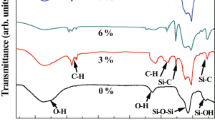
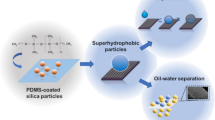
Abstract
Highly stable hydrophobic silica-based membranes were successfully fabricated through chemical post-modification of directly electrospun silica nanofibrous membranes. Five different Si-alkoxy chlorides were tried as reagents at room temperature, allowing for an easy two-step production process. Trimethylchlorosilane (TMCS) was determined as to be the most suitable modifier, for this purpose. The modified membrane exhibits long-term hydrophobicity even under high humidity and water submersion, maintaining this property after exposure to elevated temperatures and acidic conditions, surpassing the unmodified membrane. The separation effectiveness for immiscible water/solvent solutions was proven, followed by an investigation into the relation between the surface tension of some miscible water/solvent solutions and the resulting wetting behavior of the TMCS-modified membrane, to utilize the membrane as a process intensification tool, specifically as a solvent gate.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
References
Wae AbdulKadir WAF, Ahmad AL, Seng OB, Che Lah NF. Biomimetic hydrophobic membrane: a review of anti-wetting properties as a potential factor in membrane development for membrane distillation (MD). J Ind Eng Chem. 2020;91:15–36.
Xu D, Zhu Z, Li J. Recent progress in electrospun nanofibers for the membrane distillation of hypersaline wastewaters. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:6:1357–1374.
Kiani A, Bhave RR, Sirkar KK. Solvent extraction with immobilized interfaces in a microporous hydrophobic membrane. J Memb Sci. 1984;20:125–45.
Kujawska A, Knozowska K, Kujawa J, Li G, Kujawski W. Fabrication of PDMS based membranes with improved separation efficiency in hydrophobic pervaporation. Sep Purif Technol. 2020;234: 116092.
Kujawa J, Cerneaux S, Kujawski W. Removal of hazardous volatile organic compounds from water by vacuum pervaporation with hydrophobic ceramic membranes. J Memb Sci. 2015;474:11–9.
Qian X, Sun F, Sun J, Wu H, Xiao F, Wu X, et al. Imparting surface hydrophobicity to metal-organic frameworks using a facile solution-immersion process to enhance water stability for CO2 capture. Nanoscale. 2017;9:2003–8.
Rosli A, Ahmad AL, Low SC. Anti-wetting polyvinylidene fluoride membrane incorporated with hydrophobic polyethylene-functionalized-silica to improve CO2 removal in membrane gas absorption. Sep Purif Technol. 2019;221:275–85.
Hwang SH, Song JY, Il RH, Oh JH, Lee S, Lee D, et al. Adaptive electrospinning system based on reinforcement learning for uniform-thickness nanofiber air filters. Adv Fib Mater. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00247-3.
Ramakrishna S, Fujihara K, Teo WE, Lim T-C, Ma Z. An introduction to electrospinning and nanofibers. World Scientific; 2005.
Pan CY, Xu GR, Xu K, Zhao HL, Wu YQ, Su HC, et al. Electrospun nanofibrous membranes in membrane distillation: recent developments and future perspectives. Sep Purif Technol. 2019;221:44–63.
De Keer L, Kilic KI, Van Steenberge PHM, Daelemans L, Kodura D, Frisch H, et al. Computational prediction of the molecular configuration of three-dimensional network polymers. Nat Mater. 2021;20:1422–30.
Scaffaro R, Gulino EF, Citarrella MC. Biodegradable membrane with high porosity and hollow structure obtained via electrospinning for oil spill clean-up application. J Polym Environ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-02876-0.
Wendorff JH, Agarwal S, Greiner A. Electrospinning: materials, processing and applications. John Wiley & Sons; 2012.
Efome JE, Rana D, Matsuura T, Lan CQ. Experiment and modeling for flux and permeate concentration of heavy metal ion in adsorptive membrane filtration using a metal-organic framework incorporated nanofibrous membrane. Chem Eng J. 2018;352:737–44.
Su CI, Shih JH, Huang MS, Wang CM, Shih WC, Liu Y, sheng,. A study of hydrophobic electrospun membrane applied in seawater desalination by membrane distillation. Fib Polym. 2012;13:698–702.
