Abstract
To improve the understanding of cognitive processing stages, we combined two prominent traditions in cognitive science: evidence accumulation models and stage discovery methods. While evidence accumulation models have been applied to a wide variety of tasks, they are limited to tasks in which decision-making effects can be attributed to a single processing stage. Here, we propose a new method that first uses machine learning to discover processing stages in EEG data and then applies evidence accumulation models to characterize the duration effects in the identified stages. To evaluate this method, we applied it to a previously published associative recognition task (Application 1) and a previously published random dot motion task with a speed-accuracy trade-off manipulation (Application 2). In both applications, the evidence accumulation models accounted better for the data when we first applied the stage-discovery method, and the resulting parameter estimates where generally in line with psychological theories. In addition, in Application 1 the results shed new light on target-foil effects in associative recognition, while in Application 2 the stage discovery method identified an additional stage in the accuracy-focused condition — challenging standard evidence accumulation accounts. We conclude that the new framework provides a powerful new tool to investigate processing stages.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Evidence accumulation is often seen as a basic cognitive mechanism. Evidence accumulation entails that before executing an action, cognitive agents (humans or animals) accrue evidence for the appropriateness of that action, until a certain criterion amount of evidence is collected. At that point in time, the action is initiated. Typically, this action is considered an explicit motor action — a key press — but it could also be an internal decision leading to the next step in a sequence of cognitive processes.
The idea of evidence accumulation has been applied to explain a variety of cognitive processes. For example, recognition memory — that is, answering the question whether we have encountered something before — can be described as a process in which people compare a new stimulus to representations in memory. Evidence is accumulated until a certain threshold is reached, and people are confident that the stimulus represents something they have observed before or not (Gillund and Shiffrin 1984; Raaijmakers and Shiffrin 1981). Indeed, computational models that incorporate the evidence accumulation principle accurately describe the data of recognition memory tasks, such as old/new recognition judgments (Neville et al. 2019; Ratcliff 1978).
Similarly, perceptual discrimination processes can be described as the accumulation of evidence that a stimulus belongs to one category or another. The hallmark task in this domain — the random dot motion task (RDM) — has been described over and over using evidence accumulation models. In the RDM task, participants are asked to indicate the direction of motion of a cloud of moving dots. While a proportion of the dots move in a target direction, the remainder moves randomly and makes discriminating the direction more difficult. Also in this domain, evidence accumulation models accurately describe the data that have been collected, and it has been shown that the rate of evidence accumulation reflects the difficulty of the discrimination (Gold and Shadlen 2001; Mulder et al. 2013; Palmer et al. 2005; Van Maanen et al., 2016a, b).
What these examples illustrate is that the principle of evidence accumulation seems diversely applicable and that computational models describing evidence accumulation have been successful at describing all kinds of behavior (Forstmann et al. 2016; Ratcliff et al. 2016). Moreover, evidence accumulation has not only been successful as a description of cognitive processing but has also been considered as an explanatory mechanism at the level of the brain (Gold and Shadlen 2007; Mulder et al. 2014; O’Connell et al. 2012).
Evidence accumulation theories do not propose that all of behavior consists of an evidence accumulation process. Instead, most applications of evidence accumulation models assume that behavior is the result of three consecutive stages (Ratcliff and McKoon 2008): an initial perceptual encoding/attention orientation stage in which a stimulus is perceived, an accumulation stage in which evidence to engage in an action is accumulated, and a final response execution stage that executes the selected action. The perceptual and responses stages are often collectively designated as non-decision time. Although this subdivision in three processing stages seems appropriate for very simple tasks, as soon as tasks become more complex, cognition progresses through a more extended sequence of stages (Anderson 2007; Gray and Ritter 2007; Salvucci and Taatgen 2008; Van Rijn et al. 2016), and evidence accumulation models can no longer be applied straightforwardly.
In fact, there has been a long tradition in cognitive science to discover and interpret sequences of processing stages (e.g., Donders 1868; Sternberg 1969). Whereas classical methods necessarily relied on behavior alone, more recent methods have applied neuroimaging to discover processing stages (Anderson and Fincham 2014; Blankertz et al. 2011; Borst et al. 2016; Borst and Anderson 2015; King et al. 2016; King and Dehaene 2014; Sternberg 2011; Sudre et al. 2012). Recently, Anderson and colleagues developed a powerful method that can discover processing stages in M/EEG data: HsMM-MVPA analysis (Anderson et al. 2016). By combining hidden semi-Markov models (HsMMs) with multivariate-pattern analysis (MPVA), this machine-learning method has been successful in detecting latent sequences of processing stages in tasks ranging from associative recognition (Anderson et al. 2016; Portoles et al. 2018; Zhang et al. 2017) to working memory (Zhang et al. 2018) and mathematical problem-solving (Anderson et al. 2018; Zhang et al. 2017).
Among the tasks analyzed with HsMM-MVPA were an associative recognition task and two working memory tasks. Although the structure of these tasks resembles the recognition memory tasks that were previously successfully analyzed using evidence accumulation models (Neville et al. 2019; Ratcliff 1978), Anderson and colleagues found evidence for a sequence of at least five processing stages. This is an indication that the typical three-stage assumption of evidence accumulation models might not hold, even in such relatively simple tasks.
The discrepancy in the number of processing stages between the two analysis traditions may not be a critical problem for evidence accumulation models, as long as an important assumption is met. This assumption is that all observed decision-related effects (e.g., between conditions or participants) are generated by a single stage that accounts for the evidence accumulation process. Under this assumption, all other stages contribute to the non-decision time component in evidence accumulation models. Unfortunately, this assumption does not always hold (e.g., Zhang et al. 2017), rendering the application of evidence accumulation models potentially problematic, especially in tasks with multiple chained decision processes. In addition, if the non-decision time consists of multiple non-decision stages, fitting the evidence accumulation process will suffer, and estimated parameters will be less precise, as each additional stage introduces noise. Instead, if we could isolate a decision stage on a trial-by-trial basis, fitting the evidence accumulation process could be improved.
The current research therefore proposes to combine the EEG stage-discovery method (i.e., HsMM-MVPA) with evidence accumulation models. It introduces a methodology to first identify processing stages in a bottom-up manner using the stage-discovery method and subsequently test predictions about the distribution of processing stage durations using evidence accumulation models. The structure of the paper is as follows:
-
1.
We will provide an overview of the analysis tools. The first tool is the HsMM-MVPA method introduced by Anderson et al. (2016) that identifies latent processing stages. The second tool is the diffusion decision model (DDM), a prototypical evidence accumulation model for analyzing response time distributions.
-
2.
We will apply the combined methodology to two datasets. For each dataset we describe its methodological specificities and results regarding the HsMM-MVPA and the DDM, followed by a discussion of its results.
-
a.
The first dataset (Application 1) pertains the associative recognition task reported by Anderson et al. (2016). Previous work has revealed that behavior in this task can be decomposed in six serial stages, one of which differs in duration for different conditions — memory retrieval. Here, we interpret the stage with duration differences in terms of evidence accumulation. This application will illustrate how evidence accumulation models can shed light on critical cognitive processes that are embedded in complex tasks.
-
b.
The second dataset (Application 2) pertains a typical perceptual categorization task from Boehm et al. (2014). In this task, participants were asked to make a perceptually informed choice, while either being cued for fast responses or accurate responses. With our combined methodology, we found support for the often-found interpretation of the accumulator model parameters but also found surprising evidence for an additional stage in the accuracy-cued condition. This application highlights the added value of combining evidence accumulation models with the stage discovery method.
-
a.
-
3.
We will end the paper with a general discussion of the new methodology.
Methods Overview
HsMM-MVPA
The first step in the combined stage-discovery evidence accumulation framework is discovering processing stages in a task. To discover processing stages, we will apply the bottom-up HsMM-MVPA method (Anderson et al. 2016) to both EEG datasets independently. The resulting processing stages will subsequently be analyzed with evidence accumulation models.
The HsMM-MVPA method was founded on two major theories that link the measured EEG signal to cognitive processing (Makeig et al. 2002). The classical theory (Shah et al. 2004) assumes that the onset of significant cognitive events cause phasic bursts of activity and associated voltage peaks, which are added to the ongoing neural oscillations in involved brain regions. If one averages across trials, the uncorrelated EEG signal will go to zero, and the peaks will be identified — as in a standard ERP analysis. According to the synchronized oscillation theory (Basar 1980; Makeig et al. 2002), significant cognitive events do not cause a burst of activity but instead reset the phase of EEG oscillations in a certain frequency range. As a result, oscillations become briefly synchronized, leading to a similar peak in the EEG signal as predicted by the classical theory (in fact, both theories of ERP generation can produce indistinguishable waveforms; Yeung et al. 2004, 2007). Thus, both theories link the onset of a cognitive process to a peak in the EEG signal; however, such peaks typically have low signal-to-noise and can only be observed when one averages across trials . Given such a pattern of EEG activity, the HsMM-MVPA method assumes that a processing stage (except the first, which starts at stimulus onset) starts with peaks with a consistent topology across trials which are followed by zero mean amplitude throughout the remainder of the stage.
If one could measure such peaks on single trials, one would be able to identify the onset of cognitive processing stages. Unfortunately, on single trials these peaks typically disappear in the noise. If one averages across trials in standard ERP fashion instead, peaks are only clear when they are close to fixed time points (e.g., stimulus onset, response). The further away from a common fixed time point across trials, the less clear ERP components become as the variation in timing of the peaks across trials increases.
The HsMM-MVPA method solves this problem for a predefined number of processing stages by using a hidden semi-Markov model to integrate the information present across all trials (typically starting at stimulus presentation and ending at a response) of all participants, to ultimately identify multivariate bumps, the peaks at the onsets, and flats, the periods of zero mean amplitude, on single trials (Anderson et al. 2016). Thus, while the method does take all trials into account simultaneously while estimating the model, one can afterwards inspect the temporal location of bumps and flats in single trials. Given that these bumps are hypothesized to signify the same underlying cognitive events across trials, their topology is assumed to be the same for all trials and all participants (Fig. 1, red dotted arrows). In contrast, the duration of the flats can vary between trials, reflecting the variability in stage length across trials and participants. This variable flat duration is modeled by gamma-2 distributions (Fig. 1, blue dotted arrows). The HsMM-MVPA method identifies the bumps and gamma distributions that maximize the likelihood of the data from all trials simultaneously using a standard expectation maximization algorithm for HsMMs (Yu 2010). It is important to note that this is not a hierarchical method, but we optimized the likelihood of the data of all trials of all subjects simultaneously.
