Abstract
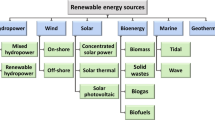
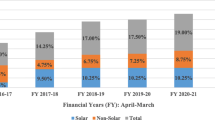
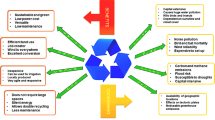
To meet India’s ever-increasing power demand and to stop dependence on coal imports, hydropower seems to be a very favourable alternative, which is clean, renewable, and eco-friendly. This paper reviews India’s hydropower scenario along with various constraints that hinder the tapping of the huge hydroelectric potential, especially in the north-eastern states. The prospects of using micro hydropower plants to outweigh the threats posed by the large dams in northeast India have been discussed along with various hurdles that impede the hydro potential of the region. An effort has also been made to highlight a few noteworthy researches in the field of micro-hydropower plants carried out in recent years. In the end, a Strength-Weakness-Opportunity-Threat analysis has been done to discuss the various aspects of setting up micro-hydroelectric power plants in this region.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, T., & Abbasi, S. A. (2011). Small hydro and the environmental implications of its extensive utilization. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15(4), 2134–2143.
Acharya, N., Kim, C. G., Thapa, B., & Lee, Y. H. (2015). Numerical analysis and performance enhancement of a cross-flow hydro turbine. Renewable Energy, 80, 819–826.
Alternate Hydro Energy Centre, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee. (2003). Study on design and development of model SHP based self sustained projects.
Anagnostopoulos, J. S., & Papantonis, D. E. (2007). Optimal sizing of a run-of-river small hydropower plant. Energy Conversion and Management, 48(10), 2663–2670.
Berrada, A., Bouhssine, Z., & Arechkik, A. (2019). Optimisation and economic modeling of micro hydropower plant integrated in water distribution system. Journal of Cleaner Production, 232, 877–887.
Borkowski, D., Węgiel, M., Ocłoń, P., & Węgiel, T. (2019). CFD model and experimental verification of water turbine integrated with electrical generator. Energy, 185, 875–883.
Brahmaputra River System. Water Resources Government of Assam. https://waterresources.assam.gov.in/portlet-innerpage/brahmaputra-river-system
Cernea, M.M. (2004). Social impacts and social risks in hydropower programs: Preemptive planning and counter-risk measures. In Keynote address: Session on social aspects of hydropower development. United Nations Symposium on Hydropower and Sustainable Development Beijing, China.
Cobb, B. R., & Sharp, K. V. (2013). Impulse (Turgo and Pelton) turbine performance characteristics and their impact on pico-hydro installations. Renewable Energy, 50, 959–964.
Comino, E., Dominici, L., Ambrogio, F., & Rosso, M. (2020). Mini-hydro power plant for the improvement of urban water-energy nexus toward sustainability—a case study. Journal of Cleaner Production, 249, 119416.
Criteria for earthquake resistant design of structures: General provisions and buildings, Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) IS 1893:2002 (Part I). https://law.resource.org/pub/in/bis/S03/is.1893.1.2002.pdf
Das, P. K. (2013). North-East, ‘the power house of India’: Prospects and problems. IOSR Journal of Humanities and Social Science (IOSR-JHSS), 18(3), 36–48.
Development and Growth in Northeast India, The natural resources, Water and Environment Nexus, Strategic report, 2007. Report No. 36397-IN.
Elbatran, A. H., Yaakob, O. B., Ahmed, Y. M., & Shabara, H. M. (2015). Operation, performance and economic analysis of low head micro-hydropower turbines for rural and remote areas: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 43, 40–50.
Fernando, S. (2002). An assessment of the small hydro potential in Sri Lanka. Energy for Sustainable Development, 6(1), 95–98.
Fuentes-Bargues, J. L., & Ferrer-Gisbert, P. S. (2015). Selecting a small run-of-river hydropower plant by the analytic hierarchy process (AHP): A case study of Miño-Sil river basin, Spain. Ecological Engineering, 85, 307–316.
Genus, A., & Iskandarova, M. (2020). Transforming the energy system? Technology and organisational legitimacy and the institutionalisation of community renewable energy. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 125, 109795.
Handique, K., & Dutta, A. (2014). Power and North East: The hydro power scenario of North East. International Journal of Science and Research, 3(12), 602–609.
Hasan, M. H., Mahlia, T. I., & Nur, H. (2012). A review on energy scenario and sustainable energy in Indonesia. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 16(4), 2316–2328.
Hatata, A. Y., El-Saadawi, M. M., & Saad, S. (2019). A feasibility study of small hydro power for selected locations in Egypt. Energy Strategy Reviews, 24, 300–313.
Hydropower Development in India: A Sector Assessment. (2017). https://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/files/file/ADB-Hydropower-Development-in-India.pdf.