Zhu Z, Li Z, Zhong L, Zhang R, Cui F, Wang W. Dual-biomimetic superwetting silica nanofibrous membrane for oily water purification. J Memb Sci. 2019;572:73–81.
Wang Y, Di J, Wang L, Li X, Wang N, Wang B, et al. Infused-liquid-switchable porous nanofibrous membranes for multiphase liquid separation. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1–7.
Padaki M, Surya Murali R, Abdullah MS, Misdan N, Moslehyani A, Kassim MA, et al. Membrane technology enhancement in oil-water separation. A review. Desalination. 2015;357:197–207.
Doshi J, Reneker DH. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. Conf Record IAS Annual Meet (IEEE Ind Appl Soc). 1993;3:1698–703.
Li D, Xia Y. Direct fabrication of composite and ceramic hollow nanofibers by electrospinning. Nano Lett. 2004;4:933–8.
Schoolaert E, Cossu L, Becelaere J, Van Guyse JFR, Tigrine A, Vergaelen M, et al. Nanofibers with a tunable wettability by electrospinning and physical crosslinking of poly(2-n-propyl-2-oxazoline). Mater Des. 2020;192:108747.
Commarieu B, Paolella A, Daigle JC, Zaghib K. Toward high lithium conduction in solid polymer and polymer–ceramic batteries. Curr Opin Electrochem. 2018;9:56–63.
Esfandiari N, Kashefi M, Mirjalili M, Afsharnezhad S. Role of silica mid-layer in thermal and chemical stability of hierarchical Fe3O4–SiO2–TiO2 nanoparticles for improvement of lead adsorption: Kinetics, thermodynamic and deep XPS investigation. Mater Sci Eng B Solid State Mater Adv Technol. 2020;262:114690.
Li J, Zhang X, Lu Y, Linghu K, Wang C, Ma Z, et al. Electrospun fluorinated polyimide/polyvinylidene fluoride composite membranes with high thermal stability for lithium ion battery separator. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:1:108–18.
Amin SK, Abdallah HAM, Roushdy MH, El-Sherbiny SA. An overview of production and development of ceramic membranes. Int J Appl Eng Res. 2016;11:7708–21.
Li JJ, Zhou YN, Jiang ZD, Luo ZH. Electrospun fibrous mat with pH-switchable superwettability that can separate layered oil/water mixtures. Langmuir. 2016;32:13358–66.
Swanckaert B, Verschatse O, Loccufier E, De Buysser K, Daelemans L, De Clerck K. Chemical and structural induced ductile-to-brittle transition in electrospun silica nanofiber membranes. Ceram Int. 2023;49:33305.
Geltmeyer J, Van Der Schueren L, Goethals F, De Buysser K, De Clerck K. Optimum sol viscosity for stable electrospinning of silica nanofibres. J Solgel Sci Technol. 2013;67:188–95.
Geltmeyer J, De Roo J, Van den Broeck F, Martins JC, De Buysser K, De Clerck K. The influence of tetraethoxysilane sol preparation on the electrospinning of silica nanofibers. J Solgel Sci Technol. 2016;77:453–62.
Verschatse O, Loccufier E, Swanckaert B, De Clerck K, Daelemans L. Microscale and macroscale deformation behavior of electrospun polymeric nanofiber membranes using in situ sem during mechanical testing. Polym (Basel). 2023;15:1630.
Lee SW, Kim YU, Choi SS, Park TY, Joo YL, Lee SG. Preparation of SiO2/TiO2 composite fibers by sol-gel reaction and electrospinning. Mater Lett. 2007;61:889–93.
Jia C, Xu Z, Luo D, Xiang H, Zhu M. Flexible ceramic fibers: recent development in preparation and application. Adv Fib Mater Springer. 2022;4:573–603.
Chen X, Cao H, He Y, Zhou Q, Li Z, Wang W, et al. Advanced functional nanofibers: strategies to improve performance and expand functions. Front Optoelectron. 2022;15:50.
Loccufier E, Geltmeyer J, Daelemans L, D’hooge DR, De Buysser K, De Clerck K. Silica nanofibrous membranes for the separation of heterogeneous azeotropes. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28:1–10.
