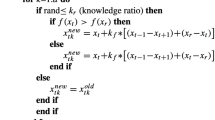Abst
The advent of Big Data has rendered Machine Learning tasks more intricate as they frequently involve higher-dimensional data. Feature Selection (FS) methods can abate the complexity of the data and enhance the accuracy, generalizability, and interpretability of models. Meta-heuristic algorithms are often utilized for FS tasks due to their low requirements and efficient performance. This paper introduces an augmented Forensic-Based Investigation algorithm (DCFBI) that incorporates a Dynamic Individual Selection (DIS) and crisscross (CC) mechanism to improve the pursuit phase of the FBI. Moreover, a binary version of DCFBI (BDCFBI) is applied to FS. Experiments conducted on IEEE CEC 2017 with other metaheuristics demonstrate that DCFBI surpasses them in search capability. The influence of different mechanisms on the original FBI is analyzed on benchmark functions, while its scalability is verified by comparing it with the original FBI on benchmarks with varied dimensions. BDCFBI is then applied to 18 real datasets from the UCI machine learning database and the Wieslaw dataset to select near-optimal features, which are then compared with six renowned binary metaheuristics. The results show that BDCFBI can be more competitive than similar methods and acquire a subset of features with superior classification accuracy.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The data involved in this study are all public data, which can be downloaded through public channels.
References
Kotsiantis, S. B., Kanellopoulos, D., & Pintelas, P. E. (2006). Data preprocessing for supervised leaning. International Journal of Computer Science, 1, 111–117.
Alelyani, S., Tang, J. L., & Liu, H. (2018). Feature selection for clustering: a review. Data Clustering (pp. 29–60). Routledge.
Zhou, X. X., & Zhang, L. (2022). Sa-fpn: An effective feature pyramid network for crowded human detection. Applied Intelligence, 52, 12556–12568.
Bermingham, M. L., Pong-Wong, R., Spiliopoulou, A., Hayward, C., Rudan, I., Campbell, H., Wright, A. F., Wilson, J. F., Agakov, F., & Navarro, P. (2015). Application of high-dimensional feature selection: Evaluation for genomic prediction in man. Scientific Reports, 5, 1–12.
Nadimi-Shahraki, M. H., BanaiE–Dezfouli, M., Zamani, H., Taghian, S., & Mirjalili, S. (2021). B-mfo: A binary moth-flame optimization for feature selection from medical datasets. Computers, 10, 136.
Anter, A. M., & Ali, M. (2020). Feature selection strategy based on hybrid crow search optimization algorithm integrated with chaos theory and fuzzy c-means algorithm for medical diagnosis problems. Soft Computing, 24, 1565–1584.
Saeys, Y., Inza, I., & Larranaga, P. (2007). A review of feature selection techniques in bioinformatics. Bioinformatics, 23, 2507–2517.
Wang, L., Wang, Y. L., & Chang, Q. (2016). Feature selection methods for big data bioinformatics: A survey from the search perspective. Methods, 111, 21–31.
Afza, F., Khan, M. A., Sharif, M., Kadry, S., Manogaran, G., Saba, T., Ashraf, I., & Damaševičius, R. (2021). A framework of human action recognition using length control features fusion and weighted entropy-variances based feature selection. Image and Vision Computing, 106, 104090.
Ma, B. T., & Xia, Y. (2017). A tribe competition-based genetic algorithm for feature selection in pattern classification. Applied Soft Computing, 58, 328–338.
Barbu, A., She, Y., Ding, L., & Gramajo, G. (2016). Feature selection with annealing for computer vision and big data learning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 39, 272–286.
Khan, M. A., Zhang, Y. D., Allison, M., Kadry, S., Wang, S. H., Saba, T., & Iqbal, T. (2021). A fused heterogeneous deep neural network and robust feature selection framework for human actions recognition. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 48, 2609.
Guyon, I., & Elisseeff, A. (2003). An introduction to variable and feature selection. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 3, 1157–1182.
Alshaer, H. N., Otair, M. A., Abualigah, L., Alshinwan, M., & Khasawneh, A. M. (2021). Feature selection method using improved chi square on arabic text classifiers: Analysis and application. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 80, 10373–10390.
Jebli, I., Belouadha, F. Z., Kabbaj, M. I., & Tilioua, A. (2021). Prediction of solar energy guided by pearson correlation using machine learning. Energy, 224, 120109.