As an example, Fig. 1 shows the scalp topologies (bumps) and gamma distributions associated with six stages identified in EEG data of an associative recognition task (Anderson et al. 2016; Portoles et al. 2018). Each bump indicates the onset of a new cognitive processing stage. The first stage is initiated by trial onset. It includes the time for the signal to reach the brain and so reflects both pre-cortical processing and time until the signal initiates cognitive processing. The last stage terminates with the response. In this example, stage four was on average much longer than the other stages, and also more variable. In addition, it was longer for more difficult associative retrievals and therefore interpreted as a memory retrieval stage. We will discuss this in more detail below as part of the first application of our combined HsMM-MVPA-evidence accumulation framework.
There are several things to note in this analysis. First, the analysis identifies bumps that signify the onset of a new stage, and not necessarily the offset. The bumps — potentially originating in the basal ganglia (Kriete et al. 2013; Stewart et al. 2012; Stocco et al. 2010) — reconfigure cortical activation, thereby starting processes in certain brain regions. However, in principle, these processes can continue while processes in other regions are started at the next bump. Thus, while the HsMM-MVPA method implies sequential stages, this is not necessarily the correct interpretation of the underlying neural processes. However, in most cases — as in the current experiments — the cognitive processes in the stages depend on each other For example, in a recent study, we manipulated only a decision rule (so not the stimuli or response options) between two experiments. We found that the duration of the penultimate stage was longer for the more difficult decision rule. Consequently the final stage was “pushed backwards” (Berberyan et al. 2021), indicating that the onset of the final stage was triggered by an event in the penultimate stage, suggesting serial dependence.
Second, the analysis is based on several assumptions. For example, it assumes that the activity following a bump is on average 0 in a region. While this is a strong assumption, it has been shown to be the case in the majority of identified stages, and even if this assumption is violated, the method can still reliably identify stages. This assumption and several other assumptions were tested using synthetic data in the original HsMM-MVPA study (Anderson et al. 2016; see in particular the Appendix). In the current manuscript, we adopt the assumptions and standard practices from these earlier HsMM-MVPA applications but discuss the assumptions and limitations again in the discussion.
Evidence accumulation
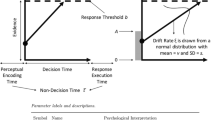
The second element of the new analysis framework is the diffusion decision model (Ratcliff 1978; Ratcliff et al. 2016; Ratcliff and McKoon 2008), a prototypical evidence accumulation model, and an important simplification, the shifted Wald model (Anders et al. 2016; Heathcote 2004; Luce 1986; Fig. 2a). This model assumes that over time, evidence samples are drawn from a normal distribution with a positive mean (v in Fig. 2) and a standard deviation s. These samples are accumulated until a threshold value is reached (a). Because on each iteration of this process (i.e., each experimental trial), this process differs slightly due to random sampling, the model predicts a specific distribution of finishing times of the process, that crucially depends on v and a. To account for processes outside of the evidence accumulation stage, the model additionally assumes an intercept t0, which is assumed to be the sum of the duration of an initial perceptual encoding stage and a final response execution stage (the non-decision time).
Standard evidence accumulators. a The shifted Wald model. The model assumes that evidence is accumulated with a mean rate of v, until a threshold value a is reached. Then, the sum of the durations of perceptual encoding and response execution is added (the additional durations marked t0). Shown is one example evidence accumulation process (i.e., one experimental trial). b The two-boundary generalization of the Wald model is the canonical diffusion decision model
The typical application of this model is to estimate the v, a, and t0 that best describe the observed distribution of response times in a particular experimental condition. The optimal set of parameters is consequently interpreted as describing the properties of cognitive processes in the task. For example, differences in the average rate of evidence accumulation are often interpreted as differences in the difficulty to extract information from a stimulus (e.g., Donkin and Van Maanen 2014) or from memory (e.g., Wagenmakers et al. 2008). Differences in the distance toward the threshold are often thought to reflect response caution (e.g., Van Maanen et al. 2011) or the prior probability of the response (that is, bias, e.g., Mulder et al. 2012; Neville et al. 2019).
The shifted Wald model describes the evidence accumulation process when one possible course of action is extremely likely. In many experimental paradigms, however, the observed behavior consists of choices between various response options and associated choice response times. A special case are so-called two-alternative forced choice paradigms (2AFC), in which participants are asked to choose between two predetermined options. 2AFC tasks are often analyzed using a two-sided version of the shifted Wald model, in which case evidence accumulation can go to two different threshold values. This model is typically referred to as the simple or standard DDM. In the two applications that follow, we estimated the parameters of the shifted Wald model (Application 1) and the DDM (Application 2), respectively, on the predicted durations of a single stage in each trial.
HsMM-MVPA Evidence Accumulation Framework
The combined HsMM-MVPA evidence accumulation framework consists of three steps. In step 1, the processing stags are identified with the HsMM-MVPA. Because the number of latent stages needs to be specified beforehand, we fit several HsMMs with increasing numbers of stages to the data. As HsMMs with more stages have more free parameters, they will typically fit the data better. To avoid overfitting, we apply leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV, Anderson et al. 2016) to each of the HsMMs. For the LOOCV, we first estimate maximum likelihood parameters of an HsMM on the data of all but one of the subjects. Given the identified bump topologies and gamma parameters, we then calculate the log-likelihood of the data of the left-out subject — this process is rotated over all subjects. To select the model with the optimal number of stages, we use a sign test: we only choose a more complex model if the data of a significant number of subjects fits better to it than to a model with fewer parameters. The underlying idea is that even if the true number of bumps is k, an HSMM with k+1 bumps might fit the data better in the estimation phase. However, it is at least as likely to fit the data of the left-out subject worse (Anderson et al. 2016; Anderson and Fincham 2014; Borst and Anderson 2015).Footnote 1
In step 2, we identify which discovered stage(s) vary in duration with experimental condition. First, we inspect results of the best-fitting HsMM. Even though we use only a single gamma distribution per stage to account for all conditions in step 1, different conditions might still have different average durations for a certain stage. To formally identify if a stage varies in duration between conditions, we can then fit an HsMM with the same number of stages but separate gamma distributions per condition on the stage that varies in duration. Then we use our LOOCV-approach to test whether such a more complex model explains significantly better the data. Thus far, the analysis is identical to previous HsMM-MVPA analyses. However, to avoid biasing the models to a group-wide pattern that would affect the evidence accumulation estimates, we added an additional step. In this step we estimate separate gamma parameters for each subject given the bump topologies common to all subjects, allowing stage length to vary by subject.Footnote 2
In step 3, we use either the shifted Wald or the DDM to fit an evidence accumulation model to the trial-by-trial stage durations of the identified processing stage. Using particle swarm optimization, we maximize the likelihood of those stage durations, given the parameters of the model. Because participants perform the tasks under various conditions, we varied the way parameters were constrained across conditions to identify parameters that systematically differ between conditions. The various model specifications obtained in this way were compared using the Bayesian information criterion (BIC, Schwarz 1978), to find the model specification that best balances the flexibility of the model across conditions with the goodness-of-fit. For each application, we report Schwarz weights, which represent the probability that a particular model generated the data, under the assumption that the data-generating model was in the set of to-be-compared models (Wagenmakers and Farrell 2004). Once the optimal model is identified, we can inspect the resulting model parameters in order to better understand the cognitive process in this stage.
To illustrate the approach and highlight the kinds of insights it can give, we will now apply it to two quite different tasks. In Application 1, we use a relatively complex associative recognition task, while in Application 2 we apply the method to a hallmark task of evidence accumulation models: the random dot motion task.
Application 1: Associative Recognition Task
Application 1 shows how we can combine the HsMM-MVPA methodology with evidence accumulation models. This will illustrate how an evidence accumulation model can help interpret and understand a cognitive processing stage. Secondly, it will show how the estimation of the evidence accumulation model will improve when it is focused on a single stage of a more complex stage sequence, in contrast to when it is fit to overall RT. We reanalyzed data of an associative recognition task collected by Borst et al. (2013), which was previously analyzed with the HsMM-MVPA method by (Anderson et al. 2016; Borst and Anderson 2015).
Associative recognition is the important ability to learn that two items co-occur. In our dataset, subjects first studied word pairs. In a subsequent test phase, they had to discriminate target pairs from re-paired foils (a recombination of target words) and new foils (entirely new words). Whereas remembering whether the component words were studied (item information) was sufficient to discriminate between targets and new foils, successful discrimination between targets and re-paired foils also required remembering how the words were paired during study (associative information). To influence a potential associative retrieval process, the associative fan, or associative strength, of the words was manipulated. Fan refers to the number of pairs a particular word appears in, and thus to the number of other items in memory the word is associated to. Fan is well-known to have strong effects on reaction time and accuracy, with higher fan resulting in longer RTs and lower accuracy (Anderson and Reder 1999; Schneider and Anderson 2012).
Theories of recognition memory are concerned with the cognitive processes that subjects go through when making the decision whether they learned a word pair. There are three major theories: global matching, dual-process, and ACT-R. All theories assume an encoding stage and a response stage, but the central cognitive stages vary (for reviews, see Malmberg 2008; Wixted 2007; Yonelinas 2002). Global matching assumes that the central stage consists of a matching process in which a cue that includes both words is compared to all relevant items in memory (Clark and Gronlund 1996; Gillund and Shiffrin 1984; Murdock 1993; Wixted and Stretch 2004). The combined similarity to all items in memory, reflecting the familiarity of the words, is compared to a response criterion. If it exceeds this criterion the model responds “yes,” if not it responds “no.” If global matching theories are correct, this implies that associative recognition data could directly be analyzed with an evidence accumulation model, without separating overall RTs into multiple accumulation stages.
According to dual-process theories, such a fast familiarity process is insufficient. An additional recollection process is proposed, which is slower and yields qualitative information about the studied items, such as associative information (e.g., Malmberg 2008; Rugg and Curran 2007; Yonelinas 2002). It is assumed that the familiarity process distinguishes between new foils and targets/re-paired foils — directly proceeding to the response stage in the case of new foils (new foils are responded to faster than either targets or re-paired foils; Gronlund and Ratcliff 1989; Ratcliff and McKoon 1989; Rotello and Heit 2000), while recollection is required to distinguish between targets and re-paired foils (which are equally familiar). In such a framework, an initial stage analysis before applying an evidence accumulation model would be useful, as the retrieval stage would only be one in a sequence of different processes.