Geltmeyer J, Vancoillie G, Steyaert I, Breyne B, Cousins G, Lava K, et al. Dye modification of nanofibrous silicon oxide membranes for colorimetric HCl and NH3 sensing. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26:5987–96.
Zhuravlev LT. The surface chemistry of amorphous silica. Zhuravlev model. Coll Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2000;173:1–38.
Hooda A, Goyat MS, Pandey JK, Kumar A, Gupta R. A review on fundamentals, constraints and fabrication techniques of superhydrophobic coatings. Prog Org Coat. 2020;142:105557.
Meng LY, Han S, Jiang N, Meng W. Study on superhydrophobic surfaces of octanol grafted electrospun silica nanofibers. Mater Chem Phys. 2014;148:798–802.
Guo M, Ding B, Li X, Wang X, Yu J, Wang M. Amphiphobic nanofibrous silica mats with flexible and high-heat-resistant properties. J Phys Chem C. 2010;114:916–21.
Zhao F, Wang X, Ding B, Lin J, Hu J, Si Y, et al. Nanoparticle decorated fibrous silica membranes exhibiting biomimetic superhydrophobicity and highly flexible properties. RSC Adv. 2011;1:1482–8.
Li JJ, Zhou YN, Luo ZH. Polymeric materials with switchable superwettability for controllable oil/water separation: a comprehensive review. Prog Polym Sci. 2018;87:1–33.
Gao S, Watanabe H, Nakane K, Zhao K. Fabrication and characterization of superhydrophobic and superlipophilic silica nanofibers mats with excellent heat resistance. J Min Metall Sect B. 2016;52:87–92.
Yao Y, Cao J, Yang M, Li J, Zhao S, Yin W, et al. Exploration of the novel stacked structure and one-step fabrication of electrospun silica microbelts with controllable wettability. RSC Adv. 2013;3:12026.
Ahmad NA, Leo CP, Ahmad AL, Ramli WKW. Membranes with great hydrophobicity: a review on preparation and characterization. Sep Purif Rev. 2015;44:109–34.
Wei Z, Li J, Wang C, Cao J, Yao Y, Lu H, et al. Thermally stable hydrophobicity in electrospun silica/polydimethylsiloxane hybrid fibers. Appl Surf Sci. 2017;392:260–7.
Wang L, Zhao Y, Tian Y, Jiang L. A general strategy for the separation of immiscible organic liquids by manipulating the surface tensions of nanofibrous membranes. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2015;54:14732–7.
Loccufier E, Geltmeyer J, Daelemans L, D’hooge DR, De Buysser K, De Clerck K. Silica nanofibrous membranes for the separation of heterogeneous azeotropes. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28:1–10.
Shewale PM, Rao AV, Rao AP. Effect of different trimethyl silylating agents on the hydrophobic and physical properties of silica aerogels. Appl Surf Sci. 2008;254:6902–7.
Sea BK, Ando K, Kusakabe K, Morooka S. Separation of hydrogen from steam using a SiC-based membrane formed by chemical vapor deposition of triisopropylsilane. J Memb Sci. 1998;146:73–82.
Roostaie A, Bargozin H, Mohammadiazar S, Ehteshami S. Nanoporous silica aerogel modified by triethylchlorosilane as a new sorbent for the needle-trap extraction. Sep Sci Plus. 2018;1:76–82.
Wonnacott DM, Patton EV. Hydrolytic stability of aminopropyl stationary phases used in the size-exclusion chromatography of cationic polymers. J Chromatogr A. 1987;389:103–13.
Arase H, Taniguchi K, Kai T, Murakami K, Adachi Y, Ooyama Y, et al. Hydrophobic modification of SiO2 surface by aminosilane derivatives. Compos Interfaces. 2019;26:15–25.
Zhao XS, Lu GQ. Modification of MCM-41 by surface silylation with trimethylchlorosilane and adsorption study. J Phys Chem B. 1998;102:1556–61.
Nebergall WH, Johnson OH. Some steric effects of the cyclohexyl group in organosilicon compounds. J Am Chem Soc. 1949;71:4022–4.
