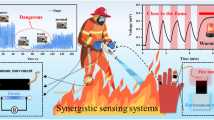
Abstract
Wearable piezoresistive sensors have shown enormous application prospects in flexible electronics and human–machine interfaces. However, current piezoresistive sensors suffer from common deficiencies including high fabrication cost, poor comfort and low attachment fastness of conductive substances on substrates, thereby impeding their large-scale production and practical use. Herein, a three-dimensional all-fabric piezoresistive sensor is reported based on coating multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) on bicomponent nonwovens composed of core-sheath fibers. The combination of core-sheath fibers with a heat-induced welding strategy greatly improves the adhesion fastness and stability of MWCNT network. The multi-layered all-fabric structure provides as-prepared sensors with high sensitivity (9.43% kPa−1 in 0–10 kPa and 0.076% kPa−1 in 20–120 kPa), wide pressure-sensing range (0–120 kPa), fast response/relaxation time (100 and 60 ms), good reproducibility and air permeability. Application of the sensor is demonstrated through the detection of human activities (such as pulse, cough and joint movements) and the wireless monitoring of forefinger bending. Moreover, our sensor is fabricated out of cost-effective materials, using scalable approach without using glue or binders. The method established in this work may provide an efficient strategy for the design and production of high-performance all-fabric piezoresistive sensors.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Tang XY, Yang WD, Yin SR, Tai GJ, Su M, Yang J, Shi HF, Wei DP, Yang J. Controllable graphene wrinkle for a high-performance flexible pressure sensor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13:20448.
Wang N, Yang X, Zhan XX. Ultrarobust subzero healable materials enabled by polyphenol nano-assemblies. Nat Commun. 2023;14:814.
Lee S, Kim J, Yun I, Bae G, Kim D, Park S, Yi IL-M, Moon W, Chung Y, Cho K. An ultrathin conformable vibration-responsive electronic skin for quantitative vocal recognition. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2468.
Luo Y, Miao YP, Wang HM, Dong K, Hou L, Xu YY, Chen WC, Zhang Y, Zhang YY, Fan W. Laser-induced Janus graphene/poly(p-phenylene benzobisoxazole) fabrics with intrinsic flame retardancy as flexible sensors and breathable electrodes for fire-fighting field. Nano Res. 2023;16:760.
Wang Y, Shu R, Zhang XX. Strong, supertough and self-healing biomimetic layered nanocomposites enabled by reversible interfacial polymer chain sliding. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2023;62: e202303446.
Lu DX, Liao SQ, Chu Y, Cai YB, Wei QF, Chen KL, Wang QQ. Highly durable and fast response fabric strain sensor for movement monitoring under extreme conditions. Adv Fiber Mater. 2023;5:223.
Feng B, Zou GS, Wang WG, Dong MG, Xiao Y, Ren H, Zhao XL, Zhao GL, Wu AP, Zhu HW, Liu L. A programmable, gradient-composition strategy producing synergistic and ultrahigh sensitivity amplification for flexible pressure sensing. Nano Energy. 2020;74: 104847.
He YX, Wu DY, Zhou MY, Zheng YJ, Wang TF, Lu C, Zhang L, Liu H, Liu CT. Wearable strain sensors based on a porous polydimethylsiloxane hybrid with carbon nanotubes and graphene. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13:15572.
Xu DW, Ouyang ZF, Dong YJ, Yu HY, Zheng S, Li SH, Tam KC. Robust, breathable and flexible smart textiles as multifunctional sensor and heater for personal health management. Adv Fiber Mater. 2023;5:282.
Han ST, Peng HY, Sun QJ, Venkatesh SS, Chung KS, Lau SC, Zhou Y, Roy VAL. An overview of the development of flexible sensors. Adv Mater. 2017;29:1700375.
Wang L, Huang XW, Wang D, Zhang WM, Gao SJ, Luo JC, Guo Z, Xue HG, Gao JF. Lotus leaf inspired superhydrophobic rubber composites for temperature stable piezoresistive sensors with ultrahigh compressibility and linear working range. Chem Eng J. 2021;405: 127025.
