Abstract
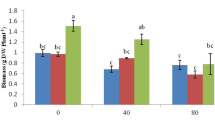
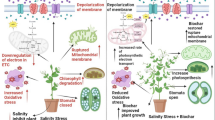
Salinity stress is one of the most important environmental factors that substantially affects the yield of plants and changes their secondary metabolites worldwide. Biochar is a vital eco-friendly amendment widely used to improve soil health and promote plant productivity under stress conditions. In the present study, the effect of biochar, a carbon-rich organic substance (0, 1, 2, and 3% of the total mass of the pot), on agro-morphological and physiological traits, essential oil and carvacrol percentage, and antioxidant activity of Satureja khuzistanica under salt stress conditions (0, 2, 4, and 8 ds m−1 NaCl). The plant agro-morphological traits and yield, including plant height, number of main and secondary branches, length and width of leaf, fresh and dry weight of aerial parts, and dry weight of leaves and flowers were decreased with increasing salinity level, but these traits were improved with the application of biochar. The highest yield was observed in the 3% biochar treatment in normal conditions. The highest percentage of essential oil (3.55%) and carvacrol (97.66%) were obtained from the plants under salinity stress (8 ds m−1) treated without and with 3% biochar. With increasing levels of salinity stress, the amount of SPAD decreased, and electrolyte leakage (EL) and the activities of peroxidase (POD), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) enzymes increased. However, biochar treatments effectively reduced the damage caused by salinity stress, so that the addition of 3% biochar treatment will decrease the destructive effects of salinity stress in the S. khuzistanica, so that decreased EL content and the activity of POD, SOD, and CAT enzymes. According to the positive effects of biochar on functional traits, essential oil content, carvacrol percentage, and SPAD index, its application can be suggested as a sustainable strategy to increase the yield of S. khuzistanica under salinity stress.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abideen Z, Koyro HW, Huchzermeyer B, Ansari R, Zulfiqar F, Gul B (2020) Ameliorating effects of biochar on photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant defence of Phragmites karka under drought stress. Plant Biol 22:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.13054
Abiven S, Hund A, Martinsen V, Cornelissen G (2015) Biochar amendment increases maize root surface areas and branching: a shovelomics study in Zambia. Plant Soil 395:45–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2533-2
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Ahmad S, Cui W, Kamran M, Ahmad I, Meng X, Wu X, Su W, Javed T, El-Serehy HA, Jia Z (2021) Exogenous application of melatonin induces tolerance to salt stress by improving the photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant defense system of maize seedling. J Plant Growth Regul 40:1270–1283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10187-0
Akhtar SS, Li G, Andersen MN, Liu F (2014) Biochar enhances yield and quality of tomato under reduced irrigation. Agric Water Manag 138:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2014.02.016
Akhtar SS, Andersen MN, Liu F (2015) Biochar mitigates salinity stress in potato. J Agron Crop Sci 201:368–378. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12132
An YM, Song LL, Liu YR, Shu YJ, Guo CH (2016) De novo transcriptional analysis of alfalfa in response to saline–alkaline stress. Front Plant Sci 7:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00931
Ashraf M, Orooj A (2006) Salt stress effects on growth, ion accumulation and seed oil concentration in an arid zone traditional medicinal plant ajwain (Trachyspermum ammi [L.] Sprague). J Arid Env 64:209–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2005.04.015
Aziz EE, Al-Amier H, Craker LE (2008) Influence of salt stress on growth and essential oil production in peppermint, pennyroyal, and apple mint. J Herbs Spices Med Plants 14:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/10496470802341375
Baghalian K, Haghiry A, Naghavi MR, Mohammadi A (2008) Effect of saline irrigation water on agronomical and phytochemical characters of chamomile (Matricaria recutita L.). Sci Hortic 116:437–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8
Banu MNA, Anamul Hoquea MD, Watanabe-Sugimoto M, Matsuoka K, Nakamaureaa Y, Shimoishia Y, Murata Y (2009) Proline and glycinebetaine induce antioxidant defense gene expression and suppress cell death in cultured tobacco cells under salt stress. J Plant Physiol 166:146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2008.03.002
Bates LS, Waldron RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant and Soil 39: 205-217 https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8