The third model is a symbolic process model developed in the ACT-R cognitive architecture (adaptive control of thought — rational; Anderson 2007). To account for associative recognition, it assumes three stages between encoding and response: a familiarity stage, an associative retrieval stage, and a decision stage (since Anderson et al. 2016, earlier it only assumed a retrieval stage and a decision stage, cf. Anderson and Reder 1999). If the individual words are familiar — not a new foil — the ACT-R model retrieves the best matching word pair from memory. In a short decision stage, the retrieved word pair is compared to the pair on the screen. Thus, also in the case of re-paired foils, a retrieval is made, but if the retrieved pair does not match with what is on the screen, a negative response is issued. Such a recall-to-reject process is consistent with a wide range of data on associative recognition (Anderson and Reder 1999; Malmberg 2008; Rotello et al. 2000; Rotello and Heit 2000; Schneider and Anderson 2012). Also in this account, an initial stage analysis would aid in fitting an evidence accumulation model to the data, as three different cognitive processes occur between perception and response.
Previously, this dataset was analyzed with the HsMM-MVPA method (Anderson et al. 2016; Portoles et al. 2018). Figures 1 and 3 show the results: 5 bumps were discovered, resulting in 6 different stages. Based on the topologies, durations, and connectivity analyses of the data, these stages were interpreted as a pre-encoding, encoding, familiarity, retrieval, decision, and a response stage. These results highlighted the value of the HsMM-MVPA analysis: it indicated that none of the theories above were complete. The matching stage as proposed by global matching theories was only one in a more complex sequence of stages; in addition to the familiarity and recollection processes proposed by dual-process models, a decision stage was necessary; and in contrast to the original ACT-R model, a familiarity stage was shown to play an important role. Finally, it was shown that only the retrieval stage — indicated in red in Fig. 3 — varied significantly in duration between conditions, which is why we will focus on explaining this stage using an evidence accumulation model. This should result in a better characterization and interpretation of the differences in retrieval duration between conditions.
HsMM-MVPA
Here, we first reproduce the analysis of Anderson et al. (2016). In the interest of explaining the proposed HsMM-MVPA evidence accumulation framework, we will briefly explain the methods and analysis that was performed.
Methods
In the first phase of the experiment, twenty participants memorized 32 word pairs. Half of these pairs were fan-1 pairs, that is, the component words only occurred in a single pair. For the other half of the pairs, the fan-2 pairs, each component word occurred in exactly two pairs. In the second phase of the experiment — during which EEG was collected — subjects were presented with probe word pairs. Their task was to discriminate targets from re-paired foils and new foils. Targets and re-paired foils were repeated 13 times over the course of the experiment, while new foils were only presented once. Subjects completed 13 blocks of 80 trials, for a total of 1040 trials. Nevertheless, for new foils, a different cognitive processing sequence was discovered in Anderson et al. (2016), and they cannot be analyzed using the same evidence accumulation model as targets and re-paired foils. Therefore, we will disregard these trials for the purposes of the current paper. Details of the experimental methods and EEG recordings are reported in Borst et al. (2013).
To preprocess the EEG data, we followed Portoles et al. (2018), which follows a similar pipeline to Anderson et al. (2016) except for minor differences. Preprocessing consisted of visual inspection to remove artifacts, removing eye blinks using independent component analysis, band-pass filtering the data between 1-35Hz, and down-sampling the data to 100 Hz to reduce computational load. As the HsMM-MVPA analysis is performed on single trial data, we then segmented the data and retained the data between stimulus onset and response for each trial. Next, each trial was detrended, and its covariance matrix was computed. Incomplete trials, incorrect trials, trials with response times greater than 3 SDs per condition and subject, and trials with amplitudes exceeding ± 80 μV were removed. Finally, a principal component analysis was performed with the mean covariance matrix across all trials of all subjects, and the first 10 components (explaining more than 95% of the variance) were normalized and used for the HsMM-MVPA analysis.
Result
In this paper, we repeat the analysis of Anderson et al. (2016) for targets and re-paired foils. For targets and re-paired foils, HsMMs with 1–8 bumps were estimated. LOOCV showed a log-likelihood increase up to 6 bumps, but it was argued in Anderson et al. (2016) that the 5-bump accounted better for the data (see also Anderson et al. 2018 for a similar analysis and conclusion based on MEG data). We will therefore use a 5-bump HsMM for the current analysis; this model is shown in Fig. 3.
In the first step, Anderson and colleagues used a single gamma distribution for each stage across conditions. To test which stage durations varied with experimental condition, Anderson and colleagues then estimated separate gamma distributions for each stage and condition. Through an LOOCV-procedure, it was shown that the log-likelihood only increased for a significant number of subjects if different gamma distributions were used for stage 4. This result is apparent in Fig. 3, where only the duration of stage 4 differs clearly between conditions.
Based on the duration effects on the different stages, as well as their connectivity patterns (Portoles et al. 2018), the six stages were identified as pre-encoding (the time for the physical appearance of the stimulus to trigger a reaction in the brain), encoding the words, a familiarity process, memory retrieval, decision, and response. As discussed above, stage 4 was the only stage that varied significantly in duration between the different conditions of the experiment. In combination with the interpretation of the other stages, and given that it is longer for more difficult associations (fan-2 pairs) and foils, this stage was interpreted as a memory retrieval stage. This was later corroborated by an HsMM-MVPA analysis of a MEG dataset of the same task, which showed hippocampal and prefrontal activation during this stage (Anderson et al. 2018; Borst et al. 2016).
The ACT-R theory explains the fan and target/foil effects on the duration of the retrieval stage as follows. It is assumed that information that we perceive in the environment spreads activation to our memory system. In the case of the current experiment, the information that spreads activation are the two encoded words of the word pair on the screen. In the case of fan-1 targets, both words spread activation to the single target pair in memory, resulting in the fastest retrieval. In the case of a re-paired foil, only one of the words spreads activation to a target word pair, as the combination does not exist in memory. Consequently, the to-be-retrieved pair receives less activation and is retrieved slower as a result.
The fan effect on retrieval duration — i.e., fan-2 pairs are slower than fan-1 pairs — has been explained by assuming that the amount of spreading activation of an encoded word depends crucially on the number of memory items that contain that word (e.g., Anderson 2007; Anderson and Reder 1999; Schneider and Anderson 2012). The basic idea is that the more predictive the encoded word is of the to-be-retrieved memory, the more activation is spread. That is, if one only has a single memory trace concerning Paris in memory, reading “Paris” will be very predictive of retrieving that memory trace. However, if one lives in Paris, reading “Paris” will be hardly predictive of what information needs to be retrieved. Thus, fan-2 pairs in memory receive less activation than fan-1 pairs, as the encoded words are less predictive of what needs to be retrieved, given that there are two pairs in memory containing each of the encoded words.
In terms of evidence accumulation, the ACT-R account predicts that the drift rate will be higher for fan-1 pairs and targets than for fan-2 pairs and foils, as more spreading activation results in a more efficient retrieval process (Anderson 2007; Schneider and Anderson 2012; Van Maanen et al. 2012; Van Maanen and Van Rijn 2007a). We will now fit evidence accumulation models to the duration of stage 4 to test whether these predictions are borne out by the data.
Evidence Accumulation
Methods
The HsMM-MVPA results suggest that all stages of the four conditions in this task are comparable, except for stage 4. Therefore, we only fit an accumulator model to the predicted durations of stage 4, as these are assumed to explain the critical differences between conditions. Henceforth we will refer to these durations as the decision times (DT). Because previous work relates stage 4 to a memory retrieval process (Anderson et al. 2016, 2018; Borst et al. 2016; Borst and Anderson 2015; Portoles et al. 2018), it is appropriate to model the retrieval process as a noisy accumulation (e.g., Criss 2010; Neville et al. 2019; Ratcliff 1978). We chose to apply the shifted Wald Model (Anders et al. 2016) to model the decision times. The choice of the Wald model was informed by the small number of errors in this task (less than five for most participants in at least one condition). A limited number of errors compromise the estimation of the error RT distribution as well as reliably estimating the HsMM stages. We performed model comparisons in which the drift rate and threshold are systematically varied over the two dimensions of the experimental design (Table 1). Additionally, we included models in which a shift parameter was estimated (t0), to investigate whether this parameter was indeed external to the retrieval stage and therefore would not meaningfully contribute to the fit.
For comparison, we additionally analyzed the observed response times of the associative recognition task, disregarding the identification of a critical retrieval stage using the HsMM-MVPA method. Again, we systematically varied which parameters were fixed or free across conditions. However, we assumed that all remaining stages are of the same duration and are therefore captured by the shift parameter (t0).
Results
The Schwarz weights in Fig. 4a reveal a consistent preference for Model 9 across participants. Specifically, each cell of the matrix in Fig. 4a is a specific model-participant combination, with the color representing the Schwarz weight. For 7 out of 20 participants, Model 9 has the highest probability of having generated the data (under the assumption that the true data-generating model was included in the comparison), with an additional 3 participants best described by model 9t. This model is equivalent to Model 9 but estimates an additional t0. The estimated value was however quite low. In fact, for 13 participants this parameter was estimated at the lower bound (0.0001 ms), meaning that effectively the best fit did not include a shift. For the remaining participants, the mean estimate was 45 ms, which seems small in comparison to the response times. Finally, the stage durations of the majority of participants are best described by models that do not include a shift parameter (14/20).
Accumulator model results for the decision times in Application 1 reveal selective influence of the experimental manipulations. a Model comparison matrix showing the Schwarz weights of all fitted models, separately for all participants. The models are ordered according to the average BIC weight, the participants are ordered by the maximum BIC weight. Model numbers refer to Table 1. Models with “t” appended additionally have an estimated t0. b The aggregate fit of the best model against the data. Shown here are the 10, 30, 50, 70, and 90% quantiles of the decision time distributions. Error bars represent between-participant standard errors of the quantiles. c Mean drift rate for each condition. d Mean threshold distance for each condition. Error bars in c and d represent within-participant standard errors of the mean
Figure 4b shows the averaged (Ratcliff, 1979; Vincent 1912) fit to the decision time distributions of the four conditions of the associative recognition task, revealing that the fit is excellent and captures the variability in the data. Figure 4 c and d shows the mean parameter estimates for Model 9. The drift rates estimated for the two levels of associative fan differ (paired t-test, t(19) = 11.1, p < 0.001), as do the threshold values for the targets and repaired foil conditions (paired t-test, t(19) = 11.9, p < 0.001).
