Abstract
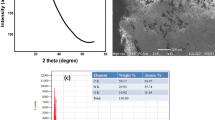
The detailed understanding of fluorescence emission processes is still unclear. This study demonstrates Aegle marmelos derived luminescent heteroatoms (N, Ca, K) doped carbon quantum dots (CQDs) using an economically and ecologically sustainable synthesis process without the necessity for any doping precursors due to its phytochemical, vitamin and mineral content. Carboxyl functionalization was done by adding lemon juice to the fruit extract. The morphological, physiochemical, compositional, crystallinity, and surface functional groups having heteroatom doped CQDs were analysed by HRTEM, EDX, XPS, XRD, FTIR etc. Besides, CQDs exhibited pH and solvent-dependent tuneable fluorescence characteristics. In fact, beyond pH 7.77, a protonation-deprotonation-driven red-shift was observed together with a decrease in the contribution of prominent peaks. Meanwhile, the features of solvatochromic fluorescence were examined in a range of aprotic and protic solvents with low and high polarity. Based on the studied Kamlet–Taft parameters and the obtained spectroscopic characterizations, a suitable fluorescence emission mechanism is provided. The observed solvatochromic fluorescence is thought to be caused by a combination of dipole moment polarisation, intramolecular charge transfer processes with or without H-bond stabilisation via the interaction of heteroatoms doped CQDs with solvent mediated by electron donation and acceptance from various surface functional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl with solvent molecules. Hence, this study is believed to promote the development of eco-tuneable fluorescent heteroatom doped CQDs and provide further insights into the fundamental fluorescence mechanisms, which include the relationship between morphology, surface properties and plausible quantum effects between CQDs and solvents.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be available on reasonable request from corresponding author.
References
Hu X, Li Y, Xu Y, Gan Z, Zou X, Shi J et al (2021) Green one-step synthesis of carbon quantum dots from orange peel for fluorescent detection of Escherichia coli in milk. Food Chem 339:127775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127775
Saboorizadeh B, Zare-Dorabei R, Shahbazi N (2021) Green synthesis of carbon quantum dots and their application as a fluorometric sensor for highly selective determination of 6-mercaptopurine in biological samples. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 129:389–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2021.09.015
Safardoust-Hojaghan H, Salavati-Niasari M, Amiri O, Rashki S, Ashrafi M (2021) Green synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of carbon quantum dots-decorated ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram Int 47:5187–5197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.10.097
Yadav PK, Upadhyay RK, Kumar D, Bano D, Chandra S, Jit S et al (2021) Synthesis of green fluorescent carbon quantum dots from the latex of Ficus benghalensis for the detection of tyrosine and fabrication of Schottky barrier diode. New J Chem 45:12549–12556. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ01655E
Li Z, Wang Q, Zhou Z, Zhao S, Zhong S, Xu L et al (2021) Green synthesis of carbon quantum dots from corn stalk shell by hydrothermal approach in near-critical water and applications in detecting and bioimaging. Microchem J 166:106250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106250
Amer WA, Rehab AF, Abdelghafar ME, Torad NL, Atlam AS, Ayad MM (2021) Green synthesis of carbon quantum dots from purslane leaves for the detection of formaldehyde using quartz crystal microbalance. Carbon N Y 179:159–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2021.03.047
Malavika JP, Shobana C, Ragupathi M, Kumar P, Lee YS, Govarthanan M et al (2021) A sustainable green synthesis of functionalized biocompatible carbon quantum dots from Aloe barbadensis Miller and its multifunctional applications. Environ Res 200:111414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111414
Zhu L, Shen D, Wang Q, Luo KH (2021) Green synthesis of tunable fluorescent carbon quantum dots from lignin and their application in anti-counterfeit printing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:56465–56475. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c16679
Wang Z, Liu Q, Leng J, Liu H, Zhang Y, Wang C et al (2021) The green synthesis of carbon quantum dots and applications for sulcotrione detection and anti-pathogen activities. J Saudi Chem Soc 25:101373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2021.101373
Li X, Wang H, Shimizu Y, Pyatenko A, Kawaguchi K, Koshizaki N (2011) Preparation of carbon quantum dots with tunable photoluminescence by rapid laser passivation in ordinary organic solvents. Chem Commun 47:932–934. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03552A
Cao L, Anilkumar P, Wang X, Liu J-H, Sahu S, Meziani MJ et al (2011) Reverse Stern–Volmer behavior for luminescence quenching in carbon nanoparticles. Can J Chem 89:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1139/V10-096
Wang X, Cao L, Lu F, Meziani MJ, Li H, Qi G et al (2009) Photoinduced electron transfers with carbon dots. Chem Commun. https://doi.org/10.1039/b906252a
Kong W, Wu H, Ye Z, Li R, Xu T, Zhang B (2014) Optical properties of pH-sensitive carbon-dots with different modifications. J Lumin 148:238–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.12.007
