Abstract
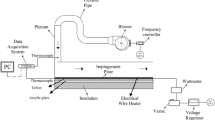
During multi-jet cooling, the complex hydrodynamic characteristics caused by the interaction between jets will affect the heat transfer of the plate. To further clarify the heat transfer characteristics in different flow regions, the double-jet cooling experiments were completed on a 50-mm-thick plate with the initial cooling temperature and jet angle in the range of 300–900 °C and 0°–60°, respectively. The inverse heat conduction was used to calculate the surface temperature and heat flux. Furthermore, the rewetting phenomenon, maximum heat flux and maximum cooling speed were studied. The results show that increasing the angle between jet and wall normal would increase the wetting front’s width downstream of the jet point. When the jet angle was 60°, the maximum value increased by 37.29 mm compared with that when the angle was 0°. The correlation between the width of the wetting front and the radial temperature gradient was further confirmed. In addition, it was found that the maximum heat flux would be affected by the duration of transition boiling, but not affected by complete wetting time. The results clarified the heat transfer mechanisms under various initial cooling temperature and inclination angle conditions on plate cooling in different flow regions, and provided valuable data for controlling heat transfer efficiency and improving cooling uniformity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.L. Fu, X.T. Deng, G.H. Liu, Z.D. Wang, G.D. Wang, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Man. 17 (2016) 1503–1514.
L. Qiu, S. Dubey, F.H. Choo, F. Duan, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 89 (2015) 42–58.
C. Agrawal, Steel Res. Int. 90 (2019) 1800285.
Z.X. Wen, Y.L. He, Z. Ma, Comput. Fluids 164 (2018) 83–93.
A. Yildizeli, S. Cadirci, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 158 (2020) 119978.
T.L. Fu, Z.D. Wang, Y. Li, J.D. Li, G.D. Wang, Appl. Therm. Eng. 70 (2014) 800–807.
T.L. Fu, Z.D. Wang, X.T. Deng, G.H. Liu, G.D. Wang, Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015 (78) 500–506.
H. Fujimoto, N. Hayashi, J. Nakahara, K. Morisawa, T. Hama, H. Takuda, ISIJ Int. 56 (2016) 2016–2021.
A.K. Mozumder, M. Monde, P.L. Woodfield, M.A. Islam, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 49 (2006) 2877–2888.
A.K. Mozumder, M. Monde, P.L. Woodfield, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 48 (2005) 5395–5407.
P.L. Woodfield, A.K. Mozumder, M. Monde, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 52 (2009) 460–465.
N. Karwa, T. Gambaryan-Roisman, P. Stephan, C. Tropea, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 35 (2011) 1435–1443.
A.K. Mozumder, P.L. Woodfield, M.A. Islam, M. Monde, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 50 (2007) 1559–1568.
S.J. Yi, M. Kim, D. Kim, H.D. Kim, K.C. Kim, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 102 (2016) 691–702.
C. Wang, X.K. Wang, W.D. Shi, W.G. Lu, S.K. Tan, L. Zhou, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 89 (2017) 189–198.
J.F. Lu, B. Bourouga, J. Ding, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 48 (2013) 15–21.
X.H. Tian, T.L. Fu, J.W. Zhang, Z.D. Wang, G.D. Wang, ISIJ Int. 60 (2020) 1993–1999.
C. Agrawal, R. Kumar, A. Gupta, B. Chatterjee, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 42 (2012) 25–37.
B.X. Wang, D. Lin, Q. Xie, Z.D. Wang, G.D. Wang, Appl. Therm. Eng. 100 (2016) 902–910.
D.E. Hall, F.P. Incropera, R. Viskanta, J. Heat Transfer 123 (2001) 911–917.
D.E. Hall, F.P. Incropera, R. Viskanta, J. Heat Transfer 123 (2001) 901–910.
N. Karwa, P. Stephan, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 64 (2013) 1118–1126.
S.A. Ebrahim, S. Chang, F.B. Cheung, S.M. Bajored, Appl. Therm. Eng. 140 (2018) 139–146.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Programs of China (Grant No. 2017YFB0305102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Xh., Fu, Tl., Wang, Zd. et al. Heat transfer characteristics for double-jet in different flow regions on a thick plate. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28, 1400–1407 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00553-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00553-3