Hu, H. Y., Shan, W. F., Tang, Y. T., Heidari, A. A., Chen, H. L., Liu, H. J., Wang, M. F., Escorcia-Gutierrez, J., Mansour, R. F., & Chen, J. (2022). Horizontal and vertical crossover of sine cosine algorithm with quick moves for optimization and feature selection. Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, 9, 2524–2555.
Bianchi, L., Dorigo, M., Gambardella, L. M., & Gutjahr, W. J. (2009). A survey on metaheuristics for stochastic combinatorial optimization. Natural Computing, 8, 239–287.
Blum, C., & Roli, A. (2003). Metaheuristics in combinatorial optimization: Overview and conceptual comparison. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 35, 268–308.
Li, R. H., Wu, X. L., Tian, H., Yu, N. A., & Wang, C. (2022). Hybrid memetic pretrained factor analysis-based deep belief networks for transient electromagnetic inversion. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 60, 1–20.
Lin, Y., Song, H., Ke, F., Yan, W. Z., Liu, Z. K., & Cai, F. M. (2022). Optimal caching scheme in d2d networks with multiple robot helpers. Computer Communications, 181, 132–142.
Holland, J. H. (1992). Genetic algorithms. Scientific American, 267, 66–73.
Storn, R., & Price, K. (1997). Differential evolution–a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. Journal of Global Optimization, 11, 341–359.
Tang, D. (2019). Spherical evolution for solving continuous optimization problems. Applied Soft Computing, 81, 105499.
Kennedy, J., & Eberhart, R. (1995). Particle swarm optimization. Proceedings of ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, 4 (pp. 1942–1948). Geneva: IEEE.
Tian, J., Hou, M. D., Bian, H. L., & Li, J. Q. (2022). Variable surrogate model-based particle swarm optimization for high-dimensional expensive problems. Complex & Intelligent Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-022-00910-7
Dorigo, M., Birattari, M., & Stutzle, T. (2006). Ant colony optimization. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 1, 28–39.
Mirjalili, S. (2015). Moth-flame optimization algorithm: A novel naturE–inspired heuristic paradigm. KnowledgE–Based Systems, 89, 228–249.
Mirjalili, S., Mirjalili, S. M., & Lewis, A. (2014). Grey wolf optimizer. Advances in Engineering Software, 69, 46–61.
Ahmadianfar, I., Heidari, A. A., Gandomi, A. H., Chu, X. F., & Chen, H. L. (2021). Run beyond the metaphor: An efficient optimization algorithm based on runge kutta method. Expert Systems with Applications, 181, 115079.
Yang, Y. T., Chen, H. L., Heidari, A. A., & Gandomi, A. H. (2021). Hunger games search: Visions, conception, implementation, deep analysis, perspectives, and towards performance shifts. Expert Systems with Applications, 177, 114864.
Chen, H. L., Li, C. Y., Mafarja, M., Heidari, A. A., Chen, Y., & Cai, Z. N. (2022). Slime mould algorithm: A comprehensive review of recent variants and applications. International Journal of Systems Science, 54, 1–32.
Li, S. M., Chen, H. L., Wang, M. J., Heidari, A. A., & Mirjalili, S. (2020). Slime mould algorithm: A new method for stochastic optimization. Future Generation Computer Systems, 111, 300–323.
Tu, J. Z., Chen, H. L., Wang, M. J., & Gandomi, A. H. (2021). The colony predation algorithm. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 18, 674–710.
Ahmadianfar, I., Asghar Heidari, A., Noshadian, S., Chen, H. L., & Gandomi, A. H. (2022). Info: An efficient optimization algorithm based on weighted mean of vectors. Expert Systems with Applications, 195, 116516.
Heidari, A. A., Mirjalili, S., Faris, H., Aljarah, I., Mafarja, M., & Chen, H. L. (2019). Harris hawks optimization: Algorithm and applications. Future Generation Computer Systems, 97, 849–872.
Zhang, Y. N., Liu, R. J., Heidari, A. A., Wang, X., Chen, Y., Wang, M. J., & Chen, H. L. (2021). Towards augmented kernel extreme learning models for bankruptcy prediction: Algorithmic behavior and comprehensive analysis. Neurocomputing, 430, 185–212.
