Abstract
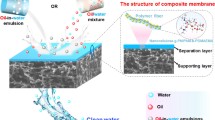
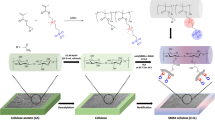
With the increasingly urgent demand for clean water resources and the growing emission of oily wastewater, high-flux oil/water separation materials with the special wettability are progressively desired. Cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) from renewable biomass has been utilized to fabricate oil/water separation membranes, but it is limited to enhancing mechanical properties. Herein, a wrinkled structure with abundant –OH is constructed on polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibers via the CNC hybridization process. And then, a super-hydrophilic nano-TiO2 shell is anchored tightly on the surface of the fiber by wrinkles and –OH. The CNC promotes significantly the in situ growth of TiO2, with the TiO2 loading ratio of up to 5.3%. The nano-TiO2 shell endows the obtained film with super-hydrophilicity and underwater super-oleophobicity, resulting in a visible increase of the permeation flux for the oil/water mixture from 1483 to 11,023 L m−2 h−1. Interestingly, the hierarchical structure facilitates the demulsification for oil-in-water emulsion stabilized by surfactant, allowing the obtained membrane to exhibit eminent antifouling property and high emulsion permeability of about 3,278 L m−2 h−1. This design strategy develops next-generation anchors for targeted modification on the non-reactive substrates and provides a novel pathway for fabricating oil/water separation membranes.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author (Wanli Cheng) upon reasonable request.
References
Guo Z, Biao L, Gao SJ, Luo JC, Wang L, Huang XW, Wang D, Xue HG, Gao JF. Carbon nanofiber based superhydrophobic foam composite for high performance oil/water separation. J Hazard Mater. 2021;402: 123838.
Ge J, Shi LA, Wang YC, Zhao HY, Yao HB, Zhu YB, Zhang Y, Zhu HW, Wu HA, Yu SH. Joule-heated graphene-wrapped sponge enables fast clean-up of viscous crude-oil spill. Nat Nanotechnol. 2017;12:434–40.
Wang D, Mhatre S, Chen JQ, Shi XT, Yang HY, Cheng WL, Yue YY, Han GP, Rojas OJ. Composites based on electrospun fibers modified with cellulose nanocrystals and SiO2 for selective oil/water separation. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;299: 120119.
Su Y, Fan TT, Cui WY, Li YN, Ramakrishna S, Long YZ. Advanced electrospun nanofibrous materials for efficient oil/water separation. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:938–58.
Li C, Ren LP, Zhang CH, Xu WL, Liu X. TiO2 coated polypropylene membrane by atomic layer deposition for oil-water mixture separation. Adv Fiber Mater. 2021;3:138–46.
Ge JL, Zong DD, Jin Q, Yu JY, Ding B. Biomimetic and superwettable nanofibrous skins for highly efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsions. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28:1705051.
Doan HN, Vo PP, Baggio A, Negoro M, Kinashi KJ, Fuse Y, Sakai W, Tsutsumi N. Environmentally friendly chitosan-modified polycaprolactone nanofiber/nanonet membrane for controllable oil/water separation. ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2021;3:3891–901.
Lu JQ, Cao ML, He XW, Hu Y, Bai L, Huan SQ, Han GP, Cheng WL. Electrospun hierarchically channeled polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous membrane for wastewater recovery. J Clean Prod. 2022;361: 132167.
Xue JJ, Wu T, Dai YQ, Xia YN. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: methods, materials, and applications. Chem Rev. 2019;119:5298–415.
Cao ML, Hu Y, Cheng WL, Huan SQ, Bai T, Niu ZX, Zhao YY, Yue GC, Zhao Y, Han GP. Lignin-based multi-scale cellular aerogels assembled from co-electrospun nanofibers for oil/water separation and energy storage. Chem Eng J. 2022;436: 135233.
Lin XD, Heo J, Choi M, Hong J. Simply realizing durable dual Janus superwettable membranes integrating underwater low-oil-adhesive with super-water-repellent surfaces for controlled oil–water permeation. J Membr Sci. 2019;580:248–55.
Bai ZX, Jia K, Liu CC, Wang LL, Lin G, Huang YM, Liu SN, Liu XB. A solvent regulated hydrogen bond crosslinking strategy to prepare robust hydrogel paint for oil/water separation. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31:2104701.
Liao XL, Sun DX, Cao S, Zhang N, Huang T, Lei YZ, Wang Y. Freely switchable super-hydrophobicity and super-hydrophilicity of sponge-like poly(vinylidene fluoride) porous fibers for highly efficient oil/water separation. J Hazard Mater. 2021;416: 125926.