Wang L, Wang D, Wu ZF, Luo JC, Huang XW, Gao Q, Lai XJ, Tang LC, Xue HG, Gao JF. Self-derived superhydrophobic and multifunctional polymer sponge composite with excellent joule heating and photothermal performance for strain/pressure sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12:13316.
Zhou HW, Wang ZW, Zhao WF, Tong XM, Jin XL, Zhang XC, Yu Y, Liu HB, Ma YC, Li SS, Chen WX. Robust and sensitive pressure/strain sensors from solution processable composite hydrogels enhanced by hollow-structured conducting polymers. Chem Eng J. 2021;403: 126307.
Jung S, Kim JH, Kim J, Choi S, Lee J, Park I, Hyeon T, Kim DH. Reverse-micelle-induced porous pressure-sensitive rubber for wearable human-machine interfaces. Adv Mater. 2014;26:4825.
Ma C, Wang M, Wang K, Uzabakiriho PC, Chen X, Zhao G. Ultrasensitive, highly selective, integrated multidimensional sensor based on a rigid-flexible synergistic stretchable substrate. Adv Fiber Mater. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00274-8.
Du DH, Tang ZH, Ouyang JY. Highly washable e-textile prepared by ultrasonic nanosoldering of carbon nanotubes onto polymer fibers. J Mater Chem C. 2018;6:883.
Lu YJ, Tian MW, Sun XT, Pan N, Chen FX, Zhu SF, Zhang XS, Chen SJ. Highly sensitive wearable 3D piezoresistive pressure sensors based on graphene coated isotropic non-woven substrate. Compos Part A: Appl S. 2019;117:202.
Fu XY, Li JZ, Li DD, Zhao LJ, Yuan ZY, Shulga V, Han W, Wang LL. MXene/ZIF-67/PAN nanofiber film for ultra-sensitive pressure sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14:12367.
Peng SH, Wu SY, Yu YY, Xia BJ, Lovell NH, Wang CH. Multimodal capacitive and piezoresistive sensor for simultaneous measurement of multiple forces. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12:22179.
Li MF, Chen JX, Zhong WB, Luo MY, Wang W, Qing X, Lu Y, Liu QZ, Liu K, Wang YD, Wang D. Large-area, wearable, self-powered pressure-temperature sensor based on 3D thermoelectric spacer fabric. ACS Sens. 2020;5:2545.
Yang T, Deng WL, Chu X, Wang X, Hu YT, Fan X, Song J, Gao YY, Zhang BB, Tian G, Xiong D, Zhong S, Tang LH, Hu YH, Yang WQ. Hierarchically microstructure-bioinspired flexible piezoresistive bioelectronics. ACS Nano. 2021;15:11555.
Cheng YF, Ma YN, Li LY, Zhu M, Yue Y, Liu WJ, Wang LF, Jia SF, Li C, Qi TY, Wang JB, Gao YH. Bioinspired microspines for a high-performance spray Ti3C2TX MXene-based piezoresistive sensor. ACS Nano. 2020;14:2145.
Zhang H, Liu NS, Shi YL, Liu WJ, Yue Y, Wang SL, Ma YN, Wen L, Li LY, Long F, Zou ZG, Gao YH. Piezoresistive sensor with high elasticity based on 3D hybrid network of Sponge@CNTs@Ag NPs. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8:22374.
Guo Y, Zhong MJ, Fang ZW, Wan PB, Yu GH. A Wearable transient pressure sensor made with MXene nanosheets for sensitive broad-range human-machine interfacing. Nano Lett. 2019;19:1143.
Wang SJ, Meng WY, Lv HF, Wang ZX, Pu JW. Thermal insulating, light-weight and conductive cellulose/aramid nanofibers composite aerogel for pressure sensing. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;270: 118414.
Zou BH, Chen YY, Liu YH, Xie RJ, Du QJ, Zhang T, Shen Y, Zheng B, Li S, Wu JS, Zhang WN, Huang W, Huang X, Huo FW. Repurposed leather with sensing capabilities for multifunctional electronic skin. Adv Sci. 2019;6:1801283.
