Abstract
Land use change caused by human activities is the main driver of biodiversity loss and changes in ecosystem functioning. However, less is known about how the conversion of a natural to pasture land favour the biological diversity of soil-litter arthropods to advance effective conservation plans and management systems. To fill the gap, this study focussed on soil-litter arthropod communities under a pasture land use in southern Rwanda. Data have been collected using pitfall traps and hand collection between April and June 2021. Sampled specimens of soil-litter arthropods have been identified to order and family levels by using dichotomous keys. Further, the species name was given when the identification key was available, while the morphological description was provided in absence of the identification keys. Results indicated a total of 3013 individuals of soil-litter arthropods grouped into 3 classes, 13 orders, 46 families and 87 morpho-species. Coleoptera showed a high number of families, while higher abundance and the number of morpho-species were found for ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Higher abundance of sampled soil-litter arthropods is a sign that the studied area offers suitable habitat for soil-litter arthropods. However, less abundance found for some groups of soil-litter arthropods might be influenced by the used sampling techniques which were not appropriate for them. We recommend surveys using multiple sampling techniques to maximize chances of capturing a wide range of soil-litter arthropods.

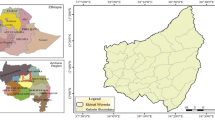
(Adapted from CGIS shapefiles and GPS data collected on the field)


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alroy J (2017) Effects of habitat disturbance on tropical forest biodiversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114(23):6056–6061. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1611855114
Andersen AN, Majer JD (2004) Ants show the way down under: invertebrates as bioindicators in land management. Front Ecol Environ 2(6):291–298. https://doi.org/10.1890/1540-9295(2004)002[0292:ASTWDU]2.0.CO;2
Andersen AN, Hoffmann BD, Müller WJ, Griffiths AD (2002) Using ants as bioindicators in land management: simplifying assessment of ant community responses. J Appl Ecol 39(1):8–17. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2664.2002.00704.x
Apolinário LCMH, Almeida AA, Queiroz JM, Vargas AB, Almeida FS (2019) Diversity and guilds of ants in different land-use systems in Rio de Janeiro state. Brazil Floresta e Ambiente 26(4):e2017115. https://doi.org/10.1590/2179-8087.115217
Bain GC, MacDonald MA, Hamer R, Gardiner R, Johnson CN, Jones ME (2020) Changing bird communities of an agricultural landscape: declines in arboreal foragers, increases in large species. Royal Society Open Sci 7(3):200076. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.200076
Birasa EC, Bizimana I, Bouchaert W, Chapelle J, Deflandre A, Gallez A, Maesshal GET, Vercruysse J (1990) Description systhetique des sols. CPR, MINAGRI, Kigali
Carrijo TF, Brandão D, de Oliveira DE, Costa DA, Santos T (2009) Effects of pasture implantation on the termite (Isoptera) fauna in the central Brazilian Savanna (Cerrado). J Insect Conserv 13:575–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10841-008-9205-y
Cassani MT, Sabatté ML, Rubín MAR, Sfeir AJ, Massobrio MJ (2021) Litter decomposition by soil fauna: effect of land use in agroecosystems. Heliyon 7(10):e08127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08127
Cenkseven S, Kizildag N, Kocak B, Sagliker AH, Darici C (2017) Soil organic matter mineralization under different temperatures and moisture conditions in Kizildağ plateau. Turkey. Sains Malaysiana 46(5):763–771
Christianini A, Oliveira PS (2010) Birds and ants provide complementary seed dispersal in a Neotropical Savanna. J Ecol 98(3):573–582. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2010.01653.x
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18:117–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9993.1993.tb00438.x
Cole RJ, Karen DH, Rakan AZ, Wickey P, Townsend AR (2016) Leaf litter arthropod responses to tropical forest restoration leaf litter arthropod responses to tropical forest restoration. Ecol Evol 6(15):5158–5168. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.2220
Cook D (2020) A historical review of management options used against the stable fly (diptera: muscidae). Insects 11(5):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11050313
