Abstract
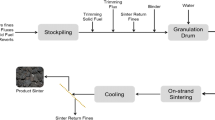
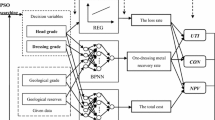
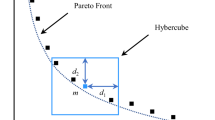
Proportioning is an important part of sintering, as it affects the cost of sintering and the quality of sintered ore. To address the problems posed by the complex raw material information and numerous constraints in the sintering process, a multi-objective optimisation model for sintering proportioning was established, which takes the proportioning cost and TFe as the optimisation objectives. Additionally, an improved multi-objective beluga whale optimisation (IMOBWO) algorithm was proposed to solve the nonlinear, multi-constrained multi-objective optimisation problems. The algorithm uses the constrained non-dominance criterion to deal with the constraint problem in the model. Moreover, the algorithm employs an opposite learning strategy and a population guidance mechanism based on angular competition and two-population competition strategy to enhance convergence and population diversity. The actual proportioning of a steel plant indicates that the IMOBWO algorithm applied to the ore proportioning process has good convergence and obtains the uniformly distributed Pareto front. Meanwhile, compared with the actual proportioning scheme, the proportioning cost is reduced by 4.3361 ¥/t, and the TFe content in the mixture is increased by 0.0367% in the optimal compromise solution. Therefore, the proposed method effectively balances the cost and total iron, facilitating the comprehensive utilisation of sintered iron ore resources while ensuring quality assurance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Li, H. Zhou, J. Huang, Z.W. Zhang, X.F. She, J.F. Wang, S.L. Wu, M.Y. Kou, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 30 (2023) 1675–1686.
H.Y. Li, X.P. Bu, X.J. Liu, X. Li, H.W. Li, F.L. Liu, Q. Lyu, ISIJ Int. 61 (2021) 108–118.
S.H. Peng, H. Liu, Z.Z. Sun, C.W. Li, Y.L. Qin, W.Q. Liu, G. Wang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 30 (2023) 2122–2132.
M. Wu, W. Cao, X. Chen, J. She, in: Intelligent Optimization and Control of Complex Metallurgical Processes Vol. 3, Springer, Singapore, 2020, pp. 33–82.
D.L. Zheng, Z.J. Zhao, W. Fang, T. Fang, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 7 (2000) No. 4, 273–276.
B. Li, W.S. Liu, Control and Decision 37 (2022) 1389–1394.
X. Shen, L.G. Chen, S.J. Xia, Z.H. Xie, X.Y. Qin, J. Clean. Prod. 172 (2018) 2153–2166.
Q.H. Gu, H.L. Liu, C.W. Lu, X.X. Li, Y.P. Yang, Metal Mine (2020) No. 3, 56–63.
Q. Feng, Q. Li, Y.Z. Wang, W. Quan, Control Theory Appl. 39 (2021) 1–9.
T.B. Wu, H.Q. Zhu, W. Long, Y.G. Li, Y.L. Liu, J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 51 (2020) 103–111.
T. Yang, X.Y. Yi, S.W. Lu, K.H. Johansson, T.Y. Chai, Engineering 7 (2021) 1224–1230.
S. Du, M. Wu, X. Chen, W. Cao, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron 67 (2020) 1233–1241.
S. Liu, Y. Zhao, X. Li, X. Liu, Q. Lyu, L. Hao, ISIJ Int. 61 (2021) 2237–2248.
C. Zhong, G. Li, Z. Meng, Knowl. Based Syst. 251 (2022) 109215.
T. Liu, G. Xiong, A.W. Mohamed, P.N. Suganthan, Inf. Sci. 609 (2022) 1721–1745.
X. Mi, Energy Rep. 8 (2022) 1020–1028.
Z.Z. Liu, Y. Wang, IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 23 (2019) 870–884.
Q. Zhang, A. Zhou, S. Zhao, P.N. Suganthan, W. Liu, S. Tiwari, Multi-objective optimization test instances for the CEC 2009 special session and competition, University of Essex, Colchester, UK, 2008.
E. Zitzler, L. Thiele, IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 3 (1999) 257–271.
C.A.C. Coello, N.C. Cortés, Genet. Program. Evolvable Mach. 6 (2005) 163–190.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFB3304700) and Hunan Province Natural Science Foundation (2022JJ50132, 2022JCYJ05 and 2022JCYJ09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Zp., Li, Xd., Yan, Xt. et al. Optimal proportioning of iron ore in sintering process based on improved multi-objective beluga whale optimisation algorithm. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01173-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01173-3