Abstract
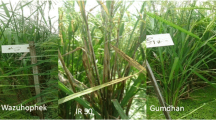
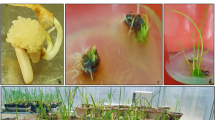
Sheath blight (ShB) is one of the most economically devastating disease affecting rice (Oryza sativa L.) crop globally. It is caused by Rhizoctonia solani Kühn. Still, there is no rice variety available that is highly resistant to ShB. Mutation breeding is one of the potential options and very less explored to develop ShB-resistant cultivars. It introduces genetic variability in desired traits. In the present investigation, mutagen sodium azide 0.03% was used for mutation of the Swarna variety for the creation of variability of ShB resistance. All total 1000 M1 plants with control were screened for ShB resistance by artificial inoculation and based on disease scores of ShB 46 contrasting M2 lines for ShB resistance were selected. The M2 lines were screened under field and humid chamber conditions. In both conditions, mutant lines were performed consistently and identified highly resistant and susceptible ShB lines. A total of 7 contrasting M2 lines with control were used for protein expression analysis and resistant lines gave an extra band between 33 and 44 kDa. Further, it was confirmed by gene expression study these proteins were pathogen-related (PR) proteins and caused the tolerant nature of ShB resistant lines. Hence, this study provides ShB tolerant line that could be advanced and used for ShB resistant variety development. Overexpression of PR genes, which may be useful as targets for crop improvement is linked to disease resistance.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Adams GC (1988) Thanatephorus cucumeris (Rhizoctonia solani), a species complex of wide host range. Adv Plant Pathol 6:535–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-033706-4.50040-2
Cerrudo I, Keller MM, Cargnel MD, Demkura PV, de Wit M, Patitucci MS, Pierik R, Pieterse CM, Ballaré CL (2012) Low red/far-red ratios reduce Arabidopsis resistance to Botrytis cinerea and jasmonate responses via a COI1-JAZ10-dependent, salicylic acid-independent mechanism. Plant Physiol 158(4):2042–2052. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.193359
Cortés LE, Weldegergis BT, Boccalandro HE, Dicke M, Ballaré CL (2016) Trading direct for indirect defense? Phytochrome B inactivation in tomato attenuates direct anti-herbivore defenses whilst enhancing volatile-mediated attraction of predators. New Phytol 212(4):1057–1071. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14210
Davla D, Sasidharan N, Macwana S, Chakraborty S, Trivedi R, Ravikiran R, Shah G (2013) Molecular characterization of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes for salt tolerance using microsatellite markers. Bioscan 8(2):498–502.
Faruq G, Mohamad O, Hadzim K, Craig MA (2003) optimization of aging time and temperature of four Malaysian Rice cultivars. Pakistan J Nutr 2(3):125–131. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjn.2003.125.131
Groth DE, Rush MC, Hollier CA (1991) Rice diseases and disorders in Louisiana. Louisiana State University, Agricultural Center, Louisiana Agricultural Experiment Station, Bulletin No. 828. Baton Rouge, LA, USA.
Hadzim K, Ajimilah NH, Othman O, Arasu NT, Latifah A, Saad A (1988) Mutant Mahsuri: Baka untuk beras bermutu. Teknol Padi 4:7–13
Hu J, Rutger JN (1992) Pollen characteristics and genetics of induced and spontaneous genetic male-sterile mutants in rice. Plant Breeding 109(2):97–107. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.1992.tb00159.x
Jia Y, Wang Z, Fjellstrom RG, Moldenhauer KAK, Adam MA, Correll FN, Xia Y, Rutger JN (2004) Rice Pi-ta gene confers resistance to the major pathotypes of the rice blast fungus in the United States. Phytopathol 94:296–301. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO.2004.94.3.296
Jia L, Yan W, Agrama HA, Yeater K, Li X et al (2011) Searching for germplasm resistant to sheath blight from the USDA rice core collection. Crop Sci 51(4):1507–1517. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2010.10.0581
Joshi V, Joshi N, Vyas A, Jadhav SK (2021) Pathogenesis-related proteins: Role in plant defense. In Biocontrol agents and secondary metabolites (pp. 573–590). Woodhead Publishing, Sawston, UK.
Khan S, Wani MR, Parveen K (2004) Induced genetic variability for quantitative traits in Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek. Pakistan J Bot 36(4):845–850.