We fit the shifted Wald model to the response time data as well, to illustrate the standard (not EEG-informed) practice in the field of evidence accumulation modeling. Figure 5 shows the results. A couple of aspects stand out. Firstly, the agreement among individual participants with respect to which model is best is less than the agreement with the EEG-informed modeling. This can be seen when comparing Fig. 5a with Fig. 4a. A wider variety of models is considered the optimal model for individual participants, and there are more individuals where the model selection is ambiguous (indicated by yellow/orange colors). Secondly, the best model for the group (Model 11, which has the highest average Schwarz weight) seems to have a less convincing fit of the model to the data. That is, the model seems to miss the tails of the RT distributions for the fan-2 conditions (Fig. 5b), which was not an issue for the model fit on stage 4 durations (cf. Fig. 4b). Supplementary simulation 1 illustrates that this is expected when inserting an additional stage, as we assume is the case here.
If the parameters of the Wald distribution are estimated using the observed responses times (RT), different conclusions are derived. a Model comparison matrix showing the Schwarz weights of all fitted models, separately for all participants. The models are ordered according to the average BIC weight, the participants are ordered by the maximum BIC weight. Model numbers refer to Table 1. The best model is less consistent across participants. b The aggregate fit of the best model against the RT data shows a poorer fit. Shown here are the 10, 30, 50, 70, and 90% quantiles of the RT distributions. Error bars represent between-participant standard errors of the quantiles
Discussion
In Application 1 we first identified processing stages using the HsMM-MVPA methodology in an associative recognition task. We used a previously fitted model with 6 processing stages (Anderson et al. 2016). Next, we identified the stage that shows differences in mean stage durations across conditions. Fitting an evidence accumulator model to those data revealed that the experimental manipulation of associative fan seems to result in a difference in drift rates and presenting target and foil stimuli results in a different threshold distance. In other words, the observation that stage 4 in this task varies in duration across experimental conditions can be attributed to two distinct cognitive mechanisms. In addition, estimating an additional t0 did not improve the fits, suggesting that we were successful in isolating a retrieval stage.
Previous work has clearly linked stage 4 to a memory retrieval process (Anderson et al. 2016, 2018; Borst et al. 2016; Borst and Anderson 2015; Portoles et al. 2018). In this stage, participants retrieve from memory the closest pair that they studied as compared to the pair currently shown on the screen. According to the ACT-R theory, fan-1 pairs and targets are retrieved faster due to higher spreading activation, predicting a higher drift rate for those pairs. While this was indeed shown to be the case for fan-1 pairs compared to fan-2 pairs, there was no difference in drift rate found between targets and foils. Thus, where ACT-R explained the duration effects on RT with a single mechanism, the current results show that two different mechanisms play a role.
Because stage 4 seems a memory retrieval stage, it was appropriate to analyses the stage durations using evidence accumulation models. Memory retrieval has been characterized as a noisy accumulation process before (Ratcliff 1978). The lower drift rates for higher fan pairs could be a reflection of memory interference: Stimuli that are associated with multiple item pairs may be harder to retrieve from memory (Anders et al. 2015; Van Maanen et al. 2012; Van Maanen and Van Rijn 2007b). This is in line with the standard ACT-R explanation, where fan-1 pairs retrieve more spreading activation than fan-2 pairs. Alternatively, it could be that those pairs were less well learned, making it harder to re-activate the associated memory traces. This latter explanation is supported by the fact that subjects make more than twice the number of errors in the training phase on fan-2 pairs than on fan-1 pairs, while they required twice as many repetitions to memorize the fan-2 pairs (Borst et al. 2013, 2016).
The lower distance between the starting point of accumulation and the threshold that was found for target pairs relative to repaired foilsFootnote 3 could be explained by assuming that the evidence accumulation process ends when the re-activated memory item reaches a certain similarity to the used memory probe (i.e., the encoded words from the screen). Such a decision criterion could be implemented by Luce’s choice rule (Luce 1986; see also Van Maanen et al. 2012; Van Maanen and Van Rijn 2010, 2019). In the target condition, there is hardly any co-activation of competing memory traces; whereas in the repaired foil condition, there is co-activation because of additionally activated word pairs (cf. Fig. 3a and 4a in Van Maanen et al. 2012). Co-activation influences the time required to reach the critical decision criterion, assuming Luce’s choice rule. However, because the activation of the to-be-retrieved memory trace is the same in both conditions, the amount of activation at the moment of retrieval is less in the target condition than in the repaired foil condition. This level of activation at the moment of the decision is what appears to be reflected in the decision threshold parameter of the shifted Wald model.
It is important to stress that this explanation is post-hoc and would need independent confirmation. Nevertheless, a similar mechanism has been proposed in a detailed neural learning framework that accounts for familiarity, (associative) recognition, and recall processes (Norman 2010; Norman and O’Reilly 2003; O’Reilly and Norman 2002). While this seems to run counter to the standard interpretation that the threshold parameter is set independent of condition, it is in fact consistent with this idea: here the mechanism is set independent of condition, but because the to-be-compared item that is used by this mechanism is dependent on condition, it does yield a different threshold parameter per condition.
Of special interest is the observation that fitting the same 16 models to the response time data led to different conclusions. Note that we assumed that non-decision time t0 was the same for all four conditions. This assumption was based on the observation from the EEG time courses that the stages durations were comparable. When analyzing response times in the absence of additional information such as this, a researcher might consider the option of varying the t0 parameter across conditions as well, leading to a total of 64 different model specifications to compare. Nevertheless, such simplifying assumptions are very common, even when no neurophysiological data is available to inform such assumptions. For example, Gayet et al. (2016) tested and compared two evidence accumulation models that represented two competing hypotheses about the content of visual working memory. In doing so, they ignored potential variability in the remaining parameters in much the same way as we do here.
Application 2: Perceptual Speed-Accuracy Trade-off
With Application 2, we aim to validate the new analysis framework in an experimental paradigm that is traditionally the domain of evidence accumulation modeling. Firstly, we expect to find support for previous conclusions regarding the way people make perceptual discriminations that did not isolate the critical decision stage. Secondly, we aim to identify the stages in a relatively simple perceptual decision task, to illustrate that (1) the task structure may not (always) be as straightforward as typically assumed by evidence accumulation models, (2) identification of stages contributes to our understanding of perceptual decisions over and beyond what we already know, and (3) to illustrate how HsMM-MPVA handles erroneous responses. Finally, we will use this application to demonstrate in more detail how one can decide between HsMM solutions with different numbers of stages.
The task we chose here is a perceptual choice task, with an instruction to switch between speed-focused and accuracy-focused response regimes. In the context of our current study, this is an interesting experiment for multiple reasons. The first reason is that the random-dot motion task that participants had to perform is the hallmark task in the field of perceptual decision-making. In this task, participants were asked to indicate the direction of motion of a cloud of moving dots. While a proportion of the dots moved in a target direction, the remainder moved randomly and makes the direction discrimination more difficult. Previous research shows that the difficulty of the task can be directly expressed as the rate of evidence accumulation (e.g., Mulder et al. 2013; Palmer et al. 2005). The second reason is that the speed-accuracy trade-off manipulation is typically assumed to be related to the threshold setting in an evidence accumulation model (e.g., Van Maanen et al. 2011). That is, if participants are instructed to respond quickly, they lower their threshold, allowing for a shorter accumulation process and faster responses. However, a lower threshold also increases the probability that the participant makes errors, resulting in the classical speed-accuracy trade-off (Bogacz et al. 2010; Heitz 2014; Schouten and Bekker 1967; Wickelgren 1977).
Although the notion that speed-accuracy trade-off is purely driven by response threshold adjustment is theoretically appealing, this is not always found. In particular, in some studies, it is found that in addition to adjustments in response threshold, also an adjustment of non-decision time best explains the differences between speed-focused and accuracy-focused conditions (e.g., Mulder et al. 2010; Rinkenauer et al. 2004; Van Maanen et al. 2016a, b). A shorter non-decision time for speeded choices is often interpreted as a form of motor preparation. Another observation that is sometimes made is that the rates of accumulation are higher for speeded choices than for accuracy-focused choices (Ho et al. 2012; Rae et al. 2014). This is interpreted as increased attention, although other interpretations are possible as well (Miletić and Van Maanen 2019).
We reanalyzed the data of Boehm et al. (2014), who collected behavioral responses and EEG of participants who performed a random-dot motion task. In this task, participants were asked to indicate the direction of motion of a cloud of moving dots. While a proportion of the dots moved in a target direction, the remainder moved randomly and makes the direction discrimination more difficult. Difficulty of the task was calibrated per subject. Prior to each trial, participants received a cue that indicated whether they should respond as quickly as possible or whether they should focus on giving an accurate response. We reanalyzed the data of 25 participants (17 female, mean age 21 years), who each performed 200 trials. For more details about the experimental design and apparatus, we refer to Boehm et al. (2014).
HsMM-MVPA
Methods
The EEG data were preprocessed similar to Application 1, although the first preprocessing steps were done according to Boehm et al. (2014). Preprocessing was performed with the FieldTrip toolbox (Oostenveld et al. 2011). First, trials with artifacts were removed: artifactual events with amplitudes exceeding ± 300 μV, clipping artifacts longer than 10 ms, z-values higher than 50, and z-values higher than 25 in the 110 to 140 Hz interval. Next, EEG data were low-pass filtered at 35 Hz and eye blinks corrected with independent component analysis. A 1-Hz high-pass filter was applied. Then, trials were defined from stimulus onset to response. Each trial was detrended and a covariance matrix computed. Finally, a principal component analysis was carried out with the average covariance matrix of trials and subjects. The first ten principal components (explaining more than 95% of the variance) were z-scored and kept for the HsMM.
Results
We estimated an overall HsMM across both experimental conditions (speed and accuracy focus), as well as separate HsMMs for each condition. In the overall HsMM, bump topologies and gamma distributions were the same across conditions, while they were fully independent for the separate HsMMs.
Figure 6 shows the results of the LOOCV procedure that we applied. Panel 7A indicates that the log-likelihood for the overall model did not increase for a significant number of subjects over a 1-bump-2-stage solution (yellow line; a ratio higher or equal to 18/25 subjects indicates a significant improvement in a sign test). If we fit separate models for the speed- and accuracy-focused conditions and inspect their summed log-likelihood, it increases up to a 3-bump-4-stage solution (red line). In addition, when comparing this summed speed-accuracy log-likelihood to the log-likelihood of the overall model, we find a significant improvement for any number of stages (gray arrows). Thus, separate HsMMs for the accuracy- and speed-focused conditions are clearly preferred over a single overall model, and on average a 3-bump solution is preferred.