Liu, Y., Heidari, A. A., Cai, Z. N., Liang, G. X., Chen, H. L., Pan, Z. F., Alsufyani, A., & Bourouis, S. (2022). Simulated annealing-based dynamic step shuffled frog leaping algorithm: Optimal performance design and feature selection. Neurocomputing, 503, 325–362.
Xue, Y., Xue, B., & Zhang, M. J. (2019). Self-adaptive particle swarm optimization for large–scale feature selection in classification. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data (TKDD), 13, 1–27.
Xue, Y., Cai, X., & Neri, F. (2022). A multi-objective evolutionary algorithm with interval based initialization and self-adaptive crossover operator for largE–scale feature selection in classification. Applied Soft Computing, 127, 109420.
Dong, R. Y., Chen, H. L., Heidari, A. A., Turabieh, H., Mafarja, M., & Wang, S. S. (2021). Boosted kernel search: Framework, analysis and case studies on the economic emission dispatch problem. Knowledge–Based Systems, 233, 107529.
Yu, K. J., Zhang, D. Z., Liang, J., Chen, K., Yue, C. T., Qiao, K. J., & Wang, L. (2022). A correlation-guided layered prediction approach for evolutionary dynamic multiobjective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2022.3193287
Liang, J., Qiao, K. J., Yu, K. J., Qu, B. Y., Yue, C. T., Guo, W. F., & Wang, L. (2022). Utilizing the relationship between unconstrained and constrained pareto fronts for constrained multiobjective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2022.3163759
Deng, W., Xu, J. J., Gao, X. Z., & Zhao, H. M. (2022). An enhanced msiqde algorithm with novel multiple strategies for global optimization problems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 52, 1578–1587.
Huang, C., Zhou, X. B., Ran, X. J., Liu, Y., Deng, W. Q., & Deng, W. (2023). Co-evolutionary competitive swarm optimizer with three–phase for large–scale complex optimization problem. Information Sciences, 619, 2–18.
Xue, Y., Tong, Y. L., & Neri, F. (2022). An ensemble of differential evolution and adam for training feed-forward neural networks. Information Sciences, 608, 453–471.
Wen, X. Y., Wang, K. H., Li, H., Sun, H. Q., Wang, H. Q., & Jin, L. J. (2021). A two-stage solution method based on nsga-ii for green multi-objective integrated process planning and scheduling in a battery packaging machinery workshop. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 61, 100820.
Wang, G. Q., Fan, E., Zheng, G. H., Li, K. X., & Huang, H. G. (2022). Research on vessel speed heading and collision detection method based on ais data. Mobile Information Systems, 10, 1–10.
Zhao, C. L., Zhou, Y. R., & Lai, X. S. (2022). An integrated framework with evolutionary algorithm for multi-scenario multi-objective optimization problems. Information Sciences, 600, 342–361.
Hussien, A. G., Heidari, A. A., Ye, X. J., Liang, G. X., Chen, H. L., & Pan, Z. F. (2022). Boosting whale optimization with evolution strategy and Gaussian random walks: An image segmentation method. Engineering with Computers. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01542-0
Abd El Aziz, M., Ewees, A. A., & Hassanien, A. E. (2017). Whale optimization algorithm and moth-flame optimization for multilevel thresholding image segmentation. Expert Systems with Applications, 83, 242–256.
Cura, T. (2009). Particle swarm optimization approach to portfolio optimization. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 10, 2396–2406.
Perold, A. F. (1984). Large–scale portfolio optimization. Management Science, 30, 1143–1160.
Thakkar, A., & Chaudhari, K. (2021). A comprehensive survey on portfolio optimization, stock price and trend prediction using particle swarm optimization. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 28, 2133–2164.
Mirjalili, S., & Lewis, A. (2016). The whale optimization algorithm. Advances in Engineering Software, 95, 51–67.
Hüsken, M., Jin, Y. C., & Sendhoff, B. (2005). Structure optimization of neural networks for evolutionary design optimization. Soft Computing, 9, 21–28.
Loghmanian, S. M. R., Jamaluddin, H., Ahmad, R., Yusof, R., & Khalid, M. (2012). Structure optimization of neural network for dynamic system modeling using multi-objective genetic algorithm. Neural Computing and Applications, 21, 1281–1295.
