Abstract
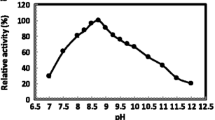
Ionic liquids (ILs) have gained immense attention as eco-friendly solvents for pretreatment of lignocellulosics for their potential bioconversion to biofuels, bio-chemicals, and other products. However, for saccharification of ionic liquid (IL)-pretreated biomass, IL-stable cellulases are desired. IL-stable cellulase and xylanase enzyme preparation developed from a previously isolated Aspergillus assiutensis VS34 was used for saccharification of IL-pretreated biomass. Current study reports the purification of IL-stable cellulase (CMCase) from A. assiutensis VS34 based on salt precipitation and ion exchange chromatography. Functionality of the purified cellulase (2.10-fold) was observed by native-PAGE and zymography, and the molecular weight (27 kDa) was assayed by SDS-PAGE. Though optimum temperature and pH of CMCase was 50 ℃ and 6.0, respectively, but the enzyme showed considerable activity and stability over a wide range of temperature (40–80 ℃, 72–99%) and pH (3–11, 60–95%). The activity of enzymes was enhanced by certain metal ions (Ca2+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Mg2+, and Co2+), but decreased considerably by Hg2+. Km and Vmax of CMCase were 6.996 mg/ml and 16.103 μmol/min/mg, respectively. Process-apt properties of A. assiutensis VS34 CMCase reflect its application potential for a variety of processes including biomass conversion.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No such data availability statement is available.
References:
Al Mousa AA, Hassane AM, Gomaa AERF, Aljuriss JA, Dahmash ND, Abo-Dahab NF (2022) Response-surface statistical optimization of submerged fermentation for pectinase and cellulase production by Mucor circinelloides and M. hiemalis. Fermentation 8:205. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8050205
Bajaj BK, Singh NP (2010) Production of xylanase from an alkali tolerant Streptomyces sp. 7b under solid-state fermentation, its purification, and characterization. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162:1804–1818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-010-8960-x
Bajaj BK, Sharma P (2011) An alkali-thermotolerant extracellular protease from a newly isolated Streptomyces sp. DP2. New Biotechnol 28:725–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2011.01.001
Bano A, Chen X, Prasongsuk S, Akbar A, Lotrakul P, Punnapayak H, Ali I (2019) Purification and characterization of cellulase from obligate halophilic Aspergillus flavus (TISTR 3637) and its prospects for bioethanol production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 189:1327–1337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03086-y
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Dotsenko AS, Rozhkova AM, Zorov IN, Sinitsyn AP (2020) Protein surface engineering of endoglucanase Penicillium verruculosum for improvement in thermostability and stability in the presence of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquid. Bioresour Technol 296:122370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122370
Ejaz U, Sohail M, Ghanemi A (2021) Cellulases: from bioactivity to a variety of industrial applications. Bioinspir Biomim 6:44. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics6030044
Elgharbawy AA, Alam MdZ, Kabbashi NA, Moniruzzaman M, Jamal P (2016) Evaluation of several ionic liquids for in situ hydrolysis of empty fruit bunches by locally-produced cellulase. 3 Biotech 6:128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0440-8
Gupta M, Sharma M, Singh S, Gupta P, Bajaj BK (2015) Enhanced production of cellulase from Bacillus licheniformis K-3 with potential for saccharification of rice straw. Energy Technol 3:216–224. https://doi.org/10.1002/ente.201402137
Haykir NI, Zahari SMSNS, Harirchi S, Sar T, Awasthi MK, Taherzadeh MJ (2023) Applications of ionic liquids for the biochemical transformation of lignocellulosic biomass into biofuels and biochemicals: a critical review. Biochem Eng J 193:108850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2023.108850
Hmad IB, Boudabbous M, Belghith H, Gargouri A (2017) A novel ionic liquidstable halophilic endoglucanase from Stachybotrys microspora. Process Biochem 54:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2017.01.007
Ilmberger N, Meske D, Juergensen J, Schulte M, Barthen P, Rabausch U, Streit WR (2012) Metagenomic cellulases highly tolerant towards the presence of ionic liquids—linking thermostability and halotolerance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3732-2
Intasit R, Cheirsilp B, Suyotha W, Boonsawang P (2021) Synergistic production of highly active enzymatic cocktails from lignocellulosic palm wastes by sequential solid state-submerged fermentation and co-cultivation of different filamentous fungi. Biochem Eng J 173:108086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2021.108086
Jaeger V, Burney P, Pfaendtner J (2015) Comparison of three ionic liquid-tolerant cellulases by molecular dynamics. Biophys J 108:880–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2014.12.043