Culliney TW (2013) Role of arthropods in maintaining soil fertility. Agriculture 3(4):629–659. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture3040629
Czimczik CI, Mund M, Detlef SE, Wirth C (2005) Effects of reforestation, deforestation, and afforestation on carbon storage. In: Griffiths H, and Jarvis PG: The Carbon Balance of Forest Biome. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203501344-15
del Toro I, Ribbons RR, Pelini SLP (2012) The little things that run the world revisited: a review of ant-mediated ecosystem services and disservices (hymenoptera: formicidae). Myrmecological News 17:133–146
Delvare G, Henri-Pierre Aberlenc HP (1989) Les Insectes d’afrique et Ameriques Tropicale. Clés Pour La Reconnaissance des Familles. Centre de Coopération Internationale en Recherche Agronomique pour le Dévelopment. MontPellier, France
Do Y, Lineman MJM, Joo GJ (2012) Impacts of different land-use patterns on the carabid beetle diversity and species assemblages in South Korea. Ekoloji 84:9–17. https://doi.org/10.5053/ekoloji.2012.842
Erskine PD, Williams ER, Mulligan DR, Erskine PD, Plowman KP (2012) Using insect diversity for determining land restoration development: examining the influence of grazing history on ant assemblages in rehabilitated pasture agriculture, ecosystems and environment. Agric Ecosyst Environ 163:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2012.02.017
Fisher BL, Barry B (2016) Ants of Africa and Madagascar: a guide to the Genera. University of California Press, Oakland, California, USA
Ghiglieno I, Simonetto A, Orlando F, Donna P, Tonni M, Valenti L, Gilioli G (2020) Response of the arthropod community to soil characteristics and management in the franciacorta viticultural area (Lombardy, Italy). Agronomy 10(5):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050740
Gold PB, Kivlighan DM, Patton MJ (2014) Non-metric multidimensional scaling profile analysis of non-growth change in groups: a demonstration. Small Group Research 45(3):235–265. https://doi.org/10.1177/1046496414528050
Henri DC, Owen J, Tsiattalos JO, Thébault E, Seymour CL, van Veen FJF (2015) Natural vegetation benefits synergistic control of the three main insect and pathogen pests of a fruit crop in southern Africa. J Appl Ecol 52:1092–1101
Hill JG (2011) Sifting soil and leaf litter to collect Arthropods. Mississipi State University
Illig J, Schatz H, Scheu S, Maraun M (2008) Decomposition and colonization by micro-arthropods of two litter types in a tropical montane rain forest in southern Ecuador. J Trop Ecol 24(2):157–167. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0266467407004750
Jones CG, Lawton JH, Shachak M (1994) Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 69(3):373. https://doi.org/10.2307/3545850
Jouquet P, Dauber J, Lagerlöf J, Lavelle P, Lepage M (2006) Soil invertebrates as ecosystem engineers: intended and accidental effects on soil and feedback loops. Appl Soil Ecol 32(2):153–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2005.07.004
Korösi A, Batáry P, Orosz A, Rédei D, Báldi A (2012) Effects of grazing, vegetation structure and landscape complexity on grassland leafhoppers (hemiptera: auchenorrhyncha) and true bugs (hemiptera: heteroptera) in Hungary. Insect Conserv Divers 5(1):57–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-4598.2011.00153.x
Kouakou LMM, Dekoninck W, Kone M, Delsinne T, Yeo K, Ouattara K, Konate S (2018) Diversity and distribution of introduced and potentially invasive ant species from the three main ecoregions of Côte d’Ivoire (West Africa). Belg J Zool 148(1):83–103
Lavelle P (1996) Diversity of Soil Fauna and Ecosystem Function. Biol Int 33:3–16
Lobry De Bruyn LA (1999) Ants as bioindicators of soil function in rural environments. Agric Ecosyst Environ 74(1–3):425–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8809(99)00047-X
Madsen BL (2012) Biological studies on adult water snipe Fly, Atherix Ibis (Fabricius, 1798) (diptera: athericidae): old myths and new facts. Aquatic Insects 34(SUPPL. 1):91–102. https://doi.org/10.1080/01650424.2012.643031
Martin JEH (1977) Collecting, preparing and preserving insects, mites and spiders. Ottowa, Canada
Mauda E, Grant SJ, Colleen LS, Thinandavha CM, Foord SH (2018) Changes in land use alter ant diversity, assemblage composition and dominant functional groups in African Savannas. Biodivers Conserv 27(4):947–965. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-017-1474-x
Menta C, Remelli S (2020) Soil health and arthropods: from complex system to worthwhile investigation. Insects 11(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11010054