Ibrahim, M., Imam, Y., & Ghanem, A. (2019). Optimal planning and design of run-of-river hydroelectric power projects. Renewable Energy, 141, 858–873.
Inayat, A., & Raza, M. (2019). District cooling system via renewable energy sources: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 107, 360–373.
India-Countries & Regions–IEA https://www.iea.org/countries/india
International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). (2012). Renewable energy technologies: Cost analysis series. International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), 1, 274.
Jawahar, C. P., & Michael, P. A. (2017). A review on turbines for micro hydro power plant. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 72, 882–887.
Kaldellis, J. K., Vlachou, D. S., & Korbakis, G. (2005). Techno-economic evaluation of small hydro power plants in Greece: A complete sensitivity analysis. Energy Policy, 33(15), 1969–1985.
Kaunda, C. S., Kimambo, C. Z., & Nielsen, T. K. (2012). Hydropower in the context of sustainable energy supply: a review of technologies and challenges. International Scholarly Research Notices, Renewable Energy. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/730631
Khan, M. A., Rehman, S., & Al-Sulaiman, F. A. (2018). A hybrid renewable energy system as a potential energy source for water desalination using reverse osmosis: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 97, 456–477.
Khurana, S., & Kumar, A. (2011). Small hydro power—a review. International Journal of Engineering, Science and Metallurgy, 1(1), 278–282.
Kumar, A. and Verma, H.K., (2007). Indian Initiative to Develop Standards, Guidelines and Manuals for Small Hydropower. In International Conference on Small Hydropower-Hydro Sri Lanka (Vol. 22, p. 24).
Kumar, R., & Singal, S. K. (2015). Penstock material selection in small hydropower plants using MADM methods. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 52, 240–255.
Leon, A. S., & Zhu, L. (2014). A dimensional analysis for determining optimal discharge and penstock diameter in impulse and reaction water turbines. Renewable Energy, 71, 609–615.
Liu, F., Tait, S., Schellart, A., Mayfield, M., & Boxall, J. (2020). Reducing carbon emissions by integrating urban water systems and renewable energy sources at a community scale. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 123, 109767.
Locker, H. (2004). Environmental issues and management for hydropower peaking operations. New York: United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN-ESA).
Mazumder S. Influx of mega dam in NE: A threat to native land. 2011. The Sentinel. https://mnre.gov.in/research-and-development/small-hydro
Michael, P. A., & Jawahar, C. P. (2017). Design of 15 kW micro hydro power plant for rural electrification at Valara. Energy Procedia, 117, 163–171.
Minar, H. (2012). Hydro Power Project Financing Scenario in India-A Case Study on Hydro Power Projects in India. In Paper Published & presented at GTU (Gujarat Technical University) sponsored International Conference on “Dynamics of Global Recession: Economics and Corporate Strategies for Survival and Growth”.
Mishra, S., Singal, S. K., & Khatod, D. K. (2011). Optimal installation of small hydropower plant—a review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15(8), 3862–3869.
MNRE Annual Report 2009–10. https://mnre.gov.in/img/documents/uploads/fafb7d5750d641228c13987ae62d8f3b.pdf
MNRE Annual Report 2019–20. https://mnre.gov.in/img/documents/uploads/file_f-1585710569965.pdf
Mohan, M. R., Paranjothi, S. R., & Prince Israel, S. (1997). Use of pumped-hydro as peak-load management plant in optimal scheduling of power systems. Electric Machines and Power Systems, 25(10), 1047–1061.
Mohibullah, M., Radzi, A.M. and Hakim, M.I.A., (2004). Basic design aspects of micro hydro power plant and its potential development in Malaysia. In PECon 2004. Proceedings. National Power and Energy Conference, 2004. (pp. 220–223). IEEE.
Murari R, Chitra R, Gupta M. 2011. Current Status and Future Scenarios of Hydropower Development in India. Proceedings of International Conference on Advances in Civil Engineering 2011; INV: 47–56.
Najmaii, M., & Movaghar, A. (1992). Optimal design of run-of-river power plants. Water Resources Research, 28(4), 991–997.
Namy, S. (2007). Addressing the social impacts of large hydropower dams. The Journal of International Policy Solutions, 7, 11–17.
Nasir, B. A. (2014). Design considerations of micro-hydro-electric power plant. Energy Procedia, 50, 19–29.
Nath, D. R. (2015). Small hydro power and its potentiality in Assam. International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology, 23(8), 391–395.
Neogi, D. (2010). Disparity in socio-economic development and its implications on communal conflicts: A study on India’s North-Eastern region. International Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 4(3), 259–266.
Nigussie, T., Engeda, A., & Dribssa, E. (2017). Design, modeling, and CFD analysis of a micro hydro Pelton turbine runner: For the case of selected site in Ethiopia. International Journal of Rotating Machinery. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3030217
Omer, A. M. (2008). Energy, environment and sustainable development. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 12(9), 2265–2300.
Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques. (2015). Understanding energy challenges in India: Policies, players and issues. IEA. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264247444-en
Ozdemir, M. T., & Orhan, A. (2012). An experimental system for electrical and mechanical education: Micro hydro power plant prototype. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 47, 2114–2119.
Paish, O. (2002). Small hydro power: Technology and current status. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 6(6), 537–556.
Pasalli, Y. R., & Rehiara, A. B. (2014). Design planning of micro-hydro power plant in hink river. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 20, 55–63.
Power Potential of North East by NEEPCO, https://neepco.co.in/projects/power-potential
Punys, P., & Pelikan, B. (2007). Review of small hydropower in the new Member States and Candidate Countries in the context of the enlarged European Union. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 11(7), 1321–1360.
Rahaman, M. M., & Varis, O. (2009). Integrated water management of the Brahmaputra basin: Perspectives and hope for regional development. In Natural Resources Forum, 33(1), 60–75.
Rai, A. K., & Kumar, A. (2016). Analyzing hydro abrasive erosion in Kaplan turbine: A case study from India. Journal of Hydrodynamics Series B, 28(5), 863–872.
Ramanathan, K., & Abeygunawardena, P. (2007). Hydropower development in India: A sector assessment. Mandaluyong: Asian Development Bank.
Ranjitkar, G., Huang, J. and Tung, T. (2006). Application of micro-hydropower technology for remote regions. In 2006 IEEE EIC Climate Change Conference (pp. 1–10).
Ratnata, I. W., Saputra, W. S., Somantri, M., Mulyana, E., & Ardhika, A. (2018). Preliminary study of micro-hydro power plant (MHPP) in the rural area. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 384(1), 012067.
Razan, J. I., Islam, R. S., Hasan, R., Hasan, S., & Islam, F. (2012). A comprehensive study of micro-hydropower plant and its potential in Bangladesh. ISRN Renewable Energy. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/635396
Sammartano, V., Morreale, G., Sinagra, M., Collura, A., & Tucciarelli, T. (2014). Experimental study of cross-flow micro-turbines for aqueduct energy recovery. Procedia Engineering, 89, 540–547.
Signe, E. B. K., Hamandjoda, O., & Nganhou, J. (2017). Methodology of feasibility studies of micro-hydro power plants in cameroon: Case of the micro-hydro of KEMKEN. Energy Procedia, 119, 17–28.
Statistics, E., (2013). Twentieth Issue. National Statistical Organisation, Government of India. Study on Design and Development of Model SHP Based Self Sustained Projects, Alternate Hydro Energy Centre, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, 2003
Tanutwutthigorn, K., & Suntivarakorn, R. (2019). Efficiency improvement and economic analysis of micro hydro power plant by using twin vertical hydro turbine. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 257(1), 012038.
Tapia, A., Reina, D. G., & Millán, P. (2020). Optimized micro-hydro power plants layout design using messy genetic algorithms. Expert Systems with Applications, 159, 113539.
Vagholikar, N. and Das, P.J. (2010). Damming northeast India: juggernaut of hydropower projects theatens social and environmental security of region, Kalpavriksh. https://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/files/Damming%20Northeast%20India_%20Kalpavriksh_%20Aaranyak_ActionAid%20India_2010.pdf
Varun, Bhat, & I. K., & Prakash, R., (2009). LCA of renewable energy for electricity generation systems—a review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 13(5), 1067–1073.
Wagner, B., Hauer, C., & Habersack, H. (2019). Current hydropower developments in Europe. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 37, 41–49.
Wazed, M., & Ahmed, S. (2008). Micro hydro energy resources in Bangladesh: A review. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 2(4), 1209–1222.
World Bank, (2007). Development and Growth in Northeast India: The Natural Resources, Water, and Environment Nexus. Joint Study of DONER, Ministry of Development of North Eastern India, Govt of India and World Bank.
Yumnam, J. (2012). An assessment of Dams in Northeast India seeking carbon credits from clean development mechanism of the United Nations framework convention on climate change. https://www.internationalrivers.org/sites/default/files/attachedfiles/damsandcdm_ne_india_april__2012.pdf
Zema, D. A., Nicotra, A., Tamburino, V., & Zimbone, S. M. (2016). A simple method to evaluate the technical and economic feasibility of micro hydro power plants in existing irrigation systems. Renewable Energy, 85, 498–506.
Zhang, M., Valentín, D., Valero, C., Egusquiza, M., & Egusquiza, E. (2019). Failure investigation of a Kaplan turbine blade. Engineering Failure Analysis, 97, 690–700.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Agnimitra Biswas, Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering NIT Silchar, Assam, India for offering constructive suggestions and valuable feedback to develop this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors. The author declares that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deshamukhya, T., Choubey, G. Prospects of micro-hydropower plants in Northeast India: a brief review. Int J Energ Water Res 7, 297–308 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-022-00197-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-022-00197-x