Li SM, Wu GZ, Hu YJ, Fang MQ, He LX, He Y, Xiao XL. Preparation of pressure distribution monitoring socks and related sensing properties. Fangzhi Xuebao/J Text Res. 2019;40:138.
Ma JJ, Zhang N, Cheng Y, Kou XR, Niu YW, Jin XY, Ke QF, Zhao Y. Green fabrication of multifunctional three-dimensional superabsorbent nonwovens with thermo-bonding fibers. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:293.
Fan W, Zhang C, Liu Y, Wang SJ, Dong K, Li Y, Wu F, Liang JH, Wang CL, Zhang YY. An ultra-thin piezoelectric nanogenerator with breathable, superhydrophobic, and antibacterial properties for human motion monitoring. Nano Res. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5413-8.
Tian MW, Li ZQ, Lu YJ, Zhu SF, Zhang XS, Qu LJ. Recent progress of textile-based flexible mechanical sensors. Fangzhi Xuebao/J Text Res. 2018;39:170.
Shi YH, Tian GL, Ni RY, Zhang L, Hu WF, Zhao Y. Facile and green lyocell/feather nonwovens with in-situ growth of ZIF-8 as adsorbent for physicochemical CO2 capture. Sep Purif Technol. 2023;322: 124356.
Zhang L, Li HQ, Lai XJ, Gao TY, Yang J, Zeng XR. Thiolated graphene@polyester fabric-based multilayer piezoresistive pressure sensors for detecting human motion. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:41784.
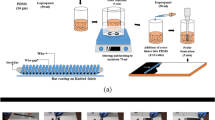
Tian GL, Zhan L, Deng JX, Liu HG, Li J, Ma JJ, Jin XY, Ke QF, Huang C. Coating of multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) on three-dimensional, bicomponent nonwovens as wearable and high-performance piezoresistive sensors. Chem Eng J. 2021;425: 130682.
Yang LY, Ma J, Zhong WB, Liu QZ, Li MF, Wang W, Wu Y, Wang YD, Liu X, Wang D. Highly accurate fabric piezoresistive sensor with anti-interference from both high humidity and sweat based on hydrophobic non-fluoride titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Mater Chem C. 2021;9:5217.
Ma C, Yuan Q, Du HS, Ma MG, Si CL, Wan PB. Multiresponsive MXene (Ti3C2TX)-decorated textiles for wearable thermal management and human motion monitoring. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12:34226.
Cao XY, Zhang J, Chen SW, Varley RJ, Pan K. 1D/2D nanomaterials synergistic, compressible, and response rapidly 3D graphene aerogel for piezoresistive sensor. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30:2003618.
Liu MM, Pu X, Jiang CY, Liu T, Huang X, Chen LB, Du CH, Sun JM, Hu WG, Wang ZL. Large-area all-textile pressure sensors for monitoring human motion and physiological signals. Adv Mater. 2017;29:1703700.
Zheng YJ, Yin R, Zhao Y, Liu H, Zhang DB, Shi XZ, Zhang B, Liu CT, Shen CY. Conductive MXene/cotton fabric based pressure sensor with both high sensitivity and wide sensing range for human motion detection and E-skin. Chem Eng J. 2021;420: 127720.
Zhu SM, Kang ZX, Wang F, Long Y. Copper nanoparticle decorated non-woven polypropylene fabrics with durable superhydrophobicity and conductivity. Nanotechnology. 2021;32: 035701.
Hasan MM, Zhu FC, Ahmed A, Khoso NA, Deb H, Lai YC, Islam MZ, Sun H, Yu B. Functionalization of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics using cold plasma (O2) for developing graphene-based wearable sensors. Sensor Actuat A-Phys. 2019;300: 111637.
Jiao KY, Zhu T, Li XH, Shan MJ, Xu ZW, Jiao YN. Assembly of graphene oxide on nonconductive nonwovens by the synergistic effect of interception and electrophoresis. J Nanopart Res. 2015;17:373.
Li YJ, Nie M, Wang Q. Facile fabrication of electrically conductive low-density polyethylene/carbon fiber tubes for novel smart materials via multiaxial orientation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:1005.
