Abstract
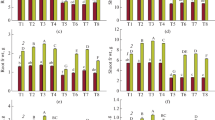
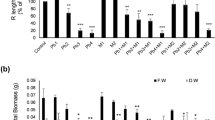
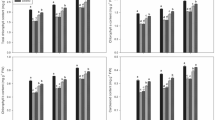
Melatonin and catechol regulate plant growth, but their effects on early growth of fragrant rice and related physio-biochemical attributes under Cd stress are rarely studied. A pot experiment was conducted to evaluate the effects of exogenous melatonin, i.e., 0 and 100 μmol L−1, and catechol, i.e., 0 and 20 μmol L−1, application regarded as M0, M100, C0, and C20, respectively, on early growth and physio-biochemical attributes of two fragrant rice cultivars, i.e., Yuxiangyouzhan and Xiangyaxiangzhan. Both rice cultivars were grown under two Cd levels, i.e., 0 and 150 μmol L−1 denoted as Cd0 and Cd150, respectively. Melatonin application improved the dry weight of rice seedlings due to modulations in the growth and antioxidant response under Cd-induced toxicity. The superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD) activities in root were increased, whereas malondialdehyde (MDA) content in root and shoot was decreased with melatonin application. Catechol also regulated the growth and antioxidant response of fragrant rice seedlings under Cd-induced toxicity. The interactive effects of melatonin and catechol, i.e., M100 + C0 treatment resulted in the maximum plant dry weight, whereas the M100 + C0 + Cd150 treatment resulted in the lowest Cd concentration in roots and shoots of Xiangyaxiangzhan as well as in roots of Yuxiangyouzhan. Furthermore, multivariate analysis revealed that the POD activity in root was an important limiting factor for fragrant rice seedlings to mitigate Cd-induced toxicity. Overall, melatonin and catechol could modulate the early growth and antioxidant response of fragrant rice seedlings under Cd-induced toxicity.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article.
Code Availability
No code.
References
Anjum SA, Tanveer M, Hussain S, Ashraf U, Khan I, Wang L (2017) Alteration in growth, leaf gas exchange, and photosynthetic pigments of maize plants under combined cadmium and arsenic stress. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3187-2
Arnao MB, Hernández-Ruiz J (2007) Melatonin promotes adventitious-and lateral root regeneration in etiolated hypocotyls of Lupinus albus L. J Pineal Res 42:147–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2006.00396.x
Ashraf U, Tang X (2017) Yield and quality responses, plant metabolism and metal distribution pattern in aromatic rice under lead (Pb) toxicity. Chemosphere 176:141–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.103
Ashraf U, Kanu AS, Deng Q, Mo Z, Pan S, Tian H, Tang X (2017) Lead (Pb) toxicity; physio-biochemical mechanisms, grain yield, quality, and Pb distribution proportions in scented rice. FrontPlant Sci 8:259. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00259
Ashraf U, Mahmood MH, Hussain S, Abbas F, Anjum SA, Tang X (2020) Lead (Pb) distribution and accumulation in different plant parts and its associations with grain Pb contents in fragrant rice. Chemosphere 248:126003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126003
Baxter A, Mittler R, Suzuki N (2013) ROS as key players in plant stress signalling. J Exp Bot 65:1229–1240. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert375
Bendary E, Francis RR, Ali HMG, Sarwat MI, Hady SEI (2013) Antioxidant and structure–activity relationships (SARs) of some phenolic and anilines compounds. Annals Agri Sci 58:173–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2013.07.002
Byeon Y, Back K (2016) Low melatonin production by suppression of either serotonin N-acetyltransferase or N-acetylserotonin methyltransferase in rice causes seedlings growth retardation with yield penalty, abiotic stress susceptibility, and enhanced coleoptile growth under anoxic conditions. J Pineal Res 60:348–359. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12317
Chen Q, Qi WB, Reiter RJ, Wei W, Wang BM (2009) Exogenously applied melatonin stimulates root growth and raises endogenous indoleacetic acid in roots of etiolated seedlings of Brassica juncea. J Plant Physiol 166:324–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2008.06.002
Chen J, Zeng X, Yang W, Xie H, Ashraf U, Mo Z, Liu J, Li G, Li W. 2021. Seed priming with multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) modulates seed germination and early growth of maize under cadmium (Cd) toxicity. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00480-6
Choi GH, Back K (2019) Suppression of melatonin 2-hydroxylase increases melatonin production leading to the enhanced abiotic stress tolerance against cadmium, senescence, salt, and tunicamycin in rice plants. Biomolecules 9:589. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100589
Ciniglia C, Pinto G, Sansone C, Pollio A (2010) Acridine orange/Ethidium bromide double staining test: a simple In-vitro assay to detect apoptosis induced by phenolic compounds in plant cells. Allelopathy J 26:301-308.
