Abstract
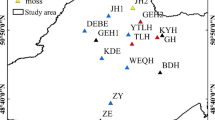
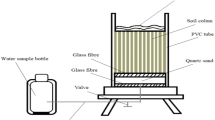
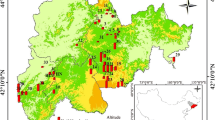
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) plays an important role in promoting or suppressing methylmercury (MeHg) production in wetlands. However, in the context of climate warming, the regulatory mechanism of DOM composition and molecular structure changes in permafrost wetland soil on mercury methylation remains unclear. In this study, we analyzed the distribution characteristics of mercury and methylmercury in permafrost wetland soils in the Greater Khingan Mountains (GKM), and elucidated the driving mechanism of mercury methylation by basic physical and chemical properties and DOM spectral characteristics of soils. The results showed that the mean value of total mercury in the permafrost wetlands of the GKM was 111 ng·g-1, the mean value of methylmercury was 5.69 ng·g-1, and the mean percentage of methylmercury was 6.16%. Hg and MeHg concentrations showed different vertical distribution patterns in the four wetlands, with Hg and MeHg concentrations in both scrub and moss wetlands showing a decreasing trend with soil deepening, but herb and forest wetlands did not satisfy this pattern. Soil warming, associated with the decomposition and mineralization of Soil Organic Matter (SOM), induces an elevation in Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) content, subsequently contributing to increased levels of mercury methylation and an upswing in methylmercury output. Throughout this process, the spectral properties of DOM play a pivotal role in regulating Hg methylation, with the input of plant sources following closely behind. The content of MeHg in the soil is minimally influenced by the mercury content in the soil.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Data would be available when be requested.
References
Abdelhafiz MA, Liu J, Jiang T, Pu Q, Aslam MW, Zhang K, Feng X (2023) DOM influences hg methylation in paddy soils across a hg contamination gradient. Environ Pollut 322:121237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121237
Adediran GA, Liem-Nguyen V, Song Y, Schaefer JK, Skyllberg U, Bjorn E (2019) Microbial biosynthesis of thiol compounds: implications for speciation, cellular uptake, and methylation of hg (II). Environ Sci Technol 53:8187–8196. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b01502
Bai H, Jiang Z, He M, Ye B, Wei S (2018) Relating Cd2+ binding by humic acids to molecular weight: a modeling and spectroscopic study. J Environ Sci 70:154–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.11.028
Barkay T, Gu B (2022) Demethylation—the other side of the mercury methylation coin: a critical review. ACS Environ Au 2:77–97. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsenvironau.1c00022
Beckers F, Awad YM, Briyuan J, Abrigata J, Mothes S, Tsang DC, OK S Y, Rinklebe J (2019) Impact of biochar on mobilization, methylation, and methylation of mercury under dynamic redox conditions in a contaminated floodplain soil. Environ Int 127:276–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.040
Chen Q, Jia R, Li L, Qu D (2020) Effects of high concentrations of sulfate on dissolved organic matter in paddy soils revealed by excitation-emission matrix analyzing. Chemosphere 249:126207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126207
Christensen GA, Somenahally AC, Moberly JG et al (2018) Carbon amendments alter microbial community structure and net mercury methylation potential in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 84:e01049–e01017. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01049-17
Ci Z, Peng F, Xue X, Zhang X (2018) Temperature sensitivity of gaseous elemental mercury in the active layer of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau permafrost. Environ Pollut 238:508–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.085
Ding JZ, Chen LY, Ji CJ, Hugelius G, Li YN, Liu L, Qin SQ, Zhang BB, Yang GB, Li F, Fang K, Chen YL, Peng YF, Zhao X, He HL, Smith P, Fang JY, Yang YH (2017) Decadal soil carbon accumulation across Tibetan permafrost regions. Nat Geosci 10:420–424
