Abstract
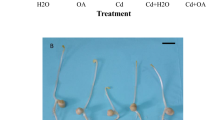
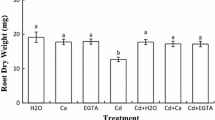
The objective of the present study was to elucidate the mechanism by which oxalic acid (OA) alleviates cadmium (Cd) stress. Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) seeds were treated with 200 µM CdCl2 for 6 days or 3 days followed by the combination 200 µM Cd + 100 µM OA for three additional days. Exogenous OA mitigated the growth inhibition by Cd of both roots and shoots. This positive effect can be attributed to the increased OA exudation from roots and the alleviation of the Cd-induced depletion of endogenous OA in shoots (80% increase versus Cd-stressed). The combination Cd + OA proved to be effective in protecting cell membrane integrity. This beneficial effect was reflected by 36 and 24% decrease in lipoxygenase (LOX) activity in roots and shoots, respectively, and 60% decrease in the accumulation of the harmful aldehyde, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE) in roots when compared to Cd-treated samples. Besides, OA restored the Cd-imposed disruption of the plasma membrane function. This effect was depicted by an optimal H+-ATPase activity and proton exudation rate. Oxalic acid counteracted the Cd-induced overproduction of hydroxyl radical (OH•) and NADPH-oxidase activity increase, leading to restore a steady cellular redox state. Furthermore, OA modulated the impact of Cd on Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (Cu/Zn-SOD), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and catalase (CAT) activities in chickpea seedlings. Present results indicate that OA is able to alleviate Cd toxicity by protecting plasma membrane integrity and modulating antioxidant activities. Moreover, our findings shed light on the interplay between plasma membrane H+-ATPase and the accumulation and root exudation of OA.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. In: Methods in enzymology. Academic Press, pp 121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Ackermann F, Stanislas T (2020) The plasma membrane—an integrating compartment for mechano-signaling. Plants 9:505. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040505
Ahanger MA, Aziz U, Alsahli A et al (2020) Combined kinetin and spermidine treatments ameliorate growth and photosynthetic inhibition in vigna angularis by up-regulating antioxidant and nitrogen metabolism under cadmium stress. Biomolecules 10:147. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010147
de AlchéD J (2019) A concise appraisal of lipid oxidation and lipoxidation in higher plants. Redox Biol 23:101136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2019.101136
Axelrod B, Cheesbrough TM, Laakso S (1981) Lipoxygenase from soybeans: EC 1.13.11.12 Linoleate: oxygen oxidoreductase. In: Methods in Enzymology. Academic Press, pp 441–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(81)71055-3
Bali AS, Sidhu GPS, Kumar V (2020) Root exudates ameliorate cadmium tolerance in plants: A review. Environ Chem Lett 18:1243–1275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01012-x
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Burzyński M, Kolano E (2003) In vivo and in vitro effects of copper and cadmium on the plasma membrane H+-ATPase from cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) roots. Acta Physiol Plant 25:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-003-0034-z
Chen A, Zeng G, Chen G et al (2014) Plasma membrane behavior, oxidative damage, and defense mechanism in Phanerochaete chrysosporium under cadmium stress. Process Biochem 49:589–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.01.014
Chen SL, Chen CT, Kao CH (1990) Acidification of deionized water by roots of intact rice seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol 31:569–573. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a077948
Dutta A, Patra A, Jatav HS, et al (2020) Toxicity of cadmium in soil-plant-human continuum and its bioremediation techniques. In: soil contamination - threats and sustainable solutions, Marcelo L. Larramendy and Sonia Soloneski. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.94307
El Rasafi T, Oukarroum A, Haddioui A, et al (2020) Cadmium stress in plants: A critical review of the effects, mechanisms, and tolerance strategies. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 1–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1835435
Falhof J, Pedersen JT, Fuglsang AT, Palmgren M (2016) Plasma membrane H+-ATPase regulation in the center of plant physiology. Mol Plant 9:323–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.11.002
Fan W, Xu JM, Lou HQ et al (2016) Physiological and molecular analysis of aluminium-induced organic acid anion secretion from grain amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus L.) roots. Int J Mol Sci 17:608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050608
Franceschi VR, Nakata PA (2005) Calcium oxalate in plants: formation and function. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:41–71. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.56.032604.144106
Fu H, Yu H, Li T, Zhang X (2018) Influence of cadmium stress on root exudates of high cadmium accumulating rice line (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 150:168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.12.014
García-Caparrós P, De Filippis L, Gul A et al (2020) oxidative stress and antioxidant metabolism under adverse environmental conditions: a Review. Bot Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12229-020-09231-1
