, S. Alawsh, Optical and luminescence properties of silicon doped alumino-phosphate-sodium glass system. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 482, 236–242 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.12.054
S. Hirano, N. Kawano, G. Okada, N. Kawaguchi, T. Yanagida, PL and TSL properties of tin-doped zinc sodium phosphate glasses. Radiat. Meas. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2018.03.002
A. Gasiorowski, P. Szajerski, Thermoluminescence characteristics and dose-response of electron beam and gamma rays irradiated alumino-phosphate glasses doped with Gd2O3 and Tb2O3. J. Lumin. 214, 116519 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2019.116519
A. Gasiorowski, P. Szajerski, Particles size increase assisted enhancement of thermoluminescence emission in gadolinium and dysprosium oxide doped phosphate glasses. J. Alloys Compds. 839, 155479 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155479
A. Gasiorowski, P. Szajerski, J.F.B. Cuevas, Use of terbium doped phosphate glasses for high dose radiation dosimetry—thermoluminescence characteristics, dose response and optimization of readout method. Appl. Sci. 11, 7221 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11167221
N.Y. Abdou, M.M. Farag, W.M. Abd-Allah, Thermoluminescent properties of nano-magnesium phosphate ceramic for radiation dosimetry. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 317 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00310-1
P. Rubalajyothi, A. Rajendran, Thermoluminescence characteristics studies of phosphor material with anti-bacterial activity. J. Crit. Rev. 7(1), 2020 (2019)
P. Vinodkumar, S. Panda, U. Madhusoodanan, B.S. Panigrahi, Thermoluminescence properties of strontium borophosphate doped with praseodymium and enhancement with uranyl cooping. Radiat. Phys. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2020.108914
A. Raja, R. Nagaraj, K. Ramachandran, V. Sivasubramani, G. Annadurai, D.J. Daniel, P. Ramasamy, A facile synthesis, structural and triple-luminescence properties of a novel fluoroperovskite RbCaF3: Sm3+ phosphor for radiation dosimetry and orange-red LED applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 255, 114531 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2020.114531
K. Munirathnam, P.C. Nagajyothi, K. Hareesh, M.M. Kumar, S.D. Dhole, Effect of Mn codopant on thermoluminescence properties of γ-rays irradiated Na3Y(PO4)2: Dy phosphors for dosimetry applications. Appl. Phys. A, Mater. Sci. Process. 127(1), 1–9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04202-0
W. Li, Z. Chen, J. Xu, P. Zhao, Y. Fan, C. He, Synthesis and optical properties of novel Gd3+-doped BaZn2(PO4)2 glass-ceramics for radiation detection applications. J. Rare Earths (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2021.11.010
R. Kaur, R.B. Rakesh, S.G. Mhatre, V. Bhatia, D. Kumar, H. Singh, S.P. Singh, A. Kumar, Physical, optical, structural and thermoluminescence behaviour of borosilicate glasses doped with trivalent neodymium ions. Optic. Mater. 121, 111109 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111109
H.A. Alazab, N.Y. Abdou, H.A. Saudi et al., Thermoluminescence properties of bioglass for radiation dosimetry. Silicon (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01364-1
G.A. Kumar, Y. Rambabu, R.K. Guntu, K. Sivaram, M.S. Reddy, C.S. Rao, V. Venkatramu, V.R. Kumar, N.C.S.N. Iyengar, ZrxCa30-xP70 thermoluminescent bio glass, structure and elasticity. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 119, 104517 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2021.104517
A.N. D’Souza, K. Sharmila, D.K. Gaikwad, M.I. Sayyed, H.M. Somashekarappa, H. Al-Ghamdi, A.H. Almuqrin, S.D. Kamath, Evaluation of bismuth added HMO glasses in terms of thermal, mechanical, gamma radiation shielding and thermoluminescence properties. Mater. Res. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2021-0243
T.N.H. Tengku KamarulBahri, H. Wagiran, R. Hussin, I. Hossain, T. Kadni, Thermoluminescence properties of CaO–B2O3 glass system doped with GeO2. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 102, 103–107 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2014.03.029
G.R. Barrera, L.F. Souza, A.L.F. Novais, L.V.E. Caldas, C.M. Abreu, R. Machado, E.M. Sussuchi, D.N. Souza, Thermoluminescence and optically stimulated luminescence of PbO–H3BO3 and PbO–H3BO3– Al2O3 glasses. Radiat. Phys. Chem. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2018.02.005
A. Ozdemir, Investigation of dosimetric properties of newly-developed Li2B4 O7:Ag+, La3+ using thermoluminescence (TL) technique. J. Alloy. Compd. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.153722
T. Sunil, C. Makaiko, Kinetic analysis and general features of thermoluminescence of B2O3-Li2O-ZnF2 glass. Radiat. Meas. 100, 1–8 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2017.03.038
H.A. Tajuddin, W.M.S. Wanhassan, S.A. Sani, N.S. Shaharin, Thermoluminescent properties of Dy doped calcium borate based glass for dose measurement subjected to photon irradiation. EPJ Web Conf. 156, 00002 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/201715600002
Y. Fujimoto, T. Yanagida, M. Koshimizu, K. Asai, Optical and dosimeter properties of Li2O–Al2O3–B2O3 based glasses. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 125, 728–731 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.17076
H. Vinod, C.S. Viswanath, M. Krishna, S. Sudha, Photoluminescence and thermally stimulated luminescence properties of Pr3+-doped zinc sodium bismuth borate glasses. Optic. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2018.06.064
N.S. Prabhu, K. Sharmila, H.M. Somashekarappa, G. Lakshminarayana, S. Mandal, M.I. Sayyed, S.D. Kamath, Thermoluminescence features of Er3+ doped BaO-ZnO-LiFB2O3 glass system for high-dose gamma dosimetry. Ceram. Int. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.04.276
R. Kaur, R.B. Rakesh, S.G. Mhatre, V. Bhatia, D. Kumar, H. Singh, S.P. Singh, A. Kumar, Thermoluminescence, structural and optical properties of Ce3+ doped borosilicate doped glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06382-8
Funding
This study is not funded by any source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, B.A., Bindu, P.H. Advances in borate- and phosphate-based TL materials for in vivo dosimetry. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 59, 537–550 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-022-00240-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-022-00240-x