Driscoll CT, Han YJ, Chen CY, Evers DC, Lambert KF, Holsen TM, Kamman NC, Munson RK (2007) Mercury contamination in forest and freshwater ecosystems in the northeastern United States. Bioscience 57:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1641/B570106
Drott A, Lambertsson L, Björn E, Skyllberg U (2008) Do potential methylation rates reflect accumulated methyl mercury in contaminated sediments? Environ Sci Technol 42:153–158. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0715851
Eagles-Smith CA, Ackerman JT (2014) Mercury bioaccumulation in estuarine wetland fishes: evaluating habitats and risk to coastal wildlife. Environ Pollut 193:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.06.015
Fichot CG, Benner R (2012) The spectral slope coefficient of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (S275–295) as a tracer of terrigenous dissolved organic carbon in river-influenced ocean margins. Limnol Oceanogr 57:1453–1466. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2012.57.5.1453
Frohne T, Rinklebe J, Langer U, Du Laing G, Mothes S, Wennrich R (2012) Biogeochemical factors affecting mercury methylation rate in two contaminated floodplain soils. Biogeosciences 9:493–507. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-9-493-2012
Gao Y, Zhao H, Gao F, Zhu H, Qu H, Zhao F (2016) Climate change trend in future and its influence on wetlands in the Greater Khingan Mountains. J Glaciol Geocryol 38:47–56
Gerbig CA, Ryan JN, Aiken GR (2012) The effects of dissolved organic matter on mercury biogeochemistry. Environmental Chemistry and Toxicology of Mercury. Wiley, 259– 92, New York
Gilmour C, Bell JT, Soren AB, Riedel G, Riedel G, Kopec AD, Bodaly RA (2018) Distribution and biogeochemical controls on net methylmercury production in Penobscot River marshes and sediment. Sci Total Environ 640:555–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.276
He RS, Xu RH, Wei CH (2015) Spectral characterization of dissolved organic matter in bio-treated effluent of coking waste water. Environmental Chemistry. 1: 129– 36. https://doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.01.2014042401
Huang H, Mitchell CP (2023) Spatial and seasonal patterns of mercury concentrations, methylation and demethylation in central Canadian boreal soils and stream sediment. Sci Total Environ 891:164447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164447
Hudelson KE, Drevnick PE, Wang F, Armstrong D, Fisk AT (2020) Mercury methylation and demethylation potentials in Arcti lake sediments. Chemosphere 248:126001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126001
Jiang S, Liu X, Chen Q (2011) Distribution of total mercury and methylmercury in lake sediments in Arctic Ny-Ålesund. Chemosphere 83:1108–1116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.01.031
Jiang T, Bravo AG, Skyllberg U, Bjorn E, Wang D, Yan H, Green NW (2018) Influence of dissolved organic matter (DOM) characteristics on dissolved mercury (hg) species composition in sediment porewater of lakes from Southwest China. Water Res 146:146–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.08.054
Jin HJ, Yu SP, Guo D, Zhi LL, Wu LY (2006) Degradation of permafrost in the Da and Xiao Hinggan Mountains, Northeast China, and preliminary assessment of its trend. J Glaciology Geocryology 04467–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-8042(06)60011-0
Jiskra M, Wiederhold JG, Skyllberg U, Kronberg R-M, Hajdas I, Kretzschmar R (2015) Mercury Deposition and Re-emission pathways in Boreal Forest Soils Investigated with hg isotope signatures. Environ Sci Technol 49:7188–7196. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00742
Karhu K et al (2014) Temperature sensitivity of soil respiration rates enhanced by microbial community response. Nature 513:81–84
Li X, Ding L, Li X, Zhu Y (2020) Abundance, diversity, and structure of Geobacteraceae community in paddy soil under long-term fertilization practices. Appl Soil Ecol 153:103577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103577
Lin H, Morrell-Falvey JL, Rao B, Liang L, Gu B (2014) Coupled mercury–cell sorption, reduction, and oxidation on methylmercury production by Geobacter sulfurreducens PCA. Environ Sci Technol 48:11969–11976. https://doi.org/10.1021/es502537a