Clemens S (2006) Toxic metal accumulation, responses to exposure and mechanisms of tolerance in plants. Biochimie 88:1707–1719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2006.07.003
Duan G, Shao G, Tang Z, Chen H, Wang B, Tang Z, Yang Y, Liu Y, Zhao FJ (2017) Genotypic and environmental variations in grain cadmium and arsenic concentrations among a panel of high yielding rice cultivars. Rice 10:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-017-0149-2
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2005) Oxidant and antioxidant signalling in plants: a re-evaluation of the concept of oxidative stress in a physiological context. Plant Cell Environ 28:1056–1071. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01327.x
Han QH, Huang B, Ding CB, Zhang ZW, Chen YE, Hu C, Zhou LJ, Huang Y, Liao JQ, Yuan S, Yuan M (2017) Effects of melatonin on anti-oxidative systems and photosystem II in cold-stressed rice seedlings. Front Plant Sci 8: 785. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00785
Hasan M, Ahammed GJ, Yin L, Shi K, Xia X, Zhou Y, Yu J, Zhou J (2015) Melatonin mitigates cadmium phytotoxicity through modulation of phytochelatins biosynthesis, vacuolar sequestration, and antioxidant potential in Solanum lycopersicum L. Front Plant Sci 6:601. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00601
Hodges DM, DeLong JM, Forney CF, Prange RK (1999) Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta 207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250050524
Huang S, Rao G, Ashraf U, He L, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Mo Z, Pan S, Tang X (2020) Application of inorganic passivators reduced Cd contents in brown rice in oilseed rape-rice rotation under Cd contaminated soil. Chemosphere 259:127404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127404.
Huang S, Rao G, Ashraf U, Deng Q, Dong H, Zhang H, Mo Z, Pan S, Tang X (2021) Ultrasonic seed treatment improved morpho-physiological and yield traits and reduced grain Cd concentrations in rice. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety. 214:112119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112119.
Huang Z, Xie W, Wang M, Liu X, Ashraf U, Qin D, Zhuang M, Li W, Li Y, Wang S, Tian H, Mo Z (2020). Response of rice genotypes with differential nitrate reductase-dependent no synthesis to melatonin under ZnO nanoparticles’ (NPs) stress. Chemosphere, 250:126337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126337
Kanu AS, Ashraf U, Mo Z, Baggie I, Charley CS, Tang X (2019) Calcium amendment improved the performance of fragrant rice and reduced metal uptake under cadmium toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(24):24748–24757
Lee DH, Lee CB (2000) Chilling stress-induced changes of antioxidant enzymes in the leaves of cucumber: in gel enzyme activity assays. Plant Sci 159:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(00)00326-5
Lee HY, Back K (2017) Cadmium disrupts subcellular organelles, including chloroplasts, resulting in melatonin induction in plants. Molecules 22:1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101791
Lee S, Kim SG, Park CM (2010) Salicylic acid promotes seed germination under high salinity by modulating antioxidant activity in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 188:626–637. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03378.x
Li S, Jiang H, Wang J, Wang Y, Pan S, Tian H, Duan MY, Wang SL, Tang XR, Mo ZW (2019) Responses of plant growth, physiological, gas exchange parameters of super and non-super rice to rhizosphere temperature at the tillering stage. Sci Rep 9:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47031-9
Li YZ, Liang LX, Li W, Ashraf U, Ma L, Tang XR, Pan SG, Tian H, Mo ZW (2021) ZnO nanoparticle-based seed priming modulates early growth and enhances physio-biochemical and metabolic profiles of fragrant rice against cadmium toxicity. J Nanobiotechnol 19:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-021-00820-9
Liang C, Zheng G, Li W, Wang Y, Hu B, Wang H, Wu H, Qian Y, Zhu X, Tan D, Chen S, Chu C, Chen SY (2015) Melatonin delays leaf senescence and enhances salt stress tolerance in rice. J Pineal Res 59:91–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12243
Lin R, Wang X, Luo Y, Du W, Guo H, Yin D (2007) Effects of soil cadmium on growth, oxidative stress and antioxidant system in wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.). Chemosphere 69:89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.04.041
Liu S, Huang Y, Luo Z, Huang Y, Bao Q, Wang P, Yuan B, Li W (2016) Effects of exogenous melatonin on germination of rice seeds under Cd stresses. J Agro-Environ Sci 35:1034–1041. https://doi.org/10.11654/jaes.2016.06.003
Lorenz SE, Hamom RE, Holm PE, Domingues HC, Sequeira EM, Christensen TH, Mcgrath SP (1997) Cadmium and zinc in plants and soil solutions from contaminated soils. Plant Soil 189:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004214923372
Lv XC, Fang YX, Zhang LT, Zhang WY, Xu L, Han JJ, Jin BL, Zhang X, Zhang XQ, Xue DW (2019) Effects of melatonin on growth, physiology and gene expression in rice seedlings under cadmium stress. Phyton-International J Exp Botany 88:91–100. https://doi.org/10.32604/phyton.2019.06622
Murch SJ, KrishnaRaj S, Saxena PK (2000) Tryptophan is a precursor for melatonin and serotonin biosynthesis in in vitro regenerated St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum L. cv. Anthos) plants. Plant Cell Rep 19:698–704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990000206
Pastorelli AA, Angeletti R, Binato G, Mariani MB, Cibin V, Morelli S, Ciardullo S, Stacchini P (2018) Exposure to cadmium through Italian rice (Oryza sativa L.): consumption and implications for human health. J Food Compos Anal 69:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2018.02.005
