Abstract
Tremor is an indicative symptom of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Healthcare professionals have clinically evaluated the tremor as part of the Unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale (UPDRS) which is inaccurate, subjective and unreliable. In this study, a novel approach to enhance the tremor severity classification is proposed. The proposed approach is a combination of signal processing and resampling techniques; over-sampling, under-sampling and a hybrid combination. Resampling techniques are integrated with well-known classifiers, such as artificial neural network based on multi-layer perceptron (ANN-MLP) and random forest (RF). Advanced metrics are calculated to evaluate the proposed approaches such as area under the curve (AUC), geometric mean (Gmean) and index of balanced accuracy (IBA). The results show that over-sampling techniques performed better than other resampling techniques, also hybrid techniques performed better than under-sampling techniques. The proposed approach improved tremor severity classification significantly and show that the best approach to classify tremor severity is the combination of ANN-MLP with Borderline SMOTE which has obtained 93.81% overall accuracy, 96% Gmean, 91% IBA and 99% AUC. Besides, it is found that different resampling techniques performed differently with different classifiers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common long-term chronic, progressive, neurodegenerative disease, affecting more than 10 million people worldwide. In the United Kingdom, two people are diagnosed every hour, and the estimated number of people diagnosed with PD in 2018 was around 145, 000 [1]. Extensive research has shown that Rest Tremor (RT) is the most common and easily recognised symptom of PD [2]. The RT describes unilateral involuntary, rhythmic and alternating movements in relaxed and supported limb mostly hands, and typically disappears with action, it might also appear in lips, chin, jaw and legs [3]. The RT presents in 70–\(90\%\) of PD patients, and it occurs at a frequency between 4 and 6 Hz [2]. In addition to RT, Kinetic Tremor (KT) and Postural Tremor (PT), considered as action tremor, could also occur [4]. The KT is a type of tremor present during voluntary hand movements such as touching the tip of the nose or writing. PT occurs when a person maintains a position against gravity, such as stretching arms. The PT tremor occurs at a frequency between 6 and 9 Hz while KT occurs at a frequency between 9 and 12 Hz [4].
Tremor severity often indicates PD progress and severity. It can also be used to evaluate treatment efficiency. Currently, Parkinson’s tremor severity is scored based on the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) from 0 to 4 with 0: normal, 1: slight, 2: mild, 3: moderate, and 4: severe [5]. The UPDRS is clinically based scale that the clinician assigns numerical scores based on qualitative observations of the patient in various postures and are often insensitive and subjective. The assessment depends on the examiners’ skills and knowledge, and it is various from one examiner to another so examiners’ disagreement on assessment and scores [6,7,8]. There is evidence showing that the UPDRS has high inter and intra-rater variability [9,10,11]. Thus, a patient’s tremor may be assigned UPDRS score by one examiner and in the next appointment assessed by a different examiner and assigned a higher score. In this situation, it is difficult to interpret these two different scores, whether symptoms worsen or due to subjectivity.
The process associated with the UPDRS assessment is also time-consuming. It requires a lengthy administrative procedure, approximately 30 min, besides it needs specialised official training to improve the coherence of data acquisition and interpretation, these make it unhandy for routine clinical practice [5, 12]. Another time burden is that many elements in the UPDRS assessment need to be completed by patients, so additional time is required besides the time required to review these elements by the examiner. This time burden limits the use of the UPDRS in routine clinical practice. Therefore, the UPDRS scale is mainly used in clinical research.
The limitations mentioned above might lead to poor management of PD and wasteful use of resources besides that they are unwieldy in routine clinical practice. Many studies have tried to classify tremor severity scores using Machine Learning (ML) algorithms with signal processing techniques [13]. A well-presented challenge to implement ML algorithms in medical applications is the issue of imbalanced data distributions or the lack of density of a class or some classes in the training data, which cause a false-negative [14]. This miss-classification can lead to wrong assessment, consequently affect treatment. Several approaches have been suggested to address the imbalanced dataset issue, and they can be divided into three major groups [15] (a) data resampling, (b) algorithmic modification, and (c) cost-sensitive learning. Data resampling techniques include over-sampling, under-sampling, and hybrid approach (over-sampling and under-sampling). Resampling techniques were proven as a perfect solution for handling imbalanced datasets in different applications [16]. However, it was established that different resampling techniques work differently with different datasets and different ML algorithms [17,18,19].
A thorough review of the relevant literature indicates that this is the first study to explore different resampling techniques with two classifiers, namely Random forest (RF) and artificial neural network based on multi-layer perceptron (ANN-MLP) to enhance tremor severity estimation of highly imbalanced tremor severity dataset. In addition, this study offers important insights into advanced metrics and how standard metrics sometimes mislead classification results. Moreover, this study was able to enhance tremor severity detection with very high accuracy without neglecting minority classes.
The remainder of this paper is organised as follows: In Section “Related Work”, a review of the related literature is presented. Section Methodology explains the proposed methodology, including dataset description, signal analysis, features extraction, applying different resampling techniques with classifiers, evaluation.followed by the results presented in Section “Results and Discussions”. Section Conclusion and Future Work” concludes the paper and gives a direction for future work.
Related Work
Parkinson’s disease severity estimation could bridge the gap between clinical scales currently used by clinicians and objective evaluation methods in such a way that objective measurements align with clinical score systems such as the UPDRS. Therefore, several studies have explored different sensors with different methods to estimate tremor severity, including soft computing techniques and statistical analysis. A few of these studies are reviewed below.
Niazmand et al. [20] have used an accelerometer to estimate tremor severity utilising data collected from 10 PD patients and 2 healthy control subjects. The Data were collected from integrated pullover triaxial accelerometers while subject performing rest and posture UPDRS motor tasks. The movement frequency calculated using peak detection technique and tremor assessment based on frequencies, as shown in Table 1. The correlation between the measurements from accelerometers and UPDRS scores calculated and achieved \(71\%\) sensitivity of detecting tremor and \(89\%\) sensitivity of detecting posture tremor. However, the study suffered from the fact that the data collected come from pullover fits exactly to the patients achieved good results. At the same time, it is lower for the loose-fitting pullover, and this limitation can be a barrier from using this pullover for PD assessment in routine and continuous assessment since it might be not comfortable for patients and it is difficult to design a pullover to fit all patients. On the other hand, using a fit pullover and might increase the tense of muscles, particularly in posture tremor, which can change accelerometer position can change depending on executed movements. Also, this study is limited by the lack of information about patients’ UPDRS severities and might be biased towards some severities, and this could affect performance measurements.
