Abstract
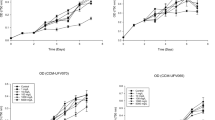
Interactive effects of ultraviolet radiation (UVR), photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) and exogenously supplied ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) was studied in the rice-field cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. HKAR-7. The cyanobacterium was cultured under varying NH4Cl concentrations i.e., 0, 50, 200, 500, 1000 and 5000 μM and 200 μM (concentration) was found to be optimum for the growth of the cyanobacterium. Detrimental effects of UV-B exposure were observed on photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll a (Chl a), carotenoids and phycocyanin (PC). However, damage to these pigments was less in the cyanobacterial samples supplemented with NH4Cl. Contents of Chl a and PC in cyanobacterial cells decreased upon UV-B exposure but decrement was less in the samples supplemented with NH4Cl. Upon UV-B exposure, carotenoids content enhanced initially (till 15 days) during the course of treatment (21 days) but significant decrease (in carotenoids content) was observed in later phase of the experiment. From the results of photosynthetic activity, maximum quantum efficiency of PSII (Fv/Fm) and maximum electron transport rate (ETRmax), it could be concluded that exogenous supplementation of NH4Cl (optimum concentration) helped in protecting the cyanobacterial cells from highly energetic UVR to certain extent. Another interesting observation was significantly higher levels of biosynthesis and accumulation of mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) in the cyanobacterial cells supplemented with NH4Cl in comparison to non-supplemented cells. The purified MAA was identified to be phorphyra-334 as evidenced by UV/VIS absorption spectra, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (ESI–MS).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed H, Pathak J, Rajneesh PP, Singh PR, Sinha RP (2019) Genomics and proteomics of photoprotective compounds mycosporine-like amino acids in cyanobacteria. In: Sinha RP, Pandey S, Ghoshal N (eds) Innovations in life science research. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge, pp 97–128
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Balskus EP, Walsh CT (2010) The genetic and molecular basis for sunscreen biosynthesis in cyanobacteria. Science 329:1653–1656. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1193637
Banaszak AT, Neale PJ (2001) Ultraviolet radiation sensitivity of photosynthesis in phytoplankton from an estuarine environment. Limnol Oceanogr 46:592–603. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2001.46.3.0592
Bandaranayake WM (1998) Mycosporines: are they nature’s sunscreens? Nat Prod Rep 15:15972. https://doi.org/10.1039/A815159Y
Batista LFZ, Kaina B, Meneghini R, Menck CFM (2009) How DNA lesions are turned into powerful killing structures: Insights from UV-induced apoptosis. Mutat Res Rev 681:197–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrrev.2008.09.001
Beardall J, Roberts S, Millhouse J (1991) Effects of nitrogen limitation on uptake of inorganic carbon and specific activity of ribulose-1, 5 biphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in green microalgae. Can J Bot 69:1146–1150. https://doi.org/10.1139/b91-147
Bhandari RR, Sharma PK (2011) Photosynthetic and biochemical characterization of pigments and UV-absorbing compounds in Phormidium tenue due to UV-B radiation. J Appl Phycol 23:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9621-8
Britt AB (1996) DNA damage and repair in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 47:75–100. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.47.1.75
Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ (2002) NH4+ toxicity in higher plants: a critical review. J Plant Physiol 159:567–584. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-0774
Bryant DA, Guglielmi G, Tandeau de Marsac N, Castlets AM, Cohen-Bazire G (1979) The structure of cyanobacterial phycobilisomes: a model. Arch Microbiol 123:113–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00446810
Conde FR, Churio MS, Previtali CM (2004) The deactivation pathways of the excited-states of the mycosporine-like amino acids shinorine and porphyra-334 in aqueous solution. Photochem Photobiol Sci 3:960–967. https://doi.org/10.1039/b405782a
Desikachary TV (1959) Cyanophyta. Indian Council of Agriculture Research, New Delhi. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2000.45.5.1144