Menta C, Delia FC, Fondón CL, Staffilani F, Remelli S (2020) Soil arthropod responses in agroecosystem: implications of different management and cropping systems. Agronomy 10(7):982. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10070982
Mignon J, Haubruge E, Francis, (2016) Clé d’identification Des Principales Familles d’insectes d’Europe. Les Presses Agronomiques de Gembloux, Gembloux, Belgique
Mukuralinda A, Tenywa JS, Verchot L, Obua J, Nabahungu NL, Chianu JN (2010) Phosphorus uptake and maize response to organic and inorganic fertilizer inputs in rubona. Southern Province of Rwanda. Agrofores Syst 80(2):211–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-010-9324-9
Munyai TC, Foord SH (2012) Ants on a mountain: spatial, environmental and habitat associations along an altitudinal transect in a centre of endemism. J Insect Conserv 16(5):677–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10841-011-9449-9
Neira J, Ortiz M, Morales L, Acevedo E (2015) Oxygen diffusion in soils: understanding the factors and processes needed for modelling. Chilean J Agri Res 75:35–44. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-58392015000500005
Newbold T, Scott A, Stapp P, Levensailor KE, Derner JD, Lauenroth WK (2014) Community responses of arthropods to a range of traditional and manipulated grazing in shortgrass steppe. Environ Entomol 43(3):556–568. https://doi.org/10.1603/EN12333
Nilsson SG, Franzén M, Pettersson LB (2013) Land-use changes, farm management, and the decline of butterflies associated with semi-natural grasslands in southern Sweden. Nature Conservation 6:31–48. https://doi.org/10.3897/natureconservation.6.5205
Nsengimana V, Kaplin AB, Francis F, Kouakou MML, Dekoninck W, Nsabimana D (2018) Use of soil and litter ants (hymenoptera: formicidae) as biological indicators of soil quality under different land uses in southern Rwanda. Environ Entomol 47(6):1394–1401. https://doi.org/10.1093/ee/nvy144
Nsengimana V, Kaplin AB, Nsabimana D, Dekoninck W, Francis F (2021) Diversity and abundance of soil-litter arthropods and their relationships with soil physicochemical properties under different land uses in Rwanda. Biodiversity 22(1–2):41–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/14888386.2021.1905064
Padgham M (2004) Reverberation and frequency attenuation in forests—implications for acoustic communication in animals. J Acoustical Soc Am 115(1):402–410. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1629304
Picker M, Griffiths C, Weaving A (2004) Field Guide to Insects of South Africa by Charles Griffiths. Penguin Random House, South Africa
Pribadi T, Rika R, Harahap IS (2011) Termites community as environmental bioindicators in highlands: a case study in eastern slopes of Mount Slamet. Central Java. Biodiversitas 12(3):235–240
Römbke J, Schmelz MR, Pélosi C (2017) Effects of organic pesticides on enchytraeids (Oligochaeta) in agroecosystems: laboratory and higher-tier tests. Front Environ Sci 5:20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2017.00020
Rosa MG, Santos JCP, Brescovit AD, Mafra AL (2018) Spiders (Arachnida: Araneae) in agricultural land use systems in subtropical environments. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 42:e0160576. https://doi.org/10.1590/18069657rbcs20160576
Sala OE, Chapin FS, Armesto JJ, Berlow E, Bloomfield J, Dirzo R, Huber-Sanwald E et al (2000) Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science 287(5459):1770–1774. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.287.5459.1770
Scasta JD, Engle DM, Talley JL, Weir JR, Stansberry JC, Fuhlendorf SD, Harr RN (2012) Pyric-herbivory to manage horn flies (diptera: muscidae) on cattle. Southwestern Entomologist 37(3):325–334. https://doi.org/10.3958/059.037.0308
Schapheer C, Lopez-Uribe MM, Vera A, Villagra CA (2017) Distribution, habitat use and plant associations of Moluchia Brevipennis (Saussure, 1864) (blattodea: ectobiidae): an endemic cockroach from chilean mediterranean matorral biome. Revista Brasileira De Entomologia 61(2):114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbe.2017.02.001
Schindler BY, Griffith AB, Jones KN (2011) Factors influencing arthropod diversity on green roofs. Cities and the Environment. 4(1):1–22
Simon S, Letsch H, Bank S, Buckley TR, Donath A, Liu S, Machida R, Meusemann K, Misof B, Podsiadlowski L, Zhou X, Wipfler B, Bradler S (2019) Old world and new world phasmatodea: phylogenomics resolve the evolutionary history of stick and leaf insects. Front Ecol Evol 7:345. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2019.00345