LOOCV results of Application 2. Colored numbers indicate the number of subjects that improve to a solution with a certain number of bumps. For example, “16/25” for the combined model at bump 2 indicates that 16 of the 25 subjects fitted better in a 2-bump model than in a 1-bump model. a A combined speed-accuracy-focus model is compared to two separate models. The number of subjects that improve between those two models is indicated in grey. b The log-likelihood of the separate models is shown for 1–6 bumps
To determine their respective most likely number of stages, we separately plotted the log-likelihoods of those models (Fig. 6b). The speed model increases up to a 2-bump-3-stage model (green line; the 4-bump model does not significantly improve over the 2-bump model). For the accuracy-focused trials, we find evidence for a 3-bump-4-stage model. Importantly, the curve for the latter model seems shifted by one bump overall. We are therefore confident that when presented with an accuracy-focus cue, subjects go through one additional cognitive stage as compared to the speed-focused cue.
Figure 7 shows the estimated stage topologies and stage durations for the separate models. Interestingly, in both conditions, the last stage is the longest stage, culminating in a response. We interpret this last stage as a decision-making stage. Another interpretation would be that state 3 in the accuracy-focused condition is the decision stage, and stage 4 reflects a check of the decision that was made. However, we deem this option unlikely, because stage 3 in the accuracy-focused condition is shorter than the last stage in the speed-focused condition, which would suggest that evidence accumulation would be faster when cued to be accurate and slower when cued to be fast. In addition, the last stage for the speed-focused condition is shorter than the last stage for the accuracy-focused condition. In combination with the extra stage, this explains the longer response times in this condition. In the next section, we will explore where the differences in duration of the decision stages originate.
Evidence Accumulation
Methods
We estimated the parameters of a simple diffusion decision model (DDM), both on the observed response times and choices and on the decision-making stages and choices. Note that we make a critical assumption here, which is that all choice errors are due to a noisy evidence accumulation process. This is a simplification, since it is conceivable that some of the incorrect (and also some of the correct) choices are due to guessing or due to problems in earlier perceptual stages. Moreover, since there was no systematic response hand effect on RT (paired t(24) = 0.52; p = 0.60), we decided to collapse the data across response hands.
Similar to Application 1, we estimate the parameters of all possible model specifications, listed in Table 2. In this case however, we also include models in which t0 differs between conditions, since there is some evidence that speed-accuracy instructions seem to affect it (Mulder et al. 2010, 2014; Rinkenauer et al. 2004; Van Maanen et al. 2016a, b; Winkel et al. 2012). Variability parameters were estimated for drift rates, non-decision times, and thresholds (Ratcliff and Rouder 1998). We used the standard variability assumptions in DDM: drift rates were assumed to vary across trials according to a normal distribution with standard deviation sv; non-decision times were assumed to vary uniformly across trials between st0 and t0; and the distance to threshold was assumed to vary uniformly across trials between sz and a.Footnote 4 These were constrained in the same way as their central tendency counterparts (cf. Archambeau et al. 2019). Again, we included models were the non-decision time was constrained to 0, to test the hypothesis that also in this dataset this parameter reflects time external to the critical decision stage.
Results
Figure 8 displays the results of fitting the DDM to the distribution of durations and choices of the decision stages. The preferred model is surprisingly consistent across participant (Fig. 8a), with only six participants better fit by another model. Model 6t fits the aggregate data reasonably well (Fig. 8b), although the tails of the distributions seem to be missed. Of note is that the decision times show an interaction between response accuracy and condition (F(1,24) = 27, p < 0.001). The model captures this pattern as well, albeit that the predicted effect size is substantially smaller (see Supplementary Materials for details). Figure 8c drives home that, consistent with an abundance of previous studies (Boehm et al. 2014; Forstmann et al. 2008, 2010; Van Maanen et al. 2011; Van Maanen et al. 2016a, b; Winkel et al. 2012), the threshold parameter is estimated higher for the accuracy-focused condition than the speed-focused condition (paired t-test, t(24) = 8.8, p < 0.001). The variability in threshold distance did not differ across conditions (paired t-test, t(24) = − 1.4, p = 0.17), and the remaining parameters were fixed across conditions. The mean non-decision time was estimated to be 87 ms (SE = 10 ms).
Accumulator model results for the critical stage duration in Application 2 reveal that the speed-accuracy trade-off is expressed in a difference in threshold. a Model comparison matrix showing the Schwarz weights of the fitted models, separately for all participants. The models are ordered according to the average BIC weight; the participants are ordered by the maximum BIC weight. Model numbers refer to Table 2. b The aggregate fit of the best model against the data. Shown here are the 10, 30, 50, 70, and 90% quantiles of the stage duration distributions. Error bars represent between-participant standard errors of the quantiles. c Mean threshold distance for each condition. Error bars represent within-participant standard errors of the mean
Contrary to Application 1, model comparison based on the RT data seems mostly consistent with model comparison based on the stage duration data, at least on the group level. Model 6t is overall the preferred model (Fig. 9a), with 7 out of 25 participants better fit by another model. However, close inspection reveals that these participants differ from the deviant participants of the stage-based fitting, suggesting more uncertainty in the results. This is supported by inspecting the aggregate fit, which seems less convincing (comparing Fig. 9b and Fig. 8b). The estimated mean non-decision based on the RT data is 406 ms (SE = 23 ms), which is substantially larger than the non-decision time estimated from the DT data.
Accumulator model results based on response times in Application 2 corroborate the stage-based results. a Model comparison matrix showing the Schwarz weights of the fitted models, separately for all participants. b The aggregate fit of the best model against the data. Shown here are the 10, 30, 50, 70, and 90% quantiles of the RT distributions. Error bars represent between-participant standard errors of the quantiles
Discussion
The results of fitting the durations of one, critical, stage in the perceptual choice task of Application 2 are in line with what was expected based on parameter estimates from response time data. However, the estimated non-decision times differed substantially depending on the DT or RT fitting procedure. The non-decision time based on RT was approximately 319 ms larger on average, representing the duration of the remaining stages. While this is a reassuring result, the analysis also led to two new theoretical findings.
The first finding was that the critical stage on which stage durations differed per condition was the final stage. This is in contrast with the typical assumption in the evidence accumulation field that the decision stage in simple perceptual tasks is the middle of three stages. The first stage, that typically does not differ across conditions, is believed to be a perceptual encoding stage, with the final stage only representing the response execution (Mulder et al. 2014; Mulder and Van Maanen 2013). Here, we show that evidence is accumulated up to the moment of the response, directly linking incoming visual information to response preparation. There is some converging evidence to support this finding (Gallivan et al. 2018). For example, Thura and Cisek (2014, 2016) report that monkeys performing a reaching decision show primary motor cortex (M1) activation prior to action execution. The pattern of M1 activation seems to reflect the evidence accumulation process of the monkey, with easy decisions resulting in a faster increase in neural firing rates in M1 than hard decisions. This pattern would be consistent with a relatively late temporal locus of the evidence accumulation process. In general, our results are in line with reports using electromyography that show that motor execution is not independent of decision stages. Prior work, in particular related to decisions with conflicting information, has revealed that both response hands can become active, even if eventually only one response button is pressed (Burle et al. 2014; Coles et al. 1985; Servant et al. 2015, 2016; Spieser et al. 2017). This line of reasoning is supported by the small non-decision time that we found in this final stage. This duration could reflect the final execution of the button press. For example, Byrne and Anderson (2001) estimate this at 60 ms, which is comparable in magnitude to the 87 ms that we found on average.
A second, even more striking finding is the presence of an additional stage when participants are asked to focus on responding accurately. This finding seems consistent with evidence accumulation modeling that reports non-decision time differences between speed focused and accuracy-focused conditions (Mulder et al. 2010, 2014; Rinkenauer et al. 2004; Van Maanen et al. 2016a, 2016b; Winkel et al. 2012). However, in our own evidence accumulation modeling of the response times in Application 2, we did not observe convincing evidence for a non-decision time difference between conditions, which seems inconsistent with the HsMM-MVPA result. The accumulator model seems to account for the non-decision time difference by estimating a much larger variability in threshold distance for the speed focused condition then for the accuracy-focused conditions. Larger variability in the distance to threshold yields faster responses, in particular faster error responses (Ratcliff and McKoon 2008). This is consistent with the overall patterns in the data, because errors in the speed focused condition are indeed faster than errors in the accuracy-focused condition. It seems therefore that the added noise by the additional stages that form the response times resulted in an inappropriate model being preferred. Ignoring those stages, The DT-based evidence accumulation model indeed does not require condition differences in this variability parameter nor differences in non-decision time.
General Discussion
The goal of this paper was to combine two prominent traditions in cognitive science: evidence accumulation modeling and stage discovery methods. To this end, we proposed a new method that first applies HsMM-MVPA EEG analysis to discover processing stages in a task and then use evidence accumulation models to investigate the stage of interest in more detail. By isolating the important stages in a task before applying evidence accumulation models, we aimed to (a) improve the estimation of such models by removing or reducing noise from auxiliary processes and importantly (b) aid the interpretation of duration effects of discovered cognitive stages.
Application 1, in which we analyzed EEG data from an associative recognition task, illustrated both goals. First, it was shown that estimating the parameters of an evidence accumulation model on stage durations compared to estimating them on RT resulted in a much clearer picture of the underlying process. That is, the agreement of fitted parameters among individual participants was higher, and it resulted in a more convincing fit of the model to the data. Second, the estimated parameters clearly indicated that the difference between fan-1 and fan-2 pairs was due to a higher drift rate for fan-1 pairs, while the difference between targets and foils was best explained by a difference in threshold. This runs counter to one of the major computational models of associative recognition, ACT-R, which assumes that both condition effects are caused by a difference in spreading activation (e.g., Anderson et al. 2016).
In Application 2 we took on a hallmark evidence accumulation task: the RDM task, with a speed-accuracy trade-off manipulation. This yielded a surprising outcome: we discovered an additional stage in the accuracy-focused condition. As a result, the DDM fitted to the stage duration seemed to account better for the data, and it did not require estimating a variable non-decision time, which was necessary for the DDM fit to the overall RT. In agreement with the general literature, the duration effects were attributed to a difference in threshold.
The two applications illustrate the added value of first discovering processing stages before using evidence accumulation models to explain the underlying cognitive mechanisms. In both cases, the evidence accumulation models explained the data better when fit to discovered stage durations as compared to overall RT. In addition, the parameter estimates of the accumulator models seem sensible: in the case of the fan effect of Application 1 and the speed-accuracy trade-off in Application 2, they are in clear agreement with the general literature, while the target-foil effect in Application 1 can be explained by some existing models and challenges others. Finally, these applications show that first applying the HsMM-MVPA analysis does not result in similar parameter estimates in all tasks: in Application 1, drift rate was the most important factor, while Application 2 resulted in different threshold settings.