Jmel MA, Anders N, Yahmed NB, Marzouki MN, Spiess A, Smaali I (2020) Efficient enzymatic saccharification of macroalgal biomass using a specific thermostable GH 12 endoglucanase from Aspergillus terreus JL1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2779-6
López-López A, Santiago-Hernández A, Cayetano-Cruz M, García-Huante Y, Campos JE, Bustos-Jaimes I, Hidalgo-Lara ME (2023) TtCel7A: a native thermophilic bifunctional cellulose/xylanase exogluclanase from the thermophilic biomass-degrading fungus Thielavia terrestris Co3Bag1, and Its application in enzymatic hydrolysis of agroindustrial derivatives. J Fungi 9:152. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9020152
Maleki M, Ariaeenejad S, Salekdeh GH (2022) Efficient saccharification of ionic liquid-pretreated rice straw in a one-pot system using novel metagenomics derived cellulases. Bioresour Technol 345:126536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126536
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60147a030
Nargotra P, Sharma V, Bajaj BK (2019) Consolidated bioprocessing of surfactant-assisted ionic liquid-pretreated Parthenium hysterophorus L. biomass for bioethanol production. Bioresour Technol 289:121611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121611
Nargotra P, Sharma V, Gupta M, Kour S, Bajaj BK (2018) Application of ionic liquid and alkali pretreatment for enhancing saccharification of sunflower stalk biomass for potential biofuel-ethanol production. Bioresour Technol 267:560–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.070
Nargotra P, Sharma V, Lee YC, Tsai YH, Liu YC, Shieh CJ, Tsai ML, Kuo CH (2022b) Microbial lignocellulolytic enzymes for the effective valorization of lignocellulosic biomass: a review. Catalysts 13:83. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010083
Nargotra P, Sharma V, Sharma S, Bangotra R, Bajaj BK (2022a) Purification of an ionic liquid stable cellulase from Aspergillus aculeatus PN14 with potential for biomass refining. Environ Sustain 5:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-022-00232-x
Nisar K, Abdullah R, Kaleem A, Iqtedar M, Aftab M, Saleem F (2022) Purification, characterization and thermodynamic analysis of cellulases produced from Thermomyces dupontii and its industrial applications. Saudi J Biol Sci 29:103483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103483
Olukunle OF, Ayodeji AO, Akinloye PO (2021) Carboxymethyl cellulase (CMCase) from UV-irradiation mutated bacillus cereus FOA-2 cultivated on plantain (Musa parasidiaca) stalk-based medium: production. Production, Purification and Characterization Sci Afr 11:e00691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00691
Pachauri P, More S, Sullia SB, Deshmukh S (2020) Purification and characterization of cellulase from a novel isolate of Trichoderma longibrachiatum. Biofuels 11:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/17597269.2017.1345357
Patel A, Shah A (2021) Purification and characterization of novel, thermostable and non-processive GH5 family endoglucanase from Fomitopsis meliae CFA 2. Int J Biol Macromol 182:1161–1169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.110
Patil SP, Shirsath LP, Chaudhari BL (2021) A halotolerant hyaluronidase from newly isolated Brevibacterium halotolerans DC1: Purification and characterization. Int J Biol Macromol 166:839–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.240
Pedersen JN, Pérez B, Guo Z (2019) Stability of cellulase in ionic liquids: correlations between enzyme activity and COSMO-RS descriptors. Sci Rep 9:17479. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53523-5
Prajapati BP, Suryawanshi RK, Agrawal S, Ghosh M, Kango N (2018) Characterization of cellulase from Aspergillus tubingensis NKBP-55 for generation of fermentable sugars from agricultural residues. Bioresour Technol 250:733–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.11.099
Sajith S, Sreedevi S, Priji P, Unni KN, Benjamin S (2014) Production and partial purification of cellulase from a novel fungus, Aspergillus flavus BS1. Ann Microbiol 64:763–771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0711-0
Saroj P, Narasimhulu K (2022) Biochemical characterization of thermostable carboxymethyl cellulase and β-glucosidase from Aspergillus fumigatus JCM 10253. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03839-2
Sawhney D, Vaid S, Bangotra R, Sharma S, Dutt HC, Kapoor N, Bajaj BK (2023) Proficient bioconversion of rice straw biomass to bioethanol using a novel combinatorial pretreatment approach based on deep eutectic solvent, microwave irradiation and laccase. Bioresour Technol 375:128791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2023.128791
Sharma S, Sharma V, Nargotra P, Bajaj BK (2018) Process desired functional attributes of an endoxylanase of GH10 family from a new strain of Aspergillus terreus S9. Int J Biol Macromol 115:663–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.096
Sharma S, Tsai ML, Sharma V, Sun PP, Nargotra P, Bajaj BK, Dong CD (2022a) Environment friendly pretreatment approaches for the bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass into biofuels and value-added products. Environments 10:6. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10010006
