Abstract
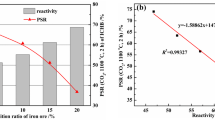
Highly reactive iron coke hot briquette (ICHB) prepared by carbonizing the agglomerate of iron-bearing substance and blended coals is regarded as an alternative fuel to mitigate carbon emission and energy consumption of blast furnace. Simultaneously, the reduction process of iron-bearing burden is extremely crucial for blast furnace smelting. The effects of ICHB on the non-isothermal reduction process of iron-bearing burden with different reduction properties were thus experimentally studied under the conditions of simulated blast furnace lump zone (below 1100 °C), and the related mechanism was discussed and analyzed. The results showed that the non-isothermal reduction process of iron-bearing burden is promoted by adding ICHB. As the charging ratio of ICHB is increased from 0% to 30%, the reduction degree of pellet is increased from 22.91% to 36.62%, but the increased amplitude is leveled off. Furthermore, the reduction degree of sinter is raised from 35.10% to 93.33%. It is also indicated that the promotion effect of ICHB on the non-isothermal reduction of iron-bearing burden depends on the reduction property of burden. Compared with the burden with poor reduction performance (such as pellet 1), the promotion is more significant for the burden with good reduction property (such as sinter 1) since the reduction reaction of iron oxide in iron-bearing burden and the gasification of carbon in ICHB are remarkably reinforced each other. The practical application of ICHB in blast furnace should be utilized with highly reductive iron-bearing burden.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.F.C. de Assis, J.A.S. Tenório, P.S. Assis, N.K. Nath, Energy Fuels 28 (2014) 7268–7273.
X. Xing, H. Rogers, G.Q. Zhang, K. Hockings, P. Zulli, A. Deev, J. Mathieson, O. Ostrovski, Fuel Process. Technol. 157 (2017) 42–51.
Z.Y. Chang, P. Wang, J.L. Zhang, K.X. Jiao, Y.Q. Zhang, Z.J. Liu, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 25 (2018) 1402–1411.
Y.J. Wang, H.B. Zuo, J. Zhao, Ironmak. Steelmak. 47 (2020) 640–649.
C. Zhou, G.W. Tang, J.C. Wang, D. Fu, T. Okosun, A. Silaen, B. Wu, JOM 68 (2016) 1353–1362.
J.A. de Castro, C. Takano, J.I. Yagi, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 6 (2017) 258–270.
M.M. Sun, J.L. Zhang, K.J. Li, K. Guo, Z.M. Wang, C.H. Jiang, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 26 (2019) 1247–1257.
R.S. Xu, B.W. Dai, W. Wang, J. Schenk, A. Bhattacharyya, Z.L. Xue, Energy Fuels 32 (2018) 1188–1195.
L.R. Lemos, S.H.F.S. da Rocha, L.F.A. de Castro, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 4 (2015) 278–282.
H.B. Zhu, W.L. Zhan, Z.J. He, Y.C. Yu, Q.H. Pang, J.H. Zhang, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 27 (2020) 1226–1233.
K.J. Li, J.L. Zhang, Z.J. Liu, X.J. Ning, T.Q. Wang, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53 (2014) 5737–5748.
X. Xing, H. Rogers, G.Q. Zhang, K. Hockings, P. Zulli, O. Ostrovski, Energy Fuels 30 (2016) 161–170.
E.A. Mousa, A. Babich, D. Senk, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) 350–358.
M. Naito, A. Okamoto, K. Yamaguchi, T. Yamaguchi, Y. Inoue, Tetsu-to-Hagané 87 (2001) 357–364.
S. Nomura, H. Ayukawa, H. Kitaguchi, T. Tahara, S. Matsuzaki, M. Naito, S. Koizumi, Y. Ogata, T. Nakayama, T. Abe, ISIJ Int. 45 (2005) 316–324.
S. Nomura, M. Naito, K. Yamaguchi, ISIJ Int. 47 (2007) 831–839.
S. Nomura, K. Higuchi, K. Kunitomo, M. Naito, ISIJ Int. 50 (2010) 1388–1395.
S. Nomura, H. Terashima, E. Sato, M. Naito, ISIJ Int. 47 (2007) 823–830.
E.M.A. Edreis, X. Li, C.F. Xu, H. Yao, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 6 (2017) 147–157.
B.Y. Tuo, J.L. Wang, Y. Yang, G.H. Nie, Mining and Metallurgical Engineering 34 (2014) No. 1, 70–73.
M. Sato, H. Matsuno, K. Ishii, in: Asia Steel International Conference 2015, The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, Yokohama, Japan, 2015, pp. 12–13.
T. Yamamoto, T. Sato, H. Fujimoto, T. Anyashiki, K. Fukada, M. Sato, K. Takeda, T. Ariyama, Tetsu-to-Hagané 97 (2011) 501–509.
K. Higuchi, S. Nomura, K. Kunitomo, H. Yokoyama, M. Naito, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) 1308–1315.
M. Naito, A. Okamoto, K. Yamaguchi, T. Yamaguchi, Y. Inoue, Nippon Steel Technical Report 94 (2006) 103–108.
H.T. Wang, W. Zhao, M.S. Chu, Z.G. Liu, J. Tang, Z.W. Ying, Powder Technol. 328 (2018) 318–328.
H.T. Wang, M.S. Chu, Z.H. Wang, W. Zhao, Z.G. Liu, J. Tang, Z.W. Ying, JOM 70 (2018) 1929–1936.
H. Wang, M. Chu, W. Zhao, R. Wang, Z. Liu, J. Tang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 43 (2016) 571–580.
H.T. Wang, M.S. Chu, J.W. Bao, Z.G. Liu, J. Tang, H.M. Long, Fuel 268 (2020) 117339.
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China-Liaoning Joint Funds (U1808212) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52074080 and 52004001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Ht., Chu, Ms., Bao, Jw. et al. Non-isothermal reduction process analysis of iron-bearing burden with charging iron coke hot briquette under simulated blast furnace conditions. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 29, 741–750 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00640-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00640-z