One of the goals of combining the HsMM-MVPA method with evidence accumulation models was to improve the interpretability of these models. When fitting such models, it is typically necessary to estimate non-decision time. This is not a problem as long as all behavioral effects are due to a single processing stage. Under this assumption, the remaining stages sum to the non-decision time. However, even in this case, fitting the evidence accumulation process would be more precise if one could isolate a decision stage on a trial-by-trial basis. This argument has also been put forward by Verdonck and Tuerlinckx (2016), who show that a non-parametric estimation of the non-decision time distribution yields a superior fit and more reliable parameters than simply assuming a standard distributional form of the non-decision time. When the non-decision time represents a compound of multiple processes, then these considerations become more important as well.
Importantly, when behavioral effects are due to multiple different processing stages, this assumption becomes problematic. This is especially the case when condition effects counter each other. For example, Zhang et al. (2017) conducted an associative recognition experiment with three-word associates, allowing them to manipulate similarity between probes and targets on a more continuous scale. They analyzed their EEG data using the HsMM-MVPA method. Their results showed that a retrieval stage was shortest when probes were most similar to the studied triple, while a comparison stage was longest in that case. They conclude that “[t] he opposing ways in which probe similarity impacted retrieval and comparison stages explained why this factor had only a modest effect on overall RT; for instance, RTs were nearly identical for similar 1 foils and targets, yet the durations of the retrieval and comparison stages clearly differed” (Zhang et al. 2017, p. 364).
This clearly poses a challenge for evidence accumulation models, including D*M (Verdonck and Tuerlinckx 2016) that only have access to overall RT. Given that RT hardly varied between conditions, it is hard to imagine how such a model would identify the variation in underlying cognitive processes. However, the new HsMM-MVPA evidence accumulation framework applied to his task would give a more precise characterization of the underlying mechanisms of both the retrieval and the comparison stage. This also illustrates how this method could open up more complex tasks in which multiple decision processes are chained to an analysis based on evidence accumulation models: first identify the different stages and then fit an accumulator model to each stage separately.
Although the HsMM-MVPA decomposition of the response times removes processing stages that do not systematically contribute to a response time difference between conditions, this does not entail that there cannot be any residual time left in the stage durations that are subsequentially modeled with the evidence accumulation framework. For this reason, we explicitly included models with a non-decision time parameter in the model comparisons of the stage durations. In Application 1, we found that models without non-decision time were preferred over models with non-decision time, but in Application 2 we found the inverse. The average non-decision time of the critical final stage was estimated at 87 ms on average. We interpreted this as the duration of a button press — necessarily part of the final stage — which would not be expected to differ between conditions.
Focusing on a single processing stage does not entail that an improvement in evidence accumulation model fit can be uniquely ascribed to this noise reduction. A first additional reason that the EAMs fit better on DTs than on RTs is because the RTs are inherently more variable (in addition to more noisy) than DTs. More variable datasets result in poorer fit of the evidence accumulation model (Ratcliff and McKoon 2008; Ratcliff and Tuerlinckx 2002). A second additional reason might lie in the fact that the stage durations are predicted using a gamma distribution. The gamma distribution effectively acts as a filter, smoothing noise in the DTs resulting in a potentially better fit.
There is a large body of work devoted to the detection of serial processing stages, often contrasted with parallel processing or co-activation accounts (e.g., Liu 1996; Miller 1993; Schweickert 1989; Townsend and Nozawa 1995). A prominent approach to address this question is systems factorial technology (SFT, Townsend and Nozawa 1995). SFT aims to differentiate between serial and parallel processing by making qualitative predictions of how RT distributions differ under serial and parallel processing assumptions and then subsequently test for those differences in highly specific experimental designs. Interestingly, one such study involves a test of serial processing in associative recognition, similar to our Application 1 (Cox and Criss 2017). Cox and Criss (2017 ) found evidence for parallel processing of associations between items of a pair, and the items themselves, which could be interpreted as evidence against strictly serial processing. This is in line with our current results, if one assumes that the familiarity stage (stage 3) continues during the associative retrieval stage (stage 4), an interpretation we have put forward in the past (Borst and Anderson 2015).
Limitations
These results rely on the assumptions underneath of our new analysis framework, as well as the validity of the HsMM-MVPA and evidence accumulation models. Several of the assumptions of the HsMM-MVPA were challenged with synthetic data in the original paper (Anderson et al. 2016). For example, they explored the effects of missing bumps, varying bump topologies, and different shape parameters of the gamma distribution. In all those cases, the method could still reliably identify stages under normal variation conditions.
An assumption of the HsMM-MVPA method that is relevant for the current analysis framework relates to the bump-flat model underlying the EEG data. This bump-flat model, as we have explained above, is grounded in the theories of ERP generation. The flat imposes that within a stage, the mean amplitude of each signal is equal to zero. This assumption might be in conflict with studies indicating that evidence accumulation is directly detectable in EEG signals O’Connell et al. (2012). However, the zero-mean amplitude assumption is flexible enough to accommodate neural processes leading to EEG signals with non-stationary properties such as zero-crossing trends or time-varying variances. In addition, even if the zero-mean amplitude assumption is violated, the HsMM-MVPA can identify the stages reasonably well in synthetic data (Anderson et al. 2016). That said, if the corresponding bump becomes too broad because of a non-stationary EEG signal, the method might have trouble detecting it.
Regarding the bumps, the HsMM-MVPA assumes that there is a fixed number of bumps and each of them last 50 ms. If the length of a bump would be compared to an ERP component, we should take into account that ERP analyses are typically time-locked to stimulus onset or to the response, which leads to smearing (elongating) of the ERP components due to the trial-to-trial temporal variability of the latent cognitive processes (Borst and Anderson 2021). Nevertheless, the HsMM-MVPA is able to identify bumps up to 110 ms in synthetic data (Anderson et al. 2016).
With respect to the number of bumps — and consequently stages — that best explain the data, there is no single correct approach. This is a limitation intrinsic to HsMM models. Here, we chose the number of stages that best generalized across subjects, using an LOOCV method combined with a sign test. This approach ensures a parsimonious sequence of stages that fits all subjects, and it has been the default approach in all applications of the HsMM-MVPA that we are aware of. There are other approaches to select the number of stages, such as taking the mean or total likelihood across subjects. Such approaches might explain more variance in the EEG data, but they might also be biased by a small set of subjects that fit extremely well or very badly to the model. Ultimately, a method that includes individual variability while still resulting in an overall model would be preferred. However, this is not feasible with the current method.
Finally, the HsMM-MVPA method is based on two theories of EEG: the classical theory (Shah et al. 2004) and the synchronized oscillation theory (Basar 1980; Makeig et al. 2002). Both theories predict multivariate peaks at the start of new processing stages, which is the main assumption underneath the HsMM-MVPA method. In a recent study, we found direct support for this assumption: we did two identical experiments, except that a decision rule was made more difficult in the second experiment. Here, we observed that the decision difficulty had a very clear effect on the duration of one of the stages (Berberyan et al. 2021). This also indicated that stages are typically serial, even though the HsMM-MVPA does not enforce this. However, even if it turns out that these theories are incorrect, the current framework will be less powerful but still useful. The HsMM-MVPA method will still be able to divide trials into segments separated by EEG components, but such a segment might not be an isolated cognitive process. Even in that case, the evidence accumulation models would have less variance to deal with and would still yield more precise results than when fitted to the overall RT data.
In the new framework, we combine the HsMM-MVPA method with evidence accumulation models. To account for stage durations, the HsMM-MVPA analysis uses gamma distributions with a shape parameter of 2. At the same time, the evidence accumulation models use the Wald distribution or the related Wiener distribution (in case of DDM) to account for these same stage durations. While both distributions are cases of generalized inverse Gaussian distributions, one might wonder if this difference in underlying distributions is a problem. This shows that the resulting distributions are highly similar and imply that the difference in underlying distributions is not problematic. That said, it would be preferred to have one analysis method that integrates evidence accumulation models directly into the HsMM-MVPA method, but that remains currently out of reach.
Conclusion
To conclude, we believe that the proposed framework provides a powerful new tool for analyzing cognitive processes. On the one hand, it enables the use of evidence accumulation models for tasks consisting of multiple stages and, on the other hand, presents a way of characterizing and interpreting previously discovered cognitive stages in more detail. Although it is particularly useful for more complex cognitive tasks, we have shown that it can even lead to surprising new insights in the standard random dot motion paradigm.
Notes
The LOOCV method followed by a sign test is relatively conservative; instead one could opt for simply taking the solution with the maximum likelihood. However, like all other HsMM-MVPA studies, we follow Anderson and Fincham (2014) who argue that adding the sign test helps to ensure that the identified stages generalize across subjects. Because the results of the analysis depend partly on the quality and resolution of the data (see also Borst and Anderson 2015), for some subjects additional substages might be identified. We used the sign test to ensure that a significant majority of the subjects indeed show evidence for each stage.
This step is not strictly necessary, the qualitative results with or without this step are the same. However, it does not unfairly bias the evidence accumulation models fit to stage durations.
The mathematical formulation used here for the Wald model is equivalent to a formulation in which separate parameters were estimated for start points of accumulation rather than thresholds.
This source of variability is typically thought of as starting point variability but can also be interpreted as variability in the distance to boundary. The predictions for choices and response times of these two conceptualizations are equivalent. We provide a simulation that illustrates this as Supplementary Material.
References
Anders, R., Riès, S., Van Maanen, L., & Alario, F. X. (2015). Evidence accumulation as a model for lexical selection. Cognitive Psychology, 82, 57–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogpsych.2015.07.002.
Anders, R., Alario, F. X., & Van Maanen, L. (2016). The shifted Wald distribution for response time data analysis. Psychological Methods, 21(3), 309–327. https://doi.org/10.1037/met0000066.
Anderson, J. R. (2007). How can the human mind occur in the physical universe? Oxford UP.
Anderson, J. R., & Fincham, J. M. (2014). Discovering the sequential structure of thought. Cognitive Science, 38(2), 322–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/cogs.12068.
Anderson, J. R., & Reder, L. M. (1999). The fan effect: new results and new theories. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 128(2), 186–197.
Anderson, J. R., Zhang, Q., Borst, J. P., & Walsh, M. M. (2016). The discovery of processing stages: extension of Sternberg’s method. Psychological Review, 123(5), 481–509. https://doi.org/10.1037/rev0000030.