Döhler G (1992) Impact of UV-B radiation on the uptake of 15N-ammonia and 15N-nitrate by phytoplankton of the Wadden Sea. Mar Biol 112:485–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00356294
Donkor VA, Häder D-P (1991) Effects of solar and ultraviolet radiation on motility, photomovement and pigmentation in filamentous, gliding cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 86:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1097(91)90661-S
Drath M, Kloft N, Batschauer A, Marin K, Novak J, Forchhammer K (2008) Ammonia triggers photodamage of photosystem II in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. Plant Physiol 147(1):206–215. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.117218
Dunlap WC, Shick JM (1998) UV radiation absorbing mycosporine-like amino acids in coral reef organisms: a biochemical and environmental perspective. J Phycol 34:418–430. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8817.1998.340418.x
Franklin LA, Kräbs G, Kuhlenkamp R (2001) Blue light and UV-A radiation control the synthesis of mycosporine-like amino acids in Chondrus crispus (Florideophyceae). J Phycol 37:257–270. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8817.2001.037002257.x
Garcia-Pichel F, Wingard CE, Castenholz RW (1993) Evidence regarding the UV sunscreen role of a mycosporine like compound in the cyanobacterium Gloecapsa sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:170–176
Götz T, Whidhovel U, Boger P, Sandmann G (1999) Protection of photosynthesis against ultraviolet-B radiation by carotenes in transformants of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus PCC 7942. Plant Physiol 120:599–604. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.120.2.599
Gröniger A, Hallier C, Häder D (1999) Influence of UV radiation and visible light on Porphyraumbilicalis: photoinhibition and MAA concentration. J Appl Phycol 11:437–445. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008179322198
Häder D-P, Williamson CE, Wängberg SÅ, Rautio M, Rose KC, Gao K, Helbling EW, Sinha RP, Worrest R (2015) Effects of UV radiation on aquatic ecosystems and interactions with other environmental factors. Photochem Photobiol Sci 14:108–126. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4pp90035a
Hoyer K, Karsten U, Sawall T, Wiencke C (2001) Photoprotective substances in Antarctic macroalgae and their variation with respect to depth distribution, different tissues and developmental stages. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 211:117–129. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps211117
Huovinen P, Matos J, Pinto IS, Figueroa FL (2006) The role of ammonium in photoprotection against high irradiance in the red alga Grateloupia lanceola. Aquat Bot 84:308–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2005.12.002
Jensen A (1978) Chlorophylls and carotenoids. In: Craige IS, Hellebust JA (eds) Handbook of phycological methods: physiological and biochemical methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 59–70
Kannaujiya VK, Sinha RP (2015) Impacts of varying light regimes on phycobiliproteins of Nostoc sp. HKAR-2 and Nostoc sp. HKAR-11 isolated from diverse habitats. Protoplasma 252:1551–1561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0786-5
Karsten U, Wiencke C (1999) Factors controlling the formation of UV-absorbing mycosporine-like amino acids in the marine red alga Palmaria palmata from Spitsbergen (Norway). J Plant Physiol 155:407–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(99)80124-2
Karsten U, Franklin LA, Lüning K, Wiencke C (1998a) Natural ultraviolet and photosynthetic active radiation induce formation of mycosporine-like amino acids in the marine macroalga Chondrus crispus (Rhodophyta). Planta 205:257–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250050319
Karsten U, Sawall T, Hanelt D, Bischof K, Figueroa FL, Flores-Moya A, Wiencke C (1998b) An inventory of UV absorbing mycosporine-like amino acids in macroalgae from polar to warm-temperate regions. Bot Mar 41:443–453. https://doi.org/10.1515/botm.1998.41.1-6.443
Korbee-Peinado N, Abdala-Díaz RT, Figueroa FL, Helbling EW (2004) Ammonium and UV radiation stimulate the accumulation of mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) in Porphyra columbina (Rhodophyta) from Patagonia, Argentina. J Phycol 40:248–259. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8817.2004.03013.x
