Abstract
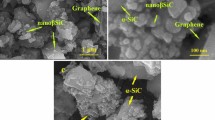
Silicon carbide (SiC) is an effective material for high-temperature engineering applications owing to its desirable properties such as high elastic modulus, high hardness, and melting temperature, high thermal conductivity, good corrosion and oxidation resistance, low density, and coefficient of thermal expansion compared with other advanced ceramics. Nevertheless, poor sinterability and low toughness limit its use, which can be overcome using appropriate additives. In this study, the effect of different amounts of nano-β-SiC (0, 5, 10, and 15 wt.%) and graphene (0, 1, 2, and 3 wt.%) particles on the sinterability behavior and microstructure of SiC composite has been investigated. After weighing, dispersing nano-β-SiC and graphene, and mixing the starting materials, milling was carried out at 180 rpm for 3 h. The materials obtained were then compressed uniaxially under a pressure of 75 MPa and then were compressed again through CIP under 150 MPa. To remove volatile products, the pyrolysis process was performed at 800 °C under Ar atmosphere. Finally, the samples were sintered at 2200 °C for 2 h by the pressureless sintering process. XRD analysis was used to investigate the phases and FESEM images were used to study the microstructure. According to the XRD patterns, β-SiC particles were converted to α-SiC, which was accompanied by the elongation of SiC grains. Also, no reaction was observed between graphene and the SiC matrix. According to the FESEM images, the samples containing 5 wt.% nano-β-SiC and 1 wt.% graphene showed a uniform distribution of reinforcement particles but with increasing the amount of the reinforcement particles, agglomeration was observed. According to the results, upon increasing the nano-β-SiC up to 5 wt% and graphene up to 1 wt.%, all the measured properties including relative density, and linear shrinkage improved and reached 99.04%, and 18.01%, respectively. However, with increasing the additives, these properties deteriorated due to increasing porosity and agglomeration in the composite structure.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Kultayeva, Y.-W. Kim, Mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of pressureless sintered SiC–AlN ceramics. Ceram. Int. 46(11), 19264–19273 (2020)
M.V. Tomkovich et al., Sintered silicon carbide based materials: mechanical properties vs. structure. Refract. Ind. Ceram 60(5), 445–454 (2020)
H.-M. Kim, Y.-W. Kim, Low temperature pressureless sintering of silicon carbide ceramics with alumina–yttria–magnesia-calcia. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 127(4), 207–214 (2019)
Y.-K. Seo, J.-H. Eom, Y.-W. Kim, Process-tolerant pressureless-sintered silicon carbide ceramics with alumina-yttria-calcia-strontia. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(2), 445–452 (2018)
Seung Hoon Jang et al., “Effects of Y2O3–RE 2O3 (RE=Sm, Gd, Lu) additives on electrical and thermal properties of silicon carbide ceramics.” J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99(1), 265–272 (2016)
Young-Wook. Kim, Tae-Young. Cho, Kwang Joo Kim, “Effect of grain growth on electrical properties of silicon carbide ceramics sintered with gadolinia and yttria.” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35(15), 4137–4142 (2015)
S. Ribeiro et al., Effect of temperature and heating rate on the sintering performance of SiC-Al2O3-Dy2O3 and SiC-Al2O3-Yb2O3 systems. Ceram. Int. 43(18), 16048–16054 (2017)
Mostafa Bahaaddini et al., “Pressureless sintering of LPS-SiC (SiC-Al2O3-Y2O3) composite in presence of the B4C additive.” Ceram. Int. 45(10), 13536–13545 (2019)
D. Ahmoye, D. Bucevac, V.D. Krstic, Mechanical properties of reaction sintered SiC-TiC composite. Ceram. Int. 44(12), 14401–14407 (2018)
Bizhe Su et al., The effect of in situ synthesized AlN on densification of SiC ceramics by pressureless sintering. Ceram. Int. 41(10), 14172–14178 (2015)
M. Khodaei, O. Yaghobizadeh, A.A. Shahraki, S. Esmaeeli, Investigation of the effect of Al2O3–Y2O3–CaO (AYC) additives on sinterability, microstructure and mechanical properties of SiC matrix composites: a review. Int. J. Refract. Met. H. 78, 9–26 (2018)
Dong Feng et al., “Effect of oxygen content on the sintering behaviour and mechanical properties of SiC ceramics.” Ceram. Int. 45(18), 23984–23992 (2019)
A.C. Santos, S. Ribeiro, “Liquid phase sintering and characterization of SiC ceramics.” Ceram. Int. 44(10), 11048–11059 (2018)
R. Malik, Y.-H. Kim, Y.-W. Kim, “Effect of additive content on the mechanical and thermal properties of pressureless liquid-phase sintered SiC.” J. Asian. Ceram. Soc. 8(2), 448–459 (2020)
Yong-Hyeon. Kim et al., “Mechanical and thermal properties of silicon carbide ceramics with yttria–scandia–magnesia.” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39(2–3), 144–149 (2019)
