Abstract
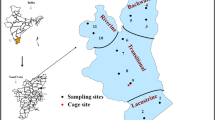
Rapid economic development and rampant urbanization are accelerating the eutrophication of coastal environments. This is the case of the bay of M’Badon in Côte d'Ivoire, located in an area not far from an open dump, which is under strong anthropogenic pressure. However, no data is available on nitrogen and phosphorus distribution in the water column and sediments of the M’Badon bay. This study not only targets the distribution of phosphorus and nitrogen, but also the speciation of phosphorus in sediments in order to assess its bioavailability. In order to do this, the waters of the bay of M’Badon were analyzed with a spectrophotometer and the speciation of phosphorus in the sediments was made according to the method of Williams. The results showed that PO43−, TP, NO3−, NO2− and TN concentrations in the water column varied significantly among the seasons. While, that of NH4+ did not vary between the seasons. In the water column, inorganic phosphorus (0.94 ± 0.12 mg L−1) is high and represents 65.3% of the TP. In addition, inorganic nitrogen concentration (0.33 ± 0.14 mg L−1) was low and organic nitrogen constituted 85% of TN in the water column. The results also indicated that Fe–P concentration (522.8 ± 233.4 μg g−1) represented the highest fraction of phosphorus in sediments with a percentage of 59.5%. Potential bioavailable P accounted for an average of 95.4% of TP in sediments. So, M’badon bay is an important reservoir of bioavailable phosphorus which might accentuate the eutrophication during several decades in the bay.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The dataset used during this study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sujitha SB, Jonathan MP, Escobedo-Urías DC, Aguirre-Bahena F, Villegas LEC, Muñoz-Sevilla NP (2017) Spatial variability of inorganic nutrients and physical parameters in the waters of Bahia Magdalena lagoon, Pacific Coast, Mexico. Acta Ecol Sin 37:187–194
De Andrade-Tubino MF, Azevedo MCC, Franco TP, Araújo FG (2020) How are fish assemblages and feeding guilds organized in different tropical coastal systems? Comparisons among oceanic beaches, bays and coastal lagoons. Hydrobiologia 847:403–419
Garzo PA, Dadon JR, Castro LN (2019) Modelling environmental vulnerability of the Biosphere Reserve Parque Atlántico Mar Chiquito, Argentina, under agricultural and urban impacts. Ocean Coast Manag 170:72–79
Zirino A, Elwany H, Facca C, Neira C, Mendoza G (2016) Nitrogen to phosphorus ratio in the Venice (Italy) lagoon (2001–2010) and its relation to macroalgae. Mar Chem 180:33–41
Hall LM, Morris LJ, Chamberlain RH, Hanisak MD, Virnstein RW, Paperno R, Jacoby CA (2022) Spatiotemporal patterns in the biomass of drift macroalgae in the Indian River Lagoon, Florida, United States. Front Mar Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2022.767440
Boadella J, Butturini A, Compte J, Gionchetta G, Perujo N, Quintana XD, Romaní AM (2021) Different microbial functioning in natural versus man-made Mediterranean coastal lagoons in relation to season. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 259:107434
De Vittor C, Faganeli J, Emili A, Covelli S, Predonzani S, Acquavita A (2012) Benthic fluxes of oxygen, carbon and nutrients in the Marano and Grado Lagoon (northern Adriatic Sea, Italy). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 113:57–70
Almeida LR, Costa IS, Eskinazi-Sant’Anna EM (2012) Composition and abundance of zooplankton community of an impacted estuarine lagoon in Northeast Brazil. Braz J Biol 72:13–24
N’Goran KM, Yao KM, Trokourey A (2019) Phosphorus and nitrogen speciation in waters and sediments highly contaminated by an illicit urban landfill: the Akouedo landfill, Côte d’Ivoire. Reg Stud Mar Sci 31:100805
Ogidi OI, Akpan UM (2022) Aquatic biodiversity loss: impacts of pollution and anthropogenic activities and strategies for conservation. Biodiversity in Africa: potentials, threats and conservation. Springer, Singapore, pp 421–448
Yao KS, Li D, Lei HJ, Van den Brink PJ, Ying GG (2021) Imidacloprid treatments induces cyanobacteria blooms in freshwater communities under sub-tropical conditions. Aquat Toxicol 240:105992
dos Santos CR, Quadra GR, do Oliveira-Souza H, de Amaral VS, Navoni JA (2021) The link between pharmaceuticals and cyanobacteria: a review regarding ecotoxicological, ecological, and sanitary aspects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:41638–41650