Bistagni ZE, Hashemi M, DaCosta M, Craker L, Maggi F, Morshedloo MR (2019) Effect of salinity stress on the physiological characteristics, phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of Thymus vulgaris L. and Thymus daenensis Celak. Ind Crops Prod 135:311–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.04.055
Brantley K, Savin M, Brye K, Longer D (2016) Nutrient availability and corn growth in a poultry litter biochar amended loam soil in a greenhouse experiment. Soil Use Manag 32:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12296
Bukhat S, Manzoor H, Athar HUR, Zafar ZU, Azeem F, Rasul S (2019) Salicylic acid induced photosynthetic adaptability of Raphanus sativus to salt stress is associated with antioxidant capacity. J Plant Growth Regul 39:809–822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-10024-
Chaganti VN, Crohn DM (2015) Evaluating the relative contribution of physiochemical and biological factors in ameliorating a saline–sodic soil amended with composts and biochar and leached with reclaimed water. Geoderma 259:45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.05.005
Chrysargyris A, Michailidi E, Tzortzakis N (2018) Physiological and biochemical responses of Lavandula angustifolia to salinity under mineral foliar application. Front Plant Sci 9:489. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00489
Clough TJ, Condron LM, Kammann C, Muller C (2013) A review of biochar and soil nitrogen dynamics. Agron 3:275–293. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy3020275
Egamberdieva D, Ma H, Alaylar B, Zoghi Z, Kistaubayeva A, Wirth S, Bellingrath-Kimura SD (2021) Biochar amendments improve licorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch) growth and nutrient uptake under salt stress. Plants 10:2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102135
El-Banna MF, AL-Huqail AA, Farouk S, Belal BEA, El-Kenawy MA, Abd El-Khalek AF (2022) Morpho-physiological and anatomical alterations of salt-affected thompson seedless grapevine (Vitis vinifera L) to brassinolide spraying. Horticulturae 8:568. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8070568
El-Danasoury M, Al-Amier H, Helaly A, Aziz E, Craker L (2010) Essential oil and enzyme activity in spearmint under salt stress. J Herbs Spices Med Plants 16:136–145. https://doi.org/10.1080/10496475.2010.508975
El-Gamal SMA, Serag El-Din WM, Farouk S, Mokhtar NYO (2021) Integrated effects of biochar and potassium silicate on borage plant under different irrigation regimes in sandy soil. J Horti Sci & Ornam Plants 13:60–76. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.jhsop.2021.60.76
Elsheery NI, Cao KF (2008) Gas exchange, chlorophyll fluorescence, and osmotic adjustment in two mango cultivars under drought stress. Acta Physiol Plant 3:769–777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-008-0179-x
FAO (2017) The future of food and agriculture: trends and challenges; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, p 163
Farasaraei S, Moghaddam M, Ghasemi Pirbalouti A (2020) Changes in growth and essential oil composition of sweet basil in response of salinity stress and superabsorbents application. Sci Hortic 271:109465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109465
Farhangi-Abriz S, Torabian S (2017) Antioxidant enzyme and osmotic adjustment changes in bean seedlings as affected by biochar under salt stress. Ecotoxico Environ Saf 137:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.11.029
Farouk S, AL-Huqail AA (2022) Sustainable biochar and/or melatonin improve salinity tolerance in borage plants by modulating osmotic adjustment, antioxidants, and ion homeostasis. Plants 11:765. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11060765
Farouk S, Elhindi KM, Alotaibi MA (2020) Silicon supplementation mitigates salinity stress on Ocimum basilicum L via improving water balance, ion homeostasis, and antioxidant defense system. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 206:111396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111396
Farouk S, AL-Huqail AA, El-Gamal SMA (2023) Potential role of biochar and silicon in improving physio-biochemical and yield characteristics of borage plants under different irrigation regimes. Plants 12:1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12081605
Farrell M, Lynne M, Macdonald Butler G, Chirino-Valle I, Leo MC (2014) Biocharand fertilizer applications influence phosphorus fractionation and wheat yield. BiolFertil Soil 50:69–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-013-0845-z
Ge Y, Xl Li, Palviainen M, Zhou X, Heinonsalo J, Berninger F, Köster K, Sun H (2023) Response of soil bacterial community to biochar application in a boreal pine forest. J for Res 34:749–759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-022-01509-x
