Abstract
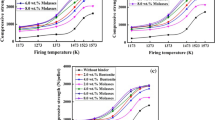
The effect of alumina occurrence form on the metallurgical properties of both hematite and magnetite pellets was investigated at the same Al2O3 level of 2 wt.%, including reduction index (RI), low-temperature reduction disintegration index (RDI), reduction swelling index (RSI), and high-temperature softening–dripping performance. The mineralogy of fired pellets was also studied to reveal the influence of alumina occurrence form on the phase composition and microstructure. From the results, the alumina occurrence form presents tremendous impacts on the metallurgical performance of both magnetite and hematite pellets. Addition of all alumina occurrence forms contributes to inferior reducibility of pellets, especially in the case of gibbsite for magnetite pellets with a RI of 58.4% and kaolinite for hematite pellets with a RI of 56.8%. However, addition of all alumina occurrence forms improves the RDI of magnetite pellets, while there is no significant difference among various alumina occurrence forms. In contrast, alumina occurrence forms have little influence on the RDI of hematite pellets. The presence of free alumina, gibbsite, and kaolinite tends to improve the RSI of hematite and magnetite pellets, whereas hercynite gives the opposite trend with a RSI of 25.6%. For softening–dripping performance of magnetite pellets, all alumina occurrence forms contribute to narrower softening–melting interval. Meanwhile, alumina, gibbsite, and kaolinite give narrower softening–dripping interval, at 229, 217, and 88 °C, respectively, whereas addition of hercynite results in the largest melting range at 276 °C due to its high melting point. Regarding hematite pellets, free alumina, gibbsite, and hercynite tend to enlarge melting range, whereas kaolinite contributes to lower dripping temperature of 1148 °C and narrow softening–dripping interval of 88 °C due to the formation of a greater amount of slag phase at high temperatures.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Zhang, D.Q. Zhu, J. Pan, Z.Q. Guo, M.J. Xu, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27 (2020) 770–781.
A.B. Kotta, D. Narsimhachary, S.K. Karak, M. Kumar, Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 73 (2020) 2561–2575.
K. Sunahara, K. Nakano, M. Hoshi, T. Inada, S. Komatsu, T. Yamamoto, ISIJ Int. 48 (2008) 420–429.
S. Wu, Y. Lu, Z. Hong, H. Zhou, ISIJ Int. 60 (2020) 1504–1511.
J.L. Zhang, Z.Y. Wang, X.D. Xing, Z.J. Liu, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 21 (2014) 339–344.
Z.Q. Guo, R.N. Zhan, Y. Shi, D.Q. Zhu, J. Pan, C.C. Yang, Y.G. Wang, J. Wang, Chem. Eng. J. 456 (2023) 141157.
S. Dwarapudi, P.K. Gupta, S.M. Rao, ISIJ Int. 47 (2007) 67–72.
Z.L. Zhang, Y. Sun, R. Chen, L.L. Li, B. Tang, Metall. Res. Technol. 117 (2020) 505.
J.R. Kim, Y.S. Lee, D.J. Min, S.M. Jung, S.H. Yi, ISIJ Int. 44 (2004) 1291–1297.
Z.M. Yan, X.W. Lv, D. Liang, J. Zhang, C.G. Bai, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 48 (2017) 1092–1099.
Y.Z. Pan, H.B. Zuo, J.S. Wang, Q.G. Xue, G. Wang, X.F. She, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27 (2020) 121–131.
S.K. Das, B. Das, R. Sakthivel, B.K. Mishra, Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 31 (2010) 97–110.
D. Oliveira, S.L. Wu, Y.M. Dai, J. Xu, H. Chen, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 19 (2012) No. 6, 1–5.
L.M. Lu, Iron ore: mineralogy, processing and environmental sustainability, Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, UK, 2015.
Y.X. Xue, J. Pan, D.Q. Zhu, Z.Q. Guo, H.Y. Tian, Y. Shi, S.H. Lu, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 12 (2021) 1157–1170.
N.A.S. Webster, D.P. O'dea, B.G. Ellis, M.I. Pownceby, ISIJ Int. 57 (2017) 41–47.
J.J. Dong, G. Wang, Y.G. Gong, Q.G. Xue, J.S. Wang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 42 (2015) 34–40.
J.G. Lu, C.C. Lan, Q. Lyu, S.H. Zhang, J.N. Sun, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 28 (2021) 629–636.
Z.Y. Wang, X.D. Xing, J.L. Zhang, in: Proceedings of the Ninth China Iron and Steel Annual Conference, The Chinese Society for Metals, Beijing, China, 2013, pp. 382–387.
Z. Wei, J. Zhang, B.P. Qin, Y. Dong, Y. Lu, Y. Li, W.X. Hao, Y.F. Zhang, Powder Technol. 332 (2018) 18–26.
Z.P. Zhu, T. Jiang, G.H. Li, Y.F. Guo, Y.B. Yang, Thermodynamics of reactions among Al2O3, CaO, SiO2 and Fe2O3 during roasting processes, in: J.C. Moreno Piraján (Eds.), Thermodynamics-Interaction Studies-Solids, Liquids and Gases. IntechOpen, 2011. https://doi.org/10.5772/21545.
Y.F. Guo, K. Liu, F. Chen, S.H. Wang, F.Q. Zheng, L.Z. Yang, Y.J. Liu, Powder Technol. 393 (2021) 291–300.
W. Zhao, M.S. Chu, C. Feng, H.T. Wang, Z.G. Liu, J. Tang, W.P. Wang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 47 (2020) 388–397.
H.T. Wang, H.Y. Sohn, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) 906–912.
T. Jiang, G.Q. He, G.H. Li, X.H. Fan, Z.X. Cui, Iron and Steel 42 (2007) No. 5, 7–11.
T. Simmonds, The high temperature decomposition of hematite under reactive gas atmospheres: for use in chemical looping combustion, The University of Queensland, Australia, 2017.
L. Lu, R.J. Holmes, J.R. Manuel, ISIJ Int. 47 (2007) 349–358.
Z.C. Yang, Z.G. Liu, M.S. Chu, L.H. Gao, C. Feng, J. Tang, ISIJ Int. 61 (2021) 1431–1438.
K. Kanbara, T. Hagiwara, A. Shigemi, S.I. Kondo, Y. Kanayama, K.I. Wakabayashi, N. Hiramoto, Tetsu-to-Hagane 62 (1976) 535–546.
Y. Shimomura, K. Nishikawa, S. Arino, T. Katayama, Y. Hida, T. Isoyama, Tetsu-to-Hagane 62 (1976) 547–558.
M. Hino, T. Nagasaka, A. Katsumata, K.I. Higuchi, K. Yamaguchi, N. Kon-No, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 30 (1999) 671–683.
J.B. Kim, I. Sohn, ISIJ Int. 54 (2014) 2050–2058.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52004339), the Key Research and Development Project of Hunan Province, China (No. 2022SK2075), China Baowu Low Carbon Metallurgy Innovation Foudation (BWLCF202216) and the Open Sharing Fund for the Large-Scale Instruments and Equipment of Central South University (CSUZC202207).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. Cong-cong Yang is an editorial board member for Journal of Iron and Steel Research International and was not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, J., Tang, Cm., Yang, Cc. et al. Effect of alumina occurrence form on metallurgical properties of hematite and magnetite pellets. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 31, 797–809 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01066-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01066-5