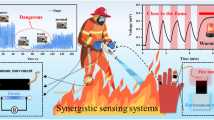
Abstract
Noninvasive human augmentation, namely a desirable approach for enhancing the quality of life, can be achieved through wearable electronic devices that interact with the external environment. Wearable electronic devices endure limitations, such as unreliable signal interaction when bent or deformed, excessive wiring requirements, and lack of programmability and multifunctionality. Herein, we report an intelligent and programmable (IP) fabric sensor with bending insensitivity that overcomes these challenges associated with a rapid response time (< 400 μs) and exceptional durability (> 20,000 loading–unloading cycles). A single-layer parallel electrical bilateral structure is utilized to design the IP fabric sensor with reconfigurability and only two electrodes, which caters to the requirement of stable interactions and simple wiring. The multifunctionality of the IP fabric sensor is demonstrated by designing a closed-loop interactive entertainment system, a smart home system, and a user identification and verification system. This integrated system reveals the potential of combining Internet of Things technology and artificial intelligence (AI). Hopefully, the integration of the noninvasive IP fabric sensor with AI will facilitate the advancement of interactive systems for human augmentation.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available on request from the authors.
References
Topol EJ. High-performance medicine: the convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat Med. 2019;25:44.
Zheng Q, Tang Q, Wang ZL, Li Z. Self-powered cardiovascular electronic devices and systems. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021;18:7.
Wang G, Wang L, Meng Z, Su X, Jia C, Qiao X, Pan S, Chen Y, Cheng Y, Zhu M. Visual detection of COVID-19 from materials aspect. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:1304.
Azimi S, Golabchi A, Nekookar A, Rabbani S, Amiri MH, Asadi K, Abolhasani MM. Self-powered cardiac pacemaker by piezoelectric polymer nanogenerator implant. Nano Energy. 2021;83:105781.
Li Q, Nan K, Floch PL, Lin Z, Sheng H, Liu J. Cyborg organoids: implantation of nanoelectronics via organogenesis for tissue-wide electrophysiology. Nano Lett. 2019;19:5781.
Doudna JA. The promise and challenge of therapeutic genome editing. Nature. 2020;578:229.
Wu Y, Zeng J, Roscoe BP, Liu P, Yao Q, Lazzarotto CR, Clement K, Cole MA, Luk K, Baricordi C, Shen AH, Ren C, Esrick EB, Manis JP, Dorfman DM, Williams DA, Biffi A, Brugnara C, Biasco L, Brendel C, Pinello L, Tsai SQ, Wolfe SA, Bauer DE. Highly efficient therapeutic gene editing of human hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Med. 2019;25:776.
Lu G, Nishio N, van den Berg NS, Martin BA, Fakurnejad S, van Keulen S, Colevas AD, Thurber GM, Rosenthal EL. Co-administered antibody improves penetration of antibody-dye conjugate into human cancers with implications for antibody-drug conjugates. Nat Commun. 2020;11:5667.
Jenssen T, Hartmann A. Post-transplant diabetes mellitus in patients with solid organ transplants. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15:172.
Niu S, Matsuhisa N, Beker L, Li J, Wang S, Wang J, Jiang Y, Yan X, Yun Y, Burnett W, Poon ASY, Tok JBH, Chen X, Bao Z. A wireless body area sensor network based on stretchable passive tags. Nat Electron. 2019;2:361.
Zhang K, Wang J, Liu T, Luo Y, Loh XJ, Chen X. Machine learning-reinforced noninvasive biosensors for healthcare. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10:2100734.
Dan X, Cao R, Cao X, Wang Y, Xiong Y, Han J, Luo L, Yang J, Xu N, Sun J, Sun Q, Wang ZL. Whirligig-inspired hybrid nanogenerator for multi-strategy energy harvesting. Adv Fiber Mater. 2023;5:362.
Lin W, Wei C, Yu S, Chen Z, Zhang C, Guo Z, Liao Q, Wang S, Lin M, Zheng Y, Liao X, Chen Z. Programmable and ultrasensitive haptic interfaces enabling closed-loop human–machine interactions. Adv Funct Mater. 2023;33:2305919.
Liao X, Wang W, Wang L, Tang K, Zheng Y. Controllably enhancing stretchability of highly sensitive fiber-based strain sensors for intelligent monitoring. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;11:2431.
Mansouri M, Hussherr M-D, Strittmatter T, Buchmann P, Xue S, Camenisch G, Fussenegger M. Smart-watch-programmed green-light-operated percutaneous control of therapeutic transgenes. Nat Commun. 2021;12:3388.
Wan C, Cai P, Guo X, Wang M, Matsuhisa N, Yang L, Lv Z, Luo Y, Loh XJ, Chen X. An artificial sensory neuron with visual-haptic fusion. Nat Commun. 2020;11:4602.
Liao X, Song W, Zhang X, Yan C, Li T, Ren H, Liu C, Wang Y, Zheng Y. A bioinspired analogous nerve toward artificial intelligence. Nat Commun. 2020;11:268.
Ye C, Yang S, Ren J, Dong S, Cao L, Pei Y, Ling S. Electroassisted core-spun triboelectric nanogenerator fabrics for intellisense and artificial intelligence perception. ACS Nano. 2022;16:4415.
