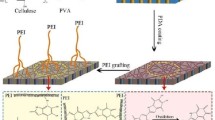
Abstract
Currently, most of the materials for oil–water separation membranes are limited to fluorine-based polymers with low surface energy. However, it is not biodegradable and requires large amounts of organic and toxic solvents in the membrane manufacturing process. Therefore, interest in the development of a new eco-friendly oil–water separation membrane that does not cause secondary pollution and exhibits selective wettability characteristics in water or oil is increasing. The biopolymeric nanofibrous membranes inspired by fish skin can provide specific underwater oleophobicity, which is effective for excellent oil–water separation efficiency and prevention of secondary contamination. Fish gelatin, which is highly soluble in water and has a low gelation temperature, can be electrospun in an aqueous solution and has the same polar functional groups as the hydrophilic mucilage of fish skin. In addition, the micro/nanostructure of fish skin, which induces superoleophobicity in water, introduces a bead-on-string structure using the Rayleigh instability of electrospinning. The solubility of fish gelatin in water was removed using an eco-friendly crosslinking method using reducing sugars. Fish skin-mimicking materials successfully separated suspended oil and emulsified oil, with a maximum flux of 2086 Lm−2 h−1 and a separation efficiency of more than 99%. The proposed biopolymeric nanofibrous membranes use fish gelatin, which can be extracted from fish waste and has excellent biodegradability with excellent oil–water separation performance. In addition, polymer material processing, including membrane manufacturing and crosslinking, can be realized through eco-friendly processes. Therefore, fish skin-inspired biopolymeric membrane is expected to be a promising candidate for a sustainable and effective oil–water separation membrane in the future.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Liu Y, Qian X, Wang L, Bai H, Cui Y. Electrospun polyimide nanofibrous membranes for absorption of oil spills. J Ind Text 2019;50:584.
Su Y, Zhao Q, Liu J, Zhao J, Li Y, Jiang Z. Improved oil/water emulsion separation performance of PVC/CPVC blend ultrafiltration membranes by fluorination treatment. Desalination Water Treat 2015;55:304.
Shu D, Xi P, Cheng B, Wang Y, Yang L, Wang X, Yan X. One-step electrospinning cellulose nanofibers with superhydrophilicity and superoleophobicity underwater for high-efficiency oil-water separation. Int J Biol Macromol 2020;162:1536.
Machín-Ramírez C, Okoh A, Morales D, Mayolo-Deloisa K, Quintero R, Trejo-Hernández M. Slurry-phase biodegradation of weathered oily sludge waste. Chemosphere 2008;70:737.
Otitoju T, Ahmad A, Ooi B. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane for oil rejection from oily wastewater: a performance review. J Water Process Eng 2016;14:41.
Tanudjaja HJ, Hejase CA, Tarabara VV, Fane AG, Chew JW. Membrane-based separation for oily wastewater: a practical perspective. Water Res 2019;156:347.
Yu L, Han M, He F. A review of treating oily wastewater. Arab J Chem 2017;10:S1913.
Adetunji AI, Olaniran AO. Treatment of industrial oily wastewater by advanced technologies: a review. Appl Water Sci 2021;11:1.
Gupta RK, Dunderdale GJ, England MW, Hozumi A. Oil/water separation techniques: a review of recent progresses and future directions. J Mater Chem 2017;5:16025.
Zhu Y, Wang D, Jiang L, Jin J. Recent progress in developing advanced membranes for emulsified oil/water separation. NPG Asia Mater 2014;6:e101.
Padaki M, Murali RS, Abdullah MS, Misdan N, Moslehyani A, Kassim M, Hilal N, Ismail A. Membrane technology enhancement in oil–water separation. A review. Desalination 2015;357:197.
Tang F, Wang D, Zhou C, Zeng X, Du J, Chen L, Zhou W, Lu Z, Tan L, Dong L. Natural polyphenol chemistry inspired organic-inorganic composite coating decorated PVDF membrane for oil-in-water emulsions separation. Mater Res Bull 2020;132:110995.
