Abstract
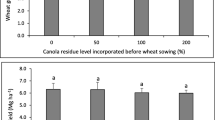
This study aims to evaluate the medium-term effect of two biannual rotations and four residue rate incorporation on durum wheat production and its nutritional composition and nutrient extraction. The effects of two biannual rotations of canola (Brassica napus L.) durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L.) and bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.)-durum wheat and four incorporation rates (0%, 50%, 100%, and 200%) of residues of each preceding crop were evaluated after four seasons on durum wheat production and on its nutritional composition and nutrient extraction, in a volcanic soil in south-central Chile. Results indicated that the highest grain yield and residue production of durum wheat was obtained after bean (7.40 and 7.92 Mg ha−1, respectively). In the grain were obtained lower N and P concentrations after bean, and higher K, Ca, and Mg concentrations in the residue. The extraction of most durum wheat grain and residue nutrients was higher after bean. Nutrient distribution in the durum wheat plant concentrated in the grain was 79.9 to 80.7% N, 91.3 to 92.1% P, 27.1 to 27.4% K, 16.8 to 18.8% Ca, 68.3 to 70.4% Mg, and 56.3 to 57.4% S. In the residue, nutrient distribution was 19.3 to 20.4% N, 7.9 to 8.7% P, 72.6 to 72.9% K, 81.2 to 83.2%, Ca, 29.6 to 31.7% Mg, and 42.6 to 43.7% S. The highest grain and residue production of durum wheat was obtained after bean crop and also the extraction of most nutrients.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
(Not applicable)
Code availability
(Not applicable)
References
Ahmed A, Aftab S, Hussain S, Nazir Cheema H, Liu W, Yang F, Yang W (2020) Nutrient accumulation and distribution assessment in response to potassium application under maize–soybean intercropping system. Agronomy 10:725. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050725
Bar-Tal A, Yermiyahu U, Beraud J, Keinan M, Rosenberg R, Zohar D, Rosen V, Fine P (2004) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium uptake by wheat and their distribution in soil following successive, annual compost applications. J Environ Qual 33:1855–1865
Basir A, Jan MT, Alam M, Shah AS, Afridi K, Adnan M et al (2016) Impacts of tillage, stubble management, and nitrogen on wheat production and soil properties. Can J Soil Sci 97:133–140
Blanco-Canqui H, Lal R (2009) Crop residue removal impacts on soil productivity and environmental quality. Crit. Rev Plant Sci 28:139–163. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352680902776507
Chen X, Mao A, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Chang J, Gao H, Thompson ML (2017) Carbon and nitrogen forms in soil organic matter influenced by incorporated wheat and corn residues. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 63:377–387
Chen Z, Wang Q, Wang H, Bao L, Zhou J (2018) Crop yields and soil organic carbon fractions as influenced by straw incorporation in a rice–wheat cropping system in southeastern China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 112:61–73
De Stefanis E, Sgrulletta D, Pucciarmati S, Ciccoritti R, Quaranta F (2017) Influence of durum wheat-faba bean intercrop on specific quality traits of organic durum wheat. Biol Agric Hortic 33:28–39
Govaerts B, Sayre KD, Deckers J (2005) Stable high yields with zero tillage and permanent bed planting? Field Crops Res 94:33–42
Hirzel J (2011) Chilean crops fertilization [Fertilización de cultivos en Chile]. Collection Books of INIA N°28. 434 p. Agriculture Research Institute [Instituto de Investigaciones Agropecuarias (INIA)], Chillán, Chile
Hirzel J, Undurraga P, González J (2011) Chemical properties of volcanic soil as affected by seven years rotations. Chil J Agr Res 71:304–312
Hirzel J, Retamal-Salgado J, Walter I, Matus I (2018) Effect of soil cadmium concentration on three Chilean durum wheat cultivars in four environments. Arch Agron Soil Sci 64:162–172. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2017.1337892
Hirzel J, Undurraga P, León L, Panichini M, González J, Carrasco J et al (2020a) Maize grain production, plant nutrient concentration and soil chemical properties in response to different residue levels from two previous crops. Acta Agr Scand B-S P 70:285–293. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710.2020.1725619
Hirzel J, Undurraga P, León L, Panichini M, González J, Carrasco J et al (2020b) Canola production and effect on soil chemical properties in response to different residue levels from three biannual crop rotations. Plant Prod Sci:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/1343943X.2020.1851142
Hirzel J, Undurraga P, León L, Panichini M, González J, Carrasco J et al (2020c) Durum wheat grain production, grain quality, and plant nutrient concentration in response to different residue levels from two biannual crop rotations. J Plant Nutr 44:619–628. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2020.1849285