Haider FU, Liqun C, Coulter JA et al (2021) Cadmium toxicity in plants: impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotox Environ Safe 211:111887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111887
Hu CH, Wang PQ, Zhang PP et al (2020) NADPH Oxidases: The vital performers and center hubs during plant growth and signaling. Cells 9:437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020437
Hussain I, Ashraf MA, Rasheed R et al (2015) Exogenous application of silicon at the boot stage decreases accumulation of cadmium in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grains. Braz J Bot 38:223–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-014-0126-6
Ishida A, Ookubo K, Ono K (1987) Formation of hydrogen peroxide by NAD(P)H oxidation with isolated cell wall-associated peroxidase from cultured liverwort cells, Marchantia polymorpha L. Plant Cell Physiol 28:723–726. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a077349
Janicka-Russak M, Kabała K, Burzyński M (2012) Different effect of cadmium and copper on H+-ATPase activity in plasma membrane vesicles from Cucumis sativus roots. J Exp Bot 63:4133–4142. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers097
Kaur S, Singh HP, Batish DR et al (2012) Arsenic (As) inhibits radicle emergence and elongation in Phaseolus aureus by altering starch-metabolizing enzymes vis-à-vis disruption of oxidative metabolism. Biol Trace Elem Res 146:360–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9258-8
Kasamo K (2003) Regulation of plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity by the membrane environment. J Plant Res 116:517–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-003-0112-8
Kharbech O, Sakouhi L, Mahjoubi Y et al (2022) Nitric oxide donor, sodium nitroprusside modulates hydrogen sulfide metabolism and cysteine homeostasis to aid the alleviation of chromium toxicity in maize seedlings (Zea mays L.). J Hazard Mater 424:127302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127302
Khare T, Srivastav A, Kumar V (2020) Calcium/calmodulin activated protein kinases in stress signaling in plants. In: Protein kinases and stress signaling in plants. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, pp 266–280. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119541578.ch11
Kosakivska IV, Babenko LM, Romanenko KO et al (2021) Molecular mechanisms of plant adaptive responses to heavy metals stress. Cell Biol Int 45:258–272. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11503
Larsson C, Widell S, Kjellbom P (1987) Preparation of high-purity plasma membranes. In: Methods in Enzymology. Academic Press, pp 558–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(87)48054-3
Liu K, Xu J, Dai C et al (2021) Exogenously applied oxalic acid assists in the phytoremediation of Mn by Polygonum pubescens Blume cultivated in three Mn-contaminated soils. Front Environ Sci Eng 15:86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-020-1380-4
Mano J, Biswas MS, Sugimoto K (2019) Reactive carbonyl species: a missing link in ROS signaling. Plants 8:391. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8100391
Mehla N, Sindhi V, Josula D, et al (2017) An introduction to antioxidants and their roles in plant stress tolerance. In: Khan MIR, Khan NA (eds) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant systems in plants: role and regulation under abiotic stress. Springer, Singapore, pp 1–23 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5254-5_1
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)45228-9
Naik VV, Patil NS, Aparadh VT, Karadge BA (2014) Methodology in determination of oxalic acid in plant tissue: a comparative approach. J. Glob Trends Pharm Sci 5:1662–1672. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260835371. Accessed 30 May 2020
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a076232
Nouairi I, Jalali K, Essid S et al (2019) Alleviation of cadmium-induced genotoxicity and cytotoxicity by calcium chloride in faba bean (Vicia faba L. var. minor) roots. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 25:921–931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00681-5
Osmolovskaya N, Dung VV, Kuchaeva L (2018) The role of organic acids in heavy metal tolerance in plants. Biol Commun 63:9–16. https://doi.org/10.21638/spbu03.2018.103
Podazza G, Rosa M, González JA et al (2006) Cadmium induces changes in sucrose partitioning, invertase activities, and membrane functionality in roots of rangpur lime (Citrus limonia L. Osbeck). Plant Biol 8:706–714. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-924171
Pompella A, Maellaro E, Casini AF, Comporti M (1987) Histochemical detection of lipid peroxidation in the liver of bromobenzene-poisoned mice. Am J Pathol 129:295–301. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1899716/. Accessed 1 April 2020
Sakouhi L, Rahoui S, Gharsallah C et al (2018) Effects of calcium and EGTA on thiol homeostasis and defense-related enzymes in Cd-exposed chickpea roots. Acta Physiol Plant 40:20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2596-1
Sakouhi L, Kharbech O, Massoud MB et al (2021a) Calcium and ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid mitigate toxicity and alteration of gene expression associated with cadmium stress in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) shoots. Protoplasma 258:849–861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-020-01605-x