Korbee-Peinado N, Huovinen P, Figueroa FL, Aguilera J, Karsten U (2005) Availability of ammonium influences photosynthesis and the accumulation of mycosporine-like amino acids in two Porphyra species (Bangiales: Rhodophyta). Mar Biol 146:645–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-004-1484-6
Kumar A, Tyagi MB, Jha PN, Srinivas G, Singh A (2003) Inactivation of cyanobacterial nitrogenase after exposure to ultraviolet-B radiation. Curr Microbiol 46:380–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-001-3894-3
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lesser MP, Cullen JJ, Neale PJ (1994) Carbon uptake in a marine diatom during acute exposure to ultraviolet radiation: relative importance of damage and repair. J Phycol 30:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-3646.1994.00183.x
Lesser MP, Neale PJ, Cullen JJ (1996) Acclimation of Antarctic phytoplankton to ultraviolet radiation: ultraviolet-absorbing compounds and carbon fixation. Mol Mar Biol Biotech 5:314–325
Litchman E, Neale PJ, Banaszak AT (2002) Increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation in nitrogen-limited dinoflagellates: photoprotection and repair. Limnol Oceanogr 47:86–94. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2002.47.1.0086
Lohman M, Döhler G, Huckenbeck N, Veridni S (1998) Effects of UV radiation of different wavebands on pigmentation, 15N-ammonium uptake, amino acid pools and adenylate contents of marine diatoms. Mar Biol 130:501–507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050270
Marwood CA, Greenberg BM (1996) Effect of supplementary UV-B radiation on chlorophyll synthesis and accumulation of photosystems during chloroplast development in Spirodela oligorrhiza. Photochem Photobiol 64:664–670. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-1097.1996.tb03121.x
Neale PJ, Banaszak AT, Jarriel CR (1998) Ultraviolet sunscreens in Gymnodinium sanguineum (Dinophyceae): mycosporine-like amino acids protect against inhibition of photosynthesis. J Phycol 34:928–938. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8817.1998.340928.x
Oren A, Gunde-Cimerman N (2007) Mycosporines and mycosporine-like amino acids: UV protectants or multipurpose secondary metabolites? FEMS Microbiol Lett 269:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00650.x
Paerl HW, Tucker J, Bland PT (1983) Carotene enhancement and its role in maintaining blue-green algal (Microcystis aeruginosa) surface blooms. Limnol Oceanogr 28:847–857. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1983.28.5.0847
Pandey A, Ahmed H, Singh V, Singh DK, Rajneesh PJ, Sinha RP (2018) Impacts of UV-B radiation on the enzymes of nitrogen metabolism in cyanobacteria. In: Sinha RP, Srivastava UP (eds) Trends in life science. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge, pp 243–287
Pandey A, Pathak J, Singh DK, Ahmed H, Singh V, Kumar D, Sinha RP (2020) Photoprotective role of UV-screening pigment scytonemin against UV-B-induced damages in the heterocyst-forming cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. strain HKAR-2. Braz J Bot 43:67–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-020-00589-5
Pathak J, Ahmed H, Rajneesh SSP, Häder DP, Sinha RP (2019) Genetic regulation of scytonemin and mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) biosynthesis in cyanobacteria. Plant Gene 17:100172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plgene.2019.100172
Pathak J, Rajneesh SPR, Häder D-P, Sinha RP (2019) UV-induced DNA damage and repair: a cyanobacterial perspective. Plant Gene 22:100194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plgene.2019.100194
Pattanaik B, Roleda MY, Schumann R, Karsten U (2008) Isolate-specific effects of ultraviolet radiation on photosynthesis, growth and mycosporine-like amino acids in the microbial mat-forming cyanobacterium Microcoleus chthonoplastes. Planta 227:907–916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0666-0
Porra RJ (2002) The chequered history of the development and use of simultaneous equations for the accurate determination of chlorophylls a and b. Photosynth Res 73:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020470224740
Prasad SM, Zeeshan M (2005) UV-B radiation and cadmium induced changes in growth, photosynthesis, and antioxidant enzymes of cyanobacterium Plectonema boryanum. Biol Plant 49:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-005-0236-x