Anderson, J. R., Borst, J. P., Fincham, J. M., Ghuman, A. S., Tenison, C., & Zhang, Q. (2018). The common time course of memory processes revealed. Psychological Science., 29, 1463–1474. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797618774526.
Archambeau, K., De Visscher, A., Noël, M. P., & Gevers, W. (2019). Impact of ageing on problem size and proactive interference in arithmetic facts solving. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 72(3), 446–456. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747021818759262.
Basar, E. (1980). EEG-brain dynamics: relation between EEG and brain evoked potentials. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press.
Berberyan, H. S. H. S., Van Maanen, L., van Rijn, H., & Borst, J. (2021). EEG-based identification of evidence accumulation stages in decision-making. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 33(3), 510–527. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_01663.
Blankertz, B., Lemm, S., Treder, M., Haufe, S., & Müller, K. R. (2011). Single-trial analysis and classification of ERP components - a tutorial. NeuroImage., 56, 814–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.048.
Boehm, U., Van Maanen, L., Forstmann, B. U., & Van Rijn, H. (2014). Trial-by-trial fluctuations in CNV amplitude reflect anticipatory adjustment of response caution. NeuroImage, 96, 95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.03.063.
Bogacz, R., Wagenmakers, E.-J., Forstmann, B. U., & Nieuwenhuis, S. (2010). The neural basis of the speed–accuracy tradeoff. Trends in Neurosciences, 33(1), 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2009.09.002.
Borst, J. P., & Anderson, J. R. (2015). The discovery of processing stages: analyzing EEG data with hidden semi-Markov models. Neuroimage, 108, 60–73.
Borst, J. P., & Anderson, J. R. (2021). Discovering cognitive stages in M/EEG data to inform cognitive models. In B. U. Forstmann & B. M. Turner (Eds.), An Introduction to Model-Based Cognitive Neuroscience (2nd ed.). Springer.
Borst, J. P., Schneider, D. W., Walsh, M. M., & Anderson, J. R. (2013). Stages of processing in associative recognition: evidence from behavior, EEG, and classification. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 25(12), 2151–2166. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00457.
Borst, J. P., Ghuman, A. S., & Anderson, J. R. (2016). Tracking cognitive processing stages with MEG: a spatio-temporal model of associative recognition in the brain. NeuroImage., 141, 416–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.08.002.
Burle, B., Spieser, L., Servant, M., & Hasbroucq, T. (2014). Distributional reaction time properties in the Eriksen task: marked differences or hidden similarities with the Simon task? Psychonomic Bulletin and Review., 21, 1003–1010. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-013-0561-6.
Byrne, M. D., & Anderson, J. R. (2001). Serial modules in parallel: the psychological refractory period and perfect time-sharing. Psychol Rev, 108(4), 847–869.
Clark, S. E., & Gronlund, S. D. (1996). Global matching models of recognition memory: how the models match the data. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review., 3, 37–60. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03210740.
Coles, M. G. H., Gratton, G., Bashore, T. R., Eriksen, C. W., & Donchin, E. (1985). A psychophysiological investigation of the continuous flow model of human information processing. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.11.5.529.
Cox, G. E., & Criss, A. H. (2017). Parallel interactive retrieval of item and associative information from event memory. Cognitive Psychology, 97, 31–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogpsych.2017.05.004.
Criss, A. H. (2010). Differentiation and response bias in episodic memory: evidence from reaction time distributions. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn, 36(2), 484–499. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0018435.
Donders, F. C. (1868). Over de snelheid van psychische processen (pp. 92–120). II: Onderzoekingen Gedaan in Het Physiologisch Lbaoratorium Der Utrechtsche Hoogeschool.
Donkin, C., & Van Maanen, L. (2014). Piéron’s law is not just an artifact of the response mechanism. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 62–63, 22–32.
Forstmann, B. U., Dutilh, G., Brown, S. D., Neumann, J., von Cramon, D. Y., Ridderinkhof, K. R., & Wagenmakers, E.-J. (2008). Striatum and pre-SMA facilitate decision-making under time pressure. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 17538–17542.
Forstmann, B. U., Anwander, A., Schäfer, A., Neumann, J., Brown, S. D., Wagenmakers, E.-J., Bogacz, R., & Turner, R. S. (2010). Cortico-striatal connections predict control over speed and accuracy in perceptual decision making. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107, 15916–15920.
Forstmann, B. U., Ratcliff, R., & Wagenmakers, E.-J. (2016). Sequential sampling models in cognitive neuroscience: advantages, applications, and extensions. Annual Review of Psychology, 67, 641–666.
Gallivan, J. P., Chapman, C. S., Wolpert, D. M., & Flanagan, J. R. (2018). Decision-making in sensorimotor control. In Nature Reviews Neuroscience., 19, 519–534. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-018-0045-9.
Gayet, S., Van Maanen, L., Heilbron, M., Paffen, C. L. E., & Van der Stigchel, S. (2016). Visual input that matches the content of visual working memory requires less (not faster) evidence sampling to reach conscious access. Journal of Vision, 16(11), 26. https://doi.org/10.1167/16.11.26.
Gillund, G., & Shiffrin, R. M. (1984). A retrieval model for both recognition and recall. Psychological Review, 91(1), 1–67. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.91.1.1.
Gold, J. I., & Shadlen, M. N. (2001). Neural computations that underlie decisions about sensory stimuli. Trends Cogn Sci, 5(1), 10–16.
Gold, J. I., & Shadlen, M. N. (2007). The neural basis of decision making. Annu Rev Neurosci, 30, 535–574. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.29.051605.113038.
Gray, W. D., & Ritter, F. E. (2007). Composition and control of integrated cognitive systems. In W. D. Gray (Ed.), Integrated Models of Cognitive Systems Oxford UP.
Gronlund, S. D., & Ratcliff, R. (1989). Time course of item and associative information: implications for global memory models. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.15.5.846.
Heathcote, A. (2004). Fitting wald and ex-Wald distributions to response time data: an example using functions for the S-PLUS package. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput, 36(4), 678–694.
Heitz, R. P. (2014). The speed-accuracy tradeoff: history, physiology, methodology, and behavior. In Frontiers in Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2014.00150
Ho, T. C., Brown, S. D., Van Maanen, L., Forstmann, B. U., Wagenmakers, E.-J., & Serences, J. T. (2012). The optimality of sensory processing during the speed-accuracy tradeoff. J Neurosci, 32(23), 7992–8003. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0340-12.2012.
King, J. R., & Dehaene, S. (2014). Characterizing the dynamics of mental representations: the temporal generalization method. In Trends in Cognitive Sciences., 18, 203–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2014.01.002.
King, J. R., Pescetelli, N., & Dehaene, S. (2016). Brain mechanisms underlying the brief maintenance of seen and unseen sensory information. Neuron., 92, 1122–1134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.10.051.
Kriete, T., Noelle, D. C., Cohen, J. D., & O’Reilly, R. C. (2013). Indirection and symbol-like processing in the prefrontal cortex and basal ganglia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(41), 16390–16395. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1303547110.
Liu, Y. (1996). Queueing network modeling of elementary mental processes. Psychological Review, 103(1), 116–136. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.103.1.116.
Luce, R. D. (1986). Response Times Oxford UP.
Makeig, S., Westerfield, M., Jung, T. P., Enghoff, S., Townsend, J., Courchesne, E., & Sejnowski, T. J. (2002). Dynamic brain sources of visual evoked responses. Science., 295, 690–694. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1066168.
Malmberg, K. J. (2008). Recognition memory: a review of the critical findings and an integrated theory for relating them. Cognitive Psychology., 57, 335–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogpsych.2008.02.004.
Miletić, S., & Van Maanen, L. (2019). Caution in decision-making under time pressure is mediated by timing ability. Cognitive Psychology, 110, 16–29.
Miller, J. (1993). A queue-series model for reaction time, with discrete-stage and continuous-flow models as special cases. Psychological Review, 100(4), 702–715. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.100.4.702.
Mulder, M. J., & Van Maanen, L. (2013). Are accuracy and reaction time affected via different processes? PLoS One, 8, e80222.
Mulder, M. J., Bos, D., Weusten, J. M. H., van Belle, J., van Dijk, S. C., Simen, P., van Engeland, H., & Durston, S. (2010). Basic impairments in regulating the speed-accuracy tradeoff predict symptoms of ADHD. Biological Psychiatry, 68, 1114–1119.
Mulder, M. J., Wagenmakers, E.-J., Ratcliff, R., Boekel, W., & Forstmann, B. U. (2012). Bias in the brain: a diffusion model analysis of prior probability and potential payoff. J Neurosci, 32(7), 2335–2343. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4156-11.2012.
Mulder, M. J., Keuken, M. C., Van Maanen, L., Boekel, W., Forstmann, B. U., & Wagenmakers, E.-J. (2013). The speed and accuracy of perceptual decisions in a random-tone pitch task. Attention, Perception & Psychophysics, 75, 1048–1058.
Mulder, M. J., Van Maanen, L., & Forstmann, B. U. (2014). Perceptual decision neurosciences - a model-based review. Neuroscience, 277, 872–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.07.031.
Murdock, B. B. (1993). TODAM2: A model for the storage and retrieval of item, associative, and serial-order information. Psychological Review., 100, 183–203. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.100.2.183.
Neville, D., Raaijmakers, J. G. W., & Van Maanen, L. (2019). Modulation of the word frequency effect in recognition memory after an unrelated lexical decision task. Journal of Memory and Language, 108, 104026.
Norman, K. A. (2010). How hippocampus and cortex contribute to recognition memory: revisiting the complementary learning systems model. Hippocampus., 20, 1217–1227. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20855.
Norman, K. A., & O’Reilly, R. C. (2003). Modeling hippocampal and neocortical contributions to recognition memory: a complementary-learning-systems approach. Psychological Review., 110, 611–646. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.110.4.611.
O’Connell, R. G., Dockree, P. M., & Kelly, S. P. (2012). A supramodal accumulation-to-bound signal that determines perceptual decisions in humans. Nature Neuroscience., 15, 1729–1735. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3248.
O’Reilly, R. C., & Norman, K. A. (2002). Hippocampal and neocortical contributions to memory: advances in the complementary learning systems framework. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 6(11), 505–510.
Oostenveld, R., Fries, P., Maris, E., & Schoffelen, J. M. (2011). FieldTrip: Open source software for advanced analysis of MEG, EEG, and invasive electrophysiological data. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/156869
Palmer, J., Huk, A. C., & Shadlen, M. N. (2005). The effect of stimulus strength on the speed and accuracy of a perceptual decision. Journal of Vision, 5, 376–404 10:1167/5.5.1.