Rigas et al. [21] conducted a study to estimate tremor severity using a set of wearable accelerometers on arms and rest of subjects. This study involved 10 PD patients with tremor range from 0 to 3 according to the UPDRS score, 8 PD patients without tremor and 5 healthy subjects. Data were collected from subjects while there were performing Activities of Daily Living (ADLs). The collected data was processed through low-pass and band-pass filters with cut-off frequencies of 3 Hz and 3–12 Hz, respectively. Set of features (dominant frequency, the energy of dominant frequency, high and low frequencies energy, spectrum entropy and mechanical energy) extracted from filtered signals. For severity classification, a Hidden Markov Models (HMM) employed with LOOCV. They have achieved \(87\%\) overall accuracy with \(91\%\) sensitivity and \(94\%\) specificity for tremor 0, \(87\%\) sensitivity \(82\%\) specificity for tremor 1, \(69\%\) sensitivity and \(79\%\) specificity for tremor 2, \(91\%\) sensitivity and \(83\%\) specificity for tremor 3. However, this study suffered from lack of severe severity (tremor severity 4) in collected data; thus, it cannot be generalised and used to assess all patients, particularly PD patients with severity 4 tremors, besides the relatively low sensitivity of \(69\%\) and specificity \(79\%\) for classification severity 2 tremor.
Bazgir et al. [22] used smartphone built-in triaxial accelerometer to estimate tremor severity for 52 PD patients. Data acquired from a triaxial accelerometer attached to patients’ hands. Set of features were extracted including power spectral density (PSD), median frequency, dispersion frequency and the fundamental tremor frequency. Then tremor severity was estimated using artificial neural network (ANN) classifier. The results were significant and achieved \(91\%\) accuracy. However, no other performance metrics reported such as error rate, sensitivity, specificity, precision and F-score which are very important to evaluate classification models, especially in medicine classification problems, since accuracy neglects the difference between types of errors [23]. In a recent follow-up study, Bazgir et al. [24] tried to improve the accuracy utilising Sequential Forward Selection (SFS) approach for features selection with the same approaches for signal processing and features extraction. In this study, \(100\%\) accuracy achieved with Naïve Bayesian classifier. However, like the previous study, no other performance metrics such as sensitivity and specificity have been reported.
Authors in [25] collected triaxial accelerometer data from 19 PD patients using a smartwatch while they are performing five motor tasks including sitting quietly, folding towels, drawing, hand rotation and walking. A wavelet features extraction technique was used to process the acquired signal and extract relative energy and mean relative energy for each triaxial accelerometer axis. Extracted features were used to predict tremor severity into three tremor levels 0, 1 and 2 where 2 represents tremor severities 2, 3 and 4 using support vector machine (SVM) classifier, the prediction made by summing all axis prediction since the tremor is often in only one axis. The model was evaluated using LOOCV and achieved \(78.91\%\) overall accuracy, \(67\%\) average precision and \(79\%\) average recall. However, severity 2 prediction precision was \(28\%\), and it is very low in comparisons with severity 1 and 3 as they achieved \(98\%\) and \(75\%\) respectively. Moreover, a major problem with this experiment was that severities 2, 3 and 4 combined into one score 2, which does not reflect the actual severity of the tremor and it might not be helpful for neurologists to assess the tremor and does not identify tremor development, especially in advanced stages.
Based on an extensive review of the literature, only one study was identified that utilised over-sampling technique to identify PD patients from healthy people using speech signals [26]. Authors combined RF classifier with over-sampling technique and obtained \(94.89\%\) accuracy. However, their study did not classify tremor severity.
A common limitation in most of the previous studies was that the authors did not take into consideration all tremor levels and imbalanced classes distribution among collected data. Also, some of these studies only used data collected while subject performing specific tasks which do not necessarily include ADLs. Some studies did not report advanced performance metrics such as sensitivity, specificity, F-score, AUC and IBA, which are very important to evaluate classification models.
Methodology
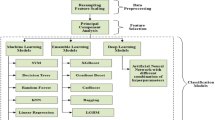
Figure 1 illustrates the proposed framework to classify imbalanced tremor severity dataset using resampling techniques. In the first step, raw accelerometer signal prepossessed to eliminate sensor orientation dependency, non-tremor data and artefacts. Set of tremor severity features extracted from the prepossessed signal in the second step. In the third step, data is split into training and test subsets and training data resampled to avoid classifiers bias. Finally, training and test data are passed into a classifier to estimate tremor severity and the results evaluated for adoption in the fourth step. Each step is described in details in the subsequent sections.
Signal Processing
In order to extract meaningful features from accelerometer data, some preprocessing was performed to eliminate non-tremor data or artefacts. The vector magnitude of three orthogonal acceleration, namely \(A_X\), \(A_Y\), and \(A_Z\) has been calculated to avoid dependency on sensor orientation and to avoid processing signal in three dimensions. Also, since the work focus on the severity of any tremor type, and in order to remove low and high-frequency bands and retain tremors bands from the data as suggested by earlier work [4], a band-pass Butterworth filters with cut-off frequencies 3–6 Hz for RT and 6–9 Hz for PT and 9–12 Hz for KT are applied.
The filtered signals were split into 4s windows that can be labelled and used as inputs. Fixed-length sliding windows with \(50\%\) overlap was utilised, which has shown in the literature to be effective in activity recognition [27]. The window time series represents as:
where \(a_t\) is the acceleration at time t and \(w_l\) is the window length (number of samples).
Guided by previous work, a set of features were extracted from each window in time and frequency domains. A list of the selected features and their descriptions are presented in Appendix A (Table 8). The features were extracted from three filtered signals frequencies, 3–6 Hz for RT, 6–9 Hz for PT, and 9–12 Hz for KT, to form a 102 features vector. Frequency domain features were calculated after transforming the raw signal from the time domain to the frequency domain using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) according to Expression 2 provided below.
where F(k) complex sequence that has the same dimensions as the input sequence \({(a_t)}_{t=0}^{w_l}\) and \(e^\frac{{ -j2\pi }}{W_l}\) is a primitive \(N\text{th}\) root of unity.
The features were carefully selected to provide detailed and discriminatory information of signal characteristics and that are highly correlated with tremor severity, such as distribution, autocorrelation, central tendency, degree of dispersion, shape of the data, stationarity, entropy measures and dissimilarity.
Tremor severity can be distinguished by amplitude, as the tremor amplitude showed a high correlation to the UPDRS score [28], as the amplitude increases when severity increases. Similarly, a previous study showed that tremor severity is highly correlated with frequency sub-bands [20], as every tremor severity or score appears within a specific frequency range, as shown in Table 1. Therefore, features such as mean, max, energy, number of peaks, number of values above and below mean are chosen besides median in case the values are not normally distributed. In addition, these features showed high correlation with tremor severity classification in previous studies [29,30,31]. In order to measure signal dispersion, the standard deviation is selected since it is found to be an effective measure to quantify tremor severity [32, 33].
Skewness and kurtosis are chosen to measure data distribution. Kurtosis has been used in previous studies to detect tremor because tremor signal are more spiky (high Kurtosis) than non-tremor signals [30, 34, 35]. Consequently, high severity tremor is almost certainly has high kurtosis value and vice versa. On the other hand, skewness measures the lack of symmetry, and it has been used to measure random movements to asses medication response, as while patients are on medication the tremor will decrease, thereby tremor signal skewness decrease [30]. Therefore, skewness is expected to decrease with less severe tremor and increase with high severe tremor. Spectral Centroid Amplitude (SCA), which is the weighted power distribution, and maximum weighted PSD are other features related to spectral energy distribution [36]. As every frequency sub-band represents a tremor severity [20], thus the maximum weighted power and the weighted power distribution can quantify tremor severity.