Gao SJ, Shi Z, Zhang WB, Zhang F, Jin J. Photoinduced superwetting single-walled carbon nanotube/TiO2 ultrathin network films for ultrafast separation of oil-in-water emulsions. ACS Nano 2014;8:6344.
Hu L, Gao S, Ding X, Wang D, Jiang J, Jin J, Jiang L. Photothermal-responsive single-walled carbon nanotube-based ultrathin membranes for on/off switchable separation of oil-in-water nanoemulsions. ACS Nano 2015;9:4835.
Si Y, Fu Q, Wang X, Zhu J, Yu J, Sun G, Ding B. Superelastic and superhydrophobic nanofiber-assembled cellular aerogels for effective separation of oil/water emulsions. ACS Nano 2015;9:3791.
Ge J, Zong D, Jin Q, Yu J, Ding B. Biomimetic and superwettable nanofibrous skins for highly efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsions. Adv Funct Mater 2018;28:1705051.
Xue Z, Cao Y, Liu N, Feng L, Jiang L. Special wettable materials for oil/water separation. J Mater Chem A 2014;2:2445.
Chen C, Weng D, Mahmood A, Chen S, Wang J. Separation mechanism and construction of surfaces with special wettability for oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019;11:11006.
Waghmare PR, Gunda NSK, Mitra SK. Under-water superoleophobicity of fish scales. Sci Rep 2014;4:1.
Yong J, Chen F, Yang Q, Huo J, Hou X. Superoleophobic surfaces. Chem Soc Rev 2017;46:4168.
Jiang T, Guo Z, Liu W. Biomimetic superoleophobic surfaces: focusing on their fabrication and applications. J Mater Chem A 2015;3:1811.
Ma W, Xu H, Takahara A. Substrate-independent underwater superoleophobic surfaces inspired by fish-skin and mussel-adhesives. Adv Mater Interfaces 2014;1:1300092.
Huang S, Ras RH, Tian X. Antifouling membranes for oily wastewater treatment: Interplay between wetting and membrane fouling. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 2018;36:90.
Pendergast MM, Hoek EM. A review of water treatment membrane nanotechnologies. Energy Environ Sci 2011;4:1946.
Wang Y, Gong X. Special oleophobic and hydrophilic surfaces: approaches, mechanisms, and applications. J Mater Chem A 2017;5:3759.
Du C, Wang Z, Liu G, Wang W, Yu D. One-step electrospinning PVDF/PVP-TiO2 hydrophilic nanofiber membrane with strong oil-water separation and anti-fouling property. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng 2021;624:126790.
Jia L, Huang X, Tao Q. Enhanced hydrophilic and antibacterial efficiencies by the synergetic effect TiO2 nanofiber and graphene oxide in cellulose acetate nanofibers. Int J Biol Macromol 2019;132:1039.
Jang W, Yun J, Park Y, Park IK, Byun H, Lee CH. Polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane modified with Ag/GO composite for water purification system. Polymers 2020;12:2441.
Fang Q, Zhu M, Yu S, Sui G, Yang X. Studies on soy protein isolate/polyvinyl alcohol hybrid nanofiber membranes as multi-functional eco-friendly filtration materials. Mater Sci Eng B 2016;214:1.
Kim H-J, Park SJ, Park CS, Le T-H, Lee SH, Ha TH, Kim H-i, Kim J, Lee C-S, Yoon H. Surface-modified polymer nanofiber membrane for high-efficiency microdust capturing. J Chem Eng 2018;339:204.
Kim Y-J, Uyama H. Biocompatible hydrogel formation of gelatin from cold water fish via enzymatic networking. Polym J 2007;39:1040.
Lv L-C, Huang Q-Y, Ding W, Xiao X-H, Zhang H-Y, Xiong L-X. Fish gelatin: the novel potential applications. J Funct Foods 2019;63:103581.
Zhang T, Sun R, Ding M, Li L, Tao N, Wang X, Zhong J. Commercial cold-water fish skin gelatin and bovine bone gelatin: Structural, functional, and emulsion stability differences. Lwt 2020;125:109207.
Ghorani B, Emadzadeh B, Rezaeinia H, Russell SJ. Improvements in gelatin cold water solubility after electrospinning and associated physicochemical, functional and rheological properties. Food Hydrocoll 2020;104:105740.
