Abstract
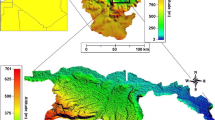
The Tafilalet plain in south-eastern Morocco is characterized by two main economic activities -agriculture and tourism- supported by water from the Quaternary aquifer. This aquifer is under increasing pressure due to low annual rainfall (71.5 mm/year) and intense agricultural activities. Consequently, identifying groundwater recharge mechanisms and assessing their quality is essential for efficient management and sustainable socioeconomic development. This study aims to define the hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics and assess groundwater quality and recharge mechanisms in this area. The methodology consists of an investigation coupled with multivariate statistical analysis and combining hydrogeological, hydrogeochemical, and isotopic hydrology data. Results show that the main water types in the study area are sodium chloride and calcium magnesium chloride facies. The groundwater is mainly degraded and highly mineralized. Water shows increasing concentrations of Cl− and Na+ due to the evapotranspiration of irrigation water. The isotopic data show average oxygen-18 and deuterium contents of δ18Oavg = − 6.7‰ and δ2Havg = − 48‰, respectively, with tritium activity varying over a wide range, between 3 and 6 TU, indicating recent recharge. The 18O and 2H values indicate that the Quaternary aquifer recharge occurred under present climatic conditions. This modern recharge, attested by thermonuclear tritium, is confirmed by radiocarbon (14C = 94.9 to 107.6 cfm). In the study area, the approximate soil and groundwater salinity maintenance in irrigated areas is closely related to the current hydrological conditions and the adopted irrigation mode. Therefore, water management measures such as using modern irrigation methods should be encouraged.



Data from HBAGZR








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal PK, Froehlich KF, Gat JR (2005) Isotopes in the water cycle. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Allison GB (1982) The relationship between 18O and deuterium in water in sand columns undergoing evaporation. J Hydrol 55(1–4):163–169
Amharref M (1991) Contribution à l'étude hydrogéologique de la vallée du Ziz (province d'Errachidia Sud-Est du Maroc): Incidences respectives de la sécheresse et du Barrage Hassan Addakhil sur les ressources à l'aval (Doctoral dissertation, Besançon)
Ammary B (2007) Etude Géochimique ET Isotopique des Principaux Aquifères du Bassin CRétacé d’Errachidia ET de la Plaine de Tafilalet. Ph.D. Thesis, Universit Mohammed V-Agdal, Rabat, Morocco, p 134
Bakalowicz M (1999) Connaissance et gestion des ressources en eaux souterraines dans les régions karstiques. SDAGE Rhône Mediterranee Corse
Barnes CJ, Allison GB (1988) Tracing of water movement in the unsaturated zone using stable isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen. J Hydrol 100(1–3):143–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(88)90184-9
Benmohammadi A, Benmohammadi L, Ballais JL, Riser J (2001) Analyse des inter-relations anthropiques et naturelles: leur impact sur la recrudescence des phénomènes d’ensablement et de désertification au sud-est du Maroc (vallée de Drâa et vallée de Ziz). Science Et Changements Planétaires/sécheresse 11(4):297–308
Blavoux B, Letolle R (1995) Contribution of isotopic techniques to the knowledge of groundwater. Géochroniques 54:12–15
Boudad L, Kabiri L (2002) Désertification et Crise de quelques Oasis dans les bassins versants de Ziz et Ghèris. Revue De Géographie Du Maroc 20(1):2
Bouhlassa S, Paré S (2006) Évapotranspiration de référence dans la région aride de Tafilalet au sud-est du Maroc. Afr J Environ Assess Manag 11:1–16
Clark ID, Fritz P (2013) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. CRC Press
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 133(3465):1702–1703. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.133.3465.1702
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16(4):436–468
Dao A, Kamagate B, Mariko A, Maiga HB, Tie AGB, Savane I (2014) Discrimination physico-chimique des réservoirs hydriques en milieu de socle: cas du bassin versant de kolondieba au sud du mali. Rev Ivoir Sci Technol 24:238–265
Dogramaci S, Skrzypek G, Dodson W, Grierson PF (2012) Stable isotope and hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in the semi-arid Hamersley Basin of subtropical northwest Australia. J Hydrol 475:281–293
Eisenlohr L, Király L, Bouzelboudjen M, Rossier Y (1997) Numerical simulation as a tool for checking the interpretation of karst spring hydrographs. J Hydrol 193(1–4):306–315
El Hmaidi A, Talhaoui A, Manssouri I et al (2022) Assessment of the physicochemical water quality of the Moulouya River, Morocco, using the SEQ-Eau index. Environ Monit Assess 194:37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09636-4
El Ouali A, El Hafyani M, Roubil A, Lahrach A, Essahlaoui A, Hamid FE, Muzirafuti A, Paraforos DS, Lanza S, Randazzo G (2021) Modeling and spatiotemporal mapping of water quality through remote sensing techniques : a case study of the Hassan Addakhil Dam. Appl Sci 11(19):9297. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199297