Lu N, Cai JZ, Niu BL, Zhou Y, Zhao GH. Preferential removal of phthalic esters by photocatalysis on selective TiO2. Chem Eng J. 2023;460: 141735.
Bayles A, Tian S, Zhou JY, Yuan L, Yuan YG, Jacobson CR, Farr C, Zhang M, Swearer DF, Solti D, Lou MH, Everitt HO, Nordlander P, Halas NJ. Al@TiO2 core-shell nanoparticles for plasmonic photocatalysis. ACS Nano. 2022;16:5839–50.
Sezer S, Yucel A, Turhan DO, Emre FB, Sarikaya M. Comparison of ZnO doped different phases TiO2 nanoparticles in terms of toxicity using zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere. 2023;325: 138342.
Cho SY, Lee S, Yang K, Kim YM, Choe D, Kim JU, Lee DU, Park J, Roh YH. Hyaluronic acid hydrolysis using vacuum ultraviolet TiO2 photocatalysis combined with an oxygen nanobubble system. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;299: 120178.
Gong ZQ, Yang N, Chen ZX, Jiang B, Sun YL, Yang XD, Zhang LH. Fabrication of meshes with inverse wettability based on the TiO2 nanowires for continuous oil/water separation. Chem Eng J. 2020;380: 122524.
Yang MP, Liu WQ, Jiang C, Liu CH, He S, Xie YK, Wang ZF. Facile preparation of robust superhydrophobic cotton textile for self-cleaning and oil-water separation. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2018;58:187–94.
Meng XY, Xu WL, Li ZH, Yang JH, Zhao JW, Zou XX, Sun YM, Dai YQ. Coupling of hierarchical Al2O3/TiO2 nanofibers into 3D photothermal aerogels toward simultaneous water evaporation and purification. Adv Fiber Mater. 2020;2:93–104.
Bedford NM, Steckl AJ. Photocatalytic self cleaning textile fibers by coaxial electrospinning. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2010;2:2448–55.
Li XH, Qing WH, Wu YF, Shao SL, Peng LE, Yang Y, Wang P, Liu F, Tang CY. Omniphobic nanofibrous membrane with pine-needle-like hierarchical nanostructures: toward enhanced performance for membrane distillation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11:47963–71.
He ZW, Wu HQ, Shi Z, Gao XM, Sun YP, Liu XG. Mussel-inspired durable TiO2/PDA-based superhydrophobic paper with excellent self-cleaning, high chemical stability, and efficient oil/water separation properties. Langmuir. 2022;38:6086–98.
Zou D, Kim HW, Jeon SM, Lee Y. Robust PVDF/PSF hollow-fiber membranes modified with inorganic TiO2 particles for enhanced oil-water separation. J Membr Sci. 2022;652: 120470.
Zhang ZM, Gan ZQ, Bao RY, Ke K, Liu ZY, Yang MB, Yang W. Green and robust superhydrophilic electrospun stereocomplex polylactide membranes: multifunctional oil/water separation and self-cleaning. J Membr Sci. 2020;593: 117420.
Chen XM, Zhan YQ, Sun A, Feng QY, Yang W, Dong HY, Chen YW, Zhang YJ. Anchoring the TiO2@crumpled graphene oxide core–shell sphere onto electrospun polymer fibrous membrane for the fast separation of multi-component pollutant-oil–water emulsion. Sep Puri Technol. 2022;298: 121605.
Trache D, Hussin MH, Haafiz MK, Thakur VK. Recent progress in cellulose nanocrystals: sources and production. Nanoscale. 2017;9:1763–86.
Mali P, Sherje AP. Cellulose nanocrystals: Fundamentals and biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;275: 118668.
Wang D, Yang HY, Wang QX, Lu Y, Yan J, Cheng WL, Rojas OJ, Han GP. Composite membranes of polyacrylonitrile cross-linked with cellulose nanocrystals for emulsion separation and regeneration. Compos Pt A-Appl Sci Manuf. 2023;164:107300.
Bangar SP, Harussani MM, Ilyas RA, Ashogbon AO, Singh A, Trif M, Jafari SM. Surface modifications of cellulose nanocrystals: Processes, properties, and applications. Food Hydrocolloids. 2022;130: 107689.
Lee Y, Zhang HY, Yu HY, Tam KC. Electroconductive cellulose nanocrystals—synthesis, properties and applications: a review. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;289: 119419.