The PD tremor is a rhythmical movement, hence sample entropy and autocorrelation have been chosen to measure regularity and complexity in time series data, as tremor’s sample entropy and autocorrelation are significantly lower when compared to non-tremor movements which has been established by previous work [37,38,39]. Another complexity measures have been selected are the Complexity-Invariant Distance (CID) [40, 41] and the Sum of Absolute Differences (SAD) [42]. SAD and CID measures time series complexity differently, as the more complex time series has more peaks and valleys, which increase the difference between two consecutive values in the window. Consequently, the tremor signal is more complex because tremor frequency and amplitude are higher than normal movements which increase the peaks and valleys in the signal. As a result, complexity is correlated with tremor severity.
Previous research has established that tremor intensity identifies tremor severity [4]. Therefore, tremor intensity at various frequencies can be quantified through PSD, and since tremor severity correlated with frequency ranges or bandwidth spread [20], thus three features are chosen; fundamental frequency, median frequency, and frequency dispersion. The fundamental frequency which has the highest power among all frequencies in power the spectrum. The median frequency divides PSD into two parts equally. The frequency dispersion is the width of the frequency band which contains \(68\%\) of the PSD. In addition, guided by previous work, the difference between the fundamental frequency and the median frequency was extracted as an additional feature since tremor fundamental frequency could be different between patients [22].
Resampling Techniques
This section presents a brief about resampling techniques employed in this study. Resampling methods can be categorised into three groups: over-sampling, under-sampling, and hybrid (Combination of over- and under-sampling).
Over-Sampling Techniques
Over-sampling techniques are consists of adding samples to the minority classes, in this study, three over-sampling techniques are explored as described below:
-
(a)
Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE) [43] synthetically creates samples in the minority class instead of replacing original samples, which lead to an over-fitting issue. The SMOTE create samples based on similarities in feature space along the line segments joining the minority instance and its ‘k’ minority class nearest neighbours in feature space.
-
(b)
Adaptive Synthetic Sampling Approach (ADASYN) [44] generate samples in the minority class according to their weighted distributions using K-nearest neighbour (K-NN). The ADASYN assign higher weights for instances that are difficult to classify using K-nn classifier, where more instances generated for higher weights classes.
-
(c)
Borderline SMOTE [45] identifies decision boundary (borderline) minority samples and then SMOTE algorithm is applied to generate synthetic samples along decision boundary of minority and majority classes.
Under-Sampling Techniques
Under-sampling techniques work by removing samples from the majority classes. In this study, five under-sampling techniques are examined as described below:
-
(a)
Condensed Nearest Neighbour (CNN) [46] was originally designed to reduce the memory used by K-nearest neighbours algorithm. It works by iterating over majority classes and selecting subset samples that are correctly classified by 1-nearest neighbour algorithm, thus including only relevant samples and eliminating insignificant samples from majority classes.
-
(b)
Tomek-links [47] is an enhancement of CNN technique, as the CNN initially chose samples randomly, but the Tomek-links firstly finds Tomek link samples, which are pairs samples belong to different classes and are each other’s 1-nearest neighbours. Then removes Tomek’s link samples belong to the majority classes or alternatively both. In this study, the only majority Tomek’s link classes are removed to retain minority classes and increase distances between classes by removing majority classes near the decision boundary.
-
(c)
AllKNN [48] is an under-sampling technique based on Edited nearest neighbours (ENN), [49], which is an under-sampling technique applies K-nearest neighbour (K-NN) classifier on majority class and removes samples that are misclassified i.e. removes samples whose class differs from a majority of its k-nearest neighbours. So, AllKNN technique removes all samples that are adjacent to the minority class, in order to make classes more separable. It works by removing samples from the majority class that has at least 1-nearest neighbour in the minority class.
-
(d)
Instance Hardness Threshold (IHT) [50] is a technique based on removing samples with high hardness value. The hardness value indicates the probability of being misclassified. This approach removes majority class samples that classified with low probabilities (overlap the minority classes samples).
-
(e)
NearMiss [51] technique based on the average distance of majority classes samples to minority classes samples. There are 3 versions of NearMiss technique: NearMiss-1 selects the majority class samples with the smallest average distance to three closest minority class samples, NearMiss-2 selects majority class samples with the smallest average distance to three farthest minority samples, NearMiss-3 selects majority class samples with the smallest distance to each minority class sample. In this study, NearMiss-1 is used.
Hybrid Resampling (Combination of Over- and Under-sampling)
The last group has been examined is the hybrid approach that combines over- and under-sampling techniques. This approach basically cleans the noise that has been generated from over-sampling techniques by removing majority classes samples that overlaps minority classes samples. In this study, two hybrid techniques are examined as described below:
-
(a)
Synthetic Minority Over-sampling technique combined with Tomek link (SMOTETomek) [52] works by increasing the number of minority class samples by generating synthetic samples as discussed in Section “Over-Sampling Techniques”, and, subsequently, Tomek link under-sampling technique is applied to the original and new synthetic samples as discussed in Section“ Under-Sampling Techniques”.
-
(b)
Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique combined with Edited Nearest Neighbour (SMOTEENN) [53] is the second hybrid approach SMOTEENN starts with SMOTE which has been discussed in Section “Over-Sampling Techniques”, followed by Edited Nearest Neighbour (ENN) which has bee discussed in “Under-Sampling Techniques”. In this study, 3-nearest neighbour algorithm with ENN are applied.
Classifiers
Two classifiers are considered for classification; Artificial Neural Network based on Multi-Layer Perceptron (ANN-MLP) [54], and Random Forest (RF) [55]. These classifiers were adopted based on previous studies that achieved high performance in the classification of different types of balanced and imbalanced datasets [56,57,58].
The ANN-MLP is a feed-forward ANN consists of multiple layers (input layer, one or more hidden layers, and output layer). The ANN-MLP layers are fully connected, so each node in one layer is connected to every node in the following layer with different weights. ANN-MLP training implemented through backpropagation [59] by adjusting the connection weights to minimise mean squared error between neural network predictions and the actual classes.
The RF classifier is an ensemble learning algorithm [55] composed from a set of decision trees to overcome the overfitting problem of decision trees. The decision trees randomly selected from the original training dataset using the bootstrap method [60]. The remaining training data used to estimate the error and features importance to decrease the correlation between constructed trees in the forest, hence, decrease the final model variance. The final classification based on a majority vote of the decision trees in the forest.
The results were evaluated using different traditional metrics including accuracy, precision, sensitivity,specificity and F1-score [61]. In addition, advanced metrics were used such as geometric mean (Gmean) [62], Index of Balanced Accuracy (IBA) [63], and Area Under the Curve(AUC) [64], which will be explained in Section “Performance Metrics”.