Shi X, Zuo Y, Zhai P, Shen J, Yang Y, Gao Z, Liao M, Wu J, Wang J, Xu X, Tong Q, Zhang B, Wang B, Sun X, Zhang L, Pei Q, Jin D, Chen P, Peng H. Large-area display textiles integrated with functional systems. Nature. 2021;591:240.
Yao M, Zhou R, Yuan M, Wang H, Wang L, Sun H, Fu Y, Xiao R, Wang H, Wang G, Zhu M. Multifunctional semiconducting fibers for visual detection of sarin gas. Adv Fiber Mater. 2023;5:1632.
Li X, Chen L, Yuan S, Tong H, Cheng Q, Zeng H, Wei L, Zhang Q. Stretchable luminescent perovskite-polymer hydrogels for visual-digital wearable strain sensor textiles. Adv Fiber Mater. 2023;5:1671.
Liao X, Song W, Zhang X, Huang H, Wang Y, Zheng Y. Directly printed wearable electronic sensing textiles toward human–machine interfaces. J Mater Chem C. 2018;6:12841.
Yu M, Lyu W, Liao Y, Zhu M. Snakeskin-inspired hierarchical winkled surface for ultradurable superamphiphobic fabrics via short-fluorinated polymer reactive infusion. Adv Fiber Mater. 2023;5:543.
Yin L, Kim KN, Lv J, Tehrani F, Lin M, Lin Z, Moon J-M, Ma J, Yu J, Xu S, Wang J. A self-sustainable wearable multi-modular E-textile bioenergy microgrid system. Nat Commun. 2021;12:1542.
Zhou Z, Chen K, Li X, Zhang S, Wu Y, Zhou Y, Meng K, Sun C, He Q, Fan W, Fan E, Lin Z, Tan X, Deng W, Yang J, Chen J. Sign-to-speech translation using machine-learning-assisted stretchable sensor arrays. Nat Electron. 2020;3:571.
Liao X, Wang W, Lin M, Li M, Wu H, Zheng Y. Hierarchically distributed microstructure design of haptic sensors for personalized fingertip mechanosensational manipulation. Mater Horiz. 2018;5:920.
Sundaram S, Kellnhofer P, Li Y, Zhu J-Y, Torralba A, Matusik W. Learning the signatures of the human grasp using a scalable tactile glove. Nature. 2019;569:698.
Lin Z, Yang J, Li X, Wu Y, Wei W, Liu J, Chen J, Yang J. Large-scale and washable smart textiles based on triboelectric nanogenerator arrays for self-powered sleeping monitoring. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28:1704112.
Fan W, He Q, Meng K, Tan X, Zhou Z, Zhang G, Yang J, Wang ZL. Machine-knitted washable sensor array textile for precise epidermal physiological signal monitoring. Sci Adv. 2020;6:eaay2840.
Pang Y, Xu X, Chen S, Fang Y, Shi X, Deng Y, Wang ZL, Cao C. Skin-inspired textile-based tactile sensors enable multifunctional sensing of wearables and soft robots. Nano Energy. 2022;96: 107137.
Hwang S, Kang M, Lee A, Bae S, Lee S-K, Lee SH, Lee T, Wang G, Kim T-W. Integration of multiple electronic components on a microfibre toward an emerging electronic textile platform. Nat Commun. 2022;13:3173.
Peng J, Snyder GJ. A figure of merit for flexibility. Science. 2019;366:690.
Liao X, Liao Q, Yan X, Liang Q, Si H, Li M, Wu H, Cao S, Zhang Y. Flexible and highly sensitive strain sensors fabricated by pencil drawn for wearable monitor. Adv Funct Mater. 2015;25:2395.
Wen F, Sun Z, He T, Shi Q, Zhu M, Zhang Z, Li L, Zhang T, Lee C. Machine learning glove using self-powered conductive superhydrophobic triboelectric textile for gesture recognition in VR/AR applications. Adv Sci. 2020;7:2000261.
Zhang Q, Jin T, Cai J, Xu L, He T, Wang T, Tian Y, Li L, Peng Y, Lee C. Wearable triboelectric sensors enabled gait analysis and waist motion capture for IoT-based smart healthcare applications. Adv Sci. 2022;9:2103694.
Wu C, Ding W, Liu R, Wang J, Wang AC, Wang J, Li S, Zi Y, Wang ZL. Keystroke dynamics enabled authentication and identification using triboelectric nanogenerator array. Mater Today. 2018;21:216.
Maharjan P, Shrestha K, Bhatta T, Cho H, Park C, Salauddin M, Rahman MT, Rana SS, Lee S, Park JY. Keystroke dynamics based hybrid nanogenerators for biometric authentication and identification using artificial intelligence. Adv Sci. 2021;8:2100711.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (52202117), Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (2022J01065), Collaborative Innovation Platform Project of Fu-Xia-Quan National Independent Innovation Demonstration Zone (3502ZCQXT2022005), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (20720220075).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file 1 (MP4 2811 kb)
Supplementary file 2 (MP4 4799 kb)
Supplementary file 3 (MP4 3112 kb)
Supplementary file 4 (MP4 4089 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Lin, W., Zhang, C. et al. Multifunctional and Reconfigurable Electronic Fabrics Assisted by Artificial Intelligence for Human Augmentation. Adv. Fiber Mater. 6, 229–242 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00350-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00350-z