Abstract
Purpose
Mixing of acid whey and dairy manure prior to land application could be a sustainable option for its application as plant nutrient source, without negatively impacting soil properties.
Methods
Laboratory incubation experiments were conducted to test the effect of mixing acid whey and manure (1:1, 1:4 and 1:8 ratios) in simulated storage, on pH, ammonia volatilization, and carbon mineralization. Further, effect of application rate of a 1:8 acid whey:manure mixture (at 0, 94, 187, 374 kL/ha) on soil pH, NH3 volatilization, carbon and nitrogen mineralization was tested using seven different soil types.
Results
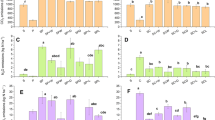
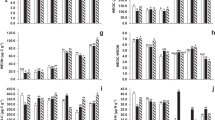
Mixing acid whey into manure initially decreased the mixture pH (by 1.4-3.0 pH units) followed by an increase in mixture pH. Consistent with the pH swing, adding acid whey to manure decreased cumulative ammonia volatilization by 44-67% compared to manure only. Application of this mixture initially increased the soil pH in all soil types, but pH returned to control levels within 21 days for Honeoye, Lima, Howard, Volusia and Rhinebeck, and within 56 days for the Barbour soil type. Acid whey and manure mixture application increased ammonia volatilization losses from calcareous soils with initial pH> 7.0 (Honeoye and Lima) but had mixed effects in other soil types.
Conclusions
Mixing of acid whey with manure in storage can reduce ammonia volatilization. Land application of the acid whey: manure mixture increases net nitrogen mineralization without causing long-term soils acidification but a high pH swing after application suggests the need for a 1-2 week delay in planting in calcareous soils. The whey: manure mixture ratio of 1:8 was preferred due to whey and manure availability and significant reduction in NH3 volatilization.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azeez JO, Van Averbeke W (2010) Nitrogen mineralization potential of three animal manures applied on a sandy clay loam soil. Biores Technol 101:5645–5651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.119
Behera SN, Sharma M, Aneja VP, Balasubramanian R (2013) Ammonia in the atmosphere: a review on emission sources, atmospheric chemistry and deposition on terrestrial bodies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8092–8131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2051-9
Billen G, Aguilera E, Einarsson R, Garnier J, Gingrich S, Grizzetti B, Lassaletta L, Le Noë J, Sanz-Cobena A (2021) Reshaping the European agro-food system and closing its nitrogen cycle: The potential of combining dietary change, agroecology, and circularity. One Earth 4:839–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oneear.2021.05.008
Braos LB, Ruiz JGCL, Lopes IG, Ferreira ME, da Cruz MCP (2020) Mineralization of nitrogen in soils with application of acid whey at different pH. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:1102–1109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00196-z
Dancer WS, Peterson LA, Chesters G (1973) Ammonification and nitrification of N as influenced by soil pH and previous N treatments. Soil Sci Soc Am Jo 37:67–69. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1973.03615995003700010024x
Dari B, Rogers CW, Walsh OS (2019) Understanding factors controlling ammonia volatilization from fertilizer nitrogen applications. Univ Ida Ext Bul 926:1–4
de Mendiburu F, de Mendiburu MF (2019) Package ‘agricolae’. R Package, version, 1(3)
Denmead OT, Chen D, Griffith DWT, Loh ZM, Bai M, Naylor T (2008) Emissions of the indirect greenhouse gases NH3 and NOx from Australian beef cattle feedlots. Aust J Exp Agric 48:213. https://doi.org/10.1071/EA07276
Erwiha GM, Ham J, Sukor A, Wickham A, Davis JG (2020) Organic fertilizer source and application method impact ammonia volatilization. Comm Soil Sci Plant Ana 51:1469–1482. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2020.1784919
Fangueiro D, Hjorth M, Gioelli F (2015) Acidification of animal slurry- a review. J Env Manag 149:46–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.10.001
Gami S, Ketterings Q (2017)Laboratory manual. http://nmsp.cals.cornell.edu/publications/NMSPLabManual2017.pdf
Hartz TK, Mitchell JP, Giannini C (2000) Nitrogen and carbon mineralization dynamics of manures and composts. HortSci 35:209–212. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.35.2.209
Islam MR, Bilkis S, Hoque TS, Uddin S, Jahiruddin M, Rahman MM, Rahman MM, Alhomrani M, Gaber A, Hossain MA (2021) Mineralization of farm manures and slurries for successive release of carbon and nitrogen in incubated soils varying in moisture status under controlled laboratory conditions. Agriculture 11:846. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11090846
Jatana BS, Kitchens C, Ray C, Gerard P, Tharayil N (2021) Dual inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphorus solubilizing fungi synergistically enhances the mobilization and plant uptake of phosphorus from meat and bone meal. Front Soil Sci 1:757839. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsoil.2021.757839
Jatana BS, Kitchens C, Ray C, Tharayil N (2020) Regulating the nutrient release rates from proteinaceous agricultural byproducts using organic amendments and its effect on soil chemical and microbiological properties. Biol Fertil Soils 56:747–758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-020-01446-z
Jensen LS, Mueller T, Tate KR, Ross DJ, Magid J, Nielsen NE (1996) Soil surface CO2 flux as an index of soil respiration in situ: A comparison of two chamber methods. Soil Biol Biochem 28:1297–1306. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(96)00136-8
Kassambara A, Kassambara MA (2020) Package ‘ggpubr’. R package version 0.1, 6(0)
Keeney DR, Nelson DW (1982) Nitrogen: inorganic forms. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wisconsin, pp 643–698
Khalil MI, Hossain MB, Schmidhalter U (2005) Carbon and nitrogen mineralization in different upland soils of the subtropics treated with organic materials. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1507–1518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.01.014