Ghassemi-Golezani K, Farhadi N (2022) The efficacy of salicylic acid levels on photosynthetic activity, growth, and essential oil content and composition of pennyroyal plants under salt stress. J Plant Growth Regul 41:1953–1965. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10515-y
Ghezzehei TA, Sarkhot DV, Berhe AA (2014) Biochar can be used to capture essential nutrients from dairy wastewater and improve soil physico-chemical properties. Solid Earth 5:953–962. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-5-953-2014
Ghorbanpour M, Hadian J, Hatami M, Salehi-Arjomand H, Aliahmadi A (2016) Comparison of chemical compounds and antioxidant and antibacterial properties of various Satureja species growing wild in Iran. Journal of Medicinal Plants 15(59):58–72
Hadian J, Mirjalili MH, Kanani MR, Salehnia A, Ganjipoor P (2011) Phytochemical and morphological characterization of Satureja khuzistanica Jamzad populations from Iran. Chem Biodivers 8:902–915. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.201000249
Hadian J, Esmaeili H, Nadjafi F, Khadivi-Khub A (2014) Essential oil characterization of Satureja rechingeri in Iran. Ind Crops Prod 61:403–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.07.034
Hadian J, Hekmati M, Ghorbanpour M (2016) Agromorphological Variations and essential oil production of Satureja khuzestanica Jamzad under different planting densities. Journal of Essential Oil Bearing Plants. TEOP 19(5):1102 – 1110
Heidari M (2012) Effects of salinity stress on growth, chlorophyll content and osmotic components of two basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) genotypes. Afr J Biotechnol 11:379–384. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2020.1833764
Heydari SH, Pirzad A (2020) Efciency of Funneliformis mosseae and Tiobacillus sp. on the secondary metabolites (essential oil, seed oil and mucilage) of Lallemantia iberica under salinity stress. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 96:249–259. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2020.1833764
Hu L, Li H, Pang H, Fu J (2012) Responses of antioxidant gene, protein and enzymes to salinity stress in two genotypes of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) differing in salt tolerance. J Plant Physiol 169:146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2011.08.020
Huang M, Zhang Z, Zhu C, Zhai Y, Lu P (2019) Effect of biochar on sweet corn and soil salinity under conjunctive irrigation with brackish water in coastal saline soil. Sci Hortic 250:405–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.02.077
Ibrahim HM, Al-Wabel MI, Usman ARA, Al-Omran A (2013) Effect of Conocarpus biochar application on the hydraulic properties of a sandy loam soil. Soil Sci 178:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1097/SS.0b013e3182979eac
Jamzad Z (2011) Thyme and savory Iran. Publishing Research Institute of Forests and Rangelands, Tehran, Iran, p 172
Jeffery S, Verheijen FGA, Van der Velde M, Bastos AC (2011) A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application to soils on crop productivity using meta-analysis. Agri Ecosyst Environ 144:175–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.08.015
Jiang D, Lu B, Liu L, Duan W, Chen L, Li J, Zhang K, Sun H, Zhang Y, Dong H, Cundong L, Bai Z (2020) Exogenous melatonin improves salt stress adaptation of cotton seedlings by regulating active oxygen metabolism. Peer J 8:e10486. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.10486
Khani S, Seyedjavadi SS, Zare-Zardini H, Mahmoodzadeh Hosseini H, Goudarzi M, Khatami S, Amani J, Imani Fooladi AA, Razzaghi Abyaneh M (2019) Isolation and functional characterization of an antifungal hydrophilic peptide, Skh-AMP1, derived from Satureja khuzistanica leaves. Phytochemisry 164:136–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2019.05.011
Kim HS, Kim RK, Yang JE, Ok YS, Owens G, Nehls T, Wessolek G, Kim KH (2016) Effect of biochar on reclaimed tidal land soil properties and maize (Zea mays L.) response. Chemosphere 142:153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.06.041
Kishor PB, Sangam S, Amrutha RN (2005) Regulation of proline biosynthesis, degradation, uptake and transport in higher plants: its implications in plant growth and abiotic stress tolerance. J Curr Sci 88:424–438
Lashari MS, Ye Y, Ji H, Li L, Kibue GW, Lu H, Zheng J, Pan G (2014) Biochar–manure compost in conjunction with pyroligneous solution alleviated salt stress and improved leaf bioactivity of maize in a saline soil from central China: a 2-year field experiment. J Sci Food Agrc 95:1321–1327. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6825
Lutts S, Almansouri M, Kinet JM (2004) Salinity and water stress have contrasting effects on the relationship between growth and cell viability during and after stress exposure in drum wheat callus. Plant Sci 167:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.02.014