Shan, W. F., Hu, H. Y., Cai, Z. N., Chen, H. L., Liu, H. J., Wang, M. F., & Teng, Y. T. (2022). Multi-strategies boosted mutative crow search algorithm for global tasks: Cases of continuous and discrete optimization. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 19, 1860–1849.
Han, X., Han, Y. Y., Chen, Q. D., Li, J. Q., Sang, H. Y., Liu, Y. P., Pan, Q. K., & Nojima, Y. (2021). Distributed flow shop scheduling with sequencE–dependent setup times using an improved iterated greedy algorithm. Complex System Modeling and Simulation, 1, 198–217.
Wang, G. G., Gao, D., & Pedrycz, W. (2022). Solving multi-objective fuzzy job-shop scheduling problem by a hybrid adaptive differential evolution algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 18, 8519–8528.
Xia, J. F., Yang, D. Q., Zhou, H., Chen, Y. Y., Zhang, H. L., Liu, T., Heidari, A. A., Chen, H. L., & Pan, Z. F. (2022). Evolving kernel extreme learning machine for medical diagnosis via a disperse foraging sine cosine algorithm. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 141, 105137.
Shan, W. F., Qiao, Z. L., Heidari, A. A., Chen, H. L., Turabieh, H., & Teng, Y. T. (2021). Double adaptive weights for stabilization of moth flame optimizer: Balance analysis, engineering cases, and medical diagnosis. Knowledge–Based Systems, 214, 106728.
Abbassi, R., Abbassi, A., Heidari, A. A., & Mirjalili, S. (2019). An efficient salp swarm-inspired algorithm for parameters identification of photovoltaic cell models. Energy Conversion and Management, 179, 362–372.
Huang, C. L., & Wang, C. J. (2006). A GA-based feature selection and parameters optimization for support vector machines. Expert Systems with Applications, 31, 231–240.
Wei, J. X., Zhang, R. S., Yu, Z. X., Hu, R. J., Tang, J. X., Gui, C., & Yuan, Y. N. (2017). A bpso-svm algorithm based on memory renewal and enhanced mutation mechanisms for feature selection. Applied Soft Computing, 58, 176–192.
Zhao, S. W., Wang, P. J., Heidari, A. A., Zhao, X. H., Ma, C., & Chen, H. L. (2021). An enhanced Cauchy mutation grasshopper optimization with trigonometric substitution: Engineering design and feature selection. Engineering with Computers, 38, 4583–4616.
Agrawal, P., Ganesh, T., & Mohamed, A. W. (2021). A novel binary gaining–sharing knowledge–based optimization algorithm for feature selection. Neural Computing and Applications, 33, 5989–6008.
Agrawal, P., Abutarboush, H. F., Ganesh, T., & Mohamed, A. W. (2021). Metaheuristic algorithms on feature selection: A survey of one decade of research (2009–2019). IEEE Access, 9, 26766–26791.
Kuyu, Y. Ç., & Vatansever, F. (2022). Modified forensic-based investigation algorithm for global optimization. Engineering with Computers, 38, 3197–3218.
Kaveh, A., Hamedani, K. B., & Kamalinejad, M. (2021). An enhanced forensic-based investigation algorithm and its application to optimal design of frequency-constrained dome structures. Computers & Structures, 256, 106643.
Hoang, N. D., Huynh, T. C., & Tran, V. D. (2021). Computer vision-based patched and unpatched pothole classification using machine learning approach optimized by forensic-based investigation metaheuristic. Complexity, 2021, 3511375.
Fathy, A., Rezk, H., & Alanazi, T. M. (2021). Recent approach of forensic-based investigation algorithm for optimizing fractional order PID-based MPPT with proton exchange membrane fuel cell. IEEE Access, 9, 18974–18992.
Chou, J. S., & Truong, D. N. (2022). Multi-objective forensic-based investigation algorithm for solving structural design problems. Automation in Construction, 134, 104084.
Chou, J. S., & Nguyen, N. M. (2020). FBI inspired meta-optimization. Applied Soft Computing, 93, 106339.
Meng, A. B., Chen, Y. C., Yin, H., & Chen, S. Z. (2014). Crisscross optimization algorithm and its application. Knowledge–Based Systems, 67, 218–229.
Meng, A., Ge, J., Yin, H., & Chen, S. (2016). Wind speed forecasting based on wavelet packet decomposition and artificial neural networks trained by crisscross optimization algorithm. Energy Conversion and Management, 114, 75–88.
