Abstract
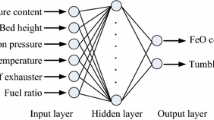
In the iron ore sintering process, it is desirable to maximize the productivity and quality of sinter while minimizing the fuel consumption for any given raw material (iron ore, flux and solid fuel) quality. However, given the complexity of the sintering process and the large number of manipulated variables, it is not practical for operators to identify appropriate set points for the manipulated variables to achieve these conflicting objectives. While significant amount of research is devoted to optimization of the on-strand sintering process, optimization of the integrated sintering process, viz. granulation and on-strand sintering together, has not received much attention. This is, however, necessary as the granulation process dictates the moisture content, mean size and voidage of the green mix bed, which in turn have a very strong influence on the sintering process and sinter quality. In this work, we have formulated and solved a multi-objective optimization problem to maximize both sinter productivity and quality for the integrated iron ore sintering process. Predictive models for productivity and quality parameters such as tumbler index (TI) and reduction degradation index (RDI) are built using machine learning algorithms. The optimization problem is solved using an evolutionary algorithm called non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II) to obtain a set of Pareto-optimal solutions. Optimal settings for key manipulated variables such as moisture content of green mix, fuel content, bed height and strand speed are obtained for the Pareto solutions. The optimization results are useful for identifying the operational range of the sintering process and can be used by operators for running the sinter plant optimally for a given set of raw materials.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cameron I T, Wang F Y, Immanuel C D, Stepanek F, Chem Eng Sci 60 (2005) 3723.
Zhang B, Zhou J, Li M, Li Y, ISIJ Int 58 (2018) 17.
Nath N K, Da Silva A J, Chakraborti N, Steel Res 68 (1997) 285.
Nath N K, Mitra K, Mater Manuf Process 20 (2005) 335.
de Castro J A, Sazaki Y, Yagi J, Mater Res 15 (2012) 848.
Cao W, Zhang Y, She J, Wu M, Cao Y, Inf Sci 466 (2018) 1.
Zhang B, Zhou J, Li M Appl Thermal Eng 131 (2018) 70.
Cheng Z, Yang J, Zhou L, Liu Y, Wang Q, Appl Thermal Eng 105 (2016) 894.
Wang F Y, Ge X Y, Balliu N, Cameron IT, Chem Eng Sci 61 (2006) 257.
Chen X, Chen X, Wu M, She J, Control Eng Pract 54 (2016) 117.
Nath N K, Mitra K, Ironmak Steelmak 31 (2004) 199.
Li Z P, Fan X H, Chen G, Yang G M, Sun Y, Neural Comput Appl 28 (2017) 2247.
Eberhart R, Kennedy J, in MHS’95, Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, IEEE (1995).
Holland J H, Sci Am 267 (1992) 66.
Abbass H A, Sarker R, Newton C, in Proceedings of the Congress on Evolutionary Computation (2001), p 971.
Deb K, IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6 (2002) 182.
Mahanta B K, Chakraborti N, Steel Res Int 89 (2018) 1800121.
Mahanta B K, Chakraborti N, Mater Manuf Process (2019), p 1.
Pal S, Halder C, Steel Res Int 88 (2017) 1600193.
Donskoi E, Manuel J R, Clout J M, Zhang Y, Israel J Chem 47 (2007) 373.
Umadevi T, Karthik P, Mahapatra P C, Prabhu M, Ranjan M, Ironmak Steelmak 39 (2012) 180.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, K., Vakkantham, P., Nistala, S.H. et al. Multi-objective Optimization of Integrated Iron Ore Sintering Process Using Machine Learning and Evolutionary Algorithms. Trans Indian Inst Met 73, 2033–2039 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-01920-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-01920-0