Experimentation
The experimental dataset used in this study are introduced in Section “Dataset” showing the imbalanced class distribution problem. Then the classifiers architecture is described in Section “Classifiers Architecture”, and the performance metrics used to evaluate proposed models are illustrated in Section “Performance Metrics”.
Dataset
Tremor datasetFootnote 1 was taken from Levodopa response trial wearable data from Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s research (MJFF) [65] . The data are collected from a wearable sensor in both laboratory and home environments using different devices; a Pebble Smartwatch, GENEActiv accelerometer and a Samsung Galaxy Mini smartphone accelerometer. Triaxial accelerometer data were collected from 30 subjects fitted with either 3 or 8 sensors for four days. On the first day of data collection, participants came to the laboratory on their regular medication regimen and performed set ADLs and items of motor examination of the movement disorder society-sponsored revision of the unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale (MDS-UPDRS) [5] which is used to assess motor symptoms. The list of tasks performed includes; standing, walking straight, walking while counting, walking upstairs, walking downstairs, walking through a narrow passage, finger to the nose (left and right hands), repeated arm movement (left and right hands), sit to stand, drawing on a paper, writing on a paper, typing on a computer keyboard, assembling nuts and bolts, taking a glass of water and drinking, organising sheets in a folder, folding a towel, and sitting. For each task, symptom severity scores (rated 0–4) were provided by a clinician. On the second and third days, accelerometers data were collected while participants at home and performing their usual activities. On the fourth day, the same procedures that were performed on the first day were performed once again, but the participants were off medication for 12 h. In this study, only GENEActiv accelerometer tremor data that were collected in the first day will be utilised.
Table 2 shows classes (severities) distribution of 32,414 instances (windows) segmented from collected data. It is clear how data distribution being skewed towards less severe tremor and this bias can cause significant changes in classification output, in this situation the classifier is more sensitive to identifying the majority classes but less sensitive to identifying the minority classes if they are eliminated. Thus, different resampling techniques are described in Section “Resampling Techniques” were utilised to eliminate imbalanced class distribution effect.
Classifiers Architecture
In this study, the ANN-MLP was built using Keras [66] with TensorFlow [67] as the back-end. The neural network contains 102 nodes in the input layer (features vector shape), 200, 180, 180, 100 nodes in each of the four hidden layers respectively, and five nodes in the output layer corresponds to the five classes (severities). Each hidden layer applied the rectified linear unit (ReLU) [68] activation function since it is computationally efficient and tend to show better convergence performance than sigmoid function [69]. The output layer applied softmax activation function [70] to predict classes probabilities.
The RF classifier was built with 100 trees based on the suggestion of Oshiro et al. [71] that number of trees should be between 64 and 128 trees. Gini impurity was selected as decision trees split criteria because it tends to split a node into one small pure node and one large impure node [72], and it can be computationally more efficient than entropy by avoiding \(\log\) computation.
To avoid over-fitting with ANN-MLP, \(20\%\) of the data was kept and used as validation data to monitor model performance and top the training when performance degrades which is a form of regularisation that guides to stop iterations before the model begins to overfit. The RF is an ensemble machine learning algorithm that uses Bagging or Bootstrap Aggregation by default which is a resampling technique that involves random sampling of a dataset with replacement, the random sampling is selected via the Out-of-Bag method which is similar to validation data where each tree in the forest is tested on \(36.8\%\) samples that are not used in building that tree.
Performance Metrics
The most frequently used metrics for evaluating the performance of classification algorithms are accuracy, precision, sensitivity (True Positive Rate), specificity (True Negative Rate) [61]. However, these metrics are illusory and insufficient to assess classifiers in an imbalanced classification problem, since they are sensitive to data distribution [73]. For example, a classifier that predicts most majority classes samples has high accuracy, but it is totally useless in detecting minority classes samples. Sensitivity and precision do not take into account true negatives, which can cause issues, especially in the medical diagnosis field where misclassified true negative can lead to unnecessary and expensive treatment. Hence, other metrics like F1-score [61] and geometric mean (Gmean) [62] are widely used to evaluate classifiers to balance between sensitivity and precision, as the ultimate goal of classifiers to improve sensitivity with impacting precision [14]. Gmean and F1-score are excellent and accurate metrics because they are less influenced by the majority classes in the imbalanced data [74]. However, Even Gmean and F1-score minimise the influence of imbalanced distribution, but they do not take into account the true negatives and classes contribution to overall performance [63]. Hence, in this study, advanced metrics are included in addition to these metrics, such as index of balanced accuracy (IBA) [63] and Area Under the Curve (AUC) [64].
where TP, FP, TN, FN, TPR, TNR, and \(\alpha\), refer respectively to, true positive, false positive, true negative, false negative, true positive rate, true negative rate, and weighting factor.
The most appropriate metrics to evaluate imbalanced data are AUC and IBA. There are many advantages of using AUC to evaluate classifiers, particularly in medical fields [75,76,77]. AUC is independent of prevalence, and it can be used to compare comparison multiple classifiers and to compare classifier performance with different classes.
IBA is a performance metric that takes into consideration the contribution of each class to the overall performances so that high IBA obtained when the accuracy of all classes are high and balanced. The IBA evaluates the relationship between TPR and TNR, which represents classes distribution. IBA can take any value between 0 and 1, and the best performance achieved when TPR = TNR = 1 with \(\alpha = 1\), then IBA = 1.
Results and Discussions
The section is presented in four parts. The first part will discuss results of over-sampling techniques. The second part presents the results of under-sampling techniques. The third part presents results of hybrid techniques. Finally, the best results obtained from each resampling techniques are compared and determining the best resampling technique and the best classifier with PD tremor dataset. In addition the results without resampling technique are presented as a baseline in order to evaluate resampling technique performance.
Over-Sampling Results
Table 3 shows the performance of two classifiers RF and ANN-MLP, on PD tremor severity dataset resampled using three over-sampling techniques, SMOTE, ADASYN and Bordline SMOTE. Overall, all the used over-sampling techniques improved classifiers performance significantly. Also, it can be observed that ANN-MLP classifier performed better than RF classifier with over-sampling, while the RF classifier achieved better results than ANN-MLP without over-sampling. The best results achieved using ANN-MLP classifier combined with Borderline, with \(95.04\%\) overall accuracy, \(96\%\) Gmean, \(93\%\) IBA and \(99\%\) AUC. However, The AUC scores of both classifiers with all over-sampling techniques were \(99\%\). Hence, it is important to evaluate classifiers with different metric such as IBA, which shows slightly different performance between classifiers with different over-sampling techniques which support the discussion about imbalanced datasets performance metrics in Section “Performance Metrics”.
The best performance is achieved using RF classifier with ADASYN technique and obtained \(92.58\%\) overall accuracy, \(95\%\) Gmean, \(91\%\) IBA and \(99\%\) AUC, while the worst performance of RF is using Borderline with \(91.54\%\) overall accuracy, \(94\%\) Gmean, \(89\%\) IBA and \(99\%\) AUC. On the other hand, ANN-MLP achieved best performance using Borderline technique and the worst with SMOTE. Both classifiers did not obtain the best performance with SMOTE, but it is still better than applying classifiers without oversampling.
