Abstract
Introduction
Transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene variants rs12255372 and rs7903146 have been consistently shown to raise genetic risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The aim of this study was to investigate the possible role of these variants in the development of impaired glucose metabolism (IGM), including impaired fasting glucose (IFG) or T2DM, in patients with metabolic syndrome (MS).
Patients and methods
The study population consisted of 228 patients with MS who were divided into two groups. The first group consisted of 148 patients with MS and IGM [39M/109F, 59.8 ± 14.6 (mean ± SD) years] and the second group of 80 patients with MS and normoglycemia (NGM) (16M/64F, 56.1 ± 15.8 years). The diagnosis of MS was based on the criteria proposed by the American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (AHA/NHLBI) Scientific Statement. Anthropometric parameters including BMI and waist circumference were recorded and blood samples were obtained after overnight fasting for biochemical tests. The rs12255372 and rs7903146 TCF7L2 polymorphisms were genotyped in peripheral blood leucocytes.
Results
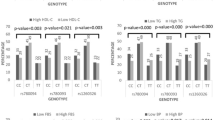
Analysis of the distribution of the TCF7L2 polymorphic alleles revealed that the frequency of the T allele of the TCF7L2 variant rs12255372 was 38.2% in the study population, while the frequency of the T allele of the TCF7L2 rs7903146 variant was 35.3%. The T allele of the rs12255372 variant was more frequently present in patients with MS and IGM (48.3%) compared to patients with MS and NGM (19.4%, p < 0.001). Also, the T allele of rs7903146 was more frequently present in patients with MS and IGM (44.6%) compared to patients with MS and NGM (18.1%, p < 0.001). Logistic regression analysis followed and revealed that the presence of the T allele for both rs12255372 and rs7903146 TCF7L2 gene variants is a very powerful predictor of the presence of glucose disorders, increasing the risk more than fourfold in patients with MS and after adjustment for potential confounders, such as age, gender, BMI, and waist circumference (TCF7L2 rs12255372: Exp(B) 4.917, p < 0.001 and TCF7L2 rs7903146: Exp(B) 5.460, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
The presence of the rs12255372 and rs7903146 TCF7L2 gene variants plays an important role in the development of T2DM among individuals with MS. These findings support the notion that among subjects with MS, those who finally develop T2DM have a genetic predisposition to β-cell dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MS:
-
Metabolic syndrome
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- IGM:
-
Impaired glucose metabolism
- NGM:
-
Normal glucose metabolism
- IFG:
-
Impaired fasting glucose
- IGT:
-
Impaired glucose tolerance
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
References
Tsatsoulis A, Mantzaris MD, Bellou S, Andrikoula M (2013) Insulin resistance: an adaptive mechanism becomes maladaptive in the current environment—an evolutionary perspective. Metabolism 62:622–633
The IDF consensus worldwide definition of the metabolic syndrome, (2006) International Diabetes Federation
Rabe K, Lehrke M, Parhofer KG, Broedl UC (2008) Adipokines and insulin resistance. Mol Med 14:741–751
Grant SF, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I, Benediktsson R, Manolescu A, Sainz J, Helgason A, Stefansson H, Emilsson V, Helgadottir A, Styrkarsdottir U, Magnusson KP, Walters GB, Palsdottir E, Jonsdottir T, Gudmundsdottir T, Gylfason A, Saemundsdottir J, Wilensky RL, Reilly MP, Rader DJ, Bagger Y, Christiansen C, Gudnason V, Sigurdsson G, Thorsteinsdottir U, Gulcher JR, Kong A, Stefansson K (2006) Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 38:320–323
Chandak GR, Janipalli CS, Bhaskar S, Kulkarni SR, Mohankrishna P, Hattersley AT, Frayling TM, Yajnik CS (2007) Common variants in the TCF7L2 gene are strongly associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Indian population. Diabetologia 50:63–67
Palizban A, Nikpour M, Salehi R, Maracy MR (2012) Association of a common variant in TCF7L2 gene with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Persian population. Clin Exp Med 12:115–119
Mayans S, Lackovic K, Lindgren P, Ruikka K, Agren A, Eliasson M, Holmberg D (2007) TCF7L2 polymorphisms are associated with type 2 diabetes in northern Sweden. Eur J Hum Genet 15:342–346
Cauchi S, Meyre D, Dina C, Choquet H, Samson C, Gallina S, Balkau B, Charpentier G, Pattou F, Stetsyuk V, Scharfmann R, Staels B, Frühbeck G, Froguel P (2006) Transcription factor TCF7L2 genetic study in the French population: expression in human beta-cells and adipose tissue and strong association with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 55:2903–2908