Khan MA, Gulzar S (2003) Germination responses of Sporobolus ioclados: a saline desert grass. J Arid Environ 53:387–394. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.2002.1045
Kumari M, Pandey S, Chauhan D, Pandey H, Divakar S, Meena K, Singh A (2023) Differential expression of the AP2/EREBP gene family in the contrasting genotypes of maize provides insights of abiotic stress tolerance. Cereal Res Commun, pp.1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-023-00358-6
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259):680–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Lo KL, Chen YN, Chiang MY, Chen MC, Panibe JP, Chiu CC, Liu LW, Chen LJ, Chen CW, Wang LWH, CS, (2022) Two genomic regions of a sodium azide induced rice mutant confer broad-spectrum and durable resistance to blast disease. Rice 15:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-021-00547-z
Meena SC, Singh V, Adhipathi P, Chandra R (2013) Screening for sheath blight resistance genotypes among mutated population of rice CV. Pusa Basmati-1. Bioscan 8(3):919–924
Molla Kutubuddin A, Subhasis K, Johiruddin M, Prasad B, Rajeev KV, Swapan KD, Karabi D (2019) Understanding sheath blight resistance in rice: the road behind and the road ahead. Plant Biotechnol J. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13312
Moreno JE, Ballaré CL (2014) Phytochrome regulation of plant immunity in vegetation canopies. J Chem Ecol 40:848–857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-014-0471-8
Naveenkumar R, Anandan A, Singh V, Prabhukarthikeyan SR, Parameswaran C, Sangeetha G, Mahender A, Keerthana U, Singh PK, Patra BC, Ali J (2022) Deciphering environmental factors and defense response of rice genotypes against sheath blight disease. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 122:101916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2022.101916
Nazir B, Mohamad O, Affrida AH, Sakinah A (1998) Research Highlights on the Use of Induced Mutations for Plant Improvement in Malaysia. Bangi, Malaysia: MINT.
Nguyen TC, Obermeier C, Friedt W, Abrams SR, Snowdon RJ (2016) Disruption of germination and seedling development in Brassica napus by mutations causing severe seed hormonal imbalance. Front Plant Sci 7:322. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00322
Omoregie UE, Mensah JK, Ikhajiagbe B (2014) Germination response of five rice varieties treated with sodium azide. Res J Mutagenesis 4(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjmutag.2014.14.22
Ou SH (1985) Rice diseases, 2nd edn. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew, UK, 380.
Park DS, Sayler RJ, Hong YG, Yang NMH (2008) A method for inoculation and evaluation of rice sheath blight disease. Plant Dis 92(1):25–29
Schweizer P, Buchala A, Dudler R, Metraux JP (1998) Induced systemic resistance in wounded rice plants. Plant J 14:475–481. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1998.00141.x
Sharma L, Goswami S, Nagrale DT (2013) Culture and physiological variability in Rhizoctonia solani, responsible for foliar and lesions on aerial part of soybean. J Appl Natural Sci 5(1):41–46. https://doi.org/10.31018/jans.v5i1.279
Singh A, Rohila R, Singh US, Savary S, Willocquet L, Duveiller E (2002) An improved inoculation technique for sheath blight of rice caused by Rhizoctonia solani. Can J Plant Path 24(1):65–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060660109506973
Srivastava D, Shamim M, Kumar M, Mishra A, Pandey P, Kumar D, Yadav P, Siddiqui MH, Singh KN (2017) Current status of conventional and molecular interventions for blast resistance in rice. Rice Sci 24:299–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2017.08.001
Sudhakar R, Rao KC, Reddy CS (1998) Studies on antagonism of Trichoderma and Glicladium species against Rhizoctonia solani of Rice. Indian J Plant Protect 26(1):25–29
Sun X, Cao Y, Yang Z, Xu C, Li X, Wang S, Zhang Q (2004) Xa26, a gene conferring resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice, encodes an LRR receptor kinase-like protein. Plant J 37:517–527. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01976
Tang Q, Peng S, Buresh RJ, Zou Y, Castilla NP, Mew TW (2007) Rice varietal difference in sheath blight development and its association with yield loss at different levels of N fertilization. Field Crop Res 102(3):219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FCR.2007.04.005
Udvardi MK, Czechowski T, Scheible WR (2008) Eleven golden rules of quantitative RT-PCR. Plant Cell 20(7):1736–1737
Van Loon LC (1985) Pathogenesis-related proteins. Plant Mol Biol 4:111–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02418757
Wani MR, Khan S, Kozgar MI (2011) Induced chlorophyll mutations. I. Mutagenic effectiveness and efficiency of EMS, HZ and SA in mungbean. Front Mech Eng China 5:514–518
Wen-chao Y, Guo-chang S, Jian-long X, Fa-ming Y, Xue-qin M, Qing-sheng J (2004) Breeding of a new Indica Rice Mutant line Zhe-101 for resistance to blast and bacterial leaf blight by space mutation. Chin J Rice Sci 18(5):415–419
Xue X, Cao ZX, Zhang XT, Wang Y, Zhang YF, Chen ZX, Zuo SM (2016) Overexpression of OsOSM1 enhances resistance to rice sheath blight. Plant Dis 100:1634–1642. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-11-15-1372-RE
Yang X, Gu X, Ding J, Yao L, Gao X, Zhang M, Meng Q, Wei S, Fu J (2022) Gene expression analysis of resistant and susceptible rice cultivars to sheath blight after inoculation with Rhizoctonia solani. BMC Genomics 23(1):278
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.S. and A.M. conducted the experiments, D.K.D. designed the experiment, and A.S. analyzed and wrote the manuscript of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
The article submitted to the journal is original has been written by the stated authors and has not been published elsewhere. This manuscript has not been submitted to, nor is it under review at, another journal or other publishing venue.
Additional information
Communicated by Janusz Zimny.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R., Dwivedi, D.K., Mishra, A. et al. Development of sheath blight resistant genotype of rice by mutation breeding and gene expression profiling after inoculation of Rhizoctonia solani. CEREAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-024-00533-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-024-00533-3