Portoles, O., Borst, J. P., & Van Vugt, M. (2018). Characterizing synchrony patterns across cognitive task stages of associative recognition memory. European Journal of Neuroscience, 48, 2759–2769.
Raaijmakers, J. G. W., & Shiffrin, R. M. (1981). Search of associative memory. Psychological Review, 88(2), 93–134.
Rae, B., Heathcote, A., Donkin, C., Averell, L., & Brown, S. D. (2014). The hare and the tortoise: Emphasizing speed can change the evidence used to make decisions. Journal of Experimental Psychology. Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 40, 1–39. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0036801.
Ratcliff, R. (1978). A theory of memory retrieval. Psychological Review, 85, 59–108.
Ratcliff, R. (1979). Group reaction time distributions and an analysis of distribution statistics. Psychol Bull, 86(3), 446–461.
Ratcliff, R., & McKoon, G. (1989). Similarity information versus relational information: differences in the time course of retrieval. Cognitive Psychology., 21, 139–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-0285(89)90005-4.
Ratcliff, R., & McKoon, G. (2008). The diffusion decision model: theory and data for two-choice decision tasks. Neural Computation, 20(4), 873–922. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.2008.12-06-420.
Ratcliff, R., & Rouder, J. N. (1998). Modeling response times for two-choice decisions. Psychological Science, 9, 347–356.
Ratcliff, R., & Tuerlinckx, F. (2002). Estimating parameters of the diffusion model: approaches to dealing with contaminant reaction times and parameter variability. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 9(3), 438–481.
Ratcliff, R., Smith, P. L., Brown, S. D., & McKoon, G. (2016). Diffusion decision model: current issues and history. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20(4), 260–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2016.01.007.
Rinkenauer, G., Osman, A., Ulrich, R., Müler-Gethmann, H., & Mattes, S. (2004). On the locus of speed-accuracy trade-off in reaction time: Inferences from the lateralized readiness potential. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.133.2.261.
Rotello, C. M., & Heit, E. (2000). Associative recognition: a case of recall-to-reject processing. Memory and Cognition., 28, 907–922. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03209339.
Rotello, C. M., MacMillan, N. A., & Van Tassel, G. (2000). Recall-to-reject in recognition: evidence from ROC curves. Journal of Memory and Language., 43, 67–88. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmla.1999.2701.
Rugg, M. D., & Curran, T. (2007). Event-related potentials and recognition memory. In Trends in Cognitive Sciences., 11, 251–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2007.04.004.
Salvucci, D. D., & Taatgen, N. A. (2008). Threaded cognition: an integrated theory of concurrent multitasking. Psychological Review, 115(1), 101–130.
Schneider, D. W., & Anderson, J. R. (2012). Modeling fan effects on the time course of associative recognition. Cogn Psychol, 64(3), 127–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogpsych.2011.11.001.
Schouten, J. F., & Bekker, J. A. (1967). Reaction time and accuracy. Acta Psychol (Amst), 27, 143–153.
Schwarz, G. (1978). Estimating the dimension of a model. Annals of Statistics, 6(2), 461–464. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1176344136.
Schweickert, R. (1989). Separable effects of factors on activation functions in discrete and continuous models: d′ and evoked potentials. Psychological Bulletin, 106(2), 318–328. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.106.2.318.
Servant, M., White, C., Montagnini, A., & Burle, B. (2015). Using covert response activation to test latent assumptions of formal decision-making models in humans. Journal of Neuroscience., 35, 10371–10385. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0078-15.2015.
Servant, M., White, C., Montagnini, A., & Burle, B. (2016). Linking theoretical decision-making mechanisms in the Simon task with electrophysiological data: a model-based neuroscience study in humans. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience., 28, 1501–1521. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00989.
Shah, A. S., Bressler, S. L., Knuth, K. H., Ding, M., Mehta, A. D., Ulbert, I., & Schroeder, C. E. (2004). Neural dynamics and the fundamental mechanisms of event-related brain potentials. Cerebral Cortex., 14, 476–483. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhh009.
Spieser, L., Servant, M., Hasbroucq, T., & Burle, B. (2017). Beyond decision! Motor contribution to speed–accuracy trade-off in decision-making. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review, 24, 950–956. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-016-1172-9.
Sternberg, S. (1969). The discovery of processing stages: extensions of Donders’ method. Acta Psychologica, 30, 276–315.
Sternberg, S. (2011). Modular processes in mind and brain. Cognitive Neuropsychology., 28, 156–208. https://doi.org/10.1080/02643294.2011.557231.
Stewart, T. C., Bekolay, T., & Eliasmith, C. (2012). Learning to select actions with spiking neurons in the basal ganglia. Frontiers in Neuroscience 6 https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2012.00002
Stocco, A., Lebiere, C., & Anderson, J. R. (2010). Conditional routing of information to the cortex: a model of the basal ganglia’s role in cognitive coordination. Psychol Rev, 117(2), 541–574. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019077.
Sudre, G., Pomerleau, D., Palatucci, M., Wehbe, L., Fyshe, A., Salmelin, R., & Mitchell, T. (2012). Tracking neural coding of perceptual and semantic features of concrete nouns. NeuroImage., 62, 451–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.04.048.
Thura, D., & Cisek, P. (2014). Deliberation and commitment in the premotor and primary motor cortex during dynamic decision making. Neuron, 81(6), 1401–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.031.
Thura, D., & Cisek, P. (2016). Modulation of premotor and primary motor cortical activity during volitional adjustments of speed-accuracy trade-off. Journal of Neuroscience, 36, 938–956.
Townsend, J. T., & Nozawa, G. (1995). Spatio-temporal properties of elementary perception: An investigation of parallel, serial, and coactive theories. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 39(4), 321–359. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmps.1995.1033.
Van Maanen, L., & Van Rijn, H. (2007a). Accounting for subliminal priming in ACT-R. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Cognitive Modeling.
Van Maanen, L., & Van Rijn, H. (2007b). An accumulator model of semantic interference. Cognitive Systems Research, 8(3), 174–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2007.05.002.
Van Maanen, L., & Van Rijn, H. (2010). The locus of the Gratton effect in picture-word interference. Topics in Cognitive Science, 2(1), 168–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-8765.2009.01069.x.
Van Maanen, L., & Van Rijn, H. (2019). The observed locus of semantic interference may not coincide with the functional locus of semantic interference: a commentary on Shitova et al. Cortex, 111, 332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2018.10.025.
Van Maanen, L., Brown, S. D., Eichele, T., Wagenmakers, E.-J., Ho, T. C., Serences, J. T., & Forstmann, B. U. (2011). Neural correlates of trial-to-trial fluctuations in response caution. Journal of Neuroscience, 31, 17488–17495.
Van Maanen, L., Van Rijn, H., & Taatgen, N. A. (2012). RACE/A: an architectural account of the interactions between learning, task control, and retrieval dynamics. Cognitive Science, 36(1), 62–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-6709.2011.01213.x.
Van Maanen, L., Fontanesi, L., Hawkins, G. E., & Forstmann, B. U. (2016a). Striatal activation reflects urgency in perceptual decision making. Neuroimage, 139, 294–303.
Van Maanen, L., Forstmann, B. U., Keuken, M. C., Wagenmakers, E.-J., & Heathcote, A. (2016b). The impact of MRI scanner environment on perceptual decision-making. Behavior Research Methods, 48(1), 184–200. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-015-0563-6.
Van Rijn, H., Borst, J. P., Taatgen, N., & Van Maanen, L. (2016). On the necessity of integrating multiple levels of abstraction in a single computational framework. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 11, 116–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cobeha.2016.07.007.
Verdonck, S., & Tuerlinckx, F. (2016). Factoring out nondecision time in choice reaction time data: Theory and implications. Psychological Review, 123(2), 208–218. https://doi.org/10.1037/rev0000019.
Vincent, S. B. (1912). The function of the viborissae in the behavior of the white rat. Behavioral Monographs, 1, 5.
Wagenmakers, E.-J., & Farrell, S. (2004). AIC model selection using Akaike weights. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 11(1), 192–196. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03206482.
Wagenmakers, E.-J., Ratcliff, R., Gomez, P., & McKoon, G. (2008). A diffusion model account of criterion shifts in the lexical decision task. Journal of Memory and Language, 58, 140–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2007.04.006.
Wickelgren, W. A. (1977). Speed-accuracy tradeoff and information-processing dynamics. Acta Psychologica, 41(1), 67–85.
Winkel, J., Van Maanen, L., Ratcliff, R., der Schaaf, M. E., Van Schouwenburg, M. R., Cools, R., & Forstmann, B. U. (2012). Bromocriptine does not alter speed-accuracy tradeoff. Frontiers in Decision Neuroscience, 6, 126.
Wixted, J. T. (2007). Dual-process theory and signal-detection theory of recognition memory. Psychological Review., 114, 152–176. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.114.1.152.
Wixted, J. T., & Stretch, V. (2004). In defense of the signal detection interpretation of remember/know judgments. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review., 11, 616–641. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03196616.
Yeung, N., Bogacz, R., Holroyd, C. B., & Cohen, J. D. (2004). Detection of synchronized oscillations in the electroencephalogram: an evaluation of methods. Psychophysiology., 41, 822–832. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8986.2004.00239.x.
Yeung, N., Bogacz, R., Holroyd, C. B., Nieuwenhuis, S., & Cohen, J. D. (2007). Theta phase resetting and the error-related negativity. Psychophysiology., 44, 39–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8986.2006.00482.x.
Yonelinas, A. P. (2002). The nature of recollection and familiarity: a review of 30 years of research. In Journal of Memory and Language., 46, 441–517. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmla.2002.2864.
Yu, S. Z. (2010). Hidden semi-Markov models. Artificial Intelligence, 174(2), 215–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artint.2009.11.011.
Zhang, Q., Walsh, M. M., & Anderson, J. R. (2017). The effects of probe similarity on retrieval and comparison processes in associative recognition. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience., 29, 352–367. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_01059.
Zhang, Q., van Vugt, M., Borst, J. P., & Anderson, J. R. (2018). Mapping working memory retrieval in space and in time: a combined electroencephalography and electrocorticography approach. NeuroImage., 174, 472–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.03.039.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 426 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
van Maanen, L., Portoles, O. & Borst, J.P. The Discovery and Interpretation of Evidence Accumulation Stages. Comput Brain Behav 4, 395–415 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42113-021-00105-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42113-021-00105-2