Tong Y, Lin Y, Zhang Y, Yang J, Zhang Y, Liu H, Zhang B (2009) Association between TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus: a large Human Genome Epidemiology (HuGE) review and meta-analysis. BMC Med Genet 10:15
Kimber CH, Doney AS, Pearson ER, McCarthy MI, Hattersley AT, Leese GP, Morris AD, Palmer CN (2007) TCF7L2 in the Go-DARTS study: evidence for a gene dose effect on both diabetes susceptibility and control of glucose levels. Diabetologia 50:1186–1191
Delgado-Lista J, Perez-Martinez P, García-Rios A, Phillips CM, Williams CM, Gulseth HL, Helal O, Blaak EE, Kiec-Wilk B, Basu S, Drevon CA, Defoort C, Saris WH, Wybranska I, Riserus U, Lovegrove JA, Roche HM, Lopez-Miranda J (2011) Pleiotropic effects of TCF7L2 gene variants and its modulation in the metabolic syndrome: from the LIPGENE study. Atherosclerosis 214:110–116
Perez-Martinez P, Perez-Caballero AI, Garcia-Rios A, Yubero-Serrano EM, Camargo A, Gomez-Luna MJ, Marin C, Gomez-Luna P, Dembinska-Kiec A, Rodriguez-Cantalejo F, Tinahones FJ, Roche HM, Perez-Jimenez F, Lopez-Miranda J, Delgado-Lista J (2012) Effects of rs7903146 variation in the Tcf7l2 gene in the lipid metabolism of three different populations. PLoS One 7:e43390
Povel CM, Boer JM, Reiling E, Feskens EJ (2011) Genetic variants and the metabolic syndrome: a systematic review. Obes Rev 12:952–967
Phillips CM, Goumidi L, Bertrais S, Field MR, McManus R, Hercberg S, Lairon D, Planells R, Roche HM (2012) Dietary saturated fat, gender and genetic variation at the TCF7L2 locus predict the development of metabolic syndrome. J Nutr Biochem 23(3):239–244
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, Gordon DJ, Krauss RM, Savage PJ, Smith SC Jr, Spertus JA, Fernando Costa. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005; 112: 2735–2752
van Vliet-Ostaptchouk JV, Shiri-Sverdlov R, Zhernakova A, Strengman E, van Haeften TW, Hofker MH, Wijmenga C (2007) Association of variants of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in the Dutch Breda cohort. Diabetologia 50:59–62
Zhang C, Qi L, Hunter DJ, Meigs JB, Manson JE, van Dam RM, Hu FB (2006) Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene and the risk of type 2 diabetes in large cohorts of U.S. women and men. Diabetes 55(9):2645–2648
Marzi C, Huth C, Kolz M, Grallert H, Meisinger C, Wichmann H-E, Rathman W, Herder C, Illig T (2007) Variants of the transcription factor 7-like 2 gene (TCF7L2) are strongly associated with type 2 diabetes but not with the metabolic syndrome in the MONICA/KORA surveys. Horm Metab Res 39(1):46–52
Cruz M, Valladares-Salgado A, Garcia-Mena J, Ross K, Edwards M, Angeles-Martinez J, Ortega-Camarillo C, de la Peña JE, Burguete-Garcia AI, Wacher-Rodarte N, Ambriz R, Rivera R, D'artote AL, Peralta J, Parra EJ, Kumate J (2010) Candidate gene association study conditioning on individual ancestry in patients with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome from Mexico City. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 26(4):261–270
Hayashi T, Iwamoto Y, Kaku K, Hirose H, Maeda S (2007) Replication study for the association of TCF7L2 with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in a Japanese population. Diabetologia 50(5):980–984
Groves CJ, Zeggini E, Minton J, Frayling TM, Weedon MN, Rayner NW, Hitman GA, Walker M, Wiltshire S, Hattersley AT, McCarthy MI (2006) Association analysis of 6,736 U.K. subjects provides replication and confirms TCF7L2 as a type 2 diabetes susceptibility gene with a substantial effect on individual risk. Diabetes 55(9):2640–2644
Ng MC, Tam CH, Lam VK, So WY, Ma RC, Chan JC (2007) Replication and identification of novel variants at TCF7L2 associated with type 2 diabetes in Hong Kong Chinese. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(9):3733–3737
Lyssenko V, Lupi R, Marchetti P, Del Guerra S, Orho-Melander M, Almgren P, Sjögren M, Ling C, Eriksson KF, Lethagen AL, Mancarella R, Berglund G, Tuomi T, Nilsson P, Del Prato S, Groop L (2007) Mechanisms by which common variants in the TCF7L2 gene increase risk of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest 117(8):2155–2163
Sjögren M, Lyssenko V, Jonsson A, Berglund G, Nilsson P, Groop L, Orho-Melander M (2008) The search for putative unifying genetic factors for components of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetologia 51(12):2242–2251
Carty CL, Bhattacharjee S, Haessler J, Cheng I, Hindorff LA, Aroda V, Carlson CS, Hsu CN, Wilkens L, Liu S, Selvin E, Jackson R, North KE, Peters U, Pankow JS, Chatterjee N, Kooperberg C (2014) Analysis of metabolic syndrome components in >15000 African Americans identifies pleiotropic variants: results from the population architecture using genomics and epidemiology study. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 7(4):505–513