Zhao, D., Liu, L., Yu, F. H., Heidari, A. A., Wang, M. J., Oliva, D., Muhammad, K., & Chen, H. L. (2021). Ant colony optimization with horizontal and vertical crossover search: Fundamental visions for multi-threshold image segmentation. Expert Systems with Applications, 167, 114122.
Liu, H. R., Liu, M. Z., Li, D. F., Zheng, W. F., Yin, L. R., & Wang, R. L. (2022). Recent advances in pulse–coupled neural networks with applications in image processing. Electronics, 11, 3264.
Xu, J. W., Pan, S. C., Sun, P. Z. H., Park, S. H., & Guo, K. (2022). Human-factors-in-driving-loop: Driver identification and verification via a deep learning approach using psychological behavioral data. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3225782
Zhang, X., Wen, S. J., Yan, L., Feng, J. F., & Xia, Y. (2022). A hybrid-convolution spatial–temporal recurrent network for traffic flow prediction. The Computer Journal. https://doi.org/10.1093/comjnl/bxac171
Cheng, L., Yin, F., Theodoridis, S., Chatzis, S., & Chang, T. H. (2022). Re-thinking Bayesian learning for data analysis: The art of prior and inference in sparsity-aware modeling. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 39, 18–52.
Wu, G., Mallipeddi, R., & Suganthan, P.N. (2017). Problem definitions and evaluation criteria for the cec 2017 competition on constrained real-parameter optimization. In: National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, Hunan, PR China and Kyungpook National University, Daegu, South Korea and Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Technical Report.
Nenavath, H., & Jatoth, R. K. (2018). Hybridizing sine cosine algorithm with differential evolution for global optimization and object tracking. Applied Soft Computing, 62, 1019–1043.
Liu, G. M., Jia, W. Y., Wang, M. J., Heidari, A. A., Chen, H. L., Luo, Y. G., & Li, C. Y. (2020). Predicting cervical hyperextension injury: A covariance guided sine cosine support vector machine. IEEE Access, 8, 46895–46908.
Jia, D. L., Zheng, G. X., Qu, B. Y., & Khan, M. K. (2011). A hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm for high-dimensional problems. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 61, 1117–1122.
Singh, R. P., Mukherjee, V., & Ghoshal, S. P. (2016). Particle swarm optimization with an aging leader and challengers algorithm for the solution of optimal power flow problem. Applied Soft Computing, 40, 161–177.
Heidari, A. A., Abbaspour, R. A., & Chen, H. L. (2019). Efficient boosted grey wolf optimizers for global search and kernel extreme learning machine training. Applied Soft Computing, 81, 105521.
Reddy, K. S., Panwar, L., Panigrahi, B., & Kumar, R. (2019). Binary whale optimization algorithm: A new metaheuristic approach for profit-based unit commitment problems in competitive electricity markets. Engineering Optimization, 51, 369–389.
Mafarja, M., Aljarah, I., Heidari, A. A., Faris, H., Fournier-Viger, P., Li, X., & Mirjalili, S. (2018). Binary dragonfly optimization for feature selection using timE–varying transfer functions. KnowledgE–Based Systems, 161, 185–204.
Pietruszkiewicz, W. (2004). Application of discrete predicting structures in an early warning expert system for financial distress (Doctoral dissertation, Ph. d. thesis, Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology, Szczecin University of Technology).
Emary, E., Zawbaa, H. M., & Hassanien, A. E. (2016). Binary grey wolf optimization approaches for feature selection. Neurocomputing, 172, 371–381.
Rashedi, E., Nezamabadi-Pour, H., & Saryazdi, S. (2010). Bgsa: Binary gravitational search algorithm. Natural Computing, 9, 727–745.
Dara, S., & Banka, H. (2014). A binary pso feature selection algorithm for gene expression data. 2014 International conference on advances in communication and computing technologies (ICACACT 2014) (pp. 1–6). Mumbai, India: IEEE.
Mirjalili, S., Mirjalili, S. M., & Yang, X.-S. (2014). Binary bat algorithm. Neural Computing and Applications, 25, 663–681.