Kuhnen F, Braos LB, Ferreira ME, da Cruz MCP (2021) Mineralization of C and N in whey-treated soils and absorption of N by plants. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21:665–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00391-y
Lindsay MJ, Walker TW, Dumesic JA, Rankin SA, Huber GW (2018) Production of monosaccharides and whey protein from acid whey waste streams in the dairy industry. Green Chem 20:1824–1834. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC00517F
Loyon L (2017) Overview of manure treatment in France. Waste Manag 61:516–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.11.040
Morgan MF (1941) Chemical soil diagnosis by the universal soil testing system. Conn Agric Stn Bull 450. Univ Conn Ext, Storrs, CT
Oldfield EE, Bradford MA, Wood SA (2019) Global meta-analysis of the relationship between soil organic matter and crop yields. Soil 5:15–32. https://doi.org/10.5194/soil-5-15-2019
Papademas P, Kotsaki P (2019) Technological utilization of whey towards sustainable exploitation. J Adv Dairy Res. 7:231. https://doi.org/10.35248/2329-888X.19.7.231
Peters J., Combs SM, Hoskins B, Jarman J, Kovar J, Watson ME, Wolf AM, and Wolf N (2003). Recommended methods of manure analysis (A3769). University of Wisconsin Extension, Madison, WI
Qiu Y (2015) Showtext: Using System Fonts in R Graphics. R J., 7(1):99
Rigolot C, Espagnol S, Robin P, Hassouna M, Béline F, Paillat JM, Dourmad J-Y (2010) Modelling of manure production by pigs and NH3, N2O and CH4 emissions. Part II: effect of animal housing, manure storage and treatment practices. Animal 4:1413–1424. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731110000509
Rocha-Mendoza D, Kosmerl E, Krentz A, Zhang L, Badiger S, Miyagusuku-Cruzado G, Mayta-Apaza A, Giusti M, Jiménez-Flores R, García-Cano I (2021) Invited review: Acid whey trends and health benefits. J Dairy Sci 104:1262–1275. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2020-19038
Rochette P, Angers DA, Chantigny MH, MacDonald JD, Bissonnette N, Bertrand N (2009) Ammonia volatilization following surface application of urea to tilled and no-till soils: A laboratory comparison. Soil Tillage Res 103:310–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2008.10.028
Rufino MC, Rowe EC, Delve RJ, Giller KE (2006) Nitrogen cycling efficiencies through resource-poor African crop–livestock systems. Agriculture, Ecosys Env 112:261–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2005.08.028
Rufino MC, Tittonell P, van Wijk MT, Castellanos-Navarrete A, Delve RJ, de Ridder N, Giller KE (2007) Manure as a key resource within smallholder farming systems: Analysing farm-scale nutrient cycling efficiencies with the NUANCES framework. Livestock Sci 112:273–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2007.09.011
Schjønning P, Thomsen IK, Møberg JP, de Jonge H, Kristensen K, Christensen BT (1999) Turnover of organic matter in differently textured soils. Geoderma 89:177–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(98)00083-4
Sepat S, Behera UK, Sharma AR, Das TK, Bhattacharyya R (2014) Productivity, organic carbon and residual soil fertility of pigeonpea–wheat cropping system under varying tillage and residue management. Proc Natl Acad Sci, India, Sect B Biol Sci 84:561–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-014-0359-y
Shahbandeh M (2022) Global yogurt market value forecast 2021–2027. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/870893/global-yogurt-market-value-forecast/
Shah GM, Rashid MI, Shah GA, Groot JCJ, Lantinga EA (2013) Mineralization and herbage recovery of animal manure nitrogen after application to various soil types. Plant Soil 365:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1347-8
Soares JR, Cantarella H, Menegale ML de C (2012) Ammonia volatilization losses from surface-applied urea with urease and nitrification inhibitors. Soil Biol Biochem 52:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.04.019
Sommer SG, Knudsen L (2021) Impact of Danish livestock and manure management regulations on nitrogen pollution, crop production, and economy. Front Sustain 2:658231. https://doi.org/10.3389/frsus.2021.658231
Storer DA (1984) A simple high sample volume ashing procedure for determination of soil organic matter. Commun Soil Sci Plant Analy 15:759–772. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103628409367515
Tao W, Ukwuani AT (2015) Coupling thermal stripping and acid absorption for ammonia recovery from dairy manure: Ammonia volatilization kinetics and effects of temperature, pH and dissolved solids content. Chem Eng J 280:188–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.119
Tittonell P, Rufino MC, Janssen BH, Giller KE (2010) Carbon and nutrient losses during manure storage under traditional and improved practices in smallholder crop-livestock systems—evidence from Kenya. Plant Soil 328:253–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0107-x
Wickham H, Chang W, Wickham MH (2016) Package ‘ggplot2’. Create elegant data visualisations using the grammar of graphics. Version, 2(1):1–189
Zandona E, Blažić M, Režek Jambrak A (2021) Whey utilisation: Sustainable uses and environmental approach. Food Technol Biotechnol (Online) 59:147–161. https://doi.org/10.17113/ftb.59.02.21.6968
Zhang H, Schroder J (2014) Animal manure production and utilization in the US. In: He Z, Zhang H (eds) Applied manure and nutrient chemistry for sustainable agriculture and environment. Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 1–21
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by a grant from the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation. We thank Greg Godwin for help with whey and manure collection and processing samples for the incubation studies and Cornell Cooperative Extension educators for helping with collection of soils for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jatana, B.S., Gami, S.K. & Ketterings, Q.M. Assessing the Impact of Mixing Acid Whey With Dairy Manure On pH and Nitrogen Dynamics During Manure Handling. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 23, 2878–2890 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01243-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01243-1