Interestingly, the worst performance among over-sampling techniques obtained using RF classifier with Borderline technique, while Borderline achieved the highest performance with ANN-MLP. This results shows that over-sampling techniques performance vary among classifiers, hence no assumption can be made about best over-sampling technique, because every dataset, classifier and oversampling technique has it is own characteristics, and different combinations could obtain different results.
Figure 2 shows the confusion matrices for ANN-MLP and RF classifiers without resampling and with best oversampling techniques. It is clear from confusion matrices how oversampling techniques improved the prediction of all classes without any bias towards majority classes. The associated ROC’s for the same results are shown in Fig. 3.
Under-Sampling Results
Table 4 shows the performance of two classifiers RF and ANN-MLP, on PD tremor severity dataset resampled using five under-sampling techniques, TomekLinks, CNN, AllKNN, IHT and NearMiss. It is clear that overall classifiers performance with under-sampling techniques is significantly worse than using over-sampling techniques. However, some under-sampling techniques improved classifiers performance. Both classifiers (ANN-MLP and RF) achieved best performance with IHT under-sampling technique, but RF classifier achieved better results with \(86.11\%\) overall accuracy, \(91.00\%\) Gmean, \(82.00\%\) IBA, and \(96.00\%\) AUC. Even though ANN-MLP achieved \(85.66\%\) accuracy with ALLKNN, it is not the best undersampling technique since it obtained only \(13\%\) IBA which indicates that some classes are not predicted correctly, also it indicates that the highest overall accuracy does not necessarily mean the classifier performed very well. The worst performance of both classifiers is with the CNN under-sampling technique and did not improve most metrics. On the contrary, it impaired the results.
What is striking about the results in Table 4 is that most important metrics such as Gmean and IBA are very low and declined dramatically with some under-sampling techniques, despite that other metrics are improved. For example, when ALLKNN technique is applied with both classifiers the accuracy, precision and sensitivity improved significantly, while the IBA and Gmean declined. The IBA declined from 26 to \(13\%\) with ANN-MLP and from 11 to \(1\%\) with RF, Gmean declined from 50 to \(34\%\) with ANN-MLP and from 32 to \(9\%\) with RF. These results indicates that depending on standard metrics is not sufficient and appropriate for multi-class imbalanced dataset classification.
Similar to over-sampling techniques, some under-sampling techniques improved the performance of one classifier and deteriorate the second. For example, NearMiss improved RF classifier performance but deteriorate ANN-MLP performance, which support the presented argument that resampling techniques does not perform similarly with different classifiers with different datasets.
Figure 4 shows the confusion matrices of ANN-MLP and RF classifiers without resampling and with best undersampling techniques. Even though, both classifiers did not achieve very high results, similar to oversampling techniques, the results are improved and the bias towards majority classes has been reduced. The associated ROC’s for the same results are shown in Fig. 5.
Hybrid Results
Table 5 shows the performance of two classifiers RF and ANN-MLP, on resampled PD tremor severity dataset using two hybrid techniques SMOTETomek and SMOTEENN. In contrast to under-sampling techniques, both hybrid techniques improved classifiers performance significantly. But the SMOTEENN performance with both classifiers better than SMOTETomek. However, SOMTEENN obtained the best results with RF classifier with \(92.61\%\) overall accuracy, \(95\%\) Gmean, \(91\%\) IBA and \(99\%\) AUC.
Figures 6 and 7 presents the confusion matrices and ROC’s of ANN-MLP and RF classifiers without resampling and with best hybrid resampling techniques. Similar to oversampling and undersampling techniques, the results are improved and the bias towards majority classes has been reduced.
Performance Comparison
Table 6 shows best results obtained from the two classifiers ANN-MLP and RF in combination with all resampling techniques. Among these results the best performance obtained from ANN-MLP classifier with Borderline and achieved \(93.81\%\) overall accuracy, \(96\%\) Gmean, \(91\%\) IBA and \(99\%\) AUC. While RF achieved best performance with ADASYN and SMOTEENN for all metrics, except the overall accuracy with very low difference \((0.03\%)\). However, both classifier did not improved significantly with IHT in comparison with other resampling techniques, despite that RF performance was higher.
As mentioned in Section “Performance Metrics”, the most important metrics are IBA and AUC, therefore the combinations of ANN-MLP with Borderline, RF with ADASYN and RF with SMOTEENN obtained same results with \(91\%\) IBA and \(99\%\) AUC, and overall performance of these combinations achieved best results with slight difference in some metrics. The worst improvements obtained among the best results is the combination of ANN-MLP with IHT then RF with IHT. So, the order of best combination from high to low is ANN-MLP with Borderline, RF with SMOTEENN, RF with ADASYN and finally ANN-MLP with SMOTEENN, as shown in Fig. 8. It can thus be suggested that the best approaches to estimate tremor severity are over-sampling and hybrid approaches, while the worst is under-sampling approaches. This hypothesis is supported by the findings in Sections “Over-Sampling Results”, “Under-Sampling Results” and “Hybrid Results”.
Table 7 shows summary results and comparison with the state-of-the-art. The measured tremor, the number of patients, the used sensors, the approach, the metrics and the measured severities are shown in the table. Although high classification performance was obtained in the literature for tremor severity estimation, most of these studies did not report advanced performance metrics such as Gmean and IBA which are very important to evaluate classification models. Also, many studies did not take into consideration all types and levels of tremor. In addition, none of these studies considered classes imbalanced issues.
Conclusion and Future Work
In this study, a set of resampling techniques are investigated to improve Parkinson’s Disease tremor severity classification. It can be concluded that that the proposed algorithms can improve classification process. classifiers with advanced metrics, such as AUC, Gmean and IBA that are not influenced by data distribution are evaluated. The results shows that ANN-MLP with Borderline SMOTE is the best classification approach to identify tremor severity. Also, the results shows that over-sampling techniques performed better than under-sampling techniques and hybrid techniques. The results shows that different resampling techniques achieved different results with different classifiers.
We acknowledge that this study has a number of limitations. First, the sample size is small, and it’s possible that it doesn’t represent the entire PD population. Second, the data was gathered in a single environment. As a result, if the environment is changed, the outcomes may vary. Third, the proposed method should be tested on a variety of datasets.
For future studies, it is suggested to apply different resampling techniques with more classifiers, also to examine resampling techniques influence on individual classes classification instead of overall performance. Extend the work to include rest of collected data to evaluate proposed algorithms with larger dataset.
Notes
It is available at https://www.michaeljfox.org/data-sets.
