Abstract
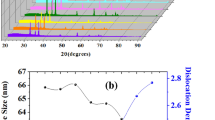
NOX (NO, NO2) is one of the most hazardous gases for the environment as well as human health. In this research, NOX (NO, NO2) gas sensor is fabricated by using a zinc oxide (ZnO) thin film. The study explored the impact of sensing layer thickness variations on gas sensing. In this work sensing response is analyzed at different thicknesses and the optimum thickness for better response. For the given samples with 355 nm optimum thickness at 180 °C optimal operating temperature, it is discovered that the sensing response with bare ZnO thin film increased dramatically from 0.1 to 8.6. The analysis has been carried out at different detecting surface thicknesses for the gas concentration of 500 ppm. In this study, the impacts of varying the ZnO-based thin film thickness are investigated through optical, structural, and gas-sensing characterizations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.U. Abideen et al., Electrospun metal oxide composite nanofibers gas sensors: A review. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 54(5), 366–379 (2017)
P. Shankar, J.B.B. Rayappan, Gas sensing mechanism of metal oxides: the role of ambient atmosphere, type of semiconductor and gases- a review. Sci. Lett. J 4(4), 126 (2015)
L. Castañeda, M. Gonzalez-Alatriste, M. Avendaño-Alejo, Thin solid films semiconducting metal oxide gas sensors: a brief review. Sens. Lett. 14(4), 331–345 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1166/sl.2016.3631
S. Basu, P.K. Basu, Nanocrystalline metal oxides for methane sensors: role of noble metals. J. Sens. 2009 (2009)
S. Bedoui, S. Gomri, H. Charfeddine Samet, A. Kachouri, Design and simulation of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) for ozone gas sensors. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 19, 41–46 (2018)
T. Zhang et al., Multi-component ZnO alloys: bandgap engineering, hetero-structures, and optoelectronic devices. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. Rep. 147, 100661 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2021.100661
P.-C. Chen, G. Shen, C. Zhou, Chemical sensors and electronic noses based on 1-D metal oxide nanostructures. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 7(6), 668–682 (2008)
G.N. Narayanan, R. Sankar Ganesh, A. Karthigeyan, Effect of annealing temperature on structural, optical and electrical properties of hydrothermal assisted zinc oxide nanorods. Thin Solid Films 598, 39–45 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2015.11.071
P. Rai, S. Raj, K. Ko, K.-K. Park, Y. Yu, Synthesis of flower-like ZnO microstructures for gas sensor applications. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 178, 107–112 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.12.031
D. Gal, G. Hodes, D. Lincot, H.-W. Schock, Electrochemical deposition of zinc oxide films from non-aqueous solution: a new buffer/window process for thin film solar cells. Thin Solid Films 361, 79–83 (2000)
T. Shibata, K. Unno, E. Makino, Y. Ito, S. Shimada, Characterization of sputtered ZnO thin film as sensor and actuator for diamond AFM probe. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 102(1–2), 106–113 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0924-4247(02)00339-4
C. Gu, L. Shanshan, J. Huang, C. Shi, J. Liu, Preferential growth of long ZnO nanowires and its application in gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 177, 453–459 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.11.044
L. Zhu, W. Zeng, Room-temperature gas sensing of ZnO-based gas sensor: a review. Sens. Actuators, A 267, 242–261 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2017.10.021
N. Isaac, I. Pikaar, G. Biskos, Metal oxide semiconducting nanomaterials for air quality gas sensors: operating principles, performance, and synthesis techniques. Microchim. Acta 189(5), 1–22 (2022)
K. Haddad et al., SnO2 nanostructured thin films for room-temperature gas sensing of volatile organic compounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10(35), 29972–29981 (2018)
A. Mirzaei, H.R. Ansari, M. Shahbaz, J.-Y. Kim, H.W. Kim, S.S. Kim, Metal oxide semiconductor nanostructure gas sensors with different morphologies. Chemosensors 10(7), 289 (2022)
P. Patial, M. Deshwal, Selectivity and sensitivity property of metal oxide semiconductor based gas sensor with dopants variation: a review. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 23, 1–13 (2021)
K. Seshan, Handbook of Thin-film Deposition Processes and Techniques (CRC Press, Baca Raton, 2002)
S.J. Mezher, K.J. Kadhim, O.M. Abdulmunem, M.K. Mejbel, Microwave properties of Mg–Zn ferrite deposited by the thermal evaporation technique. Vacuum 173, 109114 (2020)
S.P. David, R. Gaume, Electroluminescent thin film phosphors, in Thin Film Structures in Energy Applications. (Springer, Cham, 2015), pp.243–269
J. Huang et al., Large-scale synthesis of flowerlike ZnO nanostructure by a simple chemical solution route and its gas-sensing property. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 146(1), 206–212 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.02.052
K. Anand, O. Singh, M.P. Singh, J. Kaur, R.C. Singh, Hydrogen sensor based on graphene/ZnO nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 195, 409–415 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.01.029
S.C. Navale, V. Ravi, I.S. Mulla, S. Gosavi, S.K. Kulkarni, Low temperature synthesis and NOx sensing properties of nanostructured Al-doped ZnO. Sens. Actuators B: Chem 126(2), 382–386 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2007.03.019
L.B. Capeletti, F.L. Bertotto, J.H.Z. dos Santos, E. Moncada, M.B. Cardoso, The effect of the sol–gel route on the characteristics of acid–base sensors. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 151(1), 169–176 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.09.026