Florez JC, Jablonski KA, Bayley N, Pollin TI, de Bakker PI, Shuldiner AR, Knowler WC, Nathan DM, Altshuler D, Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group (2006) TCF7L2 polymorphisms and progression to diabetes in the Diabetes Prevention Program. N Engl J Med 355(3):241–250
Saxena R, Gianniny L, Burtt NP, Lyssenko V, Giuducci C, Sjögren M, Florez JC, Almgren P, Isomaa B, Orho-Melander M, Lindblad U, Daly MJ, Tuomi T, Hirschhorn JN, Ardlie KG, Groop LC, Altshuler D (2006) Common single nucleotide polymorphisms in TCF7L2 are reproducibly associated with type 2 diabetes and reduce the insulin response to glucose in nondiabetic individuals. Diabetes 55(10):2890–2895
Wang J, Kuusisto J, Vänttinen M, Kuulasmaa T, Lindström J, Tuomilehto J, Uusitupa M, Laakso M (2007) Variants of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene predict conversion to type 2 diabetes in the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study and are associated with impaired glucose regulation and impaired insulin secretion. Diabetologia 50(6):1192–1200
Dahlgren A, Zethelius B, Jensevik K, Syvänen AC, Berne C (2007) Variants of the TCF7L2 gene are associated with beta cell dysfunction and confer an increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the ULSAM cohort of Swedish elderly men. Diabetologia 50(9):1852
Melzer D, Murray A, Hurst AJ, Weedon MN, Bandinelli S, Corsi AM, Ferrucci L, Paolisso G, Guralnik JM, Frayling TM (2006) Effects of the diabetes linked TCF7L2 polymorphism in a representative older population. BMC Med 20(4):34
Palmer ND, Lehtinen AB, Langefeld CD, Campbell JK, Haffner SM, Norris JM, Bergman RN, Goodarzi MO, Rotter JI, Bowden DW (2008) Association of TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms with reduced acute insulin response in Hispanic Americans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(1):304–309
Villareal DT, Robertson H, Bell GI, Patterson BW, Tran H, Wice B, Polonsky KS (2010) TCF7L2 variant rs7903146 affects the risk of type 2 diabetes by modulating incretin action. Diabetes 59:479–485
Pilgaard K, Jensen CB, Schou JH, Lyssenko V, Wegner L, Brøns C, Vilsbøll T, Hansen T, Madsbad S, Holst JJ, Vølund A, Poulsen P, Groop L, Pedersen O, Vaag AA (2009) The T allele of rs7903146 TCF7L2 is associated with impaired insulinotropic action of incretin hormones, reduced 24 h profiles of plasma insulin and glucagon, and increased hepatic glucose production in young healthy men. Diabetologia 52:1298–1307
Schäfer SA, Tschritter O, Machicao F, Thamer C, Stefan N, Gallwitz B, Holst JJ, Dekker JM, 't Hart LM, Nijpels G, van Haeften TW, Häring HU, Fritsche A. Impaired glucagon-like peptide-1-induced insulin secretion in carriers of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene polymorphisms. Diabetologia 2007;50:2443–2450
Pearson ER (2009) Translating TCF7L2: from gene to function. Diabetologia 52:1227–1230
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.K. contributed in the acquisition, statistical analysis, and interpretation of the data and in drafting the paper. S.A.P contributed in the acquisition, statistical analysis, and interpretation of the data and in drafting the paper. E.H. contributed in the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of the data. S.T. contributed in the conception and design of the work, in the analysis and interpretation of the data, and in revising the paper critically with regard to its scientific content. I.G. contributed in the conception and design of the work, in the analysis and interpretation of the data, and in revising the paper critically with regard to its scientific content. A.T. contributed in the conception and design of the work, in the analysis and interpretation of the data, and in revising the paper critically with regard to its scientific content. All authors approved the final version of the paper to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Research was carried out in accordance with The Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki). Informed consent was obtained from participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Submission declaration and verification
This work has not been published previously and it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere. The publication is approved by all authors and, if accepted, will not be published elsewhere in the same form, in English or in any other language, including electronically, without the written consent of the copyright holder.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katsoulis, K., Paschou, S.A., Hatzi, E. et al. TCF7L2 gene variants predispose to the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus among individuals with metabolic syndrome. Hormones 17, 359–365 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-018-0047-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-018-0047-z