Xue J, Xie J, Liu W, Xia Y. Electrospun nanofibers: new concepts, materials, and applications. Acc Chem Res 2017;50:1976.
Zhang S, Liu H, Yu J, Li B, Ding B. Multi-functional flexible 2D carbon nanostructured networks. Nat Commun 2020;11:1.
Zhang J, Song J, Liu L, Zhang P, Si Y, Zhang S, Yu J, Ding B. Electroconductive nanofibrous membranes with nanosheet-based microsphere-threaded heterostructures enabling oily wastewater remediation. J Mater Chem A 2021;9:15310.
Lee MW, An S, Latthe SS, Lee C, Hong S, Yoon SS. Electrospun polystyrene nanofiber membrane with superhydrophobicity and superoleophilicity for selective separation of water and low viscous oil. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2013;5:10597.
Kwak HW, Park J, Yun H, Jeon K, Kang D-W. Effect of crosslinkable sugar molecules on the physico-chemical and antioxidant properties of fish gelatin nanofibers. Food Hydrocoll 2021;111:106259.
Stevenson M, Long J, Seyfoddin A, Guerrero P, de la Caba K, Etxabide A. Characterization of ribose-induced crosslinking extension in gelatin films. Food Hydrocoll 2020;99:105324.
Ehrmann A. Non-toxic crosslinking of electrospun gelatin nanofibers for tissue engineering and biomedicine—a review. Polymers 2021;13:1973.
Kwak HW, Kim JE, Lee KH. Green fabrication of antibacterial gelatin fiber for biomedical application. React Funct Polym 2019;136:86.
Chen H, Wu D, Ma W, Wu C, Tian Y, Wang S, Du M. Strong fish gelatin hydrogels enhanced by carrageenan and potassium sulfate. Food Hydrocoll 2021;119:106841.
Oh S, Park J, Nam J, Hyun Y, Jin H-J, Kwak HW. Antioxidant and UV-blocking glucose-crosslinked sericin films with enhanced structural integrity. React Funct Polym 2021;165:104942.
Correia DM, Padrão J, Rodrigues L, Dourado F, Lanceros-Méndez S, Sencadas V. Thermal and hydrolytic degradation of electrospun fish gelatin membranes. Polym Test 2013;32:995.
Chuaynukul K, Nagarajan M, Prodpran T, Benjakul S, Songtipya P, Songtipya L. Comparative characterization of bovine and fish gelatin films fabricated by compression molding and solution casting methods. J Polym Environ 2018;26:1239.
Kchaou H, Benbettaïeb N, Jridi M, Abdelhedi O, Karbowiak T, Brachais C-H, Léonard M-L, Debeaufort F, Nasri M. Enhancement of structural, functional and antioxidant properties of fish gelatin films using Maillard reactions. Food Hydrocoll 2018;83:326.
Zhang C, Mcadams DA, Grunlan JC. Nano/micro-manufacturing of bioinspired materials: a review of methods to mimic natural structures. Adv Mater 2016;28:6292.
Zhang J, Ge J, Si Y, Zhang F, Yu J, Liu L, Ding B. Taro leaf-inspired and superwettable nanonet-covered nanofibrous membranes for high-efficiency oil purification. Nanoscale Horiz 2019;4:1174.
Eang C, Opaprakasit P. Electrospun nanofibers with superhydrophobicity derived from degradable polylactide for oil/water separation applications. J Polym Environ 2020;28:1484.
Acknowledgements
This work was also supported by the Technology Innovation Program (20018540) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE, Korea). This research was also supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2021R1A4A2001403).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SO: investigation; methodology; writing—review and editing. JB: methodology, writing—review and editing. H-JJ: supervision, conceptualization, resources, writing—review and editing. HWK: supervision, conceptualization, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations,
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, S., Bang, J., Jin, HJ. et al. Green Fabrication of Underwater Superoleophobic Biopolymeric Nanofibrous Membranes for Effective Oil–Water Separation. Adv. Fiber Mater. 5, 603–616 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00251-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00251-7