S. Islam, N. Bidin, S. Riaz, G. Krishnan, S. Naseem, Sol–gel based fiber optic pH nanosensor: structural and sensing properties. Sens. Actuators, A 238, 8–18 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2015.12.003
Y. Zhang, S.-W. Ng, X. Lu, Z. Zheng, Solution-processed transparent electrodes for emerging thin-film solar cells. Chem. Rev. 120(4), 2049–2122 (2020)
F. Wang et al., A highly sensitive gas sensor based on CuO nanoparticles synthetized via a sol–gel method. RSC Adv. 6(83), 79343–79349 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra13876d
M. Deshwal, A. Arora, Enhanced acetone detection using Au doped ZnO thin film sensor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29(18), 15315–15320 (2018)
M. Okubo, T. Kuwahara, New Technologies for Emission Control in Marine Diesel Engines (Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2020)
C.Y. Lin, Y.Y. Fang, C.-W. Lin, J.J. Tunney, K. Ho, Fabrication of NOx gas sensors using In2O3–ZnO composite films. Sens. Actuators B: Chem 146(1), 28–34 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.02.040
A. Olabi, T. Wilberforce, M.A. Abdelkareem, Fuel cell application in the automotive industry and future perspective. Energy 214, 118955 (2021)
A. Afzal, N. Cioffi, L. Sabbatini, L. Torsi, NOx sensors based on semiconducting metal oxide nanostructures: progress and perspectives. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 171–172, 25–42 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.05.026
T.V.K. Karthik et al., Sprayed ZnO thin films for gas sensing: effect of substrate temperature, molarity and precursor solution. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(10), 7470–7480 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-02987-7
M. Alam et al., Solution processing of cadmium sulfide buffer layer and aluminum-doped zinc oxide window layer for thin films solar cells. Surf. Rev. Lett. 21(04), 1450059 (2014)
B. Sathyaseelan et al., Structural, optical and morphological properties of post-growth calcined TiO2 nanopowder for opto-electronic device application: ex-situ studies. J. Alloy. Compd. 671, 486–492 (2016)
S. Jurablu, M. Farahmandjou, T. Firoozabadi, Sol-gel synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles: study of structural and optical properties. J. Sci. Islamic Republic of Iran 26(3), 281–285 (2015)
M. Hassan, W. Khan, A. Azam, A.Z. Naqvi, Effect of size reduction on structural and optical properties of ZnO matrix due to successive doping of Fe ions. J. Lumin. 145, 160–166 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.06.024
S. Kaur, M. Deshwal, Study of molarity concentration variation over optical, structural and gas sensing response for ZnO thin film based NOx gas sensor. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 20(4), 309–314 (2019)
F. Bozon-Verduraz, A. Omar, J. Escard, B. Pontvianne, Chemical state and reactivity of supported palladium: I. Characterization by XPS and uv-visible spectroscopy. J. Catal. 53(1), 126–134 (1978)
A. Arora, M. Deshwal, Enhanced sensitivity with thickness optimization of ZnO based acetone sensor. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 56(5), 367–372 (2018)
N. Grossiord, O. Regev, J. Loos, J. Meuldijk, C.E. Koning, Time-dependent study of the exfoliation process of carbon nanotubes in aqueous dispersions by using UV−visible spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 77(16), 5135–5139 (2005)
C. Balamurugan, S.-J. Song, D.-W. Lee, Porous nanostructured GdFeO3 perovskite oxides and their gas response performance to NOx. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 272, 400–414 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.05.125
N. Yamazoe, New approaches for improving semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 5(1–4), 7–19 (1991)
A. Dey, Semiconductor metal oxide gas sensors: a review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 229, 206–217 (2018)
J. Zhang, X. Liu, G. Neri, N. Pinna, Nanostructured materials for room-temperature gas sensors. Adv. Mater. 28(5), 795–831 (2016)
L. Liu et al., Improved selective acetone sensing properties of Co-doped ZnO nanofibers by electrospinning. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 155(2), 782–788 (2011)
M.R. Miah et al., Polypyrrole-based sensors for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) sensing and capturing: A comprehensive review. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 7, 113933 (2002)
A. Kukla, Y.M. Shirshov, S. Piletsky, Ammonia sensors based on sensitive polyaniline films. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 37(3), 135–140 (1996)
P. Singh, F.M. Simanjuntak, Y.-C. Wu, A. Kumar, H.-W. Zan, T.-Y. Tseng, Sensing performance of gas sensors fabricated from controllably grown ZnO-based nanorods on seed layers. J. Mater. Sci. 55, 8850–8860 (2020)
C. Samanta, A. Ghatak, A. Raychaudhuri, B. Ghosh, ZnO/Si nanowires heterojunction array-based nitric oxide (NO) gas sensor with noise-limited detectivity approaching 10 ppb. Nanotechnology 30(30), 305501 (2019)
H.-Y. Lee, Y.-C. Heish, C.-T. Lee, High sensitivity detection of nitrogen oxide gas at room temperature using zinc oxide-reduced graphene oxide sensing membrane. J. Alloy. Compd. 773, 950–954 (2019)
Y.-T. Tsai et al., High sensitivity of NO gas sensors based on novel Ag-doped ZnO nanoflowers enhanced with a UV light-emitting diode. ACS Omega 3(10), 13798–13807 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, S., Sharma, T. & Deshwal, M. Parametric Optimization for Highly Sensitive ZnO Based NOX Gas Sensor. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-024-00521-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-024-00521-8