Kerdraon L, Balesdent M, Barret M, Laval V, Suffert F (2019) Crop residues in wheat-oilseed rape rotation system: a pivotal, shifting platform for microbial meetings. Microb Ecol 77:931–945
Kumar M, Kundu DK, Ghorai AK, Mitra S, Singh SR (2018) Carbon and nitrogen mineralization kinetics as influenced by diversified cropping systems and residue incorporation in Inceptisols of Eastern Indo-Gangetic Plain. Soil Till Res 178:108–117
Liu Z, Gao T, Liu W, Sun K, Xin Y, Liu H, Wang S, Li G, Han H, Li Z, Ning T (2019) Effects of part and whole straw returning on soil carbon sequestration in C3-C4 rotation cropland. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 182:429–440. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201800573
Malhi SS, Lemke R, Wang ZH, Chhabra BS (2006) Tillage, nitrogen and crop residue effects on crop yield, nutrient uptake, soil quality, and greenhouse gas emissions. Soil Till Res 90:171–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2005.09.00+1
Marschner P (2012) Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3rd edn. Academic Press, London
Murage E, Voroney P (2008) Distribution of organic carbon in the stable soil humic fractions as affected by tillage management. Can J Soil Sci 88:99–106. https://doi.org/10.4141/S06-059
Oliveira M, Barré P, Trindade H, Virto I (2019) Different efficiencies of grain legumes in crop rotations to improve soil aggregation and organic carbon in the short-term in a sandy Cambisol. Soil Till Res 186:23–35
Pandiaraj T, Selvaraj S, Ramu N (2015) Effects of crop residue management and nitrogen fertilizer on soil nitrogen and carbon content and productivity of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in two cropping systems. J Agric Sci Technol 17:249–260
Plaza-Bonilla D, Nogué-Serra I, Raffaillac D, Cantero-Martínez C, Justes É (2018) Carbon footprint of cropping systems with grain legumes and cover crops: a case-study in SW France. Agric Syst 167:92–102
Selim MM (2019) A review of advantages, disadvantages and challenges of crop rotations. Egypt J Agron 41:1–10
Sfez S, De Meester S, Dewulf J (2017) Co-digestion of rice straw and cow dung to supply cooking fuel and fertilizers in rural India: impact on human health, resource flows and climate change. Sci Total Environ 609:1600–1615
Stella T, Mouratiadou I, Gaiser T, Berg-Mohnicke M, Wallor E, Ewert F, Nendel C (2019) Estimating the contribution of crop residues to soil organic carbon conservation. Environ Res Lett 14:094008
Stewart C, Roosendaal D, Manter D, Delgado J, Del Grosso S (2018) Interactions of stover and nitrogen management on soil microbial community and labile carbon under irrigated no-till corn. Soil Sci Soc Am J 82:323–331
Swanepoel PA, le Roux PJG, Agenbag GA, Strauss JA, MacLaren C (2019) Seed-drill opener type and crop residue load affect canola establishment, but only residue load affects yield. Agron J 111:1658–1665. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2018.10.0695
Urra J, Mijangos I, Lanzén A, Lloveras J, Garbisu C (2018) Effects of corn stover management on soil quality. Eur J Soil Biol 88:57–64
Virk HK, Singh G, Sharma P (2017) Effect of tillage, crop residues of preceding wheat crop and nitrogen levels on biological and chemical properties of soil in the soybean-wheat cropping system. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 48:1764–1771. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2017.1395446
Virk HK, Singh G, Manes GS (2019) Nutrient uptake, nitrogen use efficiencies, and energy indices in soybean under various tillage systems with crop residue and nitrogen levels after combine harvested wheat. J Plant Nutr 43:407–417. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2019.1683190
Watson CA, Reckling M, Preissel S, Bachinger J, Bergkvist G, Kuhlman T et al (2017) Grain legume production and use in European agricultural systems. Adv Agron 144:235–303
Yang HS, Yang B, Dai YJ, Xu MM, Koide RT, Wang XH, Liu J, Bian X (2015) Soil nitrogen retention is increased by ditch-buried straw return in a rice-wheat rotation system. Eur J Agron 69:52–58
Zhang L, Wang J, Fu G, Zhao Y (2018) Rotary tillage in rotation with plowing tillage improves soil properties and crop yield in a wheat-maize cropping system. PLoS One 13:e0198193
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirzel, J., Undurraga, P., León, L. et al. Medium-Term Crop Rotations with Different Residue Incorporation Rates: Effect on Durum Wheat Production and Plant Nutrient Concentration and Extraction. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21, 2145–2152 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00510-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00510-3