Abstract
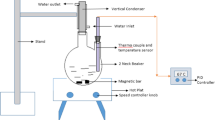
The performance of a rotating fixed bed reactor in recovering copper from industrial waste solutions by cementation is studied under various conditions. The rotating fixed bed is made of stacked woven steel screens to take advantage of two features of screens: the ability to present large area per unit volume and their ability to promote high turbulence. Variables studied are initial CuSO4 concentration, bed rotation speed, mesh number of the screens and bed thickness. The presence of baffles was found to increase the rate of cementation. The data were correlated by a dimensionless mass transfer correlation suitable for the design and operation of large scale cementation reactors.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
Screen bed Area,m2
- а,a1 :
-
Constant
- Co :
-
Initial reactant concentration, mol cm−3
- C:
-
Concentration at any time (t), mol cm−3
- D:
-
Diffusivity, cm2 s−1
- dw :
-
Wire diameter of the cylinder,cm
- d:
-
Screen diameter, cm
- h:
-
Bed height, cm
- k:
-
Mass transfer coefficient, m s−1
- N:
-
Rotation Speed, rad/s
- ΔP:
-
Pressure drop
- Q:
-
Solution volume, cm3
- r:
-
Screen radius,cm
- t:
-
Time, min
- V:
-
Linear speed of the rotating screen (V = ωr)
- Re:
-
Reynolds Number \( \left(\frac{\uprho\ \mathrm{N}\ {\mathrm{d}}^2}{\upmu .}\right) \)
- Res :
-
Surface renewal model Reynolds number \( \left(\frac{\uprho\ \mathrm{N}\ {\mathrm{r}}^2}{\upmu}\right) \)
- Sc:
-
Schmidt number \( \left(\frac{\upmu\ }{\uprho\ \mathrm{D}}\right) \)
- Sh:
-
Sherwood number \( \left(\frac{\mathrm{k}\ \mathrm{d}\ }{\mathrm{D}}\right) \)
- Res :
-
Surface renewal model Sherwood number \( \left(\frac{\mathrm{k}\ \mathrm{r}\ }{\mathrm{D}}\right) \)
- ε :
-
\Specific energy dissipation, cm2 s −3
- μ :
-
Solution viscosity, g cm−1 s−1
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity, cm2 s −1
- ρ :
-
Solution density, g cm−3
- ω :
-
Rotation speed, rpm \( \left(\upomega =\frac{2\uppi \mathrm{N}}{60}\right) \)
References
Biswas K, Davenport G (1979) Extractive metallurgy of copper. Pergamon Press, New York
Rossi G (1990) Biohydrometallurgy. Mc Graw Hill book Co., New York
Janwong A, De Wet K, Cooper R (2016) Impact of silica on cadmium cementation by zinc dust in a zinc SX/EW plant. Miner Metall Process 33:126
Casado J (2018) Revisiting the mechanism of cementation: the role of hydrogen species in acidic aqueous media. Miner Metall Process 35:55
Abdel-Aziz MH, El-Ashtoukhy E-SZ, Bassyouni M (2016) Recovery of copper from effluents by cementation on aluminum in a multirotating cylinder-agitated vessel. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B 47:657
Gros F, Baup S, Aurouseau M (2008) Intensified recovery of copper in solution: cementation onto iron in fixed or fluidized bed under electromagnetic field. Chem Eng Process 47:295
Sedahmed GH, El-Taweel YA, Konsowa AH, Abdel-Aziz MH (2011) Mass transfer intensification in an annular electrochemical reactor by an inert fixed bed under various hydrodynamic conditions. Chem Eng Process 50:1122
Gros F, Baup S, Aurousseau M (2011) Copper cementation on zinc and iron mixtures: Part2: fluidized bed configuration. Hydrometallurgy 106:119
El-Batouti M (2005) Removal of copper metal by cementation using a rotating iron cylinder. J Colloid Interface Sci 283:123
Gros F, Baup S, Aurouseau M (2011) Copper cementation on zinc and iron mixtures: Part1: results on rotating disc electrode. Hydrometallurgy 106:127
El-Ashtoukhy ESZ, Abdel-Aziz MH (2013) Removal of copper from aqueous solutions by cementation in a bubble column reactor with horizontal screens. Int J Miner Process 121:65
Kuhn W (1983) Investigation of heat transfer behind an oscillating grid. International Journal of Heat Mass Transfer 26:1347
Visscher F, Schaaf J, Nijhuis T, Schouten J (2013) Rotating reactors – a review. Chem Eng Res Des 91:1923
Abdel-Aziz MH, Nirdosh I, Sedahmed GH (2018) Liquid–solid mass transfer behaviour of heterogeneous reactor made of a rotating tubular packed bed of spheres. Int J Heat Mass Transf 126:1129
Modak J, Bhowal A, Datta S (2016) Extraction of dye from aqueous solutions in rotating packed bed. J Hazard Mater 304:337
Guo K, Wen J, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Li Z, Qian Z (2014) Optimal packing of a rotating packed bed for H2S removal. Environ Sci Technol 48:6844
Chen Y, Huang Y, Lin R, Shang N (2010) A continuous flow biodiesel production process using a rotating packed bed. Bioresour Technol 101:668
Vogel A (1961) A textbook of quantitative inorganic analysis. Longmans, London
Findlay A, Kitchner J (1965) Practical physical chemistry. Longman, London
Lobo V (1993) Mutual diffusion coefficient in aqueous electrolyte solutions. Pure Appl Chem 65:2613
Walsh F (1993) A first course in electrochemical engineering, The electrochemical consultancy. Hants U.K.
Fahidy Z (1985) Principle of electrochemical reactor analysis. Elsevier, New York
Armour J, Canon J (1968) Fluid flow through woven screens. AICHE J 14:415
Grau J, Bisang J (2005) Mass transfer studies at rotating cylinder electrodes of expanded metal. Journal Applied Electrochemistry 35:285
Cussler E (1988) Diffusion, Mass Transfer in Fluid Systems. Cambridge University Press, New York
Olds hue J (1985) Fluid mixing technology. McGraw Hill
Ruckenstein E (1958) A note concerning turbulent exchange of heat or mass with a boundary. Chem Eng Sci 7:265
Knudsen J, Katz D (1958) Fluid dynamics and heat transfer. Mc Graw Hill, New York
Calderbank P, Moo-Young M (1961) The continuous phase heat and mass transfer properties of dispersions. Chem Eng Sci 16:39
Coulson J, Richardson J, Backhurst J, Harker J (1978) Chemical engineering unit operation, vol 2. Pergamon Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Aziz, E.G., El-Naggar, M.A., Nosier, S.A. et al. Recovery of Copper from Industrial Waste Solutions by Cementation Using a Rotating Fixed Bed of Stacked Steel Screens. Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration 37, 453–458 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42461-020-00191-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42461-020-00191-z