Yan LL, Yang XB, Zeng HZ, Zhao YY, Li YX, He XZ, Ma J, Shao L. Nanocomposite hydrogel engineered hierarchical membranes for efficient oil/water separation and heavy metal removal. J Membr Sci. 2023;668: 121243.
Zhang YZ, Wang HH, Wang XM, Liu BS, Wei YH. An anti-oil-fouling and robust superhydrophilic MnCo2O4 coated stainless steel mesh for ultrafast oil/water mixtures separation. Sep Puri Technol. 2021;264: 118435.
Li H, Yin YY, Zhu L, Xiong Y, Li X, Guo TC, Xing W, Xue QZ. A hierarchical structured steel mesh decorated with metal organic framework/graphene oxide for high-efficient oil/water separation. J Hazard Mater. 2019;373:725–32.
Li H, Zhang JQ, Zhu L, Liu HL, Yu SF, Xue JW, Zhu X, Xue QZ. Reusable membrane with multifunctional skin layer for effective removal of insoluble emulsified oils and soluble dyes. J Hazard Mater. 2021;415: 125677.
Zhang YY, Chen Y, Hou LL, Guo FY, Liu JC, Qiu SS, Xu Y, Wang N, Zhao Y. Pine-branch-like TiO2 nanofibrous membrane for high efficiency strong corrosive emulsion separation. J Mater Chem A. 2017;5:16134–8.
Wang D, Cheng WL, Wang QX, Zang JJ, Zhang Y, Han GP. Preparation of electrospun chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide) composite nanofibers reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals: structure, morphology, and mechanical behavior. Compos Sci Technol. 2019;182: 107774.
Wang QX, Wang D, Cheng WL, Huang JQ, Cao ML, Niu ZX, Zhao YY, Yue YY, Han GP. Spider-web-inspired membrane reinforced with sulfhydryl-functionalized cellulose nanocrystals for oil/water separation. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;282: 119049.
Zhang CX, Ren ZY, Yin ZG, Jiang L, Fang SM. Experimental FTIR and simulation studies on H-bonds of model polyurethane in solutions I In dimethylformamide (DMF). Spectroc Acta Pt A-Mol Biomol Spectr. 2011;81:598–603.
Wang C, Zhan YF, Wu Y, Shi XW, Du YM, Luo Y, Deng HB. TiO2/rectorite-trapped cellulose composite nanofibrous mats for multiple heavy metal adsorption. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;183:245–53.
Jiang S, Zhang ML, Jiang W, Xu QY, Yu JY, Liu LY, Liu LF. Multiscale nanocelluloses hybrid aerogels for thermal insulation: the study on mechanical and thermal properties. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;247: 116701.
Achour A, Islam M, Solaymani S, Vizireanu S, Saeed K, Dinescu G. Influence of plasma functionalization treatment and gold nanoparticles on surface chemistry and wettability of reactive-sputtered TiO2 thin films. Appl Surf Sci. 2018;458:678–85.
Qi DM, Zhang YM, Jia DL, Huang JG. Self-assembly approach for synthesis of nanotubular molybdenum trioxide/titania composite anode for lithium-ion batteries. Energy Technol. 2017;5:2015–25.
Yan J, Yang LP, Lin MF, Ma J, Lu XH, Lee PS. Polydopamine spheres as active templates for convenient synthesis of various nanostructures. Small. 2013;9:596–603.
Xiong Y, Wang C, Wang HW, Yao QF, Fan BT, Chen YP, Sun QF, Jin CD, Xu XJ. A 3D titanate aerogel with cellulose as the adsorption-aggregator for highly efficient water purification. J Mater Chem A. 2017;5:5813–9.
Liu R, Dai L, Si CL. Mussel-inspired cellulose-based nanocomposite fibers for adsorption and photocatalytic degradation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2018;6:15756–63.
Mohamed MA, Salleh WSW, Jaafar J, Mohd Hir ZA, Rosmi MS, Abd Mutalib M, Ismail AF, Tanemura M. Regenerated cellulose membrane as bio-template for in-situ growth of visible-light driven C-modified mesoporous titania. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;146:166–73.
Xiao CJ, Yan YK, Wen GD, Zhou YT, Na D, Yang CL, Zhang JS. Regulating crystallinity in cellulose substrate to construct highly and homogeneously dispersed TiO2 for tetracycline hydrochloride adsorption. Mater Des. 2023;226: 111620.
Nguyen SV, Lee BK. PVA/CNC/TiO2 nanocomposite for food-packaging: improved mechanical, UV/water vapor barrier, and antimicrobial properties. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;298: 120064.