Faris, H., Mafarja, M. M., Heidari, A. A., Aljarah, I., Alam, A.-Z., Mirjalili, S., & Fujita, H. (2018). An efficient binary salp swarm algorithm with crossover scheme for feature selection problems. Knowledge-Based Systems, 154, 43–67.
Zhao, C. C., Wang, H. S., Chen, H. L., Shi, W. W., & Feng, Y. J. (2022). Jamsnet: A remote pulse extraction network based on joint attention and multi-scale fusion. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3227348
Chen, Y., Gan, H. M., Chen, H. L., Zeng, Y. G., Xu, L., Heidari, A. A., Zhu, X. D., & Liu, Y. N. (2023). Accurate iris segmentation and recognition using an end-to-end unified framework based on madnet and dsanet. Neurocomputing, 517, 264–278.
Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Cui, W. G., Lei, B. Y., Kuang, X. H., & Zhang, T. (2022). Dual encoder-based dynamic-channel graph convolutional network with edge enhancement for retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 41, 1975–1989.
Wang, S. S., Wang, B. L., Zhang, Z., Heidari, A. A., & Chen, H. L. (2023). Class-aware sample reweighting optimal transport for multi-source domain adaptation. Neurocomputing, 523, 213–223.
Yan, B., Li, Y., Li, L., Yang, X. C., Li, T. Q., Yang, G., & Jiang, M. F. (2022). Quantifying the impact of pyramid squeeze attention mechanism and filtering approaches on Alzheimer’s disease classification. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 148, 105944.
Lv, J., Li, G., Tong, X. R., Chen, W. B., Huang, J. H., Wang, C. Y., & Yang, G. (2021). Transfer learning enhanced generative adversarial networks for multi-channel MRI reconstruction. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 134, 104504.
Sun, X. H., Cao, X. Y., Zeng, B., Zhai, Q. Z., & Guan, X. H. (2022). Multi-stage dynamic planning of integrated hydrogen-electrical microgrids under multiscale uncertainties. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSG.2022.3232545
Cao, X. Y., Cao, T. X., Xu, Z. B., Zeng, B., Gao, F., & Guan, X. H. (2022). Resilience constrained scheduling of mobile emergency resources in electricity-hydrogen distribution network. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSTE.2022.3217514
Ban, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, S., Yang, B., Liu, M. Z., Yin, L. R., & Zheng, W. F. (2022). 2d/3d multimode medical image alignment based on spatial histograms. Applied Sciences, 12, 8261.
Wu, Z. D., Xuan, S. L., Xie, J., Lin, C. Z., & Lu, C. L. (2022). How to ensure the confidentiality of electronic medical records on the cloud: A technical perspective. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 147, 105726.
Wu, Z. D., Li, G. L., Shen, S. G., Lian, X., Chen, E. H., & Xu, G. D. (2021). Constructing dummy query sequences to protect location privacy and query privacy in location-based services. World Wide Web, 24, 25–49.
Wu, Z. D., Shen, S. G., Lian, X. Z., Su, X. N., & Chen, E. H. (2020). A dummy-based user privacy protection approach for text information retrieval. Knowledge–Based Systems, 195, 105679.
Wu, Z. D., Shen, S. G., Li, H. X., Zhou, H. P., & Lu, C. L. (2021). A basic framework for privacy protection in personalized information retrieval: An effective framework for user privacy protection. Journal of Organizational and End User Computing (JOEUC), 33, 1–26.
Wu, Z. D., Shen, S. G., Zhou, H. P., Li, H. X., Lu, C. L., & Zou, D. D. (2021). An effective approach for the protection of user commodity viewing privacy in E–commerce website. Knowledge–Based Systems, 220, 106952.
Wu, Z. D., Xie, J., Shen, S. G., Lin, C. Z., Xu, G. D., & Chen, E. H. (2023). A confusion method for the protection of user topic privacy in Chinese keyword based book retrieval. ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing. https://doi.org/10.1145/3571731
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Special Fund of Fundamental Scientific Research Business Expense for Higher School of Central Government (ZY20180119), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LZ22F020005), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (D2022512001) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (42164002, 62076185). We acknowledge the comments of the reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, H., Shan, W., Chen, J. et al. Dynamic Individual Selection and Crossover Boosted Forensic-based Investigation Algorithm for Global Optimization and Feature Selection. J Bionic Eng 20, 2416–2442 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42235-023-00367-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42235-023-00367-5