Dillon AC, Robinson MB, George SM, Roberts DA. Adsorption and decomposition of diethylgermane on porous silicon surfaces. Surf Sci. 1993;286:L535.
Xue Z, Wang S, Lin L, Chen L, Liu M, Feng L, et al. A novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic hydrogel-coated mesh for oil/water separation. Adv Mater. 2011;23:4270–3.
Gupta RK, Dunderdale GJ, England MW, Hozumi A. Oil/water separation techniques: a review of recent progresses and future directions. J Mater Chem A Mater. 2017;5:16025–58.
Yong J, Bai X, Yang Q, Hou X, Chen F. Filtration and removal of liquid polymers from water (polymer/water separation) by use of the underwater superpolymphobic mesh produced with a femtosecond laser. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021;582:1203–12.
Schoolaert E, Cossu L, Becelaere J, Van Guyse JFR, Tigrine A, Vergaelen M, et al. Nanofibers with a tunable wettability by electrospinning and physical crosslinking of poly(2-n-propyl-2-oxazoline). Mater Des. 2020;192:108747.
Seyed Shahabadi SM, Brant JA. Bio-inspired superhydrophobic and superoleophilic nanofibrous membranes for non-aqueous solvent and oil separation from water. Sep Purif Technol. 2019;210:587–99.
Vasanth D, Pugazhenthi G, Uppaluri R. Fabrication and properties of low cost ceramic microfiltration membranes for separation of oil and bacteria from its solution. J Memb Sci. 2011;379:154–63.
El Mourabit S, Guillot M, Toquer G, Cambedouzou J, Goettmann F, Grandjean A. Stability of mesoporous silica under acidic conditions. RSC Adv. 2012;2:10916–24.
Loccufier E, Deventer K, Manhaeghe D, Van Hulle SWH, D’hooge DR, De Buysser K, et al. Degradation kinetics of isoproturon and its subsequent products in contact with TiO2 functionalized silica nanofibers. Chem Eng J. 2020;387:124143.
Wang J, Wang L. Superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic nanofibrous membrane for separation of oil/water emulsions. J Mater Res. 2020;35:1504–13. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.137.
Guo Y, Li M, Wen X, Guo X, Zhang T. Silica-modified electrospun membrane with underwater superoleophobicity for effective gravity-driven oil/water separation. Fibers Polym. 2022;23:1906–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-022-4039-x.
Su Y, Fan T, Cui W, Li Y, Ramakrishna S, Long Y. Advanced electrospun nanofibrous materials for efficient oil/water separation. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:5:938–958.
Oh S, Bang J, Jin HJ, Kwak HW. Green fabrication of underwater superoleophobic biopolymeric nanofibrous membranes for effective oil–water separation. Adv Fiber Mater. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00251-7.
Luzar A, Svetina S, Žekš B. The contribution of hydrogen bonds to the surface tension of water. Chem Phys Lett. 1983;6:4:85–490.
Vazquez G, Alvarez E, Navaza JM. Surface tension of alcohol + water from 20 to 50 °C. J Chem Eng Data. 1995;40:611–4.
Howard KS, McAllister RA. Surface tension of acetone-water solutions up to their normal boiling points. AIChE J. 1958;4:362–6.
Acknowledgements
M.L. appreciates funding from the China Scholarship Council (Grant No. 201608230115) for the Ph.D. study at Ghent University. This Research Foundation Flanders (FWO) is gratefully acknowledged by E.L. for funding the research through an SB PhD grant under Grant No. 1S82920N. The authors would like to thank the NMR expertise centre (Ghent University) for providing support and access to its NMR infrastructure. The 300 MHz used in this work has been funded by grants from the FWO. K.D.C. thanks the Special Research Fund Ghent University (BOF) for the grants BOF.BAS.2018.0015.01 and BOF19/24J/102. The authors would like to thank Prof. Dolores Esquivel from the University of Cordoba for making possible the 29Si solid-state NMR measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Loccufier, E., Geltmeyer, J. et al. Playing with Chlorine-Based Post-modification Strategies for Manufacturing Silica Nanofibrous Membranes Acting as Stable Hydrophobic Separation Barriers. Adv. Fiber Mater. 6, 145–157 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00335-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00335-y