Sharma V, Nargotra P, Bajaj BK (2019) Ultrasound and surfactant assisted ionic liquid pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse for enhancing saccharification using enzymes from an ionic liquid tolerant Aspergillus assiutensis VS34. Bioresour Technol 285:121319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121319
Sharma V, Nargotra P, Sharma S, Bajaj BK (2020) Efficient bioconversion of sugarcane tops biomass into biofuel-ethanol using an optimized alkali-ionic liquid pretreatment approach. Biomass Convers Biorefin 13:841–854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-01123-z
Sharma V, Tsai ML, Nargotra P, Chen CW, Kuo CH, Sun PP, Dong CD (2022b) Agro-industrial food waste as a low-cost substrate for sustainable production of industrial enzymes: a critical review. Catalysts 12:1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12111373
Singh S, Gupta P, Bajaj BK (2018) Characterization of a robust serine protease from Bacillus subtilis K-1. J Basic Microbiol 58:88–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201700357
Sulyman AO, Igunnu A, Malomo SO (2020) Isolation, purification and characterization of cellulase produced by Aspergillus niger cultured on Arachis hypogaea shells. Heliyon 6:e05668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05668
Sun Y, Li P, Sun Q, Liu X, Wang Y, Zhang B, Hu X (2022) Insights into Ionic liquids-resistance mechanism and lignocellulose-degradation model of Aspergillus terreus in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate. Ind Crops Prod 178:114593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114593
Taneja K, Bajaj BK, Kumar S, Dilbaghi N (2017) Production, purification and characterization of fibrinolytic enzyme from Serratia sp. KG-2–1 using optimized media. 3 Biotech 7:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0808-4
Tiwari S, Singh R, Yadav J, Gaur R, Singh A, Yadav JS, Jamal F (2022) Three-step purification and characterization of organic solvent-tolerant and alkali-thermo-tolerant xylanase from Bacillus paramycoides T4 [MN370035]. Catalysts 12:749. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12070749
Trivedi N, Gupta V, Reddy CRK, Jha B (2013) Detection of ionic liquid stable cellulase produced by the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. isolated from brown alga Sargassum polycystum C. Agardh Bioresour Technol 132:313–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.040
Vaid S, Mishra T, Bajaj BK (2018) Ionic-liquid-mediated pretreatment and enzymatic saccharification of Prosopis sp. biomass in a consolidated bioprocess for potential bioethanol fuel production. Energy Ecol Environ 3:216–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-018-0095-x
Xu J, Xiong P, He B (2016) Advances in improving the performance of cellulase in ionic liquids for lignocellulose biorefinery. Bioresour Technol 200:961–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.10.031
Xu J, He B, Wu B, Wang B, Wang C, Hu L (2014) An ionic liquid tolerant cellulase derived from chemically polluted microhabitats and its application in in situ saccharification of rice straw. Bioresour Technol 157:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.102
Acknowledgements
Dr. Bijender Kumar Bajaj (BKB) gratefully acknowledges the grants received in the form of research projects from ICMR, UGC, DST, CSIR and DBT. BKB gratefully acknowledges various agencies for providing fellowships for overseas ‘Research Stays’ i.e. Indo-US Science and Technology Forum (Ohio State University, USA), Commonwealth Scholarship Commission, UK (Institute of Biological, Environmental and Rural Sciences, Aberystwyth University, Aberystwyth, UK), and Institute of Advanced Study, Durham University, UK (COFUND-International Senior Research Fellow at Department of Biosciences, Durham University, UK). Dr. Parushi Nargotra acknowledges Rashtriya Uchchattar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA) for providing a Ph.D. research fellowship. Dr. Vishal Sharma acknowledges the DST, Govt. of India for providing Inspire fellowship for doctoral research.
Funding
Financial support in the form of Research Projects to Dr. Bijender Kumar Bajaj (BKB) from funding agencies such as DST, DBT, UGC, CSIR and ICMR is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Vishal Sharma; Methodology: Vishal Sharma; Formal analysis and investigation: Parushi Nargotra; Writing—original draft preparation: Vishal Sharma, Parushi Nargotra; Writing—review and editing: Surbhi Sharma, Ridhika Bangotra, Akhlash P Singh, Nisha Kapoor, Ritu Mahajan; Funding acquisition: Bijender Kumar Bajaj, Resources: Bijender Kumar Bajaj; Supervision: Bijender Kumar Bajaj.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, V., Nargotra, P., Sharma, S. et al. Purification and biochemical characterization of an ionic liquid tolerant cellulase from Aspergillus assiutensis VS34 for potential biomass conversion applications. Environmental Sustainability (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-024-00311-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-024-00311-1