Mohamed MA, Salleh WWN, Jaafar J, Ismail AF, Mutalib MA, Sani NAA, Asri MSEA, Ong CSW. Physicochemical characteristic of regenerated cellulose/N-doped TiO2 nanocomposite membrane fabricated from recycled newspaper with photocatalytic activity under UV and visible light irradiation. Chem Eng J. 2016;284:202–15.
Zhang XJ, Chen WB, Lin ZD, Yao J, Tan SZ. Preparation and photocatalysis properties of bacterial cellulose/TiO2 composite membrane doped with rare earth elements. Synth React Inorg Met-Org Nano-Metal Chem. 2011;41:997–1004.
Cai S, Li Y, Liu HY, Mai YW. Damping properties of carbon fiber reinforced composites hybridized with polysulfone (PSF)/cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) interleaves. Compos Sci Technol. 2021;213: 108904.
Tummons EN, Tarabara VV, Chew JW, Fane AG. Behavior of oil droplets at the membrane surface during crossflow microfiltration of oil–water emulsions. J Membr Sci. 2016;500:211–24.
Lv WY, Mei QQ, Xiao JL, Du M, Zheng Q. 3D multiscale superhydrophilic sponges with delicately designed pore size for ultrafast oil/water separation. Adv Funct Mater. 2017;27:1704293.
Zhang Q, Song YX, Guo JL, Wu S, Chen N, Fan HG, Gao M, Yang JH, Sheng ZF, Lang JH. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of the modified carbon cloth membrane: towards visible light driven and self-cleaning for efficient oil-water separation. Surf Coat Technol. 2021;409: 126879.
Wang KZ, Wang SH, Gu KF, Yan WT, Zhou Y, Gao CJ. Ultra-low pressure PES ultrafiltration membrane with high-flux and enhanced anti-oil-fouling properties prepared via in-situ polycondensation of polyamic acid. Sci Total Environ. 2022;842: 156661.
Eang C, Opaprakasit P. Electrospun nanofibers with superhydrophobicity derived from degradable polylactide for oil/water separation applications. J Polym Environ. 2020;28:1484–91.
Shu DK, Xi P, Cheng BW, Wang Y, Yang L, Wang XQ, Yan XH. One-step electrospinning cellulose nanofibers with superhydrophilicity and superoleophobicity underwater for high-efficiency oil-water separation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;162:1536–45.
Oh S, Bang J, Jin HJ, Kwak HW. Green fabrication of underwater superoleophobic biopolymeric nanofibrous membranes for effective oil-water separation. Adv Fiber Mater. 2023;5:603–16.
Qin Y, Shen H, Han L, Zhu ZM, Pan F, Yang SW, Yin XZ. Mechanically robust janus poly(lactic acid) hybrid fibrous membranes toward highly efficient switchable separation of surfactant-stabilized oil/water emulsions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12:50879–88.
Li LL, Xiang YY, Yang WF, Liu ZL, Cai MR, Ma ZF, Wei QB, Pei XW, Yu B, Zhou F. Embedded polyzwitterionic brush-modified nanofibrous membrane through subsurface-initiated polymerization for highly efficient and durable oil/water separation. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2020;575:388–98.
Wang F, He MR, Su YL, Wang W, Liu YN, Xue J, Cao JL, Shen JL, Zhang RN, Jiang ZY. In situ construction of chemically heterogeneous hydrogel surfaces toward near-zero-flux-decline membranes for oil-water separation. J Membr Sci. 2020;594: 117455.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2572023AW53) and the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province, China (Grant No. LH2020C039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL and TB are contributed equally to this work. JL: Methodology, Investigation, Software, Writing—original draft. TB: Supervision, Formal analysis, Software, Conceptualization. DW: Formal analysis, Writing—review. HY: Investigation, Analysis. QW: Formal analysis, Writing—review. YH: Investigation, Analysis. ZN: Investigation, Analysis. XL: Investigation, Analysis. GH: Guidance, Writing—review and editing. WC: Conceptualization, Guidance, Writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MP4 916 KB)
Supplementary file3 (MP4 1938 KB)
Supplementary file4 (MP4 385 KB)
Supplementary file5 (MP4 2016 KB)
Supplementary file6 (MP4 1861 KB)
Supplementary file7 (MP4 1917 KB)
Supplementary file8 (MP4 1146 KB)
Supplementary file9 (MP4 2945 KB)
Supplementary file10 (MP4 3199 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, J., Bai, T., Wang, D. et al. Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Membrane In Situ Modified with Cellulose Nanocrystal Anchoring TiO2 for Oily Wastewater Recovery. Adv. Fiber Mater. 5, 2055–2068 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00325-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00325-0