Srivastava R, Mohapatra M, Latare A (2019) Impact of land use changes on soil quality and species diversity in the vindhyan dry tropical region of india. J Trop Ecol 36(2):72–79. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0266467419000385
Steinwandter M, Schlick-Steiner BC, Seeber GUH, Steiner FM, Seeber J (2017) Effects of alpine land-use changes: soil macrofauna community revisited. Ecol Evol 7(14):5389–5399. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.3043
Szinwelski N, Rosa CS, Schoereder JH, Mews CM, Sperber CF (2012) Effects of forest regeneration on crickets: evaluating environmental drivers in a 300-year chronosequence. Int J Zool 2012:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/793419
Taguchi YH, Oono Y (2005) Relational patterns of gene expression via non-metric multidimensional scaling analysis. Bioinformatics 21(6):730–740. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti067
Tóth Z, Hornung E (2020) Taxonomic and functional response of millipedes (diplopoda) to urban soil disturbance in a metropolitan area. Insects 11(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11010025
van der Mescht L, le Roux PC, Conrad AM, Morgan JR, Sonja M (2016) The Influence of life history characteristics on flea (siphonaptera) species distribution models. Parasit Vectors 9:178. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-016-1466-9
Vasconcelos HL, Bruna EM (2012) Arthropod responses to the experimental isolation of amazonian forest fragments. Sociedade Brasileira De Zoologia 29(6):515–530
Viana AB, Souza VB, Reis YT, Marques-Costa AP (2014) Termite assemblages in dry tropical forests of northeastern brazil: Are termites bioindicators of environmental disturbances? Sociobiology 61(3):324–31
Virić G, Drmić HZ, Čačija M, Graša Z, Petrak I, Bažok R, Lemic D (2017) Impact of environmental conditions and agro-technical factors on ground beetle populations in arable crops. Appl Ecol Environ Res 15(3):697–711
Wardle DA, Yeates GW, Barker GM, Bonner KI (2006) The influence of plant litter diversity on decomposer abundance and diversity. Soil Biol Biochem 38(5):1052–1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.09.003
Weiss N, Zucchi H, Hochkirch A (2013) The effects of grassland management and aspect on orthoptera diversity and abundance: site conditions are as important as management. Biodivers Conserv 22(10):2167–2178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-012-0398-8
Wielgoss A, Tscharntke T, Rumede A, Fiala B, Seidel H, Shahabuddin S, Clough Y (2014) Interaction complexity matters: disentangling services and disservices of ant communities driving yield in tropical agroecosystems. Proc Royal Soc B: Biol Sci 281:20132144. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2013.2144
Yeshaneh GT (2015) Assessment of micronutrient status in different land use soils in maybar lake Watershed of Albuko District, South Wello Zone, North Ethiopia. Am J Environ Protect 3(1):30–36
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Rwanda Agriculture Board (RAB), Rubona station for the authorization to sample the pasture land located at Rubona Agricultural Research Station. The Centre of Excellence in Biodiversity and Natural Resource Management (CoEB) based in the College of Science and Technology, University of Rwanda is thanked for the assistance during the identification of soil-litter arthropods and data analysis. Also Mr. Thacien Hagenimana, researcher fellow to the CoEB is acknowledged for the assistance to analyze GIS data and making the sampling point map.
Funding
This research was funded by the Global Taxonomy Initiative (GTI) within the framework of Capacities for Biodiversity and Sustainable Development (CEBioS). The CEBioS is based at the Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Science (RBINS), Brussels, Belgium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VN designed the study, analyzed the data, supported in field data collection, identification of soil litter arthropods, and wrote the manuscript; CSI and JdDN contributed to the research design, collected data, and identified soil-litter arthropods to species level; JWM proof read the manuscript; WD verified the identification and proofread the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Appendix 1
Appendix 1
See Table
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nsengimana, V., Iradukunda, C.S., de Dieu Nsenganeza, J. et al. Soil-litter arthropod communities under pasture land use in southern Rwanda. Trop Ecol 64, 369–379 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42965-022-00277-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42965-022-00277-3