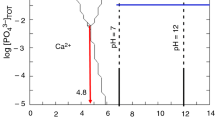
Abstract
Hydroxyapatite (HA) was synthesized through the precipitation method and different processing parameters (Ca/P molar ratio, pH, and reaction temperature) were varied to investigate their influence on the HA formation. No HA powder was obtained at pH 10 and 25 °C, even when using a Ca/P ratio as high as 2.2. However, HA powders were successfully produced at pH above 11, 25 °C, and Ca/P ratio of 2.2. At pH 10 and 25 °C, the concentration of the H+ ions in the reaction solution increased and so did the Ca loss, resulting Ca-deficient hydroxyapatite (CdHA) formation. While HA was formed instead due to a lower Ca loss when the pH was increased to 11 and 11.3. As the reaction temperature was increased to 70 and 90 °C, the HA formation occurred regardless of the pH because of the decreased solubility of HA in the solution.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.V. Dorozhkin, Calcium orthophosphates in nature, biology and medicine. Materials 2, 399–498 (2009)
H. Guler, G. Gundogmaz, F. Kurtulus, G. Celik, S.S. Gacanoglu, Solid state synthesis of calcium borohydroxyapatite. Solid State Sci. 13, 1916–1920 (2011)
X.J. Guo, H.D. Yan, S.G. Zhao, L. Zhang, Y.T. Li, X.H. Liang, Effect of calcining temperature on particle size of hydroxyapatite synthesized by solid-state reaction at room temperature. Adv. Powder Technol. 24, 1034–1038 (2013)
S. Kannan, J.M.F. Ferreira, Synthesis and thermal stability of hydroxyapatite-β-tricalcium phosphate composites with cosubstituted sodium, magnesium, and fluorine. Chem. Mater. 18, 198–203 (2006)
I.H. Arita, V.M. Castano, D.S. Wilkinson, Synthesis and processing of hydroxyapatite ceramic tapes with controlled porosity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 6, 19–23 (1995)
B. Yeong, J.M. Xue, J. Wang, Mechanochemical synthesis of hydroxyapatite from calcium oxide and brushite. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 465–467 (2001)
H. El Briak-BenAbdeslam, M.P. Ginebra, M. Vert, P. Boudeville, Wet or dry mechanochemical synthesis of calcium phosphates? Influence of the water content on DCPD-CaO reaction kinetics. Acta Biomater. 4, 378–386 (2008)
M. Toriyama, A. Ravaglioli, A. Krajewski, G. Celotti, A. Piancastelli, Synthesis of hydroxyapatite-based powders by mechano-chemical method and their sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 16, 429–436 (1996)
Y.X. Pang, X. Bao, Influence of temperature, ripening time and calcination on the morphology and crystallinity of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23, 1697–1704 (2003)
E. Bouyer, F. Gitzhofer, M.I. Boulos, Morphological study of hydroxyapatite nanocrystal suspension. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 11, 523–531 (2000)
C.S. Liu, Y. Huang, W. Shen, J.H. Cui, Kinetics of hydroxyapatite precipitation at pH 10 to 11. Biomaterials 22, 301–306 (2001)
A.L. Boskey, A.S. Posner, Conversion of amorphous calcium phosphate to microcrystalline hydroxyapatite. A pH-dependent, solution-mediated, solid-solid conversion. J. Phys. Chem. 77, 2313–2317 (1973)
M.A. Martins, C. Santos, M.M. Almeida, M.E.V. Costa, Hydroxyapatite micro- and nanoparticles: nucleation and growth mechanisms in the presence of citrate species. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 318, 210–216 (2008)
C. Santos, M.M. Almeida, M.E. Costa, Morphological evolution of hydroxyapatite particles in the presence of different citrate:calcium ratios. Cryst. Growth Des. 15, 4417–4426 (2015)
J.B. Liu, X.Y. Ye, H. Wang, M.K. Zhu, B. Wang, H. Yan, The influence of pH and temperature on the morphology of hydroxyapatite synthesized by hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 29, 629–633 (2003)