Abbreviations
- UPDRS:
-
Unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale
- ANN-MLP:
-
Artificial neural network based on multi-layer perceptron
- RF:
-
Random forest
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- Gmean:
-
Geometric mean
- IBA:
-
Index of balanced accuracy
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- RT:
-
Rest tremor
- KT:
-
Kinetic tremor
- PT:
-
Postural tremor
- RMS:
-
Root mean square
- LOOCV:
-
Leave one outcross-validation
- HMM:
-
Hidden Markov models
- EMG:
-
Electromyography
- PSD:
-
Power spectral density
- SFS :
-
Sequential forward selection
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
- IMU:
-
Inertial measurement unit
- ADLs:
-
Activities of daily living
- MJFF:
-
Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s research
- MDS-UPDRS:
-
Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale
- FFT:
-
Fast Fourier transform
- CID:
-
Complexity-invariant distance
- STD:
-
Standard deviation
- SAD:
-
Sum of absolute differences
- SCA:
-
Spectral centroid amplitude
- SMOTE::
-
Synthetic minority over-sampling technique
- ADASYN:
-
Adaptive synthetic sampling approach
- K-nn:
-
K-nearest neighbour
- CNN:
-
Condensed nearest neighbour
- ENN:
-
Edited nearest neighbours
- IHT:
-
Instance hardness threshold
- TP:
-
True positive
- FP:
-
False positive
- TN:
-
True negative
- FN:
-
False negative
- TPR:
-
True positive rate
- TNR:
-
True negative rate
References
Parkinson’s UK, Facts and figures about Parkinson’s for journalists. https://www.parkinsons.org.uk/about-us/media-and-press-office. Accessed 16 Sep 2020.
Weintraub D, Comella CL, Horn S. Parkinson’s disease-part 1: pathophysiology, symptoms, burden, diagnosis, and assessment. Am J Manag Care. 2008;14(2 Suppl):S40-8.
Shahed J, Jankovic J. Motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2007;83:329–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0072-9752(07)83013-2.
Pierleoni P, Palma L, Belli A, Pernini L. A real-time system to aid clinical classification and quantification of tremor in Parkinson’s disease. In: IEEE-EMBS International Conference on biomedical and health informatics (BHI), IEEE, 2014; p. 113–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/BHI.2014.6864317.
Goetz CG, Tilley BC, Shaftman SR, Stebbins GT, Fahn S, Martinez-Martin P, Poewe W, Sampaio C, Stern MB, Dodel R, et al. Movement disorder society-sponsored revision of the unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale (mds-updrs): scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov Disord. 2008;23(15):2129–70. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22340.
Bot BM, Suver C, Neto EC, Kellen M, Klein A, Bare C, Doerr M, Pratap A, Wilbanks J, Dorsey ER, et al. The mpower study, Parkinson disease mobile data collected using researchkit. Sci data. 2016;3(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.11.
Ossig C, Antonini A, Buhmann C, Classen J, Csoti I, Falkenburger B, Schwarz M, Winkler J, Storch A. Wearable sensor-based objective assessment of motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm. 2016;123(1):57–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-015-1439-8.
Silva de Lima AL, Hahn T, de Vries NM, Cohen E, Bataille L, Little MA, Baldus H, Bloem BR, Faber MJ. Large-scale wearable sensor deployment in Parkinson’s patients: the Parkinson@home study protocol. JMIR Res Protoc. 2016. https://doi.org/10.2196/resprot.5990.
Palmer JL, Coats MA, Roe CM, Hanko SM, Xiong C, Morris JC. Unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale-motor exam: inter-rater reliability of advanced practice nurse and neurologist assessments. J Adv Nurs. 2010;66(6):1382–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2010.05313.x.
Post B, Merkus MP, de Bie RM, de Haan RJ, Speelman JD. Unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale motor examination: are ratings of nurses, residents in neurology, and movement disorders specialists interchangeable? Mov Disord. 2005;20(12):1577–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20640.
Siderowf A, McDermott M, Kieburtz K, Blindauer K, Plumb S, Shoulson I, Group PS. Test-retest reliability of the unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale in patients with early Parkinson’s disease: results from a multicenter clinical trial. Mov Disord. 2002;17(4):758–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.10011.
Fisher JM, Hammerla NY, Ploetz T, Andras P, Rochester L, Walker RW. Unsupervised home monitoring of Parkinson’s disease motor symptoms using body-worn accelerometers. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PARKRELDIS.2016.09.009.
Belić M, Bobić V, Šolaja N, Đurić-Jovičić M, Kostić VS. Artificial intelligence for assisting diagnostics and assessment of Parkinson’s disease—a review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105442.
Ramyachitra D, Manikandan P. Imbalanced dataset classification and solutions: a review. Int J Comput Bus Res (IJCBR). 2014;5(4):1–29.
López V, Fernández A, García S, Palade V, Herrera F. An insight into classification with imbalanced data: empirical results and current trends on using data intrinsic characteristics. Inf Sci. 2013;250:113–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2013.07.007.
Kaur H, Pannu HS, Malhi AK. A systematic review on imbalanced data challenges in machine learning: applications and solutions. ACM Comput Surveys (CSUR). 2019;52(4):1–36. https://doi.org/10.1145/3343440.
Sun Y, Wong AK, Kamel MS. Classification of imbalanced data: a review. Int J Pattern Recognit Artif Intell. 2009;23(04):687–719. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218001409007326.
Haixiang G, Yijing L, Shang J, Mingyun G, Yuanyue H, Bing G. Learning from class-imbalanced data: review of methods and applications. Expert Syst Appl. 2017;73:220–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.12.035.
Wang K-J, Makond B, Chen K-H, Wang K-M. A hybrid classifier combining smote with pso to estimate 5-year survivability of breast cancer patients. Appl Soft Comput. 2014;20:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2013.09.014.
Niazmand K, Tonn K, Kalaras A, Kammermeier S, Boetzel K, Mehrkens J-H, Lueth TC. A measurement device for motion analysis of patients with Parkinson’s disease using sensor based smart clothes. In: 2011 5th International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare (PervasiveHealth) and Workshops, IEEE, 2011; p. 9–16.
Rigas G, Tzallas AT, Tsipouras MG, Bougia P, Tripoliti EE, Baga D, Fotiadis DI, Tsouli SG, Konitsiotis S. Assessment of tremor activity in the Parkinson’s disease using a set of wearable sensors. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2012;16(3):478–87. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2011.2182616.
Bazgir O, Frounchi J, Habibi SAH, Palma L, Pierleoni P. A neural network system for diagnosis and assessment of tremor in parkinson disease patients. In: 2015 22nd Iranian Conference on biomedical engineering (ICBME), IEEE, 2015; p. 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICBME.2015.7404105.
Novaković JD, Veljović A, Ilić SS, Papić Ž, Milica T. Evaluation of classification models in machine learning. Theory Appl Math Comput Sci. 2017;7(1):39–46.
Bazgir O, Habibi SAH, Palma L, Pierleoni P, Nafees S. A classification system for assessment and home monitoring of tremor in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Med Signals Sens. 2018;8(2):65. https://doi.org/10.4103/jmss.JMSS_50_17.
Wagner A, Fixler N, Resheff YS. A wavelet-based approach to monitoring Parkinson’s disease symptoms. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), IEEE, 2017; p. 5980–984. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2017.7953304.