Weng BC, Xu FH, Salina A, Lozano K. Mass production of carbon nanotube reinforced poly(methyl methacrylate) nonwoven nanofiber mats. Carbon. 2014;75:217.
Liu H, Li QM, Bu YB, Zhang N, Wang CF, Pan CF, Mi LW, Guo ZH, Liu CT, Shen CY. Stretchable conductive nonwoven fabrics with self-cleaning capability for tunable wearable strain sensor. Nano Energy. 2019;66: 104143.
Jiang XP, Ren ZL, Fu YF, Liu YF, Zou R, Ji GP, Ning HM, Li YQ, Wen J, Qi HJ, Xu CH, Fu SY, Qiu JH, Hu N. Highly compressible and sensitive pressure sensor under large strain based on 3D porous reduced graphene oxide fiber fabrics in wide compression strains. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11:37051.
Tao LQ, Zhang KN, Tian H, Liu Y, Wang DY, Chen YQ, Yang Y, Ren TL. Graphene-paper pressure sensor for detecting human motions. ACS Nano. 2017;11:8790.
Kim KH, Hong SK, Jang NS, Ha SH, Lee HW, Kim JM. Wearable resistive pressure sensor based on highly flexible carbon composite conductors with irregular surface morphology. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:17499.
Guo Y, Guo ZY, Zhong MJ, Wan PB, Zhang WX, Zhang LQ. A flexible wearable pressure sensor with bioinspired microcrack and interlocking for full-range human-machine interfacing. Small. 2018;14:1803018.
Lee JH, Kim E, Zhang H, Chen HM, Venkatesan H, Chan KY, Yang J, Shen X, Yang JL, Jeon S, Kim JK. Rational design of all resistive multifunctional sensors with stimulus discriminability. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;32:2107570.
Chun SW, Son W, Choi C. Flexible pressure sensors using highly-oriented and free-standing carbon nanotube sheets. Carbon. 2018;139:586.
Song Y, Chen HT, Su ZM, Chen XX, Miao LM, Zhang JX, Cheng XL, Zhang HX. Highly compressible integrated supercapacitor-piezoresistance-sensor system with CNT-PDMS sponge for health monitoring. Small. 2017;13:1702091.
Yao HB, Ge J, Wang CF, Wang X, Hu W, Zheng ZJ, Ni Y, Yu SH. A flexible and highly pressure-sensitive graphene-polyurethane sponge based on fractured microstructure design. Adv Mater. 2013;25:6692.
Zhao X, Wang WL, Wang Z, Wang JG, Huang T, Dong J, Zhang QH. Flexible PEDOT: PSS/polyimide aerogels with linearly responsive and stable properties for piezoresistive sensor applications. Chem Eng J. 2020;395: 125115.
Liu H, Chen XY, Zheng YJ, Zhang DB, Zhao Y, Wang CF, Pan CF, Liu CT, Shen CY. Lightweight, superelastic, and hydrophobic polyimide nanofiber/MXene composite aerogel for wearable piezoresistive sensor and oil/water separation applications. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31:2008006.
Wu XD, Han YY, Zhang XX, Zhou ZH, Lu CH. Large-area compliant, low-cost, and versatile pressure-sensing platform based on microcrack-designed carbon black@polyurethane sponge for human-machine interfacing. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26:6246.
Lu LJ, Jiang CP, Hu GS, Liu JQ, Yang B. Flexible noncontact sensing for human-machine interaction. Adv Mater. 2021;33:2100218.
Acknowledgements
Financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32271378), Henan Key Laboratory of Medical and Protective Products (No. YDFH-2022-KF-02), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and Graduate Student Innovation Fund of Donghua University (CUSF-DH-D-2020019) are acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MP4 2005 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, G., Shi, Y., Deng, J. et al. Low-Cost, Scalable Fabrication of All-Fabric Piezoresistive Sensors via Binder-Free, In-Situ Welding of Carbon Nanotubes on Bicomponent Nonwovens. Adv. Fiber Mater. 6, 120–132 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00331-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00331-2