Liu MY (2022) Experimental study on the adsorption behavior of heavy metal Cd by humic acid and soil aggregates structure [D]. China University of Mining and Technology. https://doi.org/10.27623/d.cnki.gzkyu.2022.001018
Liu W, Chen S, Qin X, Baumann F, Scholten T, Zhou Z, Qin D, Sun W, Zhang T, Ren J (2014) Storage, patterns, and control of soil organic carbon and nitrogen in the northeastern margin of the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Environ Res Lett 7:035401. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/7/3/035401
Liu YR, Dong JX, Han LL, Zheng YM, He JZ (2016) Influence of rice straw amendment on mercury methylation and nitrification in paddy soils. Environ Pollut 209:53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.11.023
Mailman M, Bodaly RA (2005) Total mercury, methylmercury, and carbon in fresh and burned plants and soil in Northwestern Ontario. Environ Pollut 138:161–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.02.005
Mitchell CP, Gilmour CC (2008) Methylmercury production in a Chesapeake Bay salt marsh. J Geophys Research: Biogeosciences 113(G2). https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JG000765
Mu C, Zhang T, Zhang X, Cao B, Peng X (2016) Sensitivity of soil organic matter decomposition to temperature at different depths in permafrost regions on the northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Eur J Soil Sci 67:773–781. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12386
Ouellet J-F, Lucotte M, Teisserenc R, Paquet S, Canuel R (2009) Lignin biomarkers as tracers of mercury sources in lakes water column. Biogeochemistry 94:123–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-009-9314-z
Patriarca C, Sedano Nú˜nez VT, Garcia SL, Bergquist J, Bertilsson S, Sj¨oberg PJR, Tranvik LJ, Hawkes JA (2021) Character and environmental lability of cyanobacteria-derived dissolved organic matter. Limnol Oceanogr 66:496–509. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.11619
Piao S, Huang M, Liu Z, Wang X, Ciais P, Canadell JG, Wang K, Bastos A, Friedlingstein P, Houghton RA, Le Quéré C, Liu Y, Myneni RB, Peng S, Pongratz J, Sitch S, Yan T, Wang Y, Zhu Z, Wu D, Wang T (2018) Lower land-use emissions responsible for increased net land carbon sink during the slow warming period. Nat Geosci 11:739–743
Ravichandran M (2004) Interactions between mercury and dissolved organic matter––a review. Chemosphere 55:319–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.11.011
Schaefer JK, Rocks SS, Zheng W, Liang L, Gu B, Morel FM (2011) Active transport, substrate specificity, and methylation of hg (II) in anaerobic bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:8714–8719. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1105781108
Schaefer JK, Kronberg RM, Morel FM, Skyllberg U (2014) Detection of a key hg methylation gene, hgcA, in wetland soils. Environ Microbiol Rep 6:441–447. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12136
Schuster PF, Schaefer KM, Aiken GR et al (2018) Permafrost stores a globally significant amount of mercury. Geophys Res Lett 45:1463–1471. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL075571
Selin NE (2009) Global biogeochemical cycling of mercury: a review. Annu Rev Environ Resour 34:43–63. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.environ.051308.084314
Shao D, Kang Y, Wu S, Wong MH (2012) Effects of sulfate reducing bacteria and sulfate concentrations on mercury methylation in freshwater sediments. Sci Total Environ 424:331–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.09.042
Skyllberg U, Qian J, Frech W, Xia K, Bleam WF (2003) Distribution of mercury, methyl mercury and organic sulphur species in soil, soil solution and stream of a boreal forest catchment. Biogeochemistry 64:53–76. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024904502633
Sun S, Kang S, Huang J, Chen S, Zhang Q, Guo J, Liu W, Neupane B, Qin D (2017) Distribution and variation of mercury in frozen soils of a high-altitude permafrost region on the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:15078–15088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9088-0
Tomiyasu T, Nagano A, Sakamoto H, Yonehara N (2020) Background levels of atmospheric mercury in Kagoshima City, and influence of mercury emission from Sakurajima Volcano, Southern Kyushu, Japan. Sci Total Environ 259:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00585-4