Sciortino A, Marino E, van Dam B, Schall P, Cannas M, Messina F (2016) Solvatochromism unravels the emission mechanism of carbon nanodots. J Phys Chem Lett 7:3419–3423. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b01590
Pan D, Zhang J, Li Z, Wu C, Yan X, Wu M (2010) Observation of pH-, solvent-, spin-, and excitation-dependent blue photoluminescence from carbon nanoparticles. Chem Commun 46:3681. https://doi.org/10.1039/c000114g
Kumar P, Bohidar HB (2013) Observation of fluorescence from non-functionalized carbon nanoparticles and its solvent dependent spectroscopy. J Lumin 141:155–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.02.043
Kozák O, Datta KKR, Greplová M, Ranc V, Kašlík J, Zbořil R (2013) Surfactant-derived amphiphilic carbon dots with tunable photoluminescence. J Phys Chem C 117:24991–24996. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp4040166
Wang H, Sun C, Chen X, Zhang Y, Colvin VL, Rice Q et al (2017) Excitation wavelength independent visible color emission of carbon dots. Nanoscale 9:1909–1915. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR09200D
Monika S, Thirumal M, Kumar P (2023) Phytochemical and biological review of Aegle marmelos Linn. Futur Sci OA. https://doi.org/10.2144/fsoa-2022-0068
Sharma N, Radha, Kumar M, Zhang B, Kumari N, Singh D et al (2022) Aegle marmelos (L.) Correa: an underutilized fruit with high nutraceutical values—a review. Int J Mol Sci 23:10889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810889
Venthodika A, Chhikara N, Mann S, Garg MK, Sofi SA, Panghal A (2021) Bioactive compounds of Aegle marmelos L., medicinal values and its food applications: a critical review. Phyther Res 35:1887–1907. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6934
Sharma CK, Sharma M, Sharma V (2016) Therapeutic potential of the medicinal plant Aegle Marmelos (Linn.) Correa: insight. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 35:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2015014485
Manandhar B, Paudel KR, Sharma B, Karki R (2018) Phytochemical profile and pharmacological activity of Aegle marmelos Linn. J Integr Med 16:153–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joim.2018.04.007
Wei Y, Chen L, Zhao S, Liu X, Yang Y, Du J et al (2021) Green-emissive carbon quantum dots with high fluorescence quantum yield: preparation and cell imaging. Front Mater Sci 15:253–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-021-0544-x
Latief U, Ul Islam S, Khan ZMSH, Khan MS (2021) A facile green synthesis of functionalized carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probes for a highly selective and sensitive detection of Fe3+ ions. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 262:120132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120132
Magdy G, Abdel Hakiem AF, Belal F, Abdel-Megied AM (2021) Green one-pot synthesis of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon quantum dots as new fluorescent nanosensors for determination of salinomycin and maduramicin in food samples. Food Chem 343:128539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128539
Preethi M, Viswanathan C, Ponpandian N (2021) A green path to extract carbon quantum dots by coconut water: another fluorescent probe towards Fe3+ ions. Particuology 58:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2021.03.019
Kamlet MJ, Abboud JLM, Abraham MH, Taft RW (1983) Linear solvation energy relationships. 23. A comprehensive collection of the solvatochromic parameters, .pi.*, alpha., and .beta., and some methods for simplifying the generalized solvatochromic equation. J Org Chem 48:2877–2887. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00165a018
Lu J, Brown JS, Liotta CL, Eckert CA (2001) Polarity and hydrogen-bonding of ambient to near-critical water: Kamlet–Taft solvent parameters. Chem Commun. https://doi.org/10.1039/b100425p
Black JJ, Dolan A, Harper JB, Aldous L (2018) Kamlet–Taft solvent parameters, NMR spectroscopic analysis and thermoelectrochemistry of lithium–glyme solvate ionic liquids and their dilute solutions. Phys Chem Chem Phys 20:16558–16567. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CP02527D
Jessop PG, Jessop DA, Fu D, Phan L (2012) Solvatochromic parameters for solvents of interest in green chemistry. Green Chem 14:1245. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2gc16670d
Liu H, Yang J, Li Z, Xiao L, Aryee AA, Sun Y et al (2019) Hydrogen-bond-induced emission of carbon dots for wash-free nucleus imaging. Anal Chem 91:9259–9265. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02147
Hu Y, Neumann C, Scholtz L, Turchanin A, Resch-Genger U, Eigler S (2022) Polarity, intramolecular charge transfer, and hydrogen bond co-mediated solvent effects on the optical properties of graphene quantum dots. Nano Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4752-1
Acknowledgements
The authors declare no acknowledgement.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VK: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, and writing- original draft preparation. VDS: methodology, investigation, and formal analysis. GC: Investigation and Formal analysis. SC: methodology and supervision. MKB: conceptualization, methodology, resources, writing- reviewing and editing, and overall supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kansay, V., Sharma, V.D., Chandan, G. et al. Facile green synthesis of heteroatoms doped Aegle marmelos-derived carbon quantum dots and its tuneable fluorescence characteristics influenced by solvent polarity. Carbon Lett. 34, 1045–1054 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-023-00659-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-023-00659-0