T.A. Kuriakose, S.N. Kalkura, M. Palanichamy, D. Arivuoli, K. Dierks, G. Bocelli, C. Betzel, Synthesis of stoichiometric nano crystalline hydroxyapatite by ethanol-based sol-gel technique at low temperature. J. Cryst. Growth 263, 517–523 (2004)
M.N. Hassan, M.M. Mahmoud, A. Abd El-Fattah, S. Kandil, Microwave-assisted preparation of nano-hydroxyapatite for bone substitutes. Ceram. Int. 42, 3725–3744 (2016)
Y. Wibisono, N.L.B. Dwijaksara, W.B. Widayatno, A.S. Wismogroho, M.I. Amal, N.T. Rochman, T. Nishimura, A. Noviyanto, Synthesis and sinterability of hydroxyapatite from fishery by-products. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 55, 570–575 (2018)
B. Ben-Nissan, Natural bioceramics: from coral to bone and beyond. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. 7, 283–288 (2003)
B. Ben-Nissan, A. Milev, R. Vago, Morphology of sol-gel derived nano-coated coralline hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials 25, 4971–4975 (2004)
P.P. Wang, C.H. Li, H.Y. Gong, X.R. Jiang, H.Q. Wang, K.X. Li, Effects of synthesis conditions on the morphology of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles produced by wet chemical process. Powder Technol. 203, 315–321 (2010)
L.Y. Huang, K.W. Xu, J. Lu, A study of the process and kinetics of electrochemical deposition and the hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite coatings. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 11, 667–673 (2000)
G.K. Lim, J. Wang, S.C. Ng, L.M. Gan, Nanosized hydroxyapatite powders from microemulsions and emulsions stabilized by a biodegradable surfactant. J. Mater. Chem. 9, 1635–1639 (1999)
I.R. Gibson, I. Rehman, S.M. Best, W. Bonfield, Characterization of the transformation from calcium-deficient apatite to beta-tricalcium phosphate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 11, 799–804 (2000)
S. Raynaud, E. Champion, D. Bernache-Assollant, P. Thomas, Calcium phosphate apatites with variable Ca/P atomic ratio I. Synthesis, characterisation and thermal stability of powders. Biomaterials 23, 1065–1072 (2002)
W.P.S.L. Wijesinghe, M.M.M.G.P.G. Mantilaka, E.V.A. Prernalal, H.M.T.U. Herath, S. Mahalingam, M. Edirisinghe, R.P.V.J. Rajapakse, R.M.G. Rajapakse, Facile synthesis of both needle-like and spherical hydroxyapatite nanoparticles: effect of synthetic temperature and calcination on morphology, crystallite size and crystallinity. Mat. Sci. Eng. C Mater. 42, 83–90 (2014)
M.C. Wang, W.J. Shih, I.M. Hung, H.T. Chen, M.H. Hon, H.H. Huang, Characterization of calcium phosphate apatite with variable Ca/P ratios sintered at low temperature. Ceram. Int. 41, 1223–1233 (2015)
N. Puvvada, P.K. Panigrahi, H. Kalita, K.R. Chakraborty, A. Pathak, Effect of temperature on morphology of triethanolamine-assisted synthesized hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 3, 203–209 (2013)
R. Kumar, K.H. Prakash, P. Cheang, K.A. Khor, Temperature driven morphological changes of chemically precipitated hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Langmuir 20, 5196–5200 (2004)
P. Moghimian, A. Najafi, S. Afshar, J. Javadpour, Effect of low temperature on formation mechanism of calcium phosphate nano powder via precipitation method. Adv. Powder Technol. 23, 744–751 (2012)
E.G. Nordström, K.H. Karlsson, Carbonate-doped hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1, 182–184 (1990)
S. Raynaud, E. Champion, D. Bernache-Assollant, Calcium phosphate apatites with variable Ca/P atomic ratio II. Calcination and sintering. Biomaterials 23, 1073–1080 (2002)
H. Monma, T. Kamiya, Preparation of hydroxyapatite by the hydrolysis of brushite. J. Mater. Sci. 22, 4247–4250 (1987)