Lv Y, Xu L, Guo X, Liu J, Zou B, Guo Y, Zhang Y, Li H, Zheng G, Guo Y et al (2023) Effect of biochar on soil physiochemical properties and bacterial diversity in dry direct-seeded rice paddy fields. Agronomy 13(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010004
Lyu S, Du G, Liu Z, Zhao L, Lyu D (2016) Effects of biochar on photosystem function and activities of protective enzymes in Pyrus ussuriensis Maxim. Under Drought Stress Acta Physiol Plant 38:220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2236-1
Majdi M, Malekzadeh-Mashhady A, Maroufi A, Crocoll C (2017) Tissue-specific gene-expression patterns of genes associated with thymol/carvacrol biosynthesis in thyme) Thymus vulgaris L.) and their differential changes upon treatment with abiotic elicitors. Plant Physiol Biochem 115:152–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.03.016
Mehdizadeh L, Moghaddam M, Lakzian A (2020) Amelioration of soil properties, growth and leaf mineral elements of summer savory under salt stress and biochar application in alkaline soil. Sci Hortic 267:109319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109319
Mohammadi H, Amirikia F, Ghorbanpour M, Fatehi F, Hashempour H (2019) Salicylic acid induced changes in physiological traits and essential oil constituents in different ecotypes of Thymus kotschyanus and Thymus vulgaris under well-watered and water stress conditions. Ind Crops Prod 129:561–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.12.046
Munns R, Gilliham M (2015) Salinity tolerance of crops—what is the cost? New Phytol 208:668–673. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13519
Nefati M, Sriti J, Hamdaoui G, Kchouk ME, Marzouk B (2011) Salinity impact on fruit yield, essential oil composition and antioxidant activities of Coriandrum sativum fruit extracts. Food Chem 124:221–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.06.022
Neffati M, Marzouk B (2008) Changes in essential oil and fatty acid composition in coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) leaves under saline conditions. Ind Crops Prod 28:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2008.02.005
Nooshkam A, Mumivand H, Hadian J, Alemardan A, Morshedloo MR (2017) Drug yield and essential oil and carvacrol contents of two species of Satureja (S. khuzistanica Jamzad and S. rechingeri Jamzad) cultivated in two different locations. J Appl Res Med Aromat Plants 6:126–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jarmap.2017.04.002
Quartacci MF, Sgherri C, Frisenda S (2017) Biochar amendment affects phenolic composition and antioxidant capacity restoring the nutraceutical value of lettuce grown in a copper-contaminated soil. Sci Hortic 215:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2016.12.002
Ran C, Gulaqa A, Zhu J, Wang X, Zhang S, Geng Y, Guo L, Jin F, Shao X (2019) Benefits of biochar for improving ion contents, cell membrane permeability, leaf water status and yield of rice under saline & and ash; sodic paddy field condition. J Plant Growth Regul 39:370–377
Rasool M, Akhter A, Haider MS (2021) Molecular and biochemical insight into biochar and Bacillus subtilis induced defense in tomatoes against Alternaria solani. Sci Hort 285:110203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110203
Rehman M, Liu L, Bashir S, Saleem MH, Chen C, Peng D, Siddique KH (2019) Influence of rice straw biochar on growth, antioxidant capacity and copper uptake in ramie (Boehmeria nivea L) grown as forage in aged copper-contaminated soil. Plant Physiol Biochem 138:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.02.021
Ren J, Ye J, Yin L, Li G, Deng X, Wang S (2020) Exogenous melatonin improves salt tolerance by mitigating osmotic, ion, and oxidative stresses in maize seedlings. Agron 10:663. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050663
Santos CV (2004) Regulation of chlorophyll biosynthesis and degradation by salt stress in sunflower leaves. Sci Horti 103:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2004.04.009
Shariat A, Sefidkon F (2021) Tetraploid induction in savory (Satureja khuzistanica): cytological, morphological, phytochemical and physiological changes. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 146:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02053-y
Sheng H, Zeng J, Liu Y, Wang X, Wang Y, Kang H, Fan X, Sha L, Zhang H, Zhou Y (2020) Differential responses of two wheat varieties differing in salt tolerance to the combined stress of Mn and salinity. J Plant Growth Regul 39:795–808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-10023-0
Shtereva LA, Vassilevska-Ivanova RD, Karceva TV (2015) Effect of salt stress on some sweet corn (Zea mays L. Var. saccharata) genotypes. Arc Biol Sci Belgrade 67:993–1000. https://doi.org/10.2298/ABS150121062S
Smirnoff N (1996) Botanical briefing: the function and metabolism of ascorbic acid in plants. Ann Bot 78:661–669. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.1996.0175