Qin HJ, Peng CG, Liu YD, Li DH (2012) Differential responses of Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 (Cyanophyceae) cultured in nitrogen deficient and nitrogen-enriched media to ultraviolet-B radiation. J Phycol 48:615–625. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2012.01162.x
Rajneesh CA, Pathak J, Ahmed H, Singh V, Singh DK, Pandey A, Singh SP, Richa HDP, Sinha RP (2018) Ultraviolet radiation-induced DNA damage and mechanisms of repair in cyanobacteria: an overview. In: Sinha RP, Shrivastava UP (eds) Trends in life science research. Nova Publisher, Hauppauge, pp 169–218
Rajneesh PJ, Richa Häder D-P, Sinha RP (2019) Impacts of ultraviolet radiation on certain physiological and biochemical processes in cyanobacteria inhabiting diverse habitats. Environ Exp Bot 161:375–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.10.037
Rastogi RP, Incharoensakdi A (2013) UV radiation-induced accumulation of photoprotective compounds in the green alga Tetraspora sp. CU2551. Plant Physiol Biochem 70:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.04.021
Rastogi RP, Kumari S, Richa HT, Sinha RP (2012) Molecular characterization of hot spring cyanobacteria and evaluation of their photoprotective compounds. Can J Microbiol 58:719–727. https://doi.org/10.1139/w2012-044
Rastogi RP, Sonani RR, Madamwar D, Incharoensakdi A (2016) Characterization and antioxidant functions of mycosporine-like amino acids in the cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. R76DM. Algal Res 16:110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.03.009
Richa SRP (2015) Biochemical characterization of sunscreening mycosporine-like amino acids from two Nostoc species inhabiting diverse habitats. Protoplasma 252:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0674-4
Richa PP, Sonker AS, Singh V, Sinha RP (2018) Potential applications of natural bioactive cyanobacterial UV protective compounds. In: La Barre S, Bates S (eds) Blue technologies: production and uses of marine molecules. Wiley VCH, Weinheim, pp 693–717
Rippka R, Denuelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111:1–61. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-111-1-1
Roy S (2000) Strategies for the minimization of UV-induced damage. In: de Mora SJ, Demers S, Vernet M (eds) The effects of UV radiation in the marine environment. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 177–205
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Schreiber U (2004) Pulse-amplitude-modulation (PAM) fluorometry and saturation pulse method: an overview. In: Godvindjee GC (ed) Chlorophyll-a fluorescence: a signature of photosynthesis. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 279–319
Senger H (1982) The effect of blue light on plants and microorganisms. Photochem Photobiol 35:911–920. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-1097.1982.tb02668x
Sicora CI, Appleton SE, Brown CM, Chung J, Chandler J, Cockshutt AM, Vass I, Campbell DA (2006) Cyanobacterial psbA families in Anabaena and Synechocystis encode trace, constitutive and UV-B-induced D1 isoforms. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1757:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2005.11.002
Singh SP, Klisch M, Häder D-P, Sinha RP (2008) Role of various growth media on shinorine (mycosporine-like amino acid) concentration and photosynthetic yield in Anabaena variabilis PCC 7937. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:3111–3115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9831-2
Singh SP, Ha SY, Sinha RP, Häder D-P (2014) Photoheterotrophic growth unprecedentedly increases the biosynthesis of mycosporine-like amino acid shinorine in the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp., isolated from hot springs of Rajgir (India). Acta Physiol Plant 36:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-013-1420-9
Singh DK, Richa KD, Chatterjee A, Rajneesh PJ, Sinha RP (2017) Response of the cyanobacterium Fischerella sp strain HKAR-5 against combined stress UV-B radiation, PAR and pyrogallic acid. JSM Environ Sci Ecol 5:1049
Singh DK, Pathak J, Pandey A, Ahmed H, Rajneesh KD, Sinha RP (2020) UV-screening compound mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) in cyanobacteria: biosynthesis, functions and applications. In: Singh PK, Kumar A, Singh VK, Shrivastava AK (eds) Advances in cyanobacterial biology. Elsevier Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 219–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819311-2.00015-2
Sinha RP, Häder D-P (2002) UV-induced DNA damage and repair: a review. Photochem Photobiol Sci 1:225–236. https://doi.org/10.1039/B201230H