Ullrich SM, Tanton TW, Abdrashitova SA (2001) Mercury in the aquatic environment: a review of factors affecting methylation. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 31:241–293. https://doi.org/10.1080/20016491089226
Vriens B, Lenz M, Charlet L, Berg M, Winkel LH (2014) Natural wetland emissions of methylated trace elements. Nat Commun 5:3035. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4035
Wang X, Lin C-J, Lu Z, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Feng X (2016) Enhanced accumulation and storage of mercury on subtropical evergreen forest floor: implications on mercury budget in global forest ecosystems. J Geophys Res-Biogeo 121:2096–2109. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JG003446
Wang X, Yuan W, Feng X, Wang D, Luo J (2019a) Moss facilitating mercury, lead and cadmium enhanced accumulation in organic soils over glacial erratic at Mt. Gongga, China. Environ Pollut 254:112974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.112974
Wang X, Yuan W, Lin CJ, Zhang L, Zhang H, Feng X (2019b) Climate and vegetation as primary drivers for global mercury storage in surface soil. Environ Sci Technol 53:10665–10675. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b02386
Wang J, Shaheen SM, Jing M, Anderson CW, Swertz AC, Wang SL, Feng X, Rinklebe J (2021) Mobilization, methylation, and demethylation of mercury in a paddy soil under systematic redox changes. Environ Sci Technol 55:10133–10141. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c07321
Wang Y, Liu J, Liem-Nguyen V, Tian S, Zhang S, Wang D, Jiang T (2022) Binding strength of mercury (II) to different dissolved organic matter: the roles of DOM properties and sources. Sci Total Environ 807:150979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150979
Wei X, Zhu Z, Liu Y et al (2020) C: N: P stoichiometry regulates soil organic carbon mineralization and concomitant shifts in microbial community composition in paddy soil. Biol Fertil Soils 56:1093–1107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-020-01468-7
Xin Y, Zhang X, Zhang D, Zhang Z, Jiang M (2023) Impacts of spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter on methylmercury contents in peatlands, Northeast China. Environ Geochem Health 45:913–923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01257-1
Xue Z, Jiang M, Zhang Z, Wu H, Zhang T (2021) Simulating potential impacts of climate changes on distribution pattern and carbon storage function of high-latitude wetland plant communities in the Xing’anling mountains, China. Land Degrad Dev 32:2704–2714. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3945
Yang Z, Fang W, Lu X, Sheng GP, Graham DE, Liang L, Gu B (2016) Warming increases methylmercury production in an Arctic soil. Environ Pollut 214:504–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.069
Zhang Z, Li M, Li Z, Xue Z, Jiang M (2020) Unexpected high methylmercury contents related to soil organic carbon and its molecular composition in wetland soils of the Yarlung Tsangbo River, Tibet. Geoderma 377:114607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114607
Funding
The authors gratefully thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U20A2083, U19A2042), the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (No. 2018265), and the Professional Association of the Alliance of International Science Organizations (Grant No. ANSO-PA-2020-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fan Sun wrote the draft, Meijie Zheng and Shan Jiang performed the chemical analysis, Qiang Guan and Dongmei Zheng designed the experiment, and Zhongsheng Zhang designed and polished the draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This work does not include any animal or patient experiments, so no ethics approval is needed. Soil sample collection was approved by the local government.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, F., Zheng, M., Jiang, S. et al. Impacts of Spectral Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter on Methyl Mercury Contents in Permafrost Wetlands, Northeast China. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-024-01800-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-024-01800-2