E.I. Dorozhkina, S.V. Dorozhkin, Mechanism of the solid-state transformation of a calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite (CDHA) into biphasic calcium phosphate (BCP) at elevated temperatures. Chem. Mater. 14, 4267–4272 (2002)
K. Ishikawa, P. Ducheyne, S. Radin, Determination of the Ca/P ratio in calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite using X-ray-diffraction analysis. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 4, 165–168 (1993)
R.Z. LeGeros, S. Lin, R. Rohanizadeh, D. Mijares, J.P. LeGeros, Biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramics: preparation, properties and applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 14, 201–209 (2003)
S.R. Kim, B.M. Lee, Y.K. Park, Effect of pH on the synthesis of hydroxyapatite. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 28, 885–891 (1991)
A. Yasukawa, K. Kandori, T. Ishikawa, TPD-TG-MS study of carbonate calcium hydroxyapatite particles. Calcif. Tissue Int. 72, 243–250 (2003)
L. Sha, Y.Y. Liu, Q. Zhang, M. Hu, Y.S. Jiang, Microwave-assisted co-precipitation synthesis of high purity beta-tricalcium phosphate crystalline powders. Mater. Chem. Phys. 129, 1138–1141 (2011)
S. Lazic, S. Zec, N. Miljevic, S. Milonjic, The effect of temperature on the properties of hydroxyapatite precipitated from calcium hydroxide and phosphoric acid. Thermochim. Acta 374, 13–22 (2001)
E.M. Levin, Phase diagrams for ceramists (American Ceramic Society, Columbus, 1956)
I. Cacciotti, A. Bianco, High thermally stable Mg-substituted tricalcium phosphate via precipitation. Ceram. Int. 37, 127–137 (2011)
S. Bose, S. Tarafder, S.S. Banerjee, N.M. Davies, A. Bandyopadhyay, Understanding in vivo response and mechanical property variation in MgO, SrO and SiO2 doped β-TCP. Bone 48, 1282–1290 (2011)
H.-S. Ryu, H.-J. Youn, K.S. Hong, B.-S. Chang, C.-K. Lee, S.-S. Chung, An improvement in sintering property of b-tricalcium phosphate by addition of calcium pyrophosphate. Biomaterials 23, 909–914 (2002)
G. Vereecke, J. Lemaître, Calculation of the solubility diagrams in the system Ca(OH)2–H3PO4–KOH–HNO3–CO2–H2O. J. Cryst. Growth 104, 820–832 (1990)
Y.N. Zhu, X.H. Zhang, Y.D. Chen, Q.L. Xie, J.K. Lan, M.F. Qian, N. He, A comparative study on the dissolution and solubility of hydroxylapatite and fluorapatite at 25°C and 45°C. Chem. Geol. 268, 89–96 (2009)
L.M. Rodriguez-Lorenzo, M. Vallet-Regi, Controlled crystallization of calcium phosphate apatites. Chem. Mater. 12, 2460–2465 (2000)
S.G. Lee, H.Y. Ko, G.J. Lee, S.H. Choi, A study on the preparation and properties of hydroxyapatite bioceramics. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 26, 157–166 (1989)
M. Uota, H. Arakawa, N. Kitamura, T. Yoshimura, J. Tanaka, T. Kijima, Synthesis of high surface area hydroxyapatite nanoparticles by mixed surfactant-mediated approach. Langmuir 21, 4724–4728 (2005)
B. Szilagyi, N. Muntean, R. Barabas, O. Ponta, B.G. Lakatos, Reaction precipitation of amorphous calcium phosphate: population balance modelling and kinetics. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 93, 278–286 (2015)
N.S. Al-Qasas, S. Rohani, Synthesis of pure hydroxyapatite and the effect of synthesis conditions on its yield, crystallinity, morphology and mean particle size. Sep. Sci. Technol. 40, 3187–3224 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (Grant No. 2018R1D1A1B07050524).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, IH., Lee, JA., Lee, JH. et al. Effects of pH and reaction temperature on hydroxyapatite powders synthesized by precipitation. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 57, 56–64 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-019-00004-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-019-00004-0