Sinha RP, Häder D-P (2016) Effects of global change, including UV and UV screening compounds. In: Borowitzka MA, Beardall J, Raven JA (eds) The physiology of microalgae. Springer, Cham, pp 373–379
Sinha RP, Klisch M, Häder D-P (1999) Induction of a mycosporine-like amino acid (MAA) in the rice-field cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. by UV irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 52:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1011-1344(99)00103-7
Sinha RP, Sinha JP, Gröniger A, Häder D-P (2002) Polychromatic action spectrum for the induction of a mycosporine-like amino acid in a rice-field cyanobacterium, Anabaena sp. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 66:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1011-1344(01)00274-3
Todo T, Ryo H, Yamamoto K, Toh H, Inui T, Ayaki H, Nomura T, Ikenaga M (1996) Similarity among the Drosophila (6–4) photolyase, a human photolyase homology, and the DNA photolyase-blue-light photoreceptor family. Science 272:109–112. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.272.5258.109
Vincent WF, Quesada A (1994) Ultraviolet radiation effects on cyanobacteria: implications for Antarctic microbial ecosystems. In: Weiler CS, Penhale PA (eds) Ultraviolet radiation in antarctica: measurements and biological effects. Antarctic Research Series, American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C., pp 111–124
Vincent WF, Roy S (1993) Solar ultraviolet-B radiation and aquatic primary production: damage, protection and recovery. Environ Rev 1:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1139/a93-001
Wulff A, Wängberg SA, Sundbäck K, Underwood GJC, Nilsson C (2000) Effects of UV-B radiation on a marine microphytobenthic community growing on a sand-substratum under different nutrient conditions. Limnol Oceanogr 45:1144–1152. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2000.45.5.1144
Wulff A, Mohlin M, Sundback K (2007) Intraspecific variation in the response of the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena to moderate UV-B radiation. Harmful Algae 6:388–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2006.11.003
Xia J, Li YJ, Zou D (2004) Effects of salinity stress on PSII in Ulvalactucaas probed by chlorophyll fluorescence measurements. Aquat Bot 80:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2004.07.006
Yakovleva IM, Titlyanov EA (2001) Effect of high visible and UV irradiance on subtidal Chondrus crispus: stress, photoinhibition and protective mechanisms. Aquat Bot 71:47–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3770(01)00167-X
Zhang F, Scheerer P, Oberpichler I, Lamparter T, Krauss N (2013) Crystal structure of a prokaryotic (6–4) photolyase with an Fe–S cluster and a 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine antenna chromophore. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 110:7217–7222. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1302377110
Zhu Z, Gerendas J, Bendixen R, Schinner K, Tabrizi H, Sattelmacher B, Hansen U-P (2000) Inhibitor-dependent stimulation of photosynthetic electron transport by far-red light in NO3− and NH4+ grown plants of Phaseolus vulgaris. L. Plant Biol 2:558–570. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2000-7498
Acknowledgements
DKS (09/013(0612)/2015-EMR-I), JP ((09/013/0515/2013-EMR-I), AP (09/013(0619)/2016-EMR-I) and VS (09/013(0568)/2014-EMR-I) are thankful to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India, for the financial support in the form of senior research fellowships. HA (UGC-JRF-21/12/2014(ii)EU-V) acknowledges University Grants Commission, New Delhi, India, for providing funds in the form of fellowship. Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and DST-INSPIRE, Govt. of India, are gratefully acknowledged for providing fellowships to Rajneesh and DK respectively. We are thankful to the Interdisciplinary School of Life Sciences (ISLS) and Laboratory of Scanning Electron Microscopy, Department of Geology, BHU, Varanasi, for providing access to the ESI-MS and SEM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, D.K., Pathak, J., Pandey, A. et al. Response of a rice-field cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. HKAR-7 upon exposure to ultraviolet-B radiation and ammonium chloride. Environmental Sustainability 4, 95–105 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-020-00146-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-020-00146-6