Polat K, A hybrid approach to Parkinson disease classification using speech signal: the combination of smote and random forests. In: 2019 Scientific Meeting on electrical-electronics & biomedical engineering and computer science (EBBT), IEEE. 2019;2019: 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1109/EBBT.2019.8741725.
Preece SJ, Goulermas JY, Kenney LP, Howard D. A comparison of feature extraction methods for the classification of dynamic activities from accelerometer data. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2008;56(3):871–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2008.2006190.
Thorp JE, Adamczyk PG, Ploeg H-L, Pickett KA. Monitoring motor symptoms during activities of daily living in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurol. 2018;9:1036. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.01036.
Cook DJ, Krishnan NC. Activity learning: discovering, recognizing, and predicting human behavior from sensor data. Hoboken: Wiley; 2015.
Hssayeni MD, Burack MA, Jimenez-Shahed J, Ghoraani B. Assessment of response to medication in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Med Eng Phys. 2019;67:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2019.03.002.
Jeon H, Lee W, Park H, Lee HJ, Kim SK, Kim HB, Jeon B, Park KS. Automatic classification of tremor severity in Parkinson’s disease using a wearable device. Sensors. 2017;17(9):2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17092067.
Alam MN, Johnson B, Gendreau J, Tavakolian K, Combs C, Fazel-Rezai R. Tremor quantification of Parkinson’s disease-a pilot study. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on electro information technology (EIT), IEEE. 2016; p. 0755–59. https://doi.org/10.1109/EIT.2016.7535334.
Raza MA, Chaudry Q, Zaidi SMT, Khan MB. Clinical decision support system for Parkinson’s disease and related movement disorders. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), IEEE, 2017; p. 1108–112. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2017.7952328.
Rissanen SM, Kankaanpää M, Meigal A, Tarvainen MP, Nuutinen J, Tarkka IM, Airaksinen O, Karjalainen PA. Surface emg and acceleration signals in Parkinson’s disease: feature extraction and cluster analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2008;46(9):849–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-008-0369-0.
Rezghian Moghadam H, Kobravi H, Homam M. Quantification of Parkinson tremor intensity based on emg signal analysis using fast orthogonal search algorithm. Iran J Electric Electron Eng. 2018;14(2):106–15. https://doi.org/10.22068/IJEEE.14.2.106.
Ali MM, Taib M, Tahir NM, Jahidin A. Eeg spectral centroid amplitude and band power features: a correlation analysis. In: IEEE 5th Control and System Graduate Research Colloquium. IEEE. 2014;2014:223–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSGRC.2014.6908726.
Ruonala V, Meigal A, Rissanen S, Airaksinen O, Kankaanpää M, Karjalainen P. Emg signal morphology and kinematic parameters in essential tremor and Parkinson’s disease patients. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2014;24(2):300–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2013.12.007.
Meigal AY, Rissanen S, Tarvainen M, Georgiadis S, Karjalainen P, Airaksinen O, Kankaanpää M. Linear and nonlinear tremor acceleration characteristics in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Physiol Meas. 2012;33(3):395. https://doi.org/10.1088/0967-3334/33/3/395.
Cole BT, Roy SH, De Luca CJ, Nawab SH. Dynamical learning and tracking of tremor and dyskinesia from wearable sensors. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2014;22(5):982–91. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2014.2310904.
Batista GE, Keogh EJ, Tataw OM, De Souza VM. Cid: an efficient complexity-invariant distance for time series. Data Min Knowl Discov. 2014;28(3):634–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-013-0312-3.
Hooman OM, Oldfield J, Nicolaou MA. Detecting early Parkinson’s disease from keystroke dynamics using the tensor-train decomposition. In: 2019 27th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), IEEE, 2019; p.1–5. https://doi.org/10.23919/EUSIPCO.2019.8902562.
Kostikis N, Hristu-Varsakelis D, Arnaoutoglou M, Kotsavasiloglou C. Smartphone-based evaluation of parkinsonian hand tremor: wuantitative measurements vs clinical assessment scores. In: 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society. IEEE. 2014;2014:906–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2014.6943738.
Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP. Smote: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J Artif Intell Res. 2002;16:321–57. https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.953.
He H, Bai Y, Garcia EA, Li S. Adasyn: adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning. In: IEEE International Joint Conference on neural networks (IEEE world congress on computational intelligence). IEEE. 2008;2008:1322–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2008.4633969.
Han H, Wang W-Y, Mao B-H. Borderline-smote: a new over-sampling method in imbalanced data sets learning. In: International Conference on intelligent computing, Springer, 2005; p. 878–887. https://doi.org/10.1007/11538059_91.
Hart P. The condensed nearest neighbor rule (corresp.). IEEE Trans Inf Theory. 1968;14(3):515–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIT.1968.1054155.
Tomek I, et al., Two modifications of CNN. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern. 1976;6:769–72.
Tomek I, et al., An experiment with the edited nearest-neighbor rule. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern. 1976;6:448–52.
Wilson DL. Asymptotic properties of nearest neighbor rules using edited data. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern. 1972;SMC–2(3):408–21. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1972.4309137.
Smith MR, Martinez T, Giraud-Carrier C. An instance level analysis of data complexity. Mach Learn. 2014;95(2):225–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-013-5422-z.
Mani I, Zhang I. kNN approach to unbalanced data distributions: a case study involving information extraction. In: Proceedings of workshop on learning from imbalanced datasets. 2003; vol. 126.
Batista GE, Prati RC, Monard MC. A study of the behavior of several methods for balancing machine learning training data. ACM SIGKDD Explor Newsl. 2004;6(1):20–9. https://doi.org/10.1145/1007730.1007735.
Batista GE, Bazzan AL, Monard MC. et al. Balancing training data for automated annotation of keywords: a case study. In: WOB, 2003; p. 10–18.
Kantardzic M. Data mining: concepts, models, methods, and algorithms. Hoboken: Wiley; 2011.
Breiman L. Random forests. Mach Learn. 2001;45(1):5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324.
Lorena AC, Jacintho LF, Siqueira MF, De Giovanni R, Lohmann LG, De Carvalho AC, Yamamoto M. Comparing machine learning classifiers in potential distribution modelling. Expert Syst Appl. 2011;38(5):5268–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.10.031.
Manzouri F, Heller S, Dümpelmann M, Woias P, Schulze-Bonhage A. A comparison of machine learning classifiers for energy-efficient implementation of seizure detection. Front Syst Neurosci. 2018;12:43. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2018.00043.
Ghorbani R, Ghousi R. Comparing different resampling methods in predicting students’ performance using machine learning techniques. IEEE Access. 2020;8:67899–678911. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2986809.
Leung H, Haykin S. The complex backpropagation algorithm. IEEE Trans Signal Process. 1991;39(9):2101–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/78.134446.
James G, Witten D, Hastie T, Tibshirani R. An introduction to statistical learning. Berlin: New York; 2013. p. 112. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-7138-7.
He H, Garcia EA. Learning from imbalanced data. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. 2009;21(9):1263–84. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2008.239.