El Ouali A, Roubil A, Lahrach A, Mudry J, El Ghali T, Qurtobi M, El Hafyani M, Alitane A, El Hmaidi A, Essahlaoui A, Van Rompaey A (2022) Isotopic characterization of rainwater for the development of a local meteoric water line in an arid climate : the case of the Wadi Ziz watershed (South-Eastern Morocco). Water 14(5):779. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050779
Etcheverry D (2002) Valorisation des méthodes isotopiques pour les questions pratiques liées aux eaux souterraines. Isotopes de l’oxygène et de l’hydrogène. Federal Office for Water and Geology. Berne, Switzerland, FOWG Reports, Geological Series 2:1–70
Fetter CW (1988) Applied hydrogeology. Merrill Publishing Company, Columbus, Ohio
Fontes JC (1976) Les isotopes du milieu dans les eaux naturelles. La Houille Blanche 3–4:205–221
Fontes JC, Edmunds WM (1989) The use of environmental isotope techniques in arid zone hydrology: a critical review. UNESCO, Paris, p 75
Gascoyne M, Kotzer T (1995) Isotopic methods in hydrogeology and their application to the underground research laboratory, Manitoba. Chalk River Laboratories, A.E.C.L., Chalk River
Gastmans D, Chang HK, Hutcheon I (2010) Groundwater geochemical evolution in the northern portion of the guarani aquifer system (Brazil) and its relationship to diagenetic features. Appl Geochem 25(1):16–33
Hem JD (1972) Chemistry and occurence of cadmium and zinc in surface water and groundwater. Water Resour Res 8:661–679
IAEA (2010) Atlas of isotope hydrology. IAEA, Vienna
Janardhana Raju N, Shukla UK, Ram P (2011) Hydrogeochemistry for the assessment of groundwater quality in Varanasi: a fast-urbanizing center in Uttar Pradesh. India Environ Monit Assess 173(1):279–300
Kabiri L. (2001). Ressources en eau dans les oasis de Tafilalt, Ghèris et Ferkla. Séminaire international sur les petits barrages dans le pourtour méditerranéen, 28–30
Kannan N, Joseph S (2010) Quality of groundwater in the shallow aquifers of a paddy dominated agricultural river basin, Kerala, India. Int J Civil Environ Eng 2(3):160–178
Kohonen T (1995) Learning vector quantization. Self-organizing maps. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 175–189
Lgourna Z, Warner N, Bouchaou L, Boutaleb S, Tagma T, Hssaisoune M, Vengosh A (2014) Nitrate contamination of alluvial groundwater in the Ziz basin, southeastern Morocco. Moroccan J Chem 2(5):2–5
Lssar A, Gat J (1981) Environmental isotopes as a tool in hydrogeological research in an arid basin. Groundwater 19(5):490–494
Margat J (1961) Hydrogéologie de la plaine du Tafilalt (Maroc Pré-Saharien). La Houille Blanche 47(sup2):678–682. https://doi.org/10.1051/lhb/1961010
Nag SK, Das S (2017) Assessment of groundwater quality from Bankura I and II Blocks, Bankura District, West Bengal. India Appl Water Sci 7(6):2787–2802
Naik PK, Awasthi AK, Anand AVSS, Behera PN (2009) Hydrogeochemistry of the Koyna River basin. India Environ Earth Sci 59(3):613–629
Payne JA, Thomas WM, Cooke JE, English E (1988) Groundwater quality beneath the City of London-overview and long-term changes. Water Environ J 2(3):305–310
Plummer LN (2005) Dating of young groundwater. Isotopes in the water cycle. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 193–218
Prasanna MV, Chidambaram S, Hameed AS, Srinivasamoorthy K (2011) Hydrogeochemical analysis and evaluation of groundwater quality in the Gadilam river basin, Tamil Nadu. India J Earth Syst Sci 120(1):85–98
Rajmohan N, Elango L (2006) Hydrogeochemistry and its relation to groundwater level fluctuation in the Palar and Cheyyar river basins, southern India. Hydrol Processes 20(11):2415–2427
Roubil A, El Ouali A, Bülbül A, Lahrach A, Mudry J, Mamouch Y, Essahlaoui A, El Hmaidi A, El Ouali A (2022) Groundwater hydrochemical and isotopic evolution from high atlas jurassic limestones to errachidia cretaceous basin (Southeastern Morocco). Water 14(11):1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111747
Schoeller H (1959) Arid zone hydrology—recent developments. UNESCO, Paris
Schoeller H (1967) Conduite de l'étude hydrogéologique et climatologique des grottes descendantes. Spelunca Mem. 4:76–93
Tanji KK, Kielen NC (2002) Agricultural drainage water management in arid and semi-arid areas. FAO, Rome
WHO (2007) Health through safe drinking and basic sanitation. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland
Zhang X, Xu Z, Sun X, Dong W, Ballantine D (2013) Nitrate in shallow groundwater in typical agricultural and forest ecosystems in China, 2004–2010. J Environ Sci 25(5):1007–1014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
El Ouali, A., Roubil, A., Lahrach, A. et al. Assessment of groundwater quality and its recharge mechanisms using hydrogeochemical and isotopic data in the Tafilalet plain (south-eastern Morocco). Med. Geosc. Rev. 5, 1–14 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42990-023-00096-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42990-023-00096-1