Chatziefthimiou AD, Banack SA, Metcalf JS (2021) Harmful algal and cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in the arabian seas: current status, implications, and future directions. The Arabian seas: biodiversity environmental challenges and conservation measures. Springer, Cham, pp 1083–1101
Paerl HW, Otten TG (2013) Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: causes, consequences, andcontrols. Microb Ecol 65:995–1010
Berbel GBB, Braga ES (2014) Phosphorus in Antarctic surface marine sedimentschemical speciation in Admiralty Bay. Antarct Sci 26:281–289
Ni JY, Lin P, Zhen Y, Yao XY, Guo LD (2015) Distribution, source and chemical speciation of phosphorus in surface sediments of the central Pacific Ocean. Deep-Sea Res I 105:74–82
Berbel GBB, Favaro DIT, Braga ES (2015) Impact of harbour, industry and sewage on the phosphorus geochemistry of a subtropical estuary in Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 93:44–52
Zhou FX, Gao XL, Yuan HM, Song JM, Chen CTA, Lui HK, Zhang Y (2016) Geochemical forms and seasonal variations of phosphorus in surface sediments of the East China Sea shelf. J Mar Syst 159:41–54
Meng J, Yao P, Yu ZG, Bianchi TS, Zhao B (2014) Speciation, bioavilability and preservation of phosphorus in surface sediments of the Changjiang Estuary and adjacent East China Sea inner shelf. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 144:27–38
Linsy P, Nagender Nath B, Mascarenhas-Pereira MBL, Chauhan T, Sebastian T, Babu CP, Khadge NH (2018) Distribution and diagenesis of phosphorus in the deep-sea sediments of the Central Indian Basin. J Geophys Res Oceans 123:7963–7982
Soro M-P, N’goran KM, Ouattara AA, Yao KM, Diaco T (2023) Nitrogen and phosphorus spatio-temporal distribution and fluxes intensifying eutrophication in three tropical rivers of Côte d’Ivoire (West Africa). Mar Pollut Bull 186:114391
Choushary AK, Sagar AMK, Kumar AK (2020) Sustainable Management of water demand in the face of rapid urbanization and depletion of groundwater. Stud Indian Place Names 40:146–160
Nguyen TT, Nemery J, Gratiot N, Garnier J, Strady E, Tran VQ, Aimé J (2019) Phosphorus adsorption/desorption processes in the tropical Saigon River estuary (Southern Vietnam) impacted by a megacity. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 227:106321
Svirčev Z, Krstič S, Miladinov-mikov M, Baltič V, Vidovič M (2009) Freshwater Cyanobacterial blooms and primary liver Cancer epidemiological studies in Serbia. J Environ Sci Health Part C: Environ Arcinogenes Ecotoxicol Rev 27:36–55
Smith DR, King KW, Williams MR (2015) What is causing the harmful algal blooms in Lake Erie? J Soil Water Conserv 70:27A-29A
Le Moal M, Gascuel-Odoux C, Ménesguen A, Souchond Y, Étrillard C, Levain A, Moatar F, Pannard A, Souchu P, Lefebvre A, Pinay G (2019) Eutrophication: a new wine in an old bottle? Sci Total Environ 651:1–11
McCarthy MJ, Lavrentyev PJ, Yang L, Zhang L, Chen Y, Qin B, Gardner WS (2007) Nitrogen dynamics and microbial food web structure during a summer cyanobacterial bloom in a subtropical, shallow, well-mixed, eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China). Hydrobiologia 581:195–207
Asare EA, Assim ZB, Wahi RB, Tahir RB, Droepenu EK (2021) Application of fuzzy evaluation technique and grey clustering method for water quality assessment of the coastal and estuaries of selected rivers in Sarawak. Bull Natl Res Centre 45:1–11
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Aminot A, Chaussepied M (1983) Manuel des analyses chimiques en milieu marin. Editions Jouve, CNEXO, Editions Jouve Paris, p 395
Rodier J, Legube B, Merlet N, Brunet R (1996) L’analyse de l’eau, eaux naturelles, eaux résiduaires, eau de mer. 8è édition Dunod. Paris, France, pp 564–571
APHA (1999) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, 20th edn, Washington DC, USA
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, 21th ed. American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation, Washington DC, USA
Kouassi NLB, Yao KM, Trokourey A, Soro MB (2014) Preliminary assessment of cadmium mobility in surface sediments of a tropical estuary. Bull Chem Soc Ethiop 28:245–254
Carbonell-Barrachina AA, Jugsujinda A, Burlo F, Delaune RD, Patrick WH (2000) Arsenic chemistry in municipal sewage sludge as affected by redox potential and pH. Water Res 34:216–224
