Key Summary Points
To study in diabetic older adults with urinary retention whether a urinary catheter inserted during hospitalization but not removed is associated with increased 1-year mortality rates.
AbstractSection FindingsDiabetic older adults with a urinary catheter inserted during hospitalization but not removed have significantly higher 1-year mortality rates relative to diabetic older adults in whom the catheter was removed, while in nondiabetic patients there is no difference in 1-year mortality rates between patients with or without a urinary catheter.
AbstractSection MessageRemoving a urinary catheter inserted during hospitalization and its association with mortality should be studied prospectively in diabetic older adults with urinary retention.
Abstract
Purpose
We have studied, in diabetic older adults with urinary retention (UR), whether a urinary catheter (UC) inserted during hospitalization but not removed is associated with 1-year mortality.
Methods
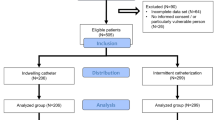
A retrospective study included 327 consecutive older adults (age ≥ 65 years; median age 83 years; 57.8% males) with UR in whom a UC was inserted during hospitalization: 139 (42.5%) diabetics and 188 (57.5%) nondiabetics. UC removal rates during hospitalization and 1-year mortality rates were studied in both groups. Cox regression analysis was used to assess whether a UC inserted during hospitalization but not removed was independently associated with 1-year mortality.
Results
Most diabetic and non-diabetic patients left the hospital with a UC (66.2% vs. 75.5%; p = 0.082). Overall, 54 (38.8%) diabetic patients and 52 (27.7%) nondiabetic patients died one year later (OR 1.66; 95% CI 1.04–2.65; p = 0.042). Diabetic patients with a UC at discharge day had significantly higher 1-year mortality rates relative to diabetic patients without a UC (48.9% vs. 19.1%; OR 4.04; 95% CI 1.75–9.30; p = 0.001), while in nondiabetic patients there was no significant difference in 1-year mortality rates between patients with or without a UC at discharge day (26.8% vs. 30.4%; p = 0.705). Cox regression analysis showed that only in diabetic patients a UC not removed was independently associated with 1-year mortality (HR 2.56; 95% CI 1.16–5.64; p = 0.019).
Conclusion
A UC inserted but not removed in diabetic older adults with UR is associated with 1-year mortality. Removing a UC and its association with mortality should be studied prospectively in this population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown JS, Wessells H, Chancellor MB, Howards SS, Stamm WE, Stapleton AE, Steers WD, Van Den Eeden SK, McVary KT (2005) Urologic complications of diabetes. Diabetes Care 28:177–185
Frimodt-Møller C (1980) Diabetic cystopathy: epidemiology and related disorders. Ann Intern Med 92:318–321
Liu G, Lin YH, Yamada Y, Daneshgari F (2008) External urethral sphincter activity in diabetic rats. Neurourol Urodyn 27:429–434
Yang Z, Dolber PC, Fraser MO (2007) Diabetic urethropathy compounds the effects of diabetic cystopathy. J Urol 178:2213–2219
Hunter KF, Moore KN (2003) Diabetes-associated bladder dysfunction in the older adult (CE). Geriatr Nurs 24:138–145
Shimoni Z, Fruger E, Froom P (2015) Measurement of post-void residual bladder volumes in hospitalized older adults. Am J Med 128:77–81
Justo D, Schwartz N, Dvorkin E, Gringauz I, Groutz A (2017) Asymptomatic urinary retention in elderly women upon admission to the internal medicine department: a prospective study. Neurourol Urodyn 36:794–797
Almeida P, Duque S, Araújo A, Vilas-Boas A, Novais A, Gruner H, Gorjão CJ (2020) The UriCath study: characterization of the use of indwelling urinary catheters among hospitalized older patients in the Internal Medicine Departments of Portugal. Eur Geriatr Med 11:511–515
Yuan Z, Tang Z, He C, Tang W (2015) Diabetic cystopathy: a review. J Diabetes 7:442–447
Fünfstück R, Nicolle LE, Hanefeld M, Naber KG (2012) Urinary tract infection in patients with diabetes mellitus. Clin Nephrol 77:40–48
Fitzgerald MP, Litman HJ, Link CL, McKinlay JB, BACH Survey Investigators (2007) The association of nocturia with cardiac disease, diabetes, body mass index, age and diuretic use: results from the BACH survey. J Urol. 177:1385–1389
Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Ewing LL (1984) The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol 132:474–479
American Diabetes Association (2013) Standards of medical care in diabetes—2013. Diabetes Care 36(Suppl 1):S11–S66
Ghuman A, Kasteel N, Karimuddin AA, Brown CJ, Raval MJ, Phang PT (2018) Urinary retention in early urinary catheter removal after colorectal surgery. Am J Surg 215:949–952
Akbari R, Rahmani Firouzi S, Akbarzadeh-Pasha A (2016) Old habits die hard; does early urinary catheter removal affect kidney size, bacteriuria and UTI after renal transplantation? J Renal Inj Prev 6:43–48
Allen MS, Blackmon SH, Nichols FC 3rd, Cassivi SD, Harmsen WS, Lechtenberg B, Pierson K, Wigle DA, Shen KR (2016) Optimal timing of urinary catheter removal after thoracic operations: a randomized controlled study. Ann Thorac Surg 102:925–930
El-Mazny A, El-Sharkawy M, Hassan A (2014) A prospective randomized clinical trial comparing immediate versus delayed removal of urinary catheter following elective cesarean section. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 181:111–114
Ahmed MR, Sayed Ahmed WA, Atwa KA, Metwally L (2014) Timing of urinary catheter removal after uncomplicated total abdominal hysterectomy: a prospective randomized trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 176:60–63
Patel R, Lepor H (2003) Removal of urinary catheter on postoperative day 3 or 4 after radical retro pubic prostatectomy. Urology 61:156–160
Egger M, Balmer F, Friedli-Wüthrich H, Mühlemann K (2013) Reduction of urinary catheter use and prescription of antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria in hospitalised patients in internal medicine: before-and-after intervention study. Swiss Med Wkly 143:w13796
Shimoni Z, Mullerad M, Niven M, Feuchtwanger Z, Froom P (2011) The effect of urinary bladder catheterization on patient care in an internal medicine department. Am J Med Sci 341:474–477
Dellimore KH, Helyer AR, Franklin SE (2013) A scoping review of important urinary catheter induced complications. J Mater Sci Mater Med 24:1825–1835
Larsen LD, Chamberlin DA, Khonsari F, Ahlering TE (1997) Retrospective analysis of urologic complications in male patients with spinal cord injury managed with and without indwelling urinary catheters. Urology 50:418–422
Drinka PJ (2006) Complications of chronic indwelling urinary catheters. J Am Med Dir Assoc 7:388–392
Vinik AI, Maser RE, Mitchell BD, Freeman R (2003) Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 26:1553–1579
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Tomer Ziv-Baran for the statistical consultation.
Funding
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the institutional review board (Sheba Medical Center, Tel-Hashomer, Israel) with adherence to the principles of the Helsinki Declaration.
Informed consent
Informed consent was waived by the IRB.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perluk, T., Dagan, A., Swartzon, M. et al. Urinary retention in diabetic older adults: mortality associated with a urinary catheter inserted during hospitalization but not removed. Eur Geriatr Med 12, 637–642 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-020-00440-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-020-00440-w