Taarit MB, Msaada K, Hosni K, Marzouk B (2011) Physiological changes and essential oil composition of clary sage (Salvia sclarea L.) rosette leaves as affected by salinity. Acta Physiol Plant 33:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0532-8
Taffouo VD, Wamba OF, Yombi E, Nono GV, Akoa A (2010) Growth, yield, water status and ionic distribution response of three bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranean (L.) verdc.) landraces grown under saline conditions. Int J Botany 6:53–58. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijb.2010.53.58
Taïbi KH, Taïbi F, Abderrahim LA, Ennajah A, Belkhodja M, Mulet JM (2016) Effect of salt stress on growth, chlorophyll content, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defence systems in Phaseolus vulgaris L. S Afr J Bot 105:306–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2016.03.011
Tang JW, Zhang SD, Zhang XT, Chen JH, He XY, Zhang QZ (2020) Effects of pyrolysis temperature on soil plant microbe responses to Solidago canadensis L derived biochar in coastal saline-alkali soil. Sci Total Environ 731:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138938
Tavakkoli E, Rengasamy P, Mcdonald GK (2010) High concentrations of Na+ and Cl− ions in soil solution have simultaneous detrimental effects on growth of faba bean under salinity stress. J Exp Bot 61:4449–4459. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq251
Trovato M, Mattioli R, Costantino P (2008) Multiple roles of proline in plant stress tolerance and development. Rend Lince 19:325–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-008-0022-8
Uddling J, Gelang-Alfredsson J, Piikki K, Pleijel H (2007) Evaluating the relationship between leaf chlorophyll concentration and spad-502 chlorophyll meter readings. Photosynth Res 91:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-006-9077-5
Xiong D, Chen J, Yu T, Gao W, Ling X, Li Y, Peng S, Huang J (2015) Spad-based leaf nitrogen estimation is impacted by environmental factors and crop leaf char-acteristics. Sci Rep 5:13389. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13389
Xu G, Zhang Y, Sun J, Shao H (2016) Negative interactive effects between biochar and phosphorus fertilization on phosphorus availability and plant yield in saline sodic soil. Sci Total Environ 568:910–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.079
Yang A, Akhtar SS, Li L, Fu Q, Li Q, Naeem MA, He X, Zhang Z, Jacobsen SE (2020) Biochar mitigates combined effects of drought and salinity stress in Quinoa. J Agron 10:912. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10060912
Younis U, Athar M, Malik S, Reza Shah M, Mahmood S (2015) Biochar impact on physiological and biochemical attributes of Spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) in nickel contaminated soil. Golbal J Environ Sci Manage 1:245–254. https://doi.org/10.7508/gjesm.2015.03.007
Zhang XZ (1992) The measurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation and SOD, POD and CAT activities in biological system. In: Zhang XZ (ed) Research Methodology of Crop Physiology. Agriculture Press, Beijing, pp 208–211
Zhang WM, Meng J, Wang JY, Fan SX, Chen WF (2013) Effect of biochar on root morphological and physiological characteristics and yield in rice. Acta Agron Sin 39:1445–1451. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1006.2013.01445
Zhang P, Liu L, Wang X, Wang Z, Zhang H, Chen J, Liu X, Wang Y, Li C (2021) Beneficial effects of exogenous melatonin on overcoming salt stress in sugar beets (Beta vulgaris L). Plants 10:886. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050886
Zulfiqar F, Chen J, Finnegan PM, Younis A, Nafees M, Zorrig W, Hamed KB (2021) Application of trehalose and salicylic acid mitigates drought stress in sweet basil and improves plant growth. Plants 10:1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10061078
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Research Council of Shahid Beheshti University for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ghasem Eghlima: conceptualization, supervision, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft. Meisam Mohammadi: methodology, validation. Mohammad Hossein Mirjalili: validation, formal analysis, writing—review and editing. Mansour Ghorbanpour: supervision, validation, formal analysis, review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Eghlima, G., Mohammadi, M., Mirjalili, M.H. et al. Exploring the Potential Impact of Biochar Amendments in Promoting Redox Reactions, Agro-Morphological, and Phytochemical Characteristics in Satureja khuzistanica Jamzad Under Salt Stress. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 24, 190–202 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01566-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01566-z