Posmyk MM, Bałabusta M, Wieczorek M, Sliwinska E, Janas KM (2009) Melatonin applied to cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seeds improves germination during chilling stress. J Pineal Res 46:214–223. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00652.x
Rascio N, Vecchia FD, La Rocca N, Barbato R, Pagliano C, Raviolo M, Gonnelli C, Gabbrielli R (2008) Metal accumulation and damage in rice (cv. Vialone nano) seedlings exposed to cadmium. Environ Exp Bot 62:267–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.09.002
Rao G, Huang S, Ashraf U, Mo Z, Duan M, Pan S, Tang X (2019) Ultrasonic seed treatment improved cadmium (Cd) tolerance in Brassica napus L. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety. 185:109659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109659
Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Rauf A, Ayub MA, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Waris AA, Naeem A, Sanaullah M (2019) Split application of silicon in cadmium (Cd) spiked alkaline soil plays a vital role in decreasing Cd accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grains. Chemosphere 226:454–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.182
Schutzendubel A, Polle A (2002) Plant responses to abiotic stresses: heavy metal-induced oxidative stress and protection by mycorrhization. J Exp Bot 53:1351–1365. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.372.1351
Shah K, Kumar RG, Verma S, Dubey RS (2001) Effect of cadmium on lipid peroxidation, superoxide anion generation and activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice seedlings. Plant Sci 161:1135–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00517-9
Song WE, Chen SB, Liu JF, Li CHEN, Song NN, Ning LI, Bin LIU (2015) Variation of Cd concentration in various rice cultivars and derivation of cadmium toxicity thresholds for paddy soil by species-sensitivity distribution. J Integr Agric 14:1845–1854. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(14)60926-6
Srivastava RK, Pandey P, Rajpoot R, Rani A, Dubey RS (2014) Cadmium and lead interactive effects on oxidative stress and antioxidative responses in rice seedlings. Protoplasma 251:1047–1065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0614-3
Tal O, Haim A, Harel O, Gerchman Y (2011) Melatonin as an antioxidant and its semi-lunar rhythm in green macroalga Ulva sp. J Exp Bot 62:1903–1910. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq378
Wang M, Schoettner M, Xu S, Paetz C, Wilde J, Baldwin IT, Groten K (2017) Catechol, a major component of smoke, influences primary root growth and root hair elongation through reactive oxygen species-mediated redox signaling. New Phytol 213:1755–1770. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14317
Wang L, Cui X, Cheng H, Chen F, Wang J, Zhao X, Lin C, Pu X (2015) A review of soil cadmium contamination in China including a health risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22 21:16441–16452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5273-1
Wu FB, Zhang G (2002) Genotypic differences in effect of Cd on growth and mineral concentrations in barley seedlings. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 69:219–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-002-0050-5
Xia J, Psychogios N, Young N, Wishart DS (2009) MetaboAnalyst: a web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W652–60 (WebServer)
Yang B, He JY, Ren YF, Wang YF, Tian D (2018) Alleviating effect of hydrogen peroxide on seed germination of rice under cadmium stress. Plant Physiol J 54:1111–1118. https://doi.org/10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2017.0553
Zeng F, Ali S, Zhang H, Ouyang Y, Qiu B, Wu F, Zhang G (2011) The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environ Pollut 159:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.09.019
Zhang H, Guo Q, Yang J, Chen T, Zhu G, Peters M, Wei RF, Tian LY, Wang CY, Tan DY, Wang GM, Ma J (2014a) Cadmium accumulation and tolerance of two castor cultivars in relation to antioxidant systems. J Environ Sci 26:2048–2055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.08.005
Zhang N, Zhang HJ, Zhao B, Sun QQ, Cao YY, Li R, Wu XX, Weeda S, Ren SX, Reiter RJ (2014b) The RNA-seq approach to discriminate gene expression profiles in response to melatonin on cucumber lateral root formation. J Pineal Res 56:39–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12095
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the funding provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31601244) and Guangzhou Agricultural Science and Technology Commissioner Project (GZKTP201815).
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31601244) and Guangzhou Agricultural Science and Technology Commissioner Project (GZKTP201815).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhaowen Mo designed the experiments; Shicong Huang, Lin Ma, and Yuzhan Li performed the investigation; Luxin Liang, Yuzhan Li, Wu Li, and Umair Ashraf analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; Zhaowen Mo and Umair Ashraf revised and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
The authors permitted that this article can be published in the Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Liang, L., Huang, S. et al. Exogenous Melatonin and Catechol Application Modulate Physio-Biochemical Attributes and Early Growth of Fragrant Rice Under Cd Toxicity. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21, 2285–2296 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00521-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00521-0