Tae-Young. Cho, Young-Wook. Kim, Kwang Joo Kim, “Thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties of pressureless sintered silicon carbide ceramics with yttria-scandia-aluminum nitride.” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36(11), 2659–2665 (2016)
Sung Il Yun et al., “Fabrication and properties of macro-porous SiC using Al2O3–Y2O3–SiO2 as bonding additives.” Ceram. Int. 47(9), 11979–11988 (2021)
Dusan Bucevac et al., “Toughening of SiC matrix with in-situ created TiB2 particles.” Ceram. Int. 36(7), 2181–2188 (2010)
M. Khodaei, O. Yaghobizadeh, S.H. Naghavi Alhosseini, S. Esmaeeli, S.R. Mousavi, The effect of oxide, carbide, nitride and boride additives on properties of pressureless sintered SiC: a review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39, 2215–2231 (2019)
Hanqin Liang et al., “The effect of powder bed on the liquid phase sintering of α-SiC.” Mater. Des. (1980–2015) 56, 1009–1013 (2014)
EunJu Lee et al., Microstructure formation of porous silicon carbide ceramics during β-α phase transformation. Int. J. Refract. Metals. Hard. Mater. 65, 64–68 (2017)
A. Malinge, A. Coupé, S. Jouannigot, Y. Le Petitcorps, R. Pailler, Pressureless sintered silicon carbide tailored with aluminium nitride sintering agent. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32–16, 4419–4426 (2012)
N.P. Padture, B.R. Lawn, Toughness properties of a silicon carbide with an in situ induced heterogeneous grain structure. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 77–10, 2518–2522 (1994)
Chenran Li et al., “Microstructure and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered SiC ceramics aided by B4C.” Ceram. Int. 46(8), 10142–10146 (2020)
Mahdi Khodaei et al., “Effects of different sintering methods on the properties of SiC-TiC, SiC-TiB2 composites.” Int. J. Refract. Metals. Hard. Mater. 70, 19–31 (2018)
J.C. Viala, P. Fortier, J. Bouix, Stable and metastable phase equilibria in the chemical interaction between aluminium and silicon carbide. J. Mater. Sci. 25–3, 1842–1850 (1990)
Laleh Kheyrinia et al., “Fabrication of SiC bodies by optimized gel-casting method.” Int. J. Ref. Metals. Hard. Mater. 81, 225–232 (2019)
M. Khodaei et al., “The effect of TiC additive with Al2O3-Y2O3 on the microstructure and mechanical properties of SiC matrix composites.” Adv. Ceram. Prog. 6(3), 15–24 (2020)
D. Foster, D.P. Thompson, The use of MgO as a densification aid for α-SiC. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 19, 2823–2831 (1999)
A. Gubernat, L. Stobierski, P. Labaj, Microstructure and mechanical properties of silicon carbide pressureless sintered with oxide additives. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 781–789 (2007)
Meng Liu et al., “Preparation of dense and high-purity SiC ceramics by pressureless solid-state-sintering.” Ceram. Int. 45(16), 19771–19776 (2019)
Giuseppe Magnani et al., “Solid-state pressureless sintering of silicon carbide below 2000 C.” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34(15), 4095–4098 (2014)
Mahdi Khodaei et al., “Improvement toughness of SiC ceramic by adding Cr2O3 and annealing process.” J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 57(4), 1–10 (2021)
Sara Ahmadbeygi et al., Fabrication of SiC body by microwave sintering process. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28(7), 5675–5685 (2017)
Kyeong Sik Cho, Kwang Soon Lee, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of spark-plasma-sintered SiC-TiC composites.” Key engineering materials (Trans Tech Publications Ltd Vol. 287, Freienbach, 2005), pp. 335–339
Jingkun Li et al., Silicon carbide hot pressing sintered by magnesium additive: microstructure and sintering mechanism. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9(1), 520–529 (2020)
C. Lorrette, A. Réau, L. Briottet, Mechanical properties of nanostructured silicon carbide consolidated by spark plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 33(1), 147–156 (2013)
D.O. Moskovskikh et al., Silicon carbide ceramics: Mechanical activation, combustion and spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. 42(11), 12686–12693 (2016)
J. GuillardFrançois et al., “Densification of SiC by SPS-effects of time, temperature and pressure.” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27(7), 2725–2728 (2007)
Giuseppe Magnani, Giuliano Sico, Alida Brentari, “Two-step pressureless sintering of silicon carbide-based materials.” Advances in science and technology, vol. 89 (Trans Tech Publications Ltd., Freienbach, 2014), pp. 70–75
Hanqin Liang et al., “The effect of rare earth oxides on the pressureless liquid phase sintering of α-SiC.” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34(12), 2865–2874 (2014)