Du J, Vong C-M, Pun C-M, Wong P-K, Ip W-F. Post-boosting of classification boundary for imbalanced data using geometric mean. Neural Netw. 2017;96:101–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2017.09.004.
García V, Mollineda RA, Sánchez JS. Index of balanced accuracy: a performance measure for skewed class distributions. In: Iberian Conference on pattern recognition and image analysis, Springer, 2009; p. 441–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02172-5_57.
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (roc) curve. Radiology. 1982;143(1):29–36. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.143.1.7063747.
Michael J. Fox foundation, data sets: MJFF levodopa response study. https://www.michaeljfox.org/data-sets. Accessed 16 Sep 2020.
Chollet F, et al. Keras: The Python deep learning library. Astrophysics source code library; 2018, ascl:1806.022. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2018ascl.soft06022C.
Abadi M, Agarwal A, Barham P, Brevdo E, Chen Z, Citro C, Corrado GS, Davis A, Dean J, Devin M, et al. Tensorflow: large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.04467.
Glorot X, Bordes A, Bengio Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks. In: Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on artificial intelligence and statistics, 2011; 15:315–23.
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, 2012;25:1097–1105.
Bridle JS. Probabilistic interpretation of feedforward classification network outputs, with relationships to statistical pattern recognition. In: Neurocomputing, Springer, 1990; p. 227–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-76153-9_28.
Oshiro TM, Perez PS, Baranauskas JA. How many trees in a random forest? In: International Workshop on machine learning and data mining in pattern recognition, Springer, 2012; p. 154–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31537-4_13.
Berk RA. Classification and regression trees (cart). In: Statistical learning from a regression perspective, Springer, 2008; p. 1–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-77501-2_3.
Elazmeh W, Japkowicz N, Matwin S. Evaluating misclassifications in imbalanced data. In: European Conference on machine learning, Springer, 2006; p. 126–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/11871842_16.
Barandela R, Sánchez JS, Garca V, Rangel E. Strategies for learning in class imbalance problems. Pattern Recognit. 2003;36(3):849–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3203(02)00257-1.
Zweig MH, Campbell G. Receiver-operating characteristic (roc) plots: a fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin Chem. 1993;39(4):561–77. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/39.4.561.
Hajian-Tilaki K. Receiver operating characteristic (roc) curve analysis for medical diagnostic test evaluation. Casp J Intern Med. 2013;4(2):627.
Kumar R, Indrayan A. Receiver operating characteristic (roc) curve for medical researchers. Indian Pediatr. 2011;48(4):277–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-011-0055-4.
Jeon H, Lee W, Park H, Lee HJ, Kim SK, Kim HB, Jeon B, Park KS. High-accuracy automatic classification of parkinsonian tremor severity using machine learning method. Physiol Meas. 2017;38(11):1980.
Angeles P, Tai Y, Pavese N, Wilson S, Vaidyanathan R. Automated assessment of symptom severity changes during deep brain stimulation (dbs) therapy for Parkinson’s disease. In: 2017 International Conference on rehabilitation robotics (ICORR), IEEE, 2017; p. 1512–517.
Kim HB, Lee WW, Kim A, Lee HJ, Park HY, Jeon HS, Kim SK, Jeon B, Park KS. Wrist sensor-based tremor severity quantification in Parkinson’s disease using convolutional neural network. Comput Biol Med. 2018;95:140–6.
Dai H, Cai G, Lin Z, Wang Z, Ye Q. Validation of inertial sensing-based wearable device for tremor and bradykinesia quantification. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf. 2020;25(4):997–1005.
Sigcha L, Pavón I, Costa N, Costa S, Gago M, Arezes P, López JM, De Arcas G. Automatic resting tremor assessment in Parkinson’s disease using smartwatches and multitask convolutional neural networks. Sensors. 2021;21(1):291.
De Marsico M, Fartade EG, Mecca A. Feature-based analysis of gait signals for biometric recognition. In: ICPRAM 2018-7th International Conference on pattern recognition applications and methods, 2018; p. 630–37.
Ejupi A, Menon C. Detection of talking in respiratory signals: a feasibility study using machine learning and wearable textile-based sensors. Sensors. 2018;18(8):2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082474.
Madsen H. Time series analysis. Boca Raton: CRC Press; New York, 2007.
Richman JS, Moorman JR. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am J Physiol-Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;278(6):H2039–49. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.2000.278.6.H2039.
Groeneveld RA, Meeden G. Measuring skewness and kurtosis. J R Stat Soc Ser D (The Statistician). 1984;33(4):391–9. https://doi.org/10.2307/2987742.
DeCarlo LT. On the meaning and use of kurtosis. Psychol Methods. 1997;2(3):292. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.2.3.292.
Wei D, Chun M, Qing W. Analysis and classification of tremor characteristics of hepatolenticular degeneration. In: International Conference on applications and techniques in cyber security and intelligence, Springer, 2019; p. 1276–1285.
Ahlrichs C, Samà Monsonís A. Is “frequency distribution” enough to detect tremor in pd patients using a wrist worn accelerometer? In: PervasiveHealth’14 8th International Conference on pervasive computing technologies for healthcare Oldenburg, Germany-May 20–23, 2014, Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), 2014;65–71. https://doi.org/10.4108/icst.pervasivehealth.2014.254928.
Marsh MT, Schilling DA. Equity measurement in facility location analysis: a review and framework. Eur J Oper Res. 1994;74(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(94)90200-3.
Rigas G, Tzallas AT, Tsalikakis DG, Konitsiotis S, Fotiadis DI, Real-time quantification of resting tremor in the parkinson’s disease, in,. Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE. 2009;2009:1306–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5332580.
Tsipouras MG, Tzallas AT, Rigas G, Tsouli S, Fotiadis DI, Konitsiotis S. An automated methodology for levodopa-induced dyskinesia: assessment based on gyroscope and accelerometer signals. Artif Intell Med. 2012;55(2):127–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2012.03.003.
Giuffrida JP, Riley DE, Maddux BN, Heldman DA, Heldmann DA. Clinically deployable kinesia technology for automated tremor assessment. Mov Disord. 2009;24(5):723–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22445.
Perumal SV, Sankar R. Gait and tremor assessment for patients with parkinson’s disease using wearable sensors. Ict Express. 2016;2(4):168–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icte.2016.10.005.
Daneault J-F, Carignan B, Codère CÉ, Sadikot AF, Duval C. Using a smart phone as a standalone platform for detection and monitoring of pathological tremors. Front Hum Neurosci. 2013;6:357. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2012.00357.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research for collecting Levodopa Response Trial dataset and provide us access to this data.
Funding
This research project was funded by Nottingham Trent University, 50 Shakespeare Street, Nottingham, United Kingdom; ICON PLC, South County Business Park, Leopardstown, Dublin 18, Ireland; and The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research, Grand Central Station, New York, NY 10163-4777
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
AlMahadin, G., Lotfi, A., Carthy, M.M. et al. Enhanced Parkinson’s Disease Tremor Severity Classification by Combining Signal Processing with Resampling Techniques. SN COMPUT. SCI. 3, 63 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-021-00953-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-021-00953-6