Kuwano BH, Nogueira MA, Santos CA, Fagotti DS, Santos MB, Lescano LEAM, Andrade DS, Barbosa GMC, Tavares-Filho J (2017) Application of landfill leachate improves wheat nutrition and yield but has minor effects on soil properties. J Environ Qual 46:153–159
Williams JDH, Jaquet JM, Thomas RL (1976) Forms of phosphorus in the surficial sediments of Lake Erie. J Fish Res Board Can 33:413–429
Ruban V, Lopez-Sanchez JF, Pardo P, Rauret G, Muntau H, Quevauviller P (2002) Sequential extraction procedures for phosphorus forms in lake sediment. Methodologies in soil and sediment fractionation studies: single and sequential extraction procedures. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 105–122
Kouassi NLB, Yao KM, Sangare N, Albert Trokourey A, Soro MB (2019) The mobility of the trace metals copper, zinc, lead, cobalt, and nickel in tropical estuarine sediments, Ebrie Lagoon, Côte d’Ivoire. J Soils Sediments 19:929–944
Naminata S, Kwa-Koffi KE, Marcel KA, Marcellin YK (2018) Assessment and impact of leachate generated by the Landfill City in Abidjan on the quality of ground water and surface water (M’Badon Bay, Côte d’Ivoire). J Water Resour Prot 10:145
Jarvie HP, Sharpley AN, Withers PJ, Scott JT, Haggard BE, Neal C (2013) Phosphorus mitigation to control river eutrophication: murky waters, inconvenient truths, and “post normal” science. J Environ Qual 42:295–304
Yao KM, Metongo BS, Trokourey A, Bokra Y (2009) La pollution des eaux de la zone urbaine d’une lagune tropicale par les matières oxydables (lagune Ebrié, Côte d’Ivoire). Int J Biol Chem Sci. https://doi.org/10.4314/ijbcs.v3i4.47168
Hunter HM, Walton RS (2008) Land-use effects on fluxes of suspended sediment, nitrogen and phosphorus from a river catchment of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. J Hydrol 356:131–146
Acquavita A, Aleffi IF, Benci C, Bettoso N, Crevatin E, Milani L, Mattassi G (2015) Annual characterization of the nutrients and trophic state in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon: the Marano and Grado Lagoon (northern Adriatic Sea). Reg Stud Mar Sci 2:132–144
Silva DML, Souza MFL, Moraes MEB, Silva FS, Strenzel GM (2015) Land use effects on nutrient concentration in a small watershed in northeast Brazil. Braz J Aquat Sci Technol 19:102–111
Mama D, Chouti W, Alassane A, Changotade O, Alapini F, Boukari M (2011) Etude dynamique des apports en éléments majeurs et nutritifs des eaux de la lagune de Porto-Novo (Sud Bénin). Int J Biol Chem Sci 5:1278–1293
Pereira-Filho J, Rörig LR, Schettini CAF, Soppa MA, Santana BL, Santos JE (2010) Spatial changes in the water quality of Itajaí-Açú Fluvial-Estuarine System, Santa Catarina, Brazil. An Acad Bras Ciênc 84:963–982
SEQ-EAU (2003) Système d'évaluation de la qualité de l'eau des cours d'eau. Grilles d'évaluation Seq-eau (Version 2). MEDD, Agences de l'eau, p 12
RCQE (2012) Recommandations canadiennes pour la qualité de l’environnement Conseil canadien des ministres de l’environnement
NRC (National Research Council) (1972) Accumulation of Nitrate. Committee on Nitrate Accumulation, Agriculture Board, National Academy of Sciences. Washington DC
USGS (US Geological Survey) (1999) The quality of our nation’s waters: nutrients and pesticides. Rapport no. 1225. US Geological Survey. Reston (Virginie), pp 1–82
Reef R, Feller IC, Lovelock CE (2010) Nutrition of mangroves. Tree Physiol 30:1148–1160
Hung J-J, Hung P-Y (2003) Carbon and nutrient dynamics in a hypertrophic lagoon in Southwestern Taiwan. J Mar Syst 42:97–114
Callender E (2003) Heavy metals in the environment—historical trends. Environ Geochem 9:67–106
Sutula M, Bianchi TS, McKee BA (2004) Effect of seasonal sediment storage in the lower Mississippi River on the flux of reactive particulate phosphorus to the Gulf of Mexico. Limnol Oceanogr 49:2223–2235
Adhikari PL, White JR, Maiti K, Nguyen N (2015) Phosphorus speciation and sedimentary phosphorus release from the Gulf of Mexico sediments: implication for hypoxia. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 164:77–85
Zhang JZ, Fischer CJ, Ortner PB (2004) Potential availability of sedimentary phosphorus to sediment resuspension in Florida Bay. Glob Biogeochem Cycles. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GB002255