Yihua Huang et al., “Enhancing toughness and strength of SiC ceramics with reduced graphene oxide by HP sintering.” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(13), 4329–4337 (2018)
Shixue Guan et al., “Production of silicon carbide reinforced molybdenum disilicide composites using high-pressure sintering.” Ceram. Int. 46(15), 23643–23650 (2020)
Eun Ju Lee et al., “Densification behavior of high purity SiC by hot pressing.” Ceram. Int. 40(10), 16389–16392 (2014)
Giuseppe Magnani et al., “Pressureless sintered silicon carbide with enhanced mechanical properties obtained by the two-step sintering method.” Ceram. Int. 40(1), 1759–1763 (2014)
Y. Hui, Z. Lingjie, G. Xingzhong, Z. Xiaoyi, F. Xiaojian, “Pressureless sintering of silicon carbide ceramics containing zirconium diboride.” Ceram. Int. 37, 2031–2035 (2011)
Qisong Li et al., “Effects of graphene on the thermal conductivity of pressureless-sintered SiC ceramics.” Ceram. Int. 41(10), 13547–13552 (2015)
Mahdi Khodaei et al., “The effect of TiO2 additive on the electrical resistivity and mechanical properties of pressureless sintered SiC ceramics with Al2O3-Y2O3.” Int. J. Refract. Metals. Hard. Mater. 76, 141–148 (2018)
Mahdi Khodaei et al., “The effect of Cr2O3 additions on sinterability and mechanical properties of liquid-phase sintered SiC ceramics.” J. Alloys. Compd. 829, 154501 (2020)
Tae-Young. Cho et al., “Electrical and mechanical properties of pressureless sintered SiC-Ti2CN composites.” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(9), 3064–3072 (2018)
Hadi Dehghani et al., “The effect of AlN-Y2O3 compound on properties of pressureless sintered SiC ceramics-a review.” Int. J. Refract. Metals. Hard. Mater. 95, 105420 (2020)
Mahdi Khodaei et al., “The effect of TiO2 additive on sinterability and properties of SiC-Al2O3-Y2O3 composite system.” Ceram. Int. 44(14), 16535–16542 (2018)
Eszter Bódis et al., “Spark plasma sintering of graphene reinforced silicon carbide ceramics.” Ceram. Int. 43(12), 9005–9011 (2017)
Mahdi Khodaei et al., “The effect of nano-TiO2 additions on the densification and mechanical properties of SiC-matrix composite.” Ceram. Int. 46(5), 6477–6483 (2020)
Hanqin Liang et al., “The relationship between microstructure and flexural strength of pressureless liquid phase sintered SiC ceramics oxidized at elevated temperatures.” Ceram. Int. 42(11), 13256–13261 (2016)
M. Petrus, J. Wozniak, A. Jastrzębska, M. Kostecki, T. Cygan, A. Olszyna, The effect of the morphology of carbon used as a sintering aid on the sinterability of silicon carbide. Ceram. Int. 44(6), 7020–7025 (2018)
Chen Chen et al., “Preferentially oriented SiC/graphene composites for enhanced mechanical and thermal properties.” Ceram. Int. 46(14), 23173–23179 (2020)
Q. Li, Y. Zhang, H. Gong, H. Sun, W. Li, Enhanced fracture toughness of pressureless-sintered SiC ceramics by addition of graphene. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 32–7, 633–638 (2016)
X. Guo, R. Wang, P. Zheng, Z. Lu, H. Yang, Pressureless sintering of multilayer graphene reinforced silicon carbide ceramics for mechanical seals. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 118–7, 409–417 (2019)
Ying-Nan. Cao et al., Preparation of zirconium diboride ultrafine hollow spheres by a combined sol–gel and boro/carbothermal reduction technique. J. Sol-gel. Sci. Technol. 72(1), 130–136 (2014)
A. Malinge, A. Coupé, Y. Le Petitcorps, R. Pailler, Pressureless sintering of beta silicon carbide nanoparticles. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 4393–4400 (2012)
H.Z. Wang, L. Gao, J.K. Guo, Effect of nanoscale SiC particles on the microstructure of Al2O3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 26(4), 391–396 (2000)
A. Razmjoo, H.R. Baharvandi, N. Ehsani, The effect of graphene addition on the properties of SiC ceramics—a review. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 58, 437–460 (2022)
S. Prochazka, R. Scanlan, Effect of boron and carbon on sintering of SiC. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 58(1–2), 72 (1975)
G. Wroblewska, E. Nold, F. ThLimmler, The role of boron and carbon additions on the microstructural development of pressureless sintered silicon carbide. Ceram. Int. 16, 201–209 (1990)
K. Raju, D.H. Yoon, Sintering additives for SiC based on the reactivity: a review. Ceram. Int. 42–16, 17947–17962 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Razmjoo, A., Baharvandi, H.R. & Ehsani, N. Pressureless sintering of SiC matrix composites reinforced with nano-β-SiC and graphene. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 59, 729–741 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-022-00213-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-022-00213-0