Sakouhi L, Kharbech O, Ben Massoud M, Munemasa S, Murata SY, Chaoui A (2021b) Oxalic acid mitigates cadmium toxicity in Cicer arietinum L. germinating seeds by maintaining the cellular redox homeostasis. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10334-1
Salin ML, Lyon DS (1983) Iron-containing superoxide dismutase in eukaryotes: localization in chloroplasts in water lily, Nuphar luteum. Oxy radicals and their scavenger systems, Cohen G. Greenwald RA. Elsevier Science Publishing Co., New York, pp 344–347
Sohail I M, Arif M, Rauf A, et al (2019) Organic manures for cadmium tolerance and remediation. In: Hasanuzzaman M, Vara Prasad MN, Nahar K (eds) Cadmium Tolerance in Plants. Academic Press, pp 19–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-815794-7.00002-3
Song J, Markewitz D, Wu S et al (2018) exogenous oxalic acid and citric acid improve lead (Pb) tolerance of Larix olgensis A. Henry Seedlings Forests 9:510. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9090510
Soyingbe OS, Ntanzi C, Makhafola TJ, Kappo AP (2020) Ameliorative effect of exogenously applied oxalic acid on nickel (heavy metal) induced stress in Zea mays. Pak J Bot 52:413–418. https://doi.org/10.30848/PJB2020-2(14)
Spickett CM (2013) The lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal: advances in chemistry and analysis. Redox Biol 1:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2013.01.007
Tao Q, Hou D, Yang X, Li T (2016) Oxalate secretion from the root apex of Sedum alfredii contributes to hyperaccumulation of Cd. Plant Soil 398:139–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2651-x
Thind S, Hussain I, Ali S et al (2020) Physiological and biochemical bases of foliar silicon-induced alleviation of cadmium toxicity in wheat. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:2714–2730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00337-4
Thind S, Hussain I, Ali S et al (2021) Silicon application modulates growth, physio-chemicals, and antioxidants in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) exposed to different cadmium regimes. Dose-Response Int J 19:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1177/15593258211014646
Ullery JC, Marnett LJ (2012) Protein modification by oxidized phospholipids and hydrolytically released lipid electrophiles: investigating cellular responses. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1818:2424–2435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.04.014
Wang D, Zhang X, Liu J et al (2012) Oxalic acid enhances Cr tolerance in the accumulating plant Leersia Hexandra Swartz. Int J Phytoremediation 14:966–977. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2011.636406
Yadu B, Chandrakar V, Meena RK, Keshavkant S (2017) Glycinebetaine reduces oxidative injury and enhances fluoride stress tolerance via improving antioxidant enzymes, proline and genomic template stability in Cajanus cajan L. S Afr J Bot 111:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2017.03.023
Yalcinkaya T, Uzilday B, Ozgur R et al (2019) Lipid peroxidation-derived reactive carbonyl species (RCS): Their interaction with ROS and cellular redox during environmental stresses. Environ Exp Bot 165:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.06.004
Yamamoto Y, Kobayashi Y, Matsumoto H (2001) Lipid peroxidation is an early symptom triggered by aluminum, but not the primary cause of elongation inhibition in pea roots. Plant Physiol 125:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.125.1.199
Yin A, Huang B, Xie J et al (2021) Boron decreases cadmium influx into root cells of Capsicum annuum by altering cell wall components and plasmalemma permeability. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14441-0
Yin L, Mano J, Wang S et al (2010) The involvement of lipid peroxide-derived aldehydes in aluminum toxicity of tobacco roots. Plant Physiol 152:1406–1417. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.151449
Yu W, Kan Q, Zhang J et al (2016) Role of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase in the regulation of organic acid exudation under aluminum toxicity and phosphorus deficiency. Plant Signal Behav 11:e1106660. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2015.1106660
Zhang Y, Li Q, Xu L et al (2020) Comparative analysis of the P-type ATPase gene family in seven Rosaceae species and an expression analysis in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.). Genomics 112:2550–2563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.02.008
Funding
This work was supported by the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, University of Carthage (LR18ES38) and the Graduate School of Environmental and Life Science, Okayama University, Okayama 700–8530, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lamia Sakouhi: Methodology, Writing-Original draft, Software, Statistical Analysis. Oussama Kharbech: Visualization, Investigation. Marouane Ben Massoud: helped in drafting. Shintaro Munemasa: Writing-Reviewing. Yoshiyuki Murata: Writing-Reviewing. Abdelilah Chaoui: Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors approved the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakouhi, L., Kharbech, O., Ben Massoud, M. et al. Exogenous Oxalic Acid Protects Germinating Chickpea Seeds Against Cadmium Injury. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22, 647–659 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00675-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00675-x