Kristensen E, Ahmed SI, Devol AH (1995) Aerobic and anaerobic decomposition of organic matter in marine sediment: which is fastest? Limnol Oceanogr 40:1430–1437
Zhang W, White JR, DeLaune RD (2012) Diverted Mississippi River sediment as a potential phosphorus source affecting coastal Louisiana water quality. J Freshw Ecol 27:575–586
Malecki LM, White JR, Reddy R (2004) Nitrogen and phosphorus flux rates from sediment in the lower St. Johns River estuary. J Environ Qual 3:1545–1555
Berner RA (1973) Phosphate removal from sea water by adsorption on volcanogenic ferric oxides. Earth Plant Sci Lett 18:77–86
Hingston FJ, Posner AM, Quirk JP (1974) Anion adsorption by goethite and gibbsite: 2. Desorption of anions from hydrous oxide surfaces. J Soil Sci 25:16–26
Khalid RA, Patrick WH, Delaune RD (1977) Phosphorus sorption characteristics of flooded soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 41:305–310
Lindstrom SM, White JR (2011) Reducing phosphorus flux from organic soils in surface flow treatment wetlands. Chemosphere 85:625–629
Christophoridis C, Fytianos K (2006) Conditions affecting the release of phosphorus from surface lake sediments. J Environ Qual 35:1181–1192
Andrieux F, Aminot A (1997) A two year survey of phosphorus speciation in the sediments of the Bay of Seine (France). Cont Shelf Res 17:1229–1245
Kang X, Song J, Yuan H, Shi X, Yang W, Li X, Li N, Duan L (2017) Phosphorus speciation and its bioavailability in sediments of the Jiaozhou Bay. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 188:127–136
Søndergaard M, Windolf J, Jeppesen E (1996) Phosphorus fractions and profiles in the sediment of shallow Danish lakes as related to phosphorus load, sediment composition and lake chemistry. Water Res 30:992–1002
Redfield AC, Ketchum BH, Richards FA (1963) The influence of organisms on the composition of sea-water. Sea N Y 2:26–77
Ingall ED, Van Cappellen P (1990) Relation between sedimentation rate and burial of organic phosphorus and organic carbon in marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:373–386
Ruttenberg KC, Goñi MA (1997) Phosphorus distribution, C:N: P ratios, and δ13 Coc in arctic, temperate, and tropical coastal sediments: tools for characterizing bulk sedimentary organic matter. Mar Geol 139:123–145
Kraal P, Slomp CP, de Lange GJ (2010) Sedimentary organic carbon to phosphorus ratios as a redox proxy in Quaternary records from the Mediterranean. Chem Geol 277:167–177
Kraal P, Slomp CP, Reed DC, Reichart G-J, Poulton SW (2012) Sedimentary phosphorus and iron cycling in and below the oxygen minimum zone of the northern Arabian Sea. Biogeosciences 9:2603–2624
Yang B, Liu SM, Wu Y, Zhang J (2016) Phosphorus speciation and availability in sediments off the eastern coast of Hainan Island South China. Sea Cont Shelf Res 118:111–127
Van der Zee C, Slomp CP, Van Raaphorst W (2002) Authigenic P formation and reactive P burial in sediments of the Nazaré canyon on the Iberian margin (NE Atlantic). Mar Geol 185:379–392
Sekula-Wood E, Benitez-Nelson CR, Bennett MA, Thunell R (2012) Magnitude and composition of sinking particulate phosphorus fluxes in Santa Barbara Basin California. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 26:1–15
Schenau SJ, Lange GJD (2001) Phosphorus regeneration vs burial in sediments of the Arabian Sea. Mar Chem 75:201–217
Xu D (2007) The research of sedimentary geochemistry of the Hainan Island nearshore sea area, Master’s thesis, Second Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, Hangzhou, China (in Chinese)
Kouassi NLB, Yao KM, Trokourey A, Soro MB (2015) Distribution, sources, and possible adverse biological effects of trace metals in surface sediments of a tropical estuary. Environ Forensics 16:96–108
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to the Director of Centre de Recherches Océanologiques for facilitating the field and laboratory work. Thanks to the reviewers whose criticism and contribution improved this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict to Interest
No conflict of interest exists between the authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
N’Goran, K.M., Soro, MP., Kouassi, N.L.B. et al. Distribution, Speciation and Bioavailability of Nutrients in M’Badon Bay of Ebrie Lagoon, West Africa (Côte d’Ivoire). Chemistry